Содержание
- 2. SECTIONS 1. Introduction: High Level Overview / Demo Network Application Interface (NAI) Radio Management (RM) Technical:
- 3. INTRODUCTION
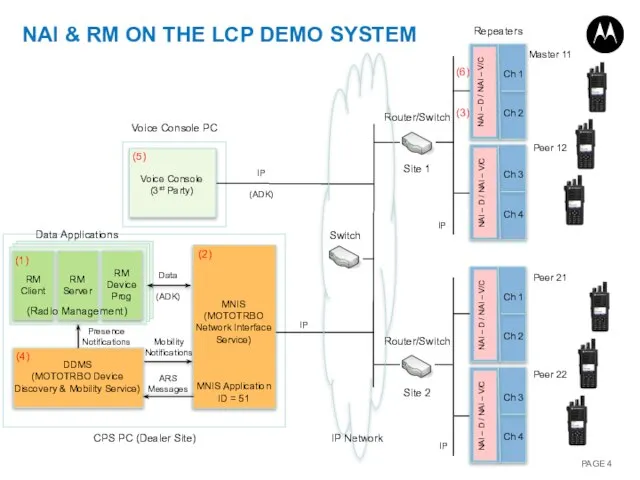
- 4. Mobility Notifications Presence Notifications ARS Messages Data (ADK) Router/Switch Site 2 Router/Switch Site 1 NAI &
- 5. NETWORK APPLICATION INTERFACE (NAI)
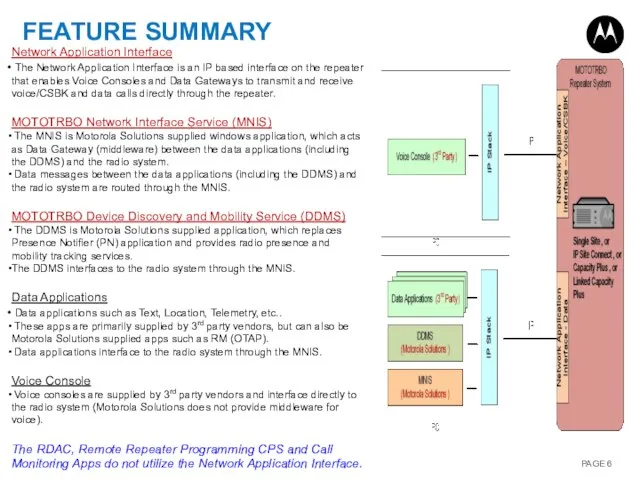
- 6. FEATURE SUMMARY Network Application Interface The Network Application Interface is an IP based interface on the
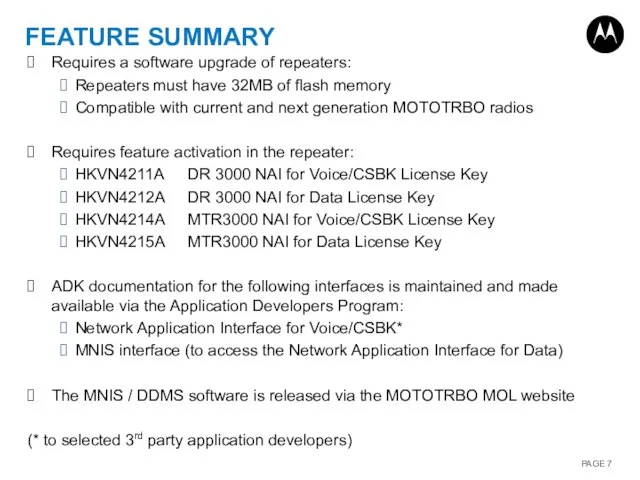
- 7. FEATURE SUMMARY Requires a software upgrade of repeaters: Repeaters must have 32MB of flash memory Compatible
- 8. NETWORK APPLICATION INTERFACE – VOICE/CSBK 3rd party Wireline Voice Consoles utilizing the Network Application Interface can
- 9. NETWORK APPLICATION INTERFACE – VOICE/CSBK A Wireline Voice Console is required to interface directly to the
- 10. NETWORK APPLICATION INTERFACE – DATA The Network Application Interface for Data is an internal interface between
- 11. MNIS OVERVIEW The MNIS is supported by Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows Server 2003 & 2008
- 12. MNIS OVERVIEW The MNIS connects with the repeater system using the Link Establishment procedure of the
- 13. MNIS APPLICATION ID The MNIS has an identifier, called the MNIS Application ID. The ID is
- 14. DDMS OVERVIEW The DDMS is supported by Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows Server 2003 & 2008.
