Содержание
- 2. Objectives To introduce several different paradigms of programming But isn’t one language pretty much like another?
- 3. Paradigms of Programming? There are several ways to think about computation: a set of instructions to
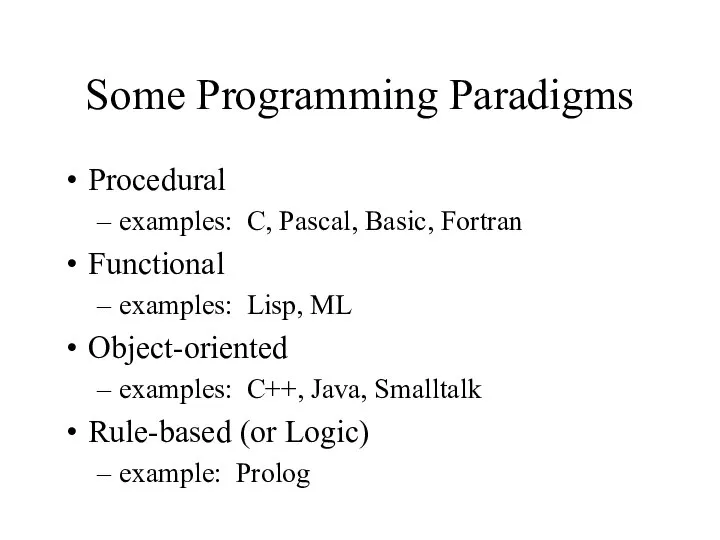
- 4. Some Programming Paradigms Procedural examples: C, Pascal, Basic, Fortran Functional examples: Lisp, ML Object-oriented examples: C++,
- 5. Why so many? Most important: the choice of paradigm (and therefore language) depends on how humans
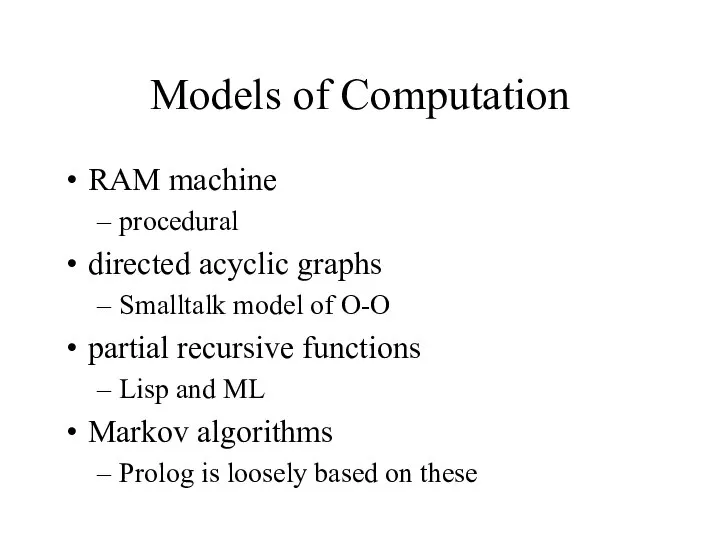
- 6. Models of Computation RAM machine procedural directed acyclic graphs Smalltalk model of O-O partial recursive functions
- 7. Lots of Languages There are many programming languages out there Lots of other PL-like objects document
- 8. Issues for all Languages Can it be understood by people and processed by machines? although translation
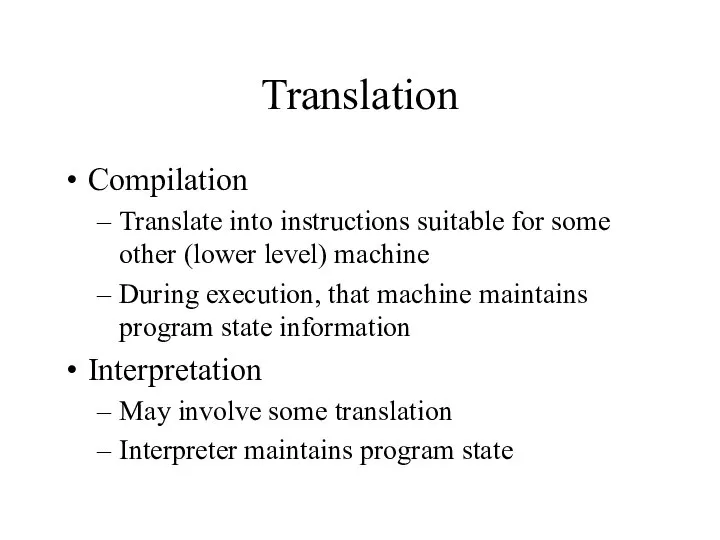
- 9. Translation Compilation Translate into instructions suitable for some other (lower level) machine During execution, that machine
- 11. Скачать презентацию





 Презентация "Пейзажи впечатления в творчестве К. Моне" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Пейзажи впечатления в творчестве К. Моне" - скачать презентации по МХК Среда программирования OpenMP. (Лекция 1)
Среда программирования OpenMP. (Лекция 1) Богатства, отданные людям
Богатства, отданные людям Как много... и как мало - презентация для начальной школы_
Как много... и как мало - презентация для начальной школы_ Презентация на тему "Начальная школа XXI" - скачать презентации по Педагогике
Презентация на тему "Начальная школа XXI" - скачать презентации по Педагогике Презентация "Энергетика одна из важнейших отраслей экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Энергетика одна из важнейших отраслей экономики" - скачать презентации по Экономике Психология воинского коллектива и ее учет в повседневной деятельности командира
Психология воинского коллектива и ее учет в повседневной деятельности командира Содержание права собственности на землю. Подготовили Студенты ЮФ-3 Группа Ю-101 Шевцова Е. и Меженько Ю.
