Содержание
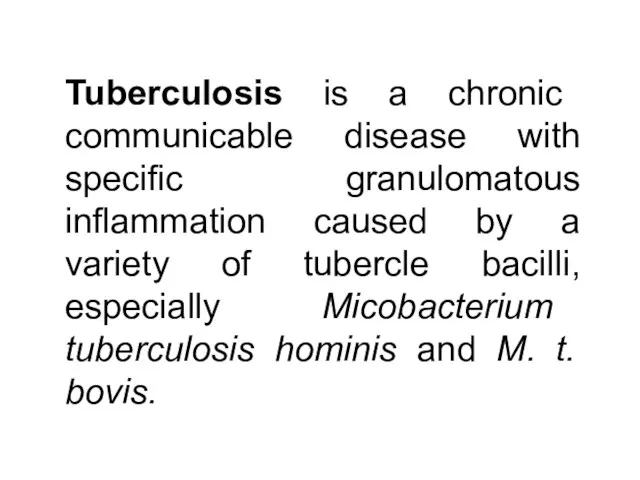
- 2. Tuberculosis is a chronic communicable disease with specific granulomatous inflammation caused by a variety of tubercle
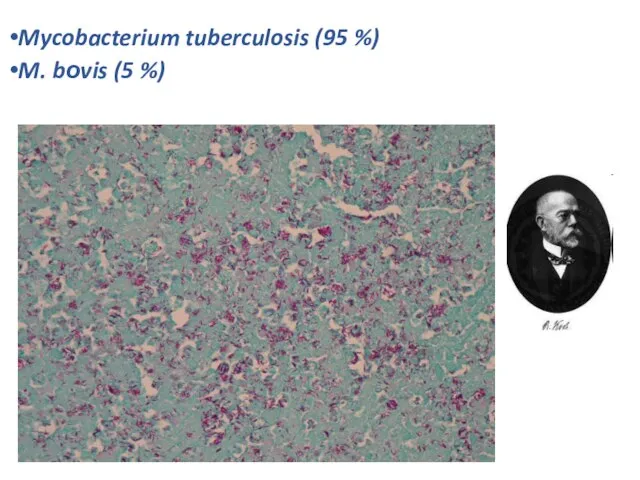
- 3. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (95 %) M. bоvis (5 %)
- 4. Mode of transmission By inhalation into the respiratory tract. Ingestion. Through ingestion into GI tract leads
- 5. 5
- 6. Features of Primary Tuberculosis Development of disease at the first getting of the activator into the
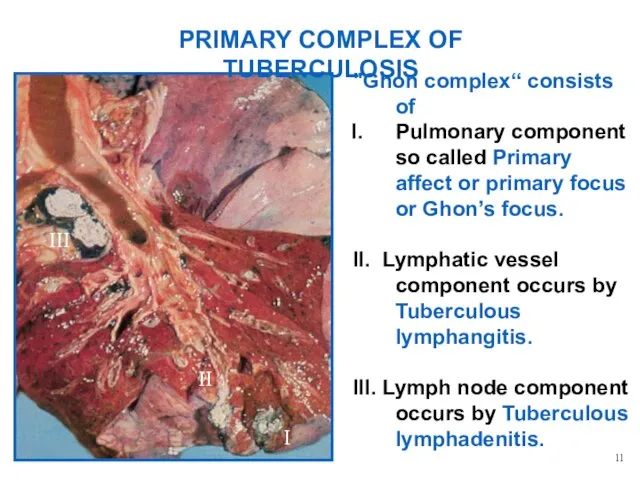
