Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS
- 3. PART 01 Welding Function Instruction and Programming Operation
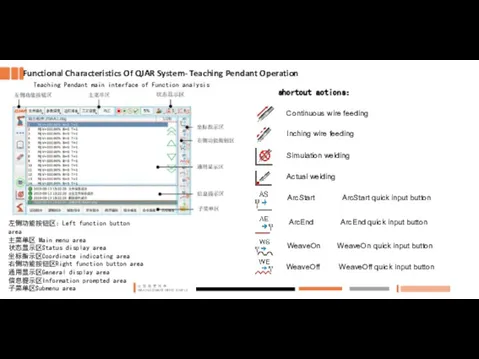
- 4. Teaching Pendant main interface of Function analysis Functional Characteristics Of QJAR System- Teaching Pendant Operation shortcut
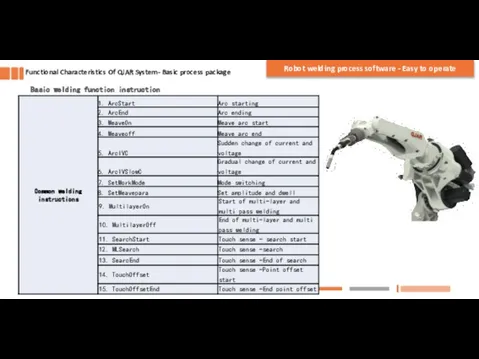
- 5. Basic welding function instruction Functional Characteristics Of QJAR System- Basic process package Robot welding process software
- 6. Functional Characteristics Of QJAR System- Basic process package Dynamically detect whether the arcing is successful or
- 7. Functional Characteristics Of QJAR System- Basic process package 7.:Swing arc process: The welding gun while welding
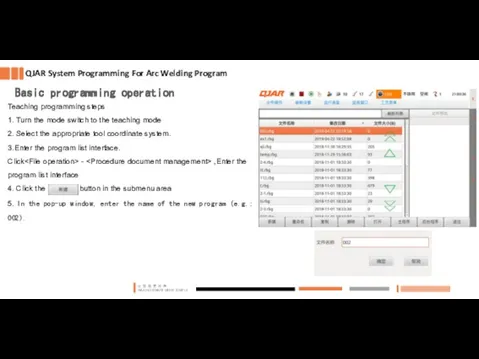
- 8. Basic programming operation QJAR System Programming For Arc Welding Program Teaching programming steps 1. Turn the
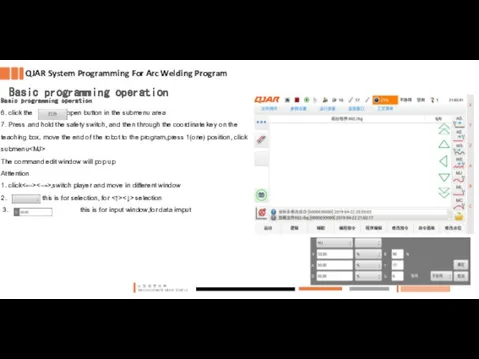
- 9. Basic programming operation 6. click the open button in the submenu area 7. Press and hold
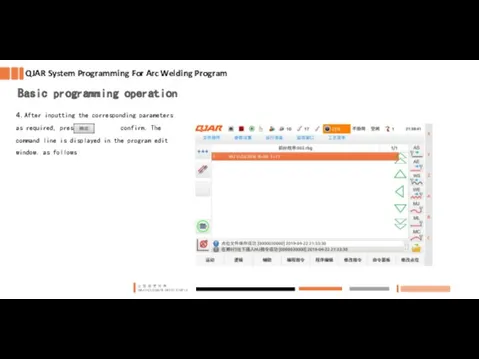
- 10. 4. After inputting the corresponding parameters as required, press confirm. The command line is displayed in
- 11. Click - - , and the following window will pop up. After entering the corresponding parameters
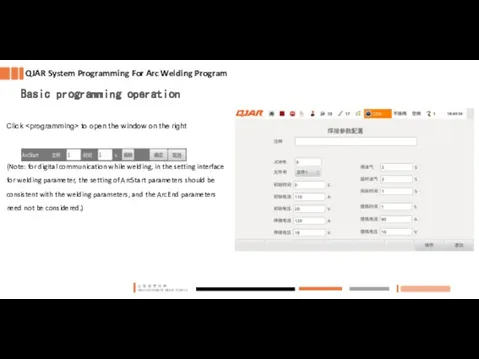
- 12. Click to open the window on the right (Note: for digital communication while welding, in the
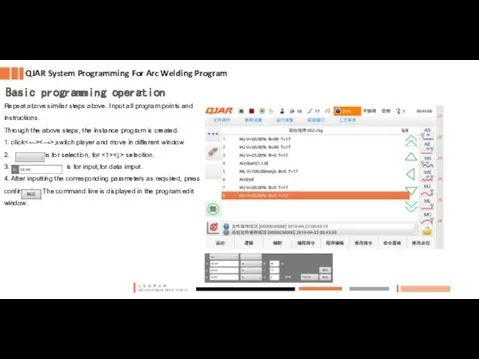
- 13. Repeat above similar steps above. Input all program points and instructions. Through the above steps, the
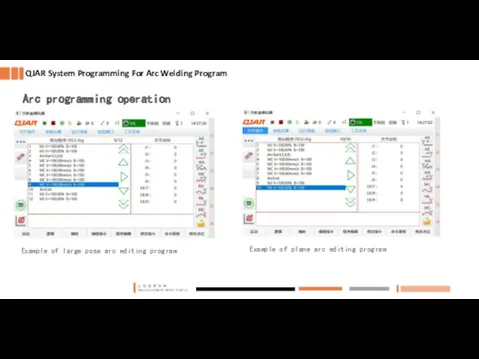
- 14. Example of large pose arc editing program Example of plane arc editing program QJAR System Programming
- 15. 1、MJV=40% B=100 2、MJV=40% B=100 3、ArcStart(1,0.0) 4、MLV=10mm/s B=100 5、 SetWorkMode low spatter 6、MLV=10mm/s B=100 7、 ArcIVC(100.0,10.1) 8、
- 16. PART 02 Arc welding power source communication and application setting
- 17. Analog / digital welding power management: Communication And Application Of Arc Welding Power Source Support Aotai
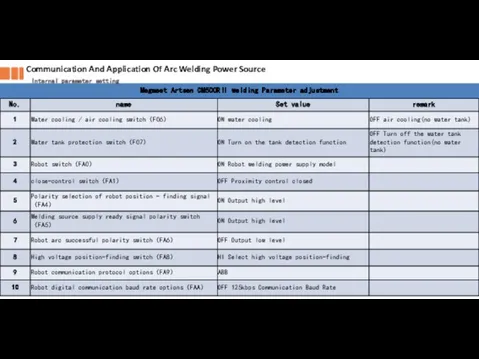
- 18. Communication And Application Of Arc Welding Power Source Internal parameter setting
- 19. PART 03 Multilayer and multipass arc welding function
- 20. Multilayer and multipass arc welding function Multilayer and multichannel arc welding function introduction The multi-layer welding