Содержание права собственности на землю. Подготовили Студенты ЮФ-3 Группа Ю-101 Шевцова Е. и Меженько Ю. БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ ЖИЗНЕДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ
БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ ЖИЗНЕДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТИ Менеджмент и управление: основные понятия
Менеджмент и управление: основные понятия Russia’s Syrian “Gambit”
Russia’s Syrian “Gambit” Психология физической культуры и спорта
Психология физической культуры и спорта 6._Система_контроля_цвета_COLOR_IQC_2015
6._Система_контроля_цвета_COLOR_IQC_2015 Конструктивное и декоративное начало в изобразительном искусстве
Конструктивное и декоративное начало в изобразительном искусстве Особые случаи применения симплекс-метода. Лекция 4
Особые случаи применения симплекс-метода. Лекция 4 Стеганография и ее использование в защите информации
Стеганография и ее использование в защите информации Эффективность борьбы с коррупцией в Китае Подготовил Котов Павел Т093
Эффективность борьбы с коррупцией в Китае Подготовил Котов Павел Т093 Предыстория появления электрических систем связи
Предыстория появления электрических систем связи Mein zuhause. Was gibt es da alles?
Mein zuhause. Was gibt es da alles? Формы правления. Формы государственно-территориального устройства
Формы правления. Формы государственно-территориального устройства Der Computer – ein Werkzeug der Zukunft
Der Computer – ein Werkzeug der Zukunft Cookie. Лекция 3
Cookie. Лекция 3 Применение программного продукта MATLAB для решения инженерной задачи
Применение программного продукта MATLAB для решения инженерной задачи МОДЕЛЬ ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИЯ БИЗНЕСА Ф. ГУИЯРА И ДЖ. КЕЛЛИ
МОДЕЛЬ ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИЯ БИЗНЕСА Ф. ГУИЯРА И ДЖ. КЕЛЛИ  ООО «Северный лес»
ООО «Северный лес» Развитие исследований: от гена до функции
Развитие исследований: от гена до функции Отстаивание
Отстаивание  Bridges and Tunnels
Bridges and Tunnels