- 15. DDMS WATCHER INTERFACE The DDMS maintains both the radio presence and mobility information. The DMMS provides
- 16. RADIO MANAGEMENT (RM) All MOTOTRBO radios can be managed and programmed / read using a wired
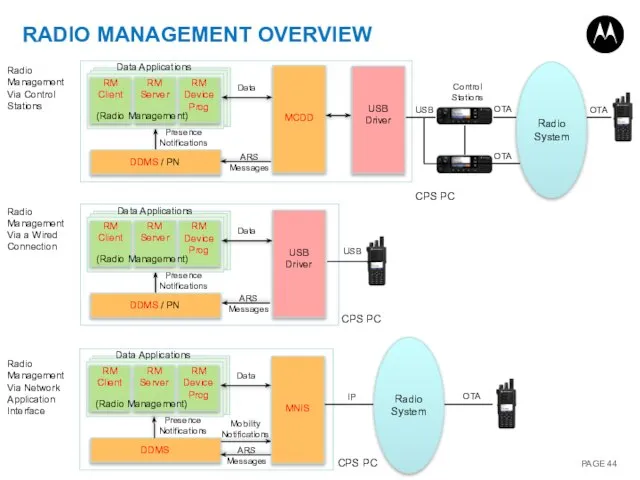
- 17. RADIO MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW Radio Management (RM) is an extension of the MOTOTRBO CPS. RM maintains historical
- 18. RADIO MANAGEMENT (RM) SOFTWARE LICENSES The Radio Management (RM) Server can store and manage up to
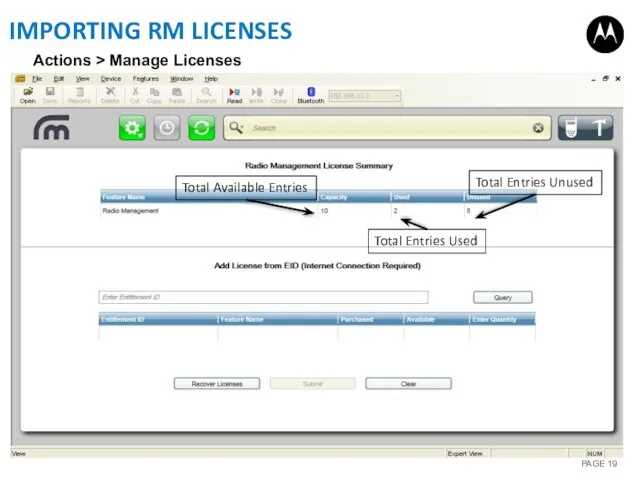
- 19. IMPORTING RM LICENSES Total Available Entries Total Entries Used Total Entries Unused Actions > Manage Licenses
- 20. TECHNICAL
- 21. NETWORK APPLICATION INTERFACE (NAI)
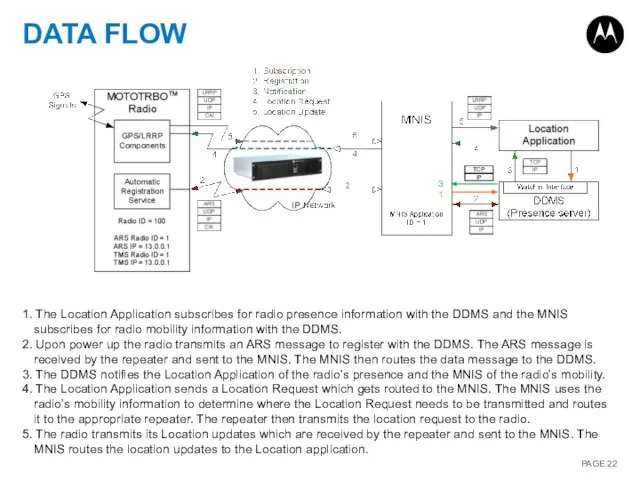
- 22. DATA FLOW 1. The Location Application subscribes for radio presence information with the DDMS and the
