Содержание
- 3. Transcription occurs by base pairing in a bubble" of unpaired DNA ·RNA polymerase separates the two
- 4. Initiation describes the stages of transcription up to synthesis of the first bond in RNA. This
- 5. T7 RNA polymerase has a specificity loop that binds positions -7 to -11 of the promoter
- 6. DNA moves through a groove in yeast RNA polymerase that makes a sharp turn at the
- 7. Ten subunits of RNA polymerase are placed in position from the crystal structure. The colors of
- 8. The end view of the crystal structure of RNA polymerase II from yeast shows that DNA
- 9. DNA is forced to make a turn at the active site by a wall of protein.
- 16. Скачать презентацию
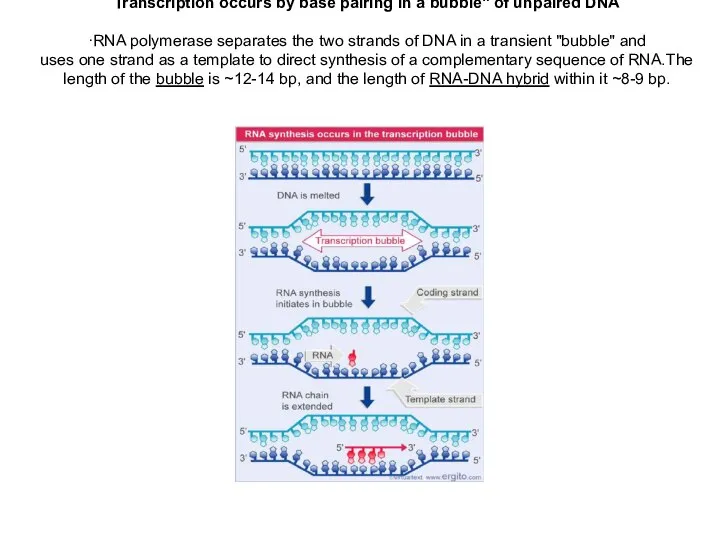
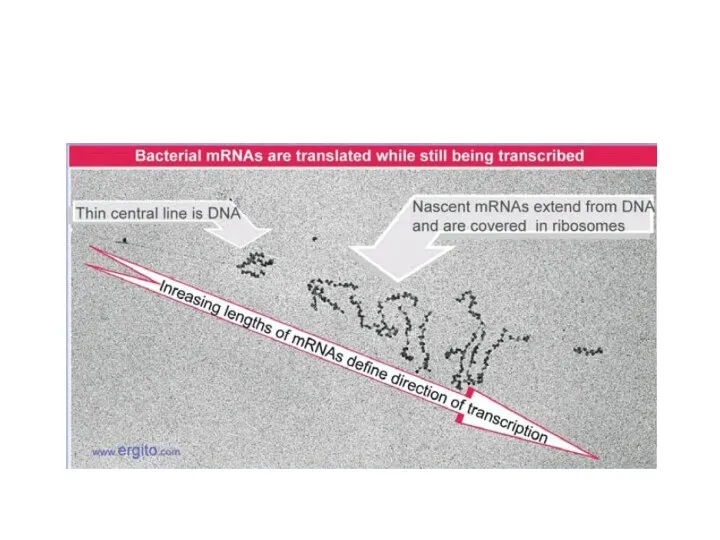
Transcription occurs by base pairing in a bubble" of unpaired DNA
Transcription occurs by base pairing in a bubble" of unpaired DNA
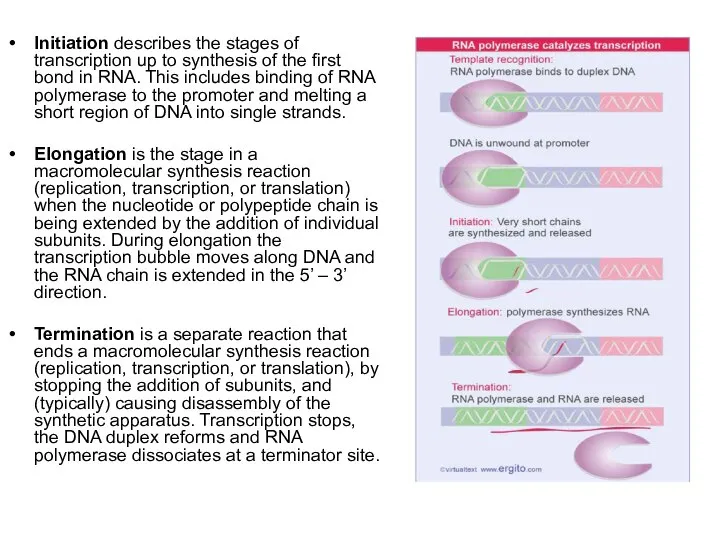