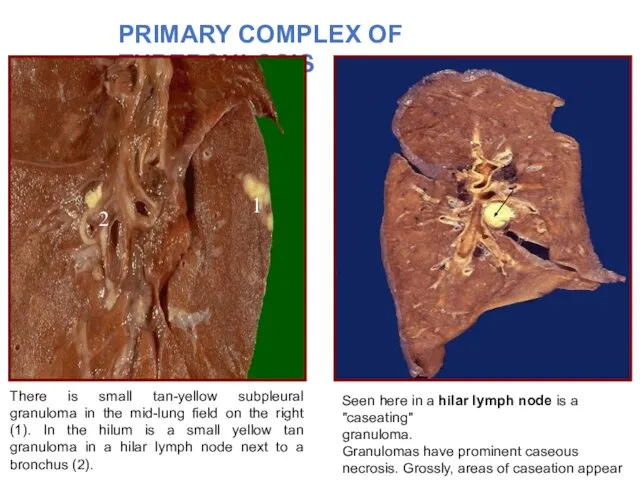
- 7. PRIMARY COMPLEX OF TUBERCULOSIS "Ghon complex“ consists of Pulmonary component so called Primary affect or primary
- 8. There is small tan-yellow subpleural granuloma in the mid-lung field on the right (1). In the
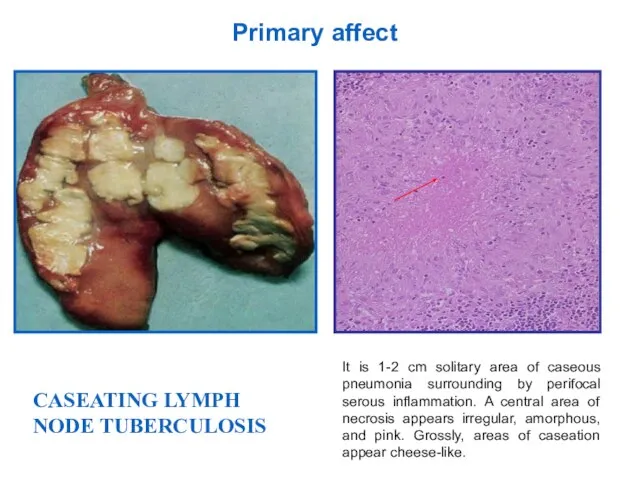
- 9. It is 1-2 cm solitary area of caseous pneumonia surrounding by perifocal serous inflammation. A central
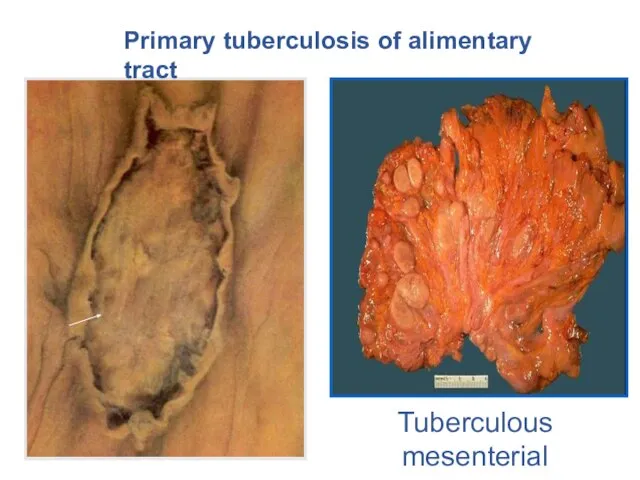
- 10. Primary tuberculosis of alimentary tract Tuberculous mesenterial lymphadenitis