- 23. SYSTEM CONFIGURATIONS The MNIS supports the following MOTOTRBO Digital system topologies: Single Site Conventional, IP Site
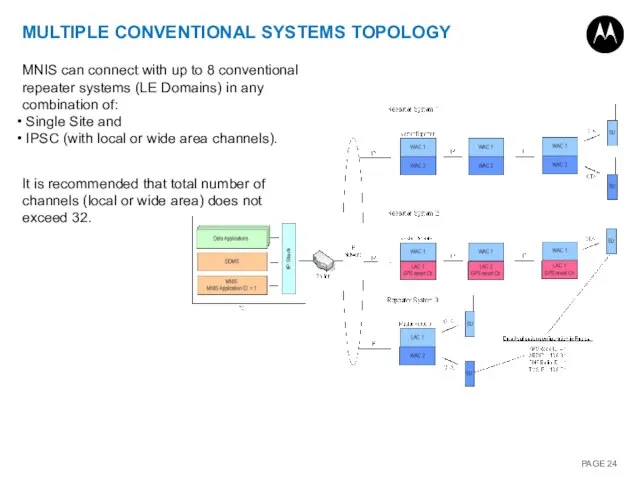
- 24. MULTIPLE CONVENTIONAL SYSTEMS TOPOLOGY MNIS can connect with up to 8 conventional repeater systems (LE Domains)
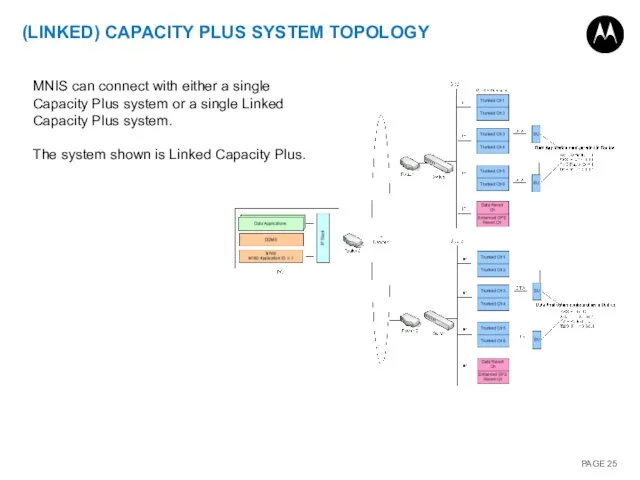
- 25. (LINKED) CAPACITY PLUS SYSTEM TOPOLOGY MNIS can connect with either a single Capacity Plus system or
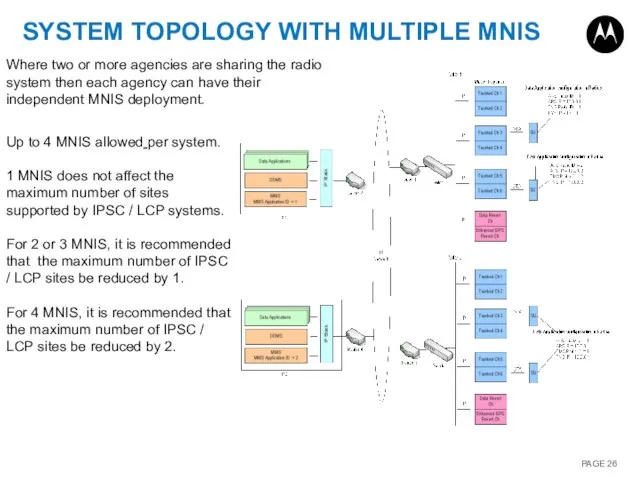
- 26. SYSTEM TOPOLOGY WITH MULTIPLE MNIS Where two or more agencies are sharing the radio system then
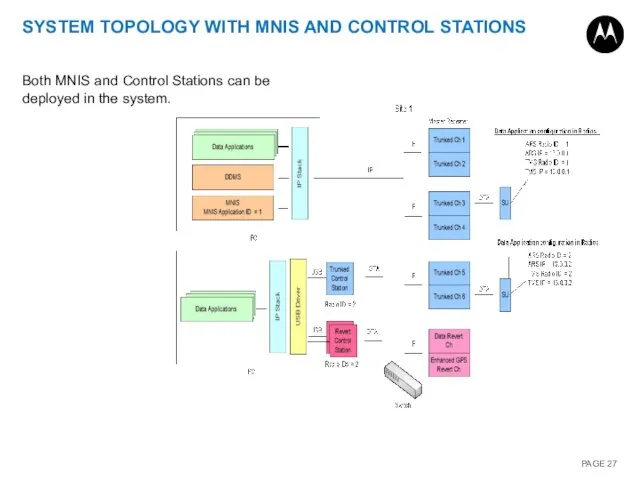
- 27. SYSTEM TOPOLOGY WITH MNIS AND CONTROL STATIONS Both MNIS and Control Stations can be deployed in
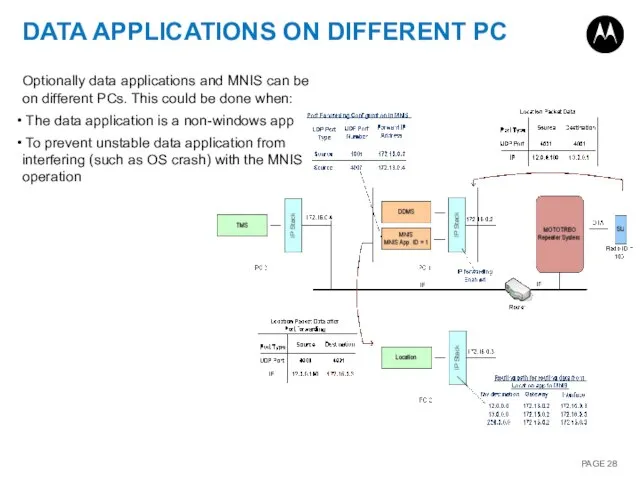
- 28. DATA APPLICATIONS ON DIFFERENT PC Optionally data applications and MNIS can be on different PCs. This