- 21. Multilayer and multipass function arc welding function Multilayer and Multichannel Parameter Setting 1、Click - - to
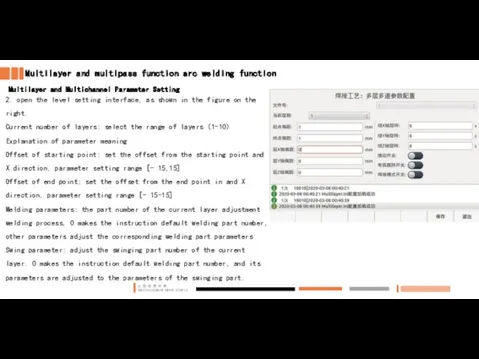
- 22. Multilayer and multipass function arc welding function Multilayer and Multichannel Parameter Setting 2. open the level
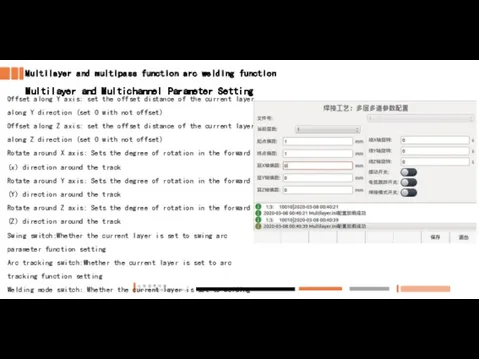
- 23. Multilayer and multipass function arc welding function Multilayer and Multichannel Parameter Setting Offset along Y axis:
- 24. Multilayer and multipass function arc welding function Multilayer and multichannel coordinate system direction 3.Welding coordinate system
- 25. Multilayer and multipass arc welding function Multilayer and multichannel Procedural programming 1. MJ V=40.00% B=0 T=1
- 26. Multilayer and multipass arc welding function Multilayer and multichannel Procedural programming 22. MJ V=80% B=0 T=1
- 27. PART 04 Touch Sense Function PART 04
- 28. Touch Sense Function Introduction for Touch Sense Function In the touch sense mode, the workpiece is
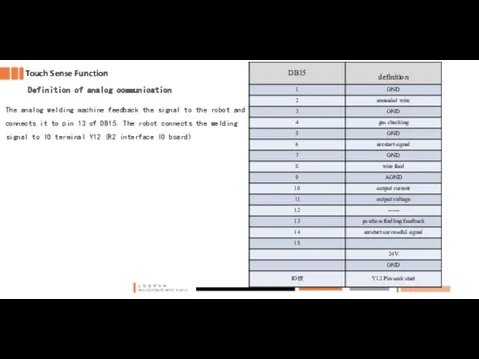
- 29. Touch Sense Function Definition of analog communication The analog welding machine feedback the signal to the
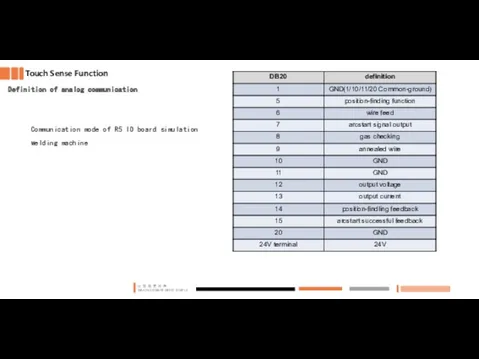
- 30. Touch Sense Function Definition of analog communication Communication mode of R5 IO board simulation welding machine
- 31. Touch Sense Function Parameter setting Open path : - - -
- 32. Touch Sense function Parameter setting It needs to create a user coordinate system, user calibration to
- 33. Touch Sense Function Parameter setting Sensor signal:From low to high by default Coordinate system number: enter
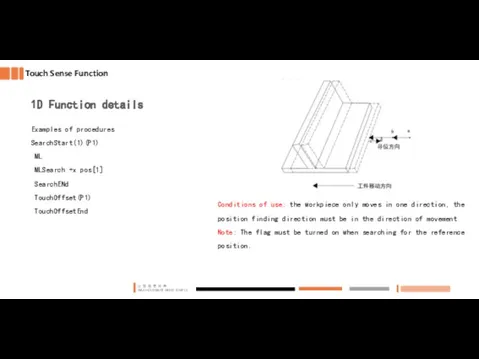
- 34. Touch Sense Function 1D Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart(1)(P1) ML MLSearch +x pos[1] SearchENd TouchOffset(P1)
- 35. Touch Sense Function 2D Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart(1) //finding position start ML Tool =1
- 36. Touch Sense Function 3D Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart(1) // finding position start ML Tool
- 37. Touch Sense Function 2D + Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart 1 P1 // finding position
- 38. Touch Sense Function 2D + Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart 1 P1 // finding position
- 39. Touch Sense Function 3D + Function details Examples of procedures SearchStart 1 P1 // Bit search