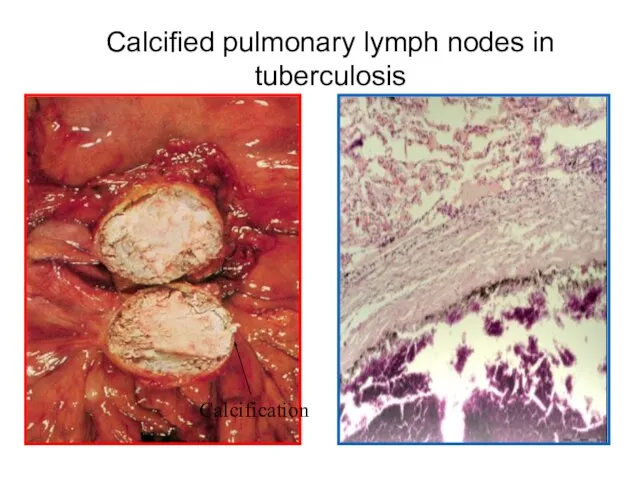
- 11. Calcified pulmonary lymph nodes in tuberculosis Calcification
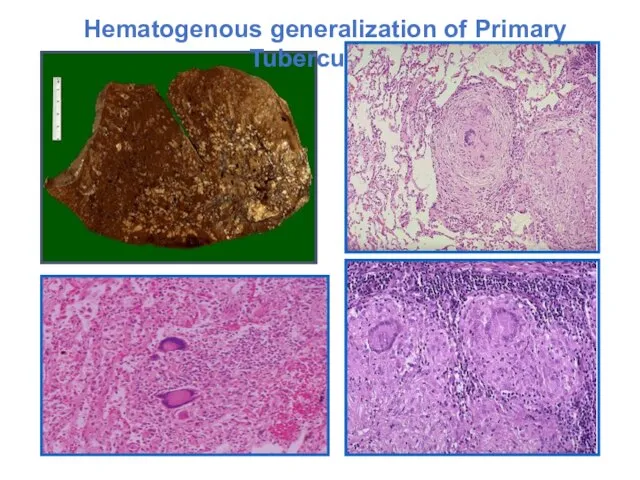
- 12. Hematogenous generalization of Primary Tuberculosis
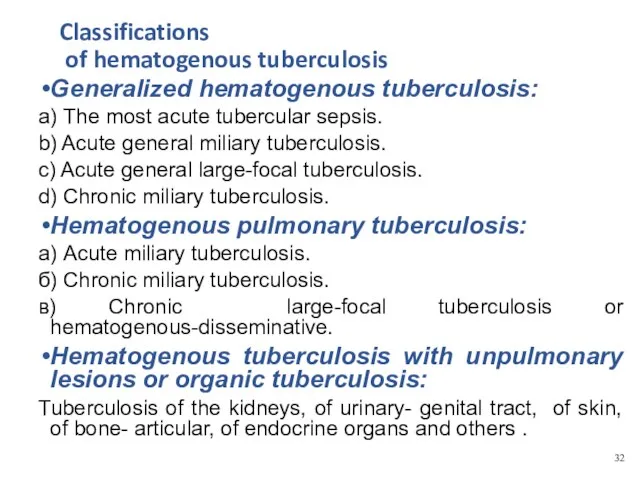
- 13. Classifications of hematogenous tuberculosis Generalized hematogenous tuberculosis: а) The most acute tubercular sepsis. b) Acute general
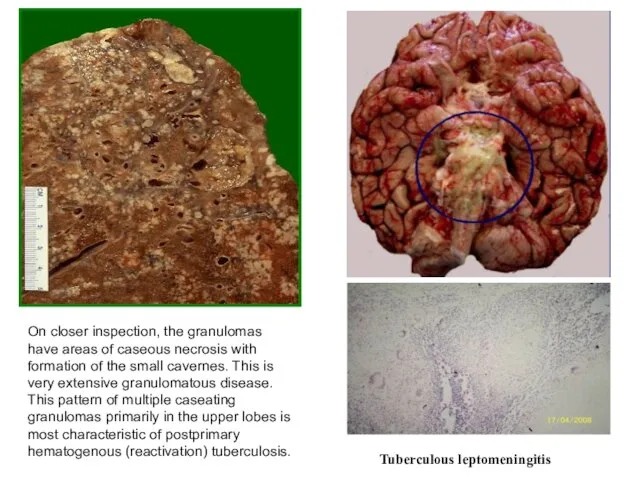
- 14. On closer inspection, the granulomas have areas of caseous necrosis with formation of the small cavernes.