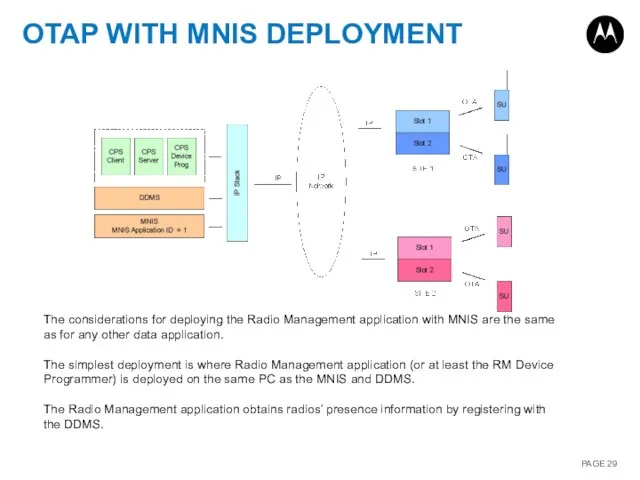
- 29. OTAP WITH MNIS DEPLOYMENT The considerations for deploying the Radio Management application with MNIS are the
- 30. DEPLOYMENT WITH OTHER APPS MNIS, DDMS, RDAC, Remote Repeater Programming and Radio Management can be deployed
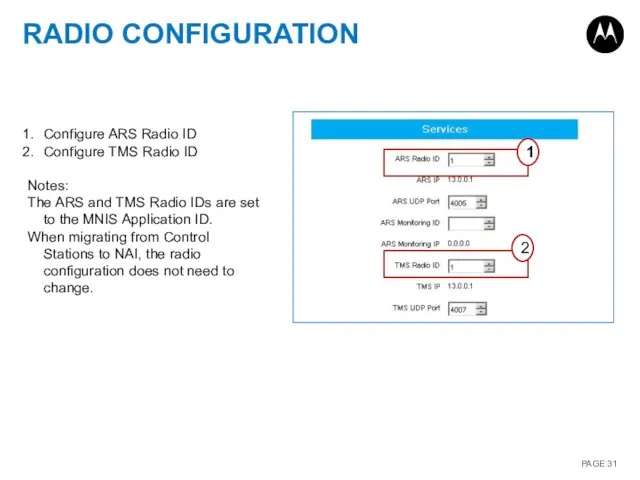
- 31. RADIO CONFIGURATION Configure ARS Radio ID Configure TMS Radio ID Notes: The ARS and TMS Radio
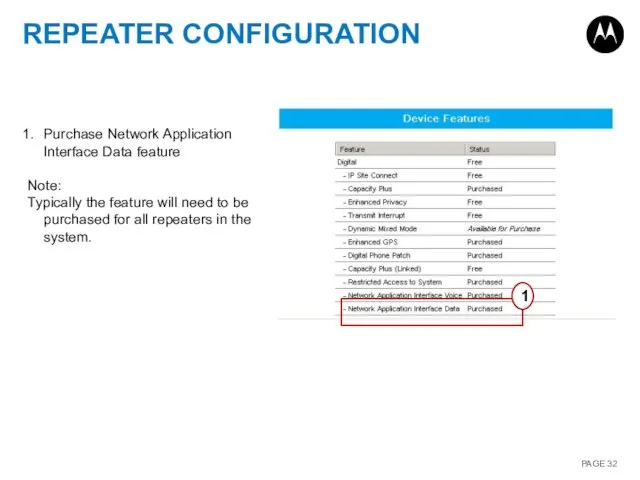
- 32. REPEATER CONFIGURATION 1 Purchase Network Application Interface Data feature Note: Typically the feature will need to
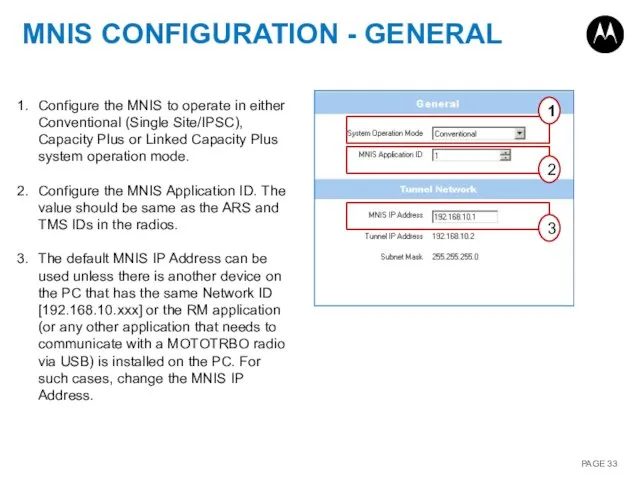
- 33. MNIS CONFIGURATION - GENERAL 1 2 3 Configure the MNIS to operate in either Conventional (Single
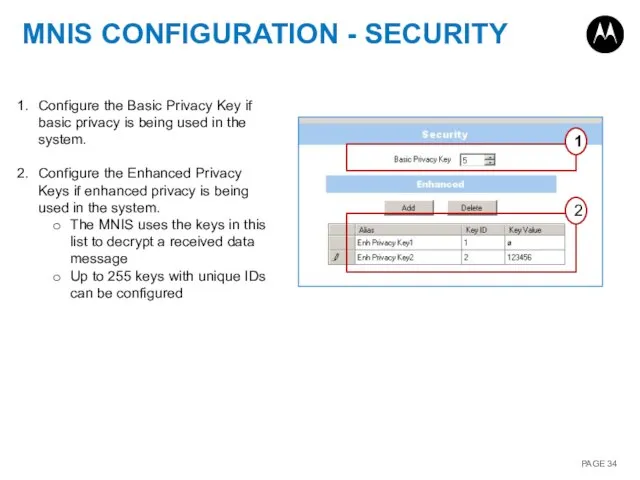
- 34. MNIS CONFIGURATION - SECURITY 1 2 Configure the Basic Privacy Key if basic privacy is being
