Содержание
- 2. Write to a Text File Example import java.io.*; public void Write(String fileId){ PrintStream outF = null;
- 3. Home Exercise: Create Deposit Report Modify 512SortDepo project to get deposit report in a text file.
- 4. Read from a Text File Example public void Read(String fileId){ BufferedReader inF = null; try{ inF
- 5. Random Access Files Random access files permit nonsequential, or random, access to a file's contents To
- 6. Random Access File Example File f = new File("test.txt"); FileChannel fc = (FileChannel.open(f, READ, WRITE)); fc.position(10);
- 7. What Is a Path? Java 7 A file is identified by its path through the file
- 8. Relative and Absolute Path A path is either relative or absolute. The latter contains the root
- 9. Creating a Path A Path instance contains the information used to specify the location of a
- 10. Path Operations Retrieving Information About a Path Converting a Path Joining Two Paths Creating a Path
- 11. The File Class The Files class is the other primary entrypoint of the java.nio.file package You
- 12. Some File Operations Verifying the Existence of a File or Directory (exists, notExists) Checking File Accessibility
- 14. Скачать презентацию











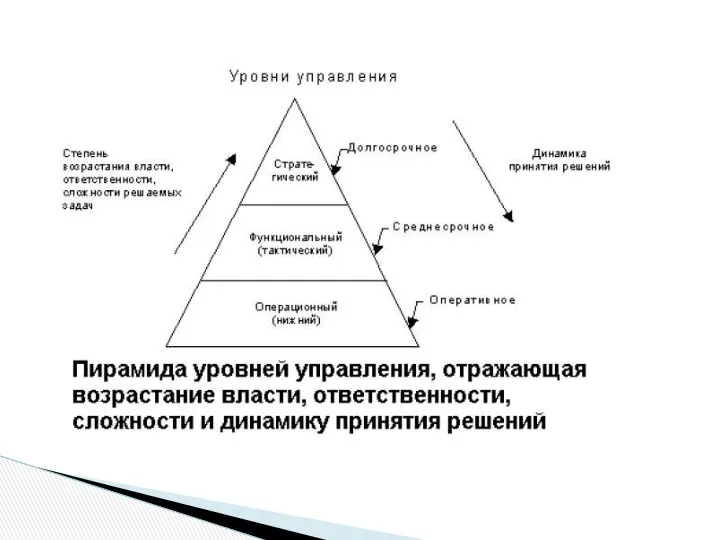 Стратегическое управление
Стратегическое управление ВандюковГалееваДолгашевПрезентация
ВандюковГалееваДолгашевПрезентация Основы вайшнавской этики
Основы вайшнавской этики Презентация "Художественная культура Востока" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Художественная культура Востока" - скачать презентации по МХК Презентация Текстильные материалы Ткани
Презентация Текстильные материалы Ткани Театр древней Греции 9 класс - Презентация
Театр древней Греции 9 класс - Презентация Патогенные грамотрицательные кокки СПбГУ 2015
Патогенные грамотрицательные кокки СПбГУ 2015  Ми-маленькі українці. Тренажер з читання - презентация для начальной школы_
Ми-маленькі українці. Тренажер з читання - презентация для начальной школы_ «Тропа здоровья» - спортивный праздник для детей и родителей
«Тропа здоровья» - спортивный праздник для детей и родителей Виды спортивного туризма, формируемые на индивидуальной основе
Виды спортивного туризма, формируемые на индивидуальной основе Квазистационарное электромагнитное поле
Квазистационарное электромагнитное поле Стиль конструктивизм в интерьере
Стиль конструктивизм в интерьере Основные факторы, вызывающие разрушение искусственных покрытий
Основные факторы, вызывающие разрушение искусственных покрытий Презентация "Осоргин Михаил Андреев" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Осоргин Михаил Андреев" - скачать презентации по МХК Общие положения Концепции внешней политики Российской Федерации, цель и сфера ее применения
Общие положения Концепции внешней политики Российской Федерации, цель и сфера ее применения Строительная светотехника. Классификация освещения по виду используемой энергии
Строительная светотехника. Классификация освещения по виду используемой энергии Баженовское месторождение. Разработка схемы получения классифицированного щебня фракции -40+20
Баженовское месторождение. Разработка схемы получения классифицированного щебня фракции -40+20 Емоційна компетентність менеджера в умовах кризи
Емоційна компетентність менеджера в умовах кризи Тройной интеграл Виды поверхностей второго порядка Замена переменных в тройном интеграле Тройной интеграл в цилиндрических коор
Тройной интеграл Виды поверхностей второго порядка Замена переменных в тройном интеграле Тройной интеграл в цилиндрических коор Пятое занятие. Функции
Пятое занятие. Функции Податкова реформа 2016
Податкова реформа 2016 Продукт добровольного медицинского страхования "Клещевой энцефалит"
Продукт добровольного медицинского страхования "Клещевой энцефалит" Физическая культура в общекультурной и профессиональной подготовке студентов
Физическая культура в общекультурной и профессиональной подготовке студентов Гибридные процессоры AMD, особенности архитектуры, аналоги Intel, преимущества и недостатки
Гибридные процессоры AMD, особенности архитектуры, аналоги Intel, преимущества и недостатки Прислівник
Прислівник Правила употребления предлогов в китайском языке
Правила употребления предлогов в китайском языке Геометрические элементы трассы в плане
Геометрические элементы трассы в плане Схема дистанции соревнований по ски-альпинизму
Схема дистанции соревнований по ски-альпинизму