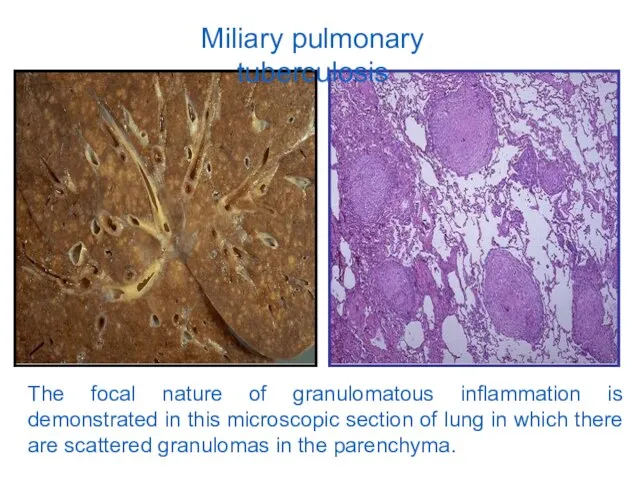
- 15. Miliary pulmonary tuberculosis The focal nature of granulomatous inflammation is demonstrated in this microscopic section of
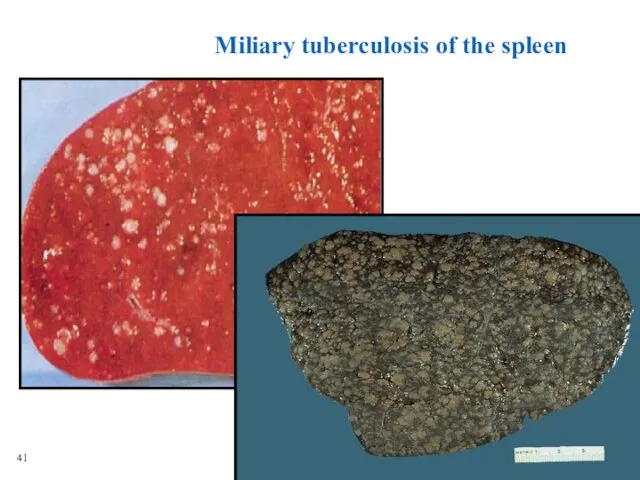
- 16. Miliary tuberculosis of the spleen 41
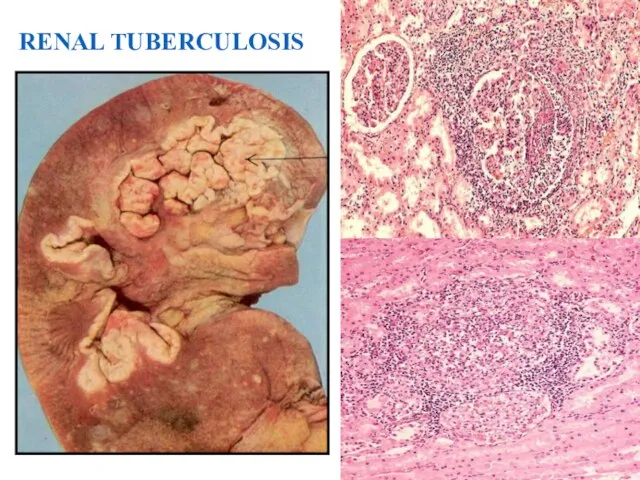
- 17. RENAL TUBERCULOSIS 39
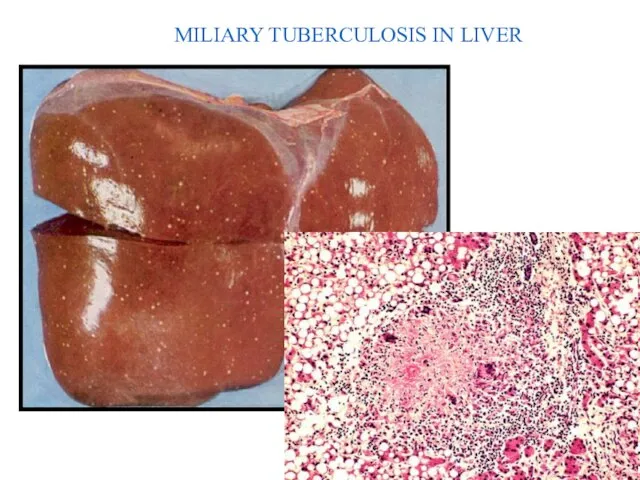
- 18. MILIARY TUBERCULOSIS IN LIVER 40
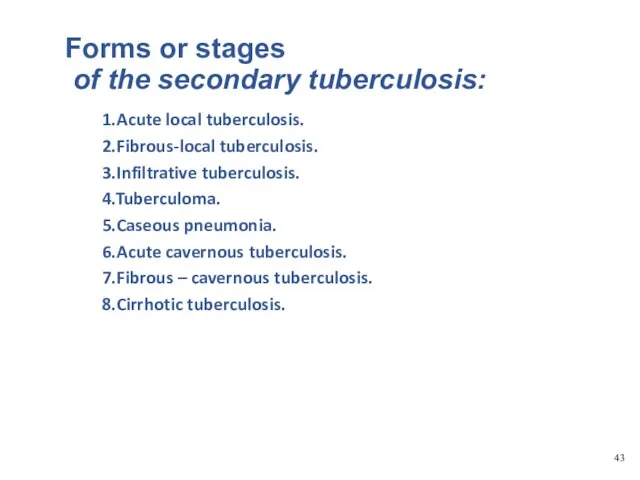
- 19. Forms or stages of the secondary tuberculosis: 1.Acute local tuberculosis. 2.Fibrous-local tuberculosis. 3.Infiltrative tuberculosis. 4.Tuberculoma. 5.Caseous
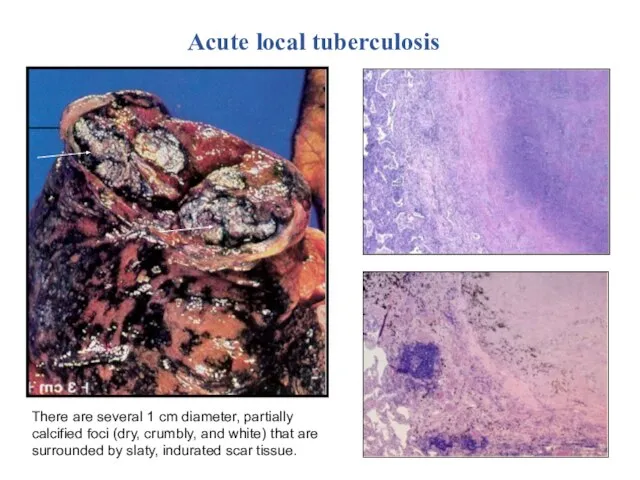
- 20. Acute local tuberculosis There are several 1 cm diameter, partially calcified foci (dry, crumbly, and white)
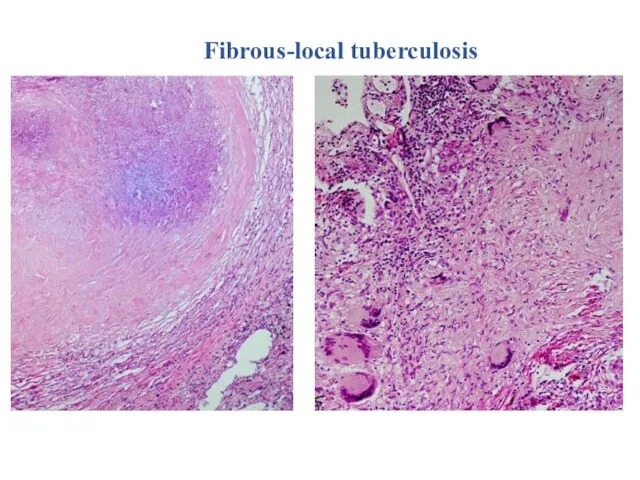
- 21. Fibrous-local tuberculosis