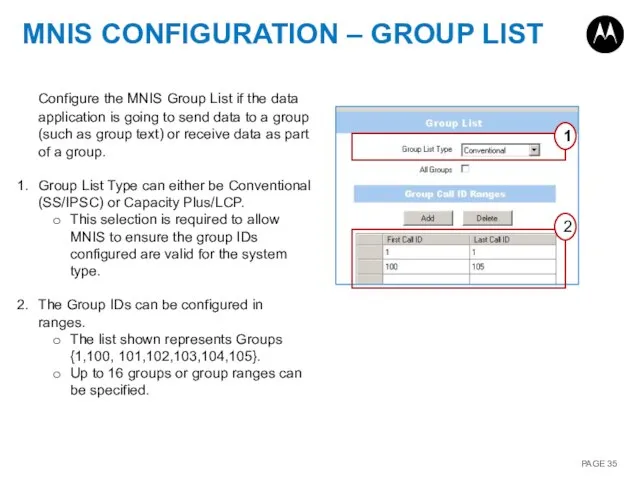
- 35. MNIS CONFIGURATION – GROUP LIST 1 2 Configure the MNIS Group List if the data application
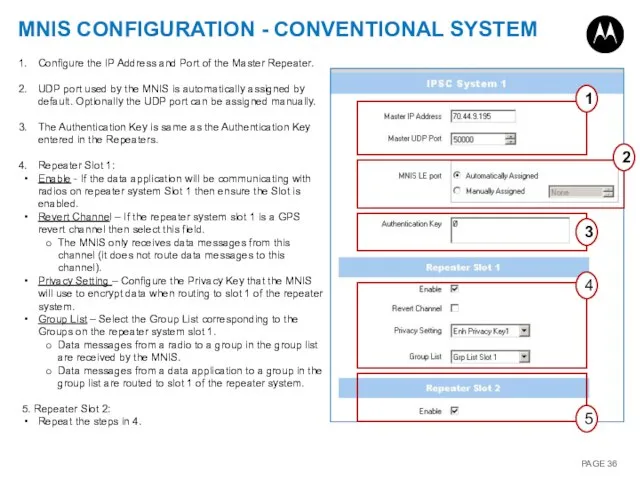
- 36. MNIS CONFIGURATION - CONVENTIONAL SYSTEM 1 4 5 2 3 Configure the IP Address and Port
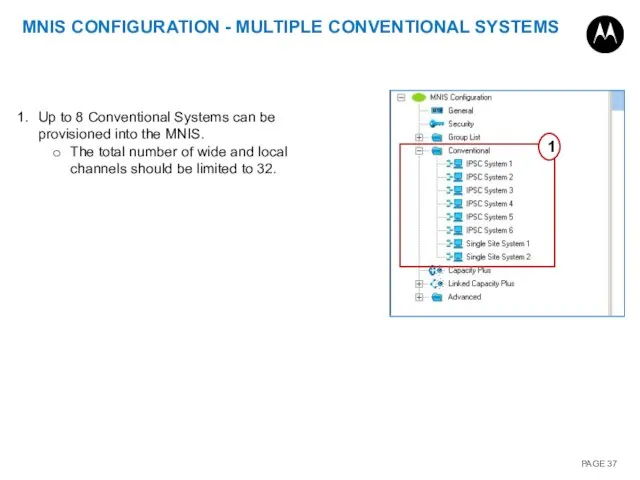
- 37. MNIS CONFIGURATION - MULTIPLE CONVENTIONAL SYSTEMS Up to 8 Conventional Systems can be provisioned into the
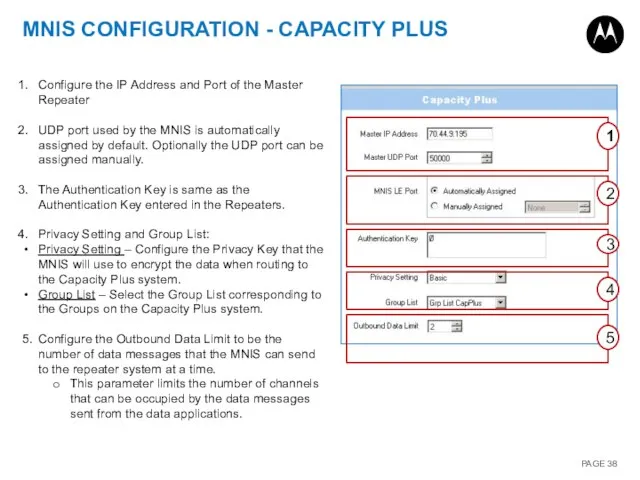
- 38. MNIS CONFIGURATION - CAPACITY PLUS 1 2 3 4 5 Configure the IP Address and Port
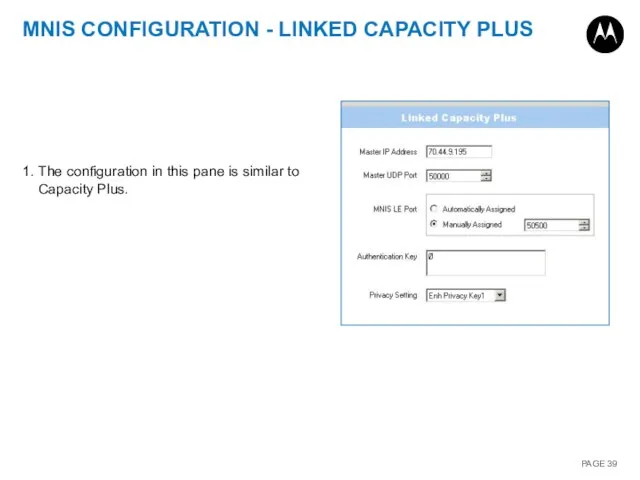
- 39. MNIS CONFIGURATION - LINKED CAPACITY PLUS 1. The configuration in this pane is similar to Capacity
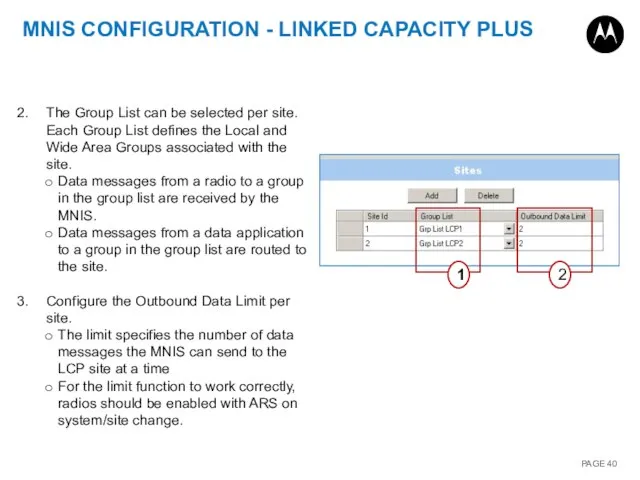
- 40. MNIS CONFIGURATION - LINKED CAPACITY PLUS 1 2 The Group List can be selected per site.