Initiation describes the stages of transcription up to synthesis of the
Initiation describes the stages of transcription up to synthesis of the
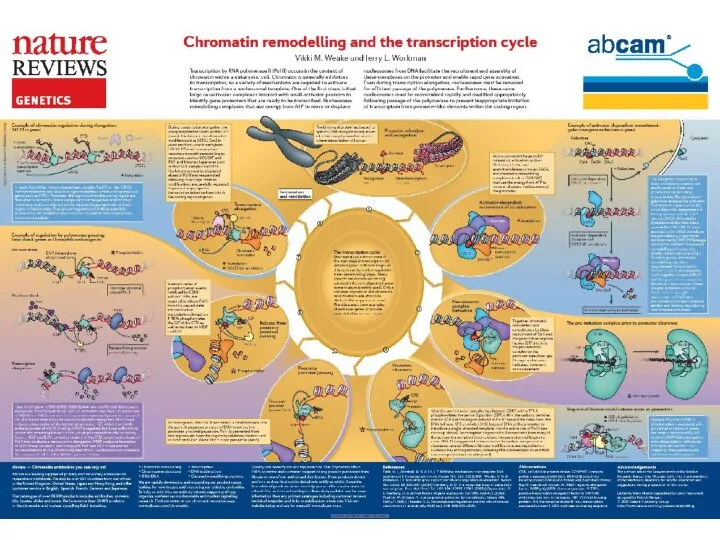
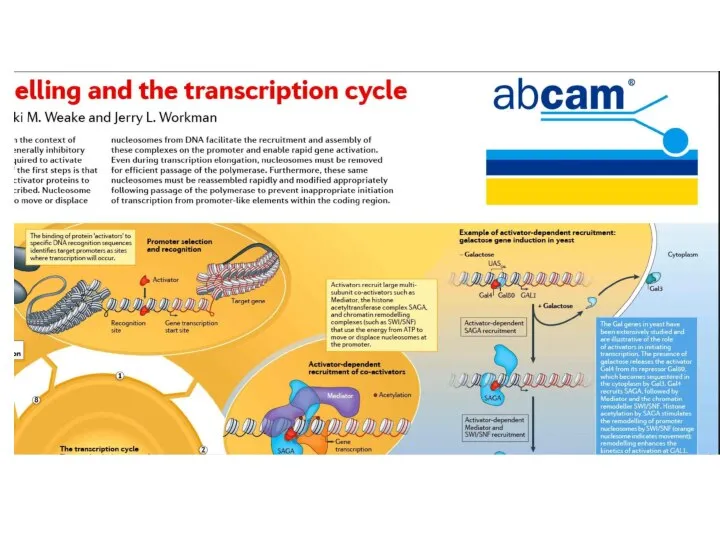
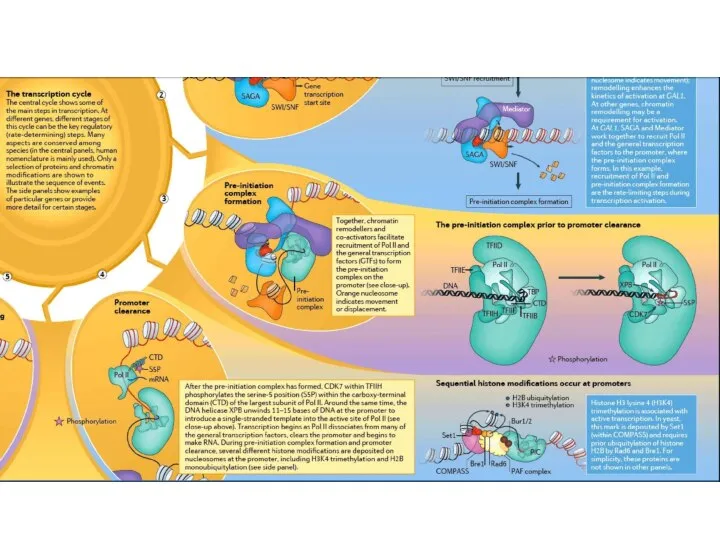
Elongation is the stage in a macromolecular synthesis reaction (replication, transcription, or translation) when the nucleotide or polypeptide chain is being extended by the addition of individual subunits. During elongation the transcription bubble moves along DNA and the RNA chain is extended in the 5’ – 3’ direction.
Termination is a separate reaction that ends a macromolecular synthesis reaction (replication, transcription, or translation), by stopping the addition of subunits, and (typically) causing disassembly of the synthetic apparatus. Transcription stops, the DNA duplex reforms and RNA polymerase dissociates at a terminator site.