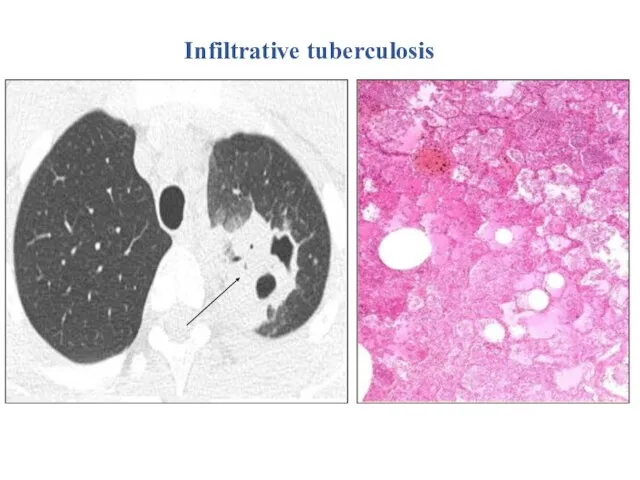
- 22. Infiltrative tuberculosis
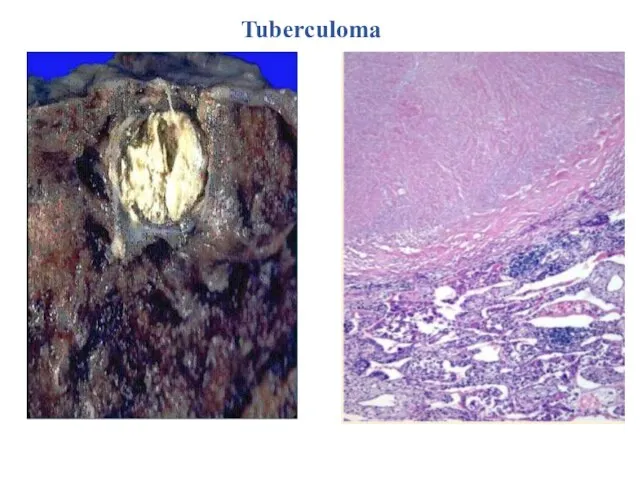
- 23. Tuberculoma
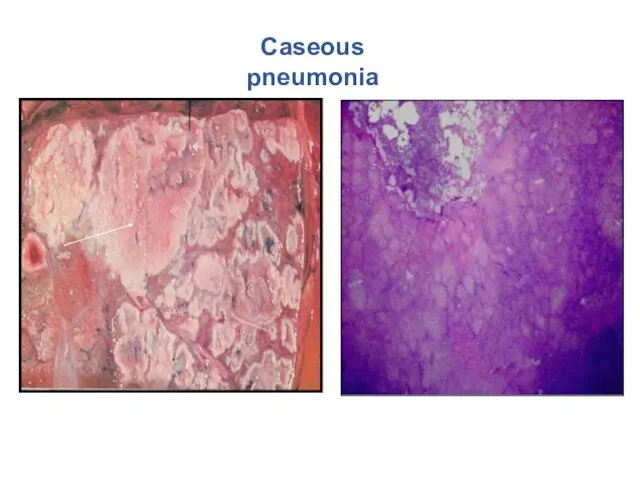
- 24. Caseous pneumonia
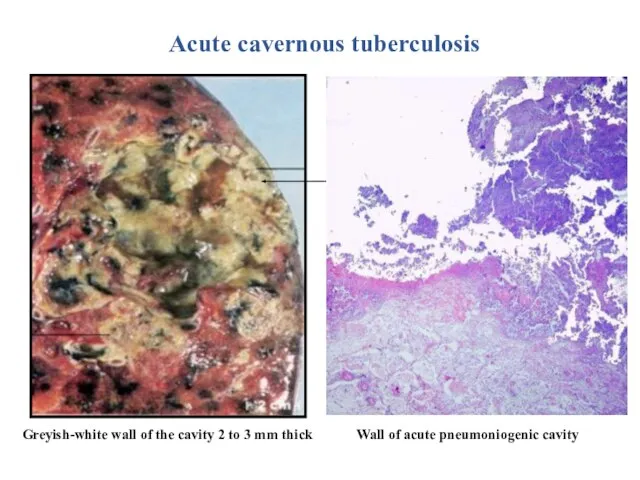
- 25. Greyish-white wall of the cavity 2 to 3 mm thick Acute cavernous tuberculosis Wall of acute
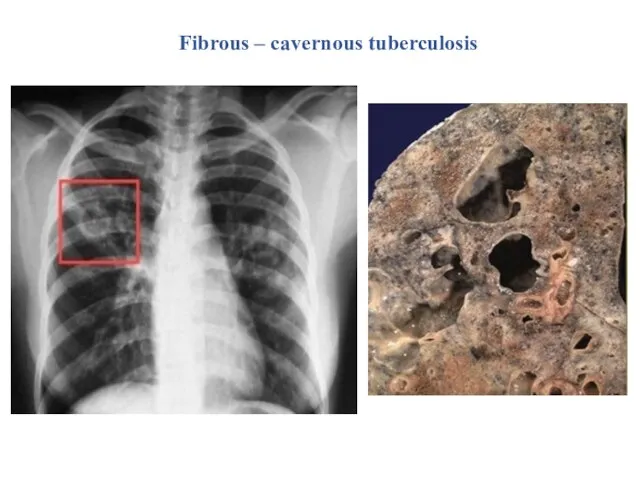
- 26. Fibrous – cavernous tuberculosis
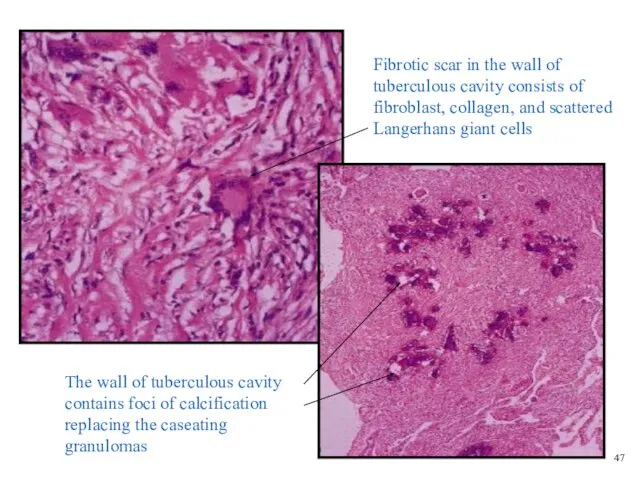
- 27. Fibrotic scar in the wall of tuberculous cavity consists of fibroblast, collagen, and scattered Langerhans giant
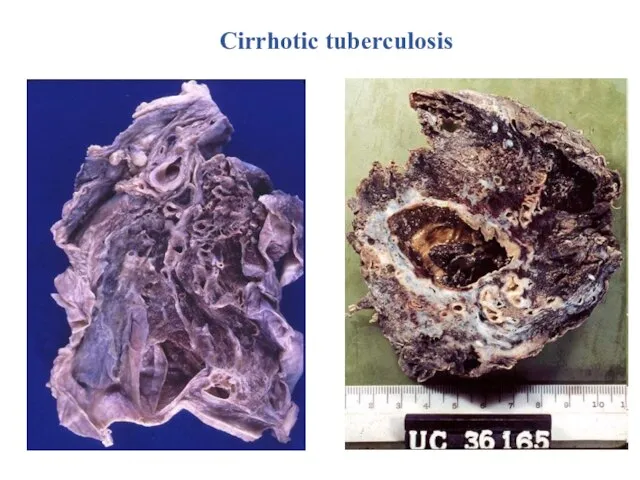
- 28. Cirrhotic tuberculosis
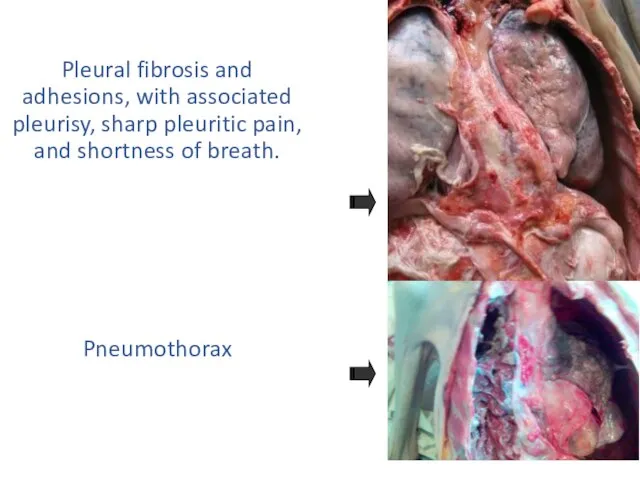
- 29. Complications and causes of death Scarring and calcification. Pneumothorax. Empyema. Pleural fibrosis and adhesions, with associated