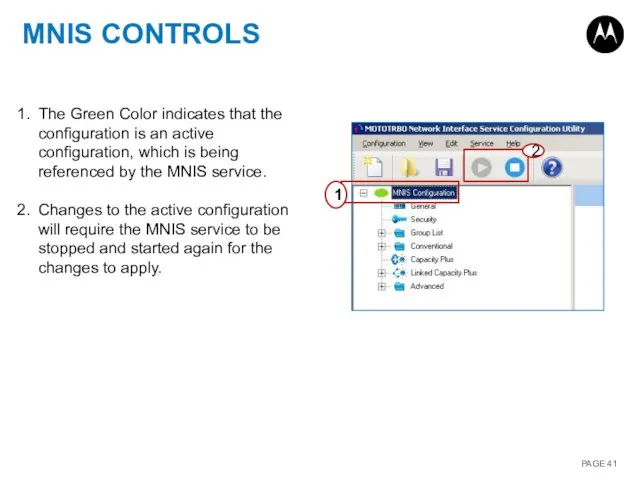
- 41. MNIS CONTROLS 1 2 The Green Color indicates that the configuration is an active configuration, which
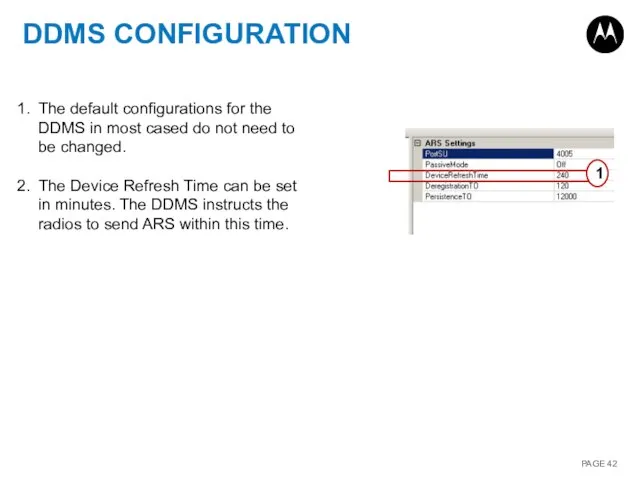
- 42. DDMS CONFIGURATION The default configurations for the DDMS in most cased do not need to be
- 43. RADIO MANAGEMENT (RM) All MOTOTRBO radios can be managed and programmed / read using a wired
- 44. USB OTA USB RADIO MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW Presence Notifications Data ARS Messages Data Applications (Radio Management) Presence
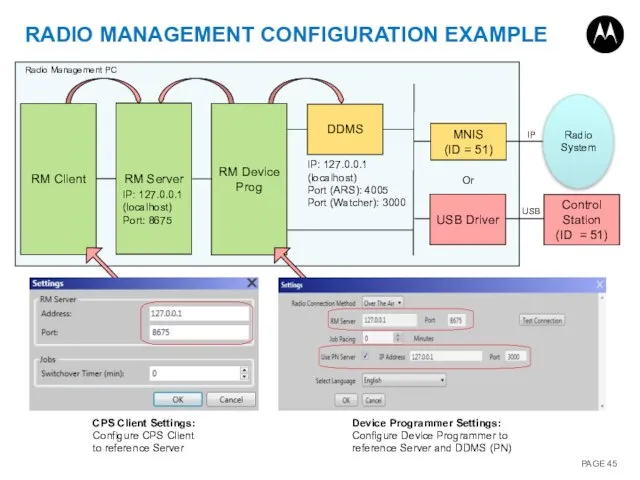
- 45. RADIO MANAGEMENT CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE RM Client RM Server RM Device Prog IP: 127.0.0.1 (localhost) Port: 8675
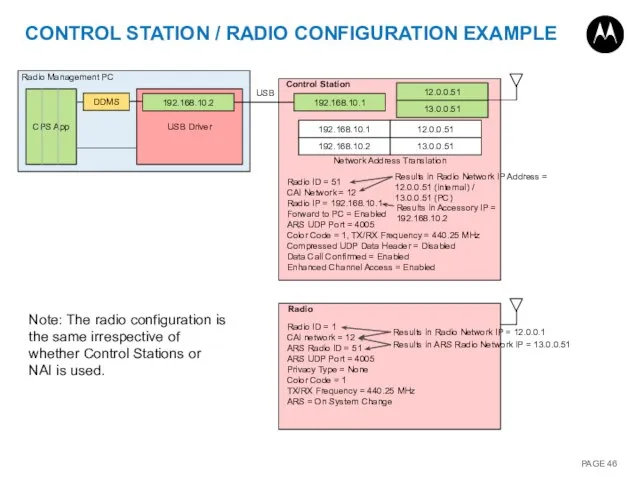
- 46. USB Driver CONTROL STATION / RADIO CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE 12.0.0.51 13.0.0.51 192.168.10.1 12.0.0.51 192.168.10.1 13.0.0.51 192.168.10.2 Network
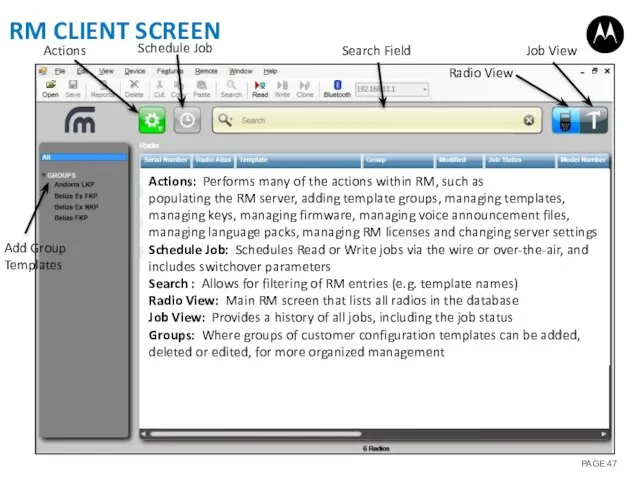
- 47. RM CLIENT SCREEN Actions Schedule Job Radio View Job View Search Field Add Group Templates Actions:
- 48. RECOMMENDED RM SERVER POPULATION METHOD The recommended RM Server population method includes a ‘Wire Read’ of
- 49. RECOMMENDED TEMPLATE MANAGEMENT METHOD A Template consists of that codeplug data which is common to all
- 50. CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT CONSIDERATIONS If the radio user is allowed to make changes via the radio front
- 51. RM allows scheduling of multiple radio configurations to be delivered over the air unattended. RM will
- 52. Delivery with Switchover - radio will apply the changes after delivery Use when changing non-critical parameters:
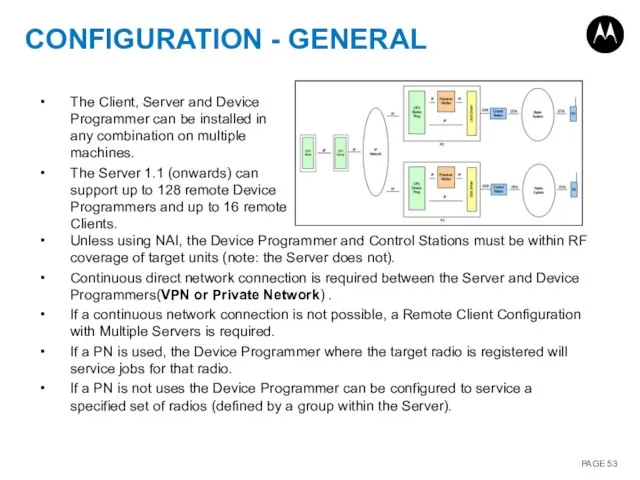
- 53. CONFIGURATION - GENERAL Unless using NAI, the Device Programmer and Control Stations must be within RF
- 54. UNIQUE RADIO ID When using a centralized RM Server to communicate to multiple systems with remote
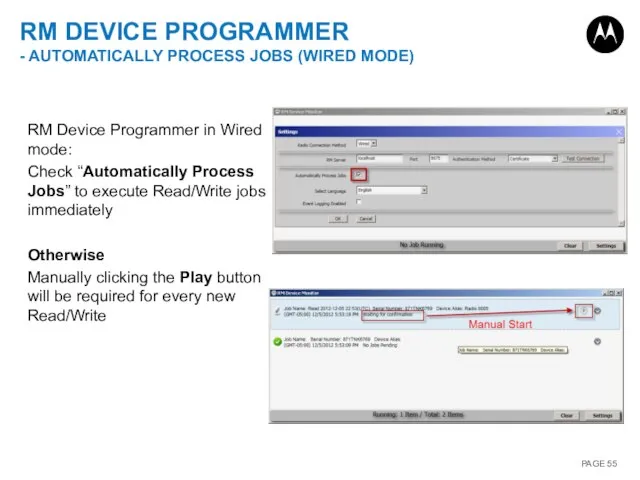
- 55. RM DEVICE PROGRAMMER - AUTOMATICALLY PROCESS JOBS (WIRED MODE) RM Device Programmer in Wired mode: Check
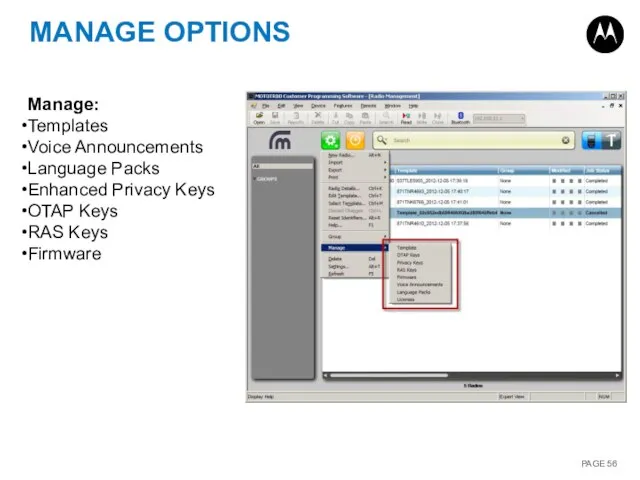
- 56. MANAGE OPTIONS Manage: Templates Voice Announcements Language Packs Enhanced Privacy Keys OTAP Keys RAS Keys Firmware
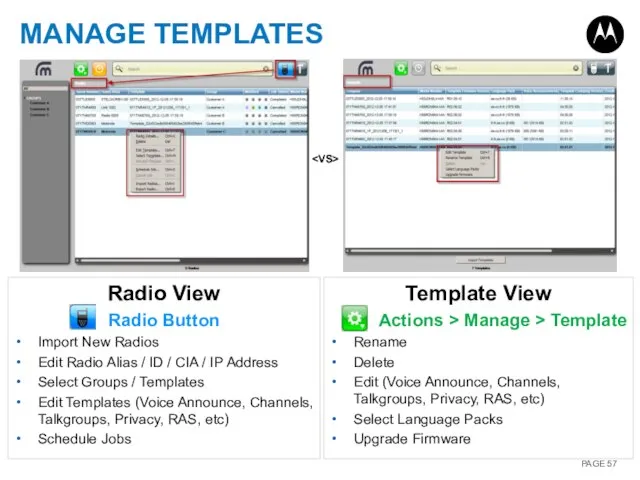
- 57. MANAGE TEMPLATES Radio View Radio Button Import New Radios Edit Radio Alias / ID / CIA
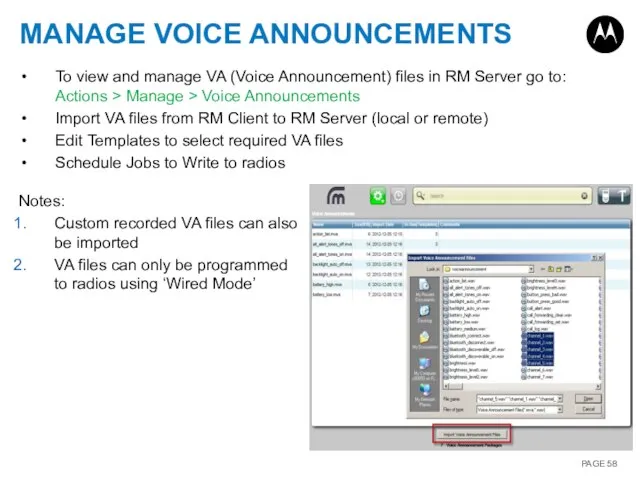
- 58. MANAGE VOICE ANNOUNCEMENTS To view and manage VA (Voice Announcement) files in RM Server go to:
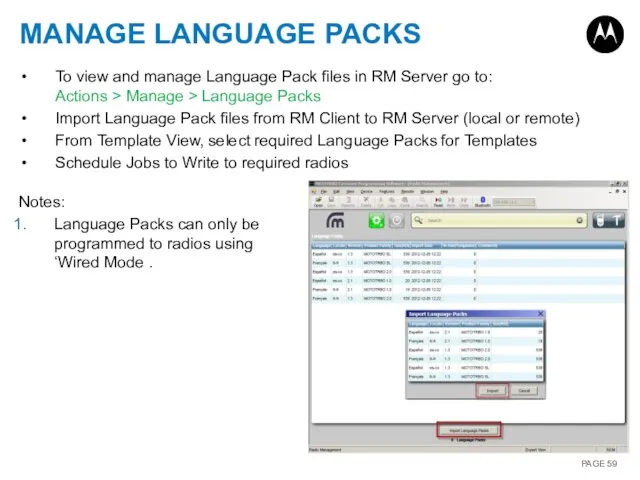
- 59. MANAGE LANGUAGE PACKS To view and manage Language Pack files in RM Server go to: Actions
- 60. MANAGE KEYS To view and manage Secure keys in RM Server go to one of the
- 61. MANAGE FIRMWARE To view and manage Firmware Packages in RM Server go to: Actions > Manage
- 62. MULTI-RADIO PROGRAMMING (WIN 7) Automatic sequential programming of up to 16 radios simultaneously connected via USB
- 64. Скачать презентацию

























 Базовые определения схемотехнического проектирования
Базовые определения схемотехнического проектирования Кто ты из Гравити Фолз?
Кто ты из Гравити Фолз? Fêtes en France
Fêtes en France Гвозди. Виды гвоздей (5 класс)
Гвозди. Виды гвоздей (5 класс) 20170509_prezentatsiya_vneklassnogo_meropriyatiya_matematicheskiy_kaleydoskop