- 40. Touch Sense Function 3D + Function details Conditions of use: Rotate or translate anywhere around X,Y,Z
- 41. Touch Sense Function Detailed explanation of internal and external diameter positioning function Examples of procedures SearchStart
- 43. Скачать презентацию

























 Газовая сварка стали
Газовая сварка стали Применение гомогенизации при производстве молока и молочных продуктов. Цель, механизм, режимы, способы
Применение гомогенизации при производстве молока и молочных продуктов. Цель, механизм, режимы, способы 20111020_syuzhet
20111020_syuzhet Урок 2
Урок 2 Стиральные машины
Стиральные машины Системы автоматической блокировки
Системы автоматической блокировки Ātri bojājušo kravu pārvadāšana izmantojot dažādus transporta veidus
Ātri bojājušo kravu pārvadāšana izmantojot dažādus transporta veidus м6 — копия
м6 — копия Самомассаж
Самомассаж Классификация строительных конструкций. Принципы формирования строительных конструкций
Классификация строительных конструкций. Принципы формирования строительных конструкций Интерьер Успенского собора
Интерьер Успенского собора Остапенко Проект fyrty
Остапенко Проект fyrty Поп-арт Гламур. Тенденции моды
Поп-арт Гламур. Тенденции моды Необходимость применения оптоэлектроники для человека
Необходимость применения оптоэлектроники для человека Арматура. Арматуралардың түрлері
Арматура. Арматуралардың түрлері Чудеса Иисуса Христа в пределах Десятиградия (Мф. 15, 29 38; Мк. 7, 31 8, 9)
Чудеса Иисуса Христа в пределах Десятиградия (Мф. 15, 29 38; Мк. 7, 31 8, 9) Технологическая оснастка обсадных колонн
Технологическая оснастка обсадных колонн Гетероперехід. Емісійна модель різкого p-n гетеропереходу
Гетероперехід. Емісійна модель різкого p-n гетеропереходу Логические поразрядные операции
Логические поразрядные операции Рукоположение достойных. Библия
Рукоположение достойных. Библия Освещение жилого помещения. Урок технологии (6 класс)
Освещение жилого помещения. Урок технологии (6 класс) Характеристика до образу Галина баба
Характеристика до образу Галина баба 10_klass_KBZh_s_sovremennoy_srede_obitania_1
10_klass_KBZh_s_sovremennoy_srede_obitania_1 Монтаж кабельной муфты
Монтаж кабельной муфты Любимый питомец. Руся
Любимый питомец. Руся Контактная точечная сварка
Контактная точечная сварка Языковая осень в КФМЛ
Языковая осень в КФМЛ Интеллектуальная игра по мотивам шоу Где логика
Интеллектуальная игра по мотивам шоу Где логика