- 30. Pleural fibrosis and adhesions, with associated pleurisy, sharp pleuritic pain, and shortness of breath. Pneumothorax
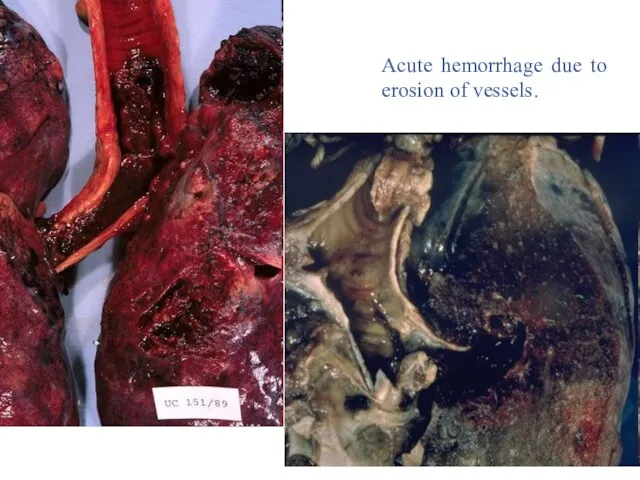
- 31. Acute hemorrhage due to erosion of vessels.
- 33. Скачать презентацию



 Внутренняя среда организм. Кровь и её состав
Внутренняя среда организм. Кровь и её состав Иммунный ответ при SARS-CoV-2
Иммунный ответ при SARS-CoV-2 Национальные особенности деловой культуры европейских стран
Национальные особенности деловой культуры европейских стран Неэпителиальные опухоли яичников
Неэпителиальные опухоли яичников Лучевые методы исследования желудочно-кишечного тракта
Лучевые методы исследования желудочно-кишечного тракта Увеиты
Увеиты Клинические задачи
Клинические задачи ЛФК при заболеваниях ОДА
ЛФК при заболеваниях ОДА Физиология и диагностика беременности. Влияние вредных факторов на плод