20170509_prezentatsiya_vneklassnogo_meropriyatiya_matematicheskiy_kaleydoskop Руководство_пользователя_для_онлайн_курса_ГПА
Руководство_пользователя_для_онлайн_курса_ГПА Технология производства качокавалло
Технология производства качокавалло 20150223_obshchenie._urok_2
20150223_obshchenie._urok_2 Материаловедение. Алюминиевые сплавы
Материаловедение. Алюминиевые сплавы 20160227_elektronnyy_uchebnik_dlya_nachalnogo_i_srednego_professionalnogo_obrazovaniya
20160227_elektronnyy_uchebnik_dlya_nachalnogo_i_srednego_professionalnogo_obrazovaniya Моя любимая мама (для школьников)
Моя любимая мама (для школьников)
 Презентация автомобилей женевского автосалона 2008
Презентация автомобилей женевского автосалона 2008 Сосны
Сосны Система договоров оптового рынка электроэнергии после 01.04.2006
Система договоров оптового рынка электроэнергии после 01.04.2006 Мой выбор профессии
Мой выбор профессии Игра Brain Штурм
Игра Brain Штурм winter clothes _ memory _ by Artem Morozov
winter clothes _ memory _ by Artem Morozov пасха 2017
пасха 2017 20140704_proektnaya_deyatelnost_kak_sredstvo_realizatsii_fgos_na_urokakh
20140704_proektnaya_deyatelnost_kak_sredstvo_realizatsii_fgos_na_urokakh Modern equipment and devices in railway transport
Modern equipment and devices in railway transport Урок 15. Периметр
Урок 15. Периметр Тепловая схема турбоустановки ТЭЦ МЭИ
Тепловая схема турбоустановки ТЭЦ МЭИ 20140911_kashpurov
20140911_kashpurov Плетёные листья
Плетёные листья 20151102_brestskiy-mir_
20151102_brestskiy-mir_ Ай да мы!
Ай да мы! Презентация инструкция для участников олимпиады
Презентация инструкция для участников олимпиады