Физиология и диагностика беременности. Влияние вредных факторов на плод Пародонт ауруларының жалпы емі. Фармакотерапия
Пародонт ауруларының жалпы емі. Фармакотерапия Организация и структура системы первичной медико-санитарной помощи
Организация и структура системы первичной медико-санитарной помощи Рубцы
Рубцы Многообразие противоинфекционных препаратов
Многообразие противоинфекционных препаратов Сохраните зубы здоровыми на долгие годы!
Сохраните зубы здоровыми на долгие годы! Лихорадка
Лихорадка Bayer HealthCare
Bayer HealthCare Методологические принципы современной психологии. Тема № 2
Методологические принципы современной психологии. Тема № 2 Новые стандарты онкологической помощи по ОМС
Новые стандарты онкологической помощи по ОМС Медицина в Канаде
Медицина в Канаде Гипоксия (кислородное голодание)
Гипоксия (кислородное голодание) Общие правила транспортировки пострадавшего
Общие правила транспортировки пострадавшего Постреанимационная болезнь
Постреанимационная болезнь Головная боль после пункции твердой мозговой оболочки
Головная боль после пункции твердой мозговой оболочки Первичная профилактика патологического старения
Первичная профилактика патологического старения Кабинет педагога-психолога
Кабинет педагога-психолога Амбулаторлы-поликлиникалық қызмет немесе бірншілік медициналық санитарлық көмек жұмыстарын ұйымдастыру қағидалары
Амбулаторлы-поликлиникалық қызмет немесе бірншілік медициналық санитарлық көмек жұмыстарын ұйымдастыру қағидалары Физическая реабилитация при заболеваниях суставов
Физическая реабилитация при заболеваниях суставов Созылмалы бүйрек ауруларының үдеу механизмі
Созылмалы бүйрек ауруларының үдеу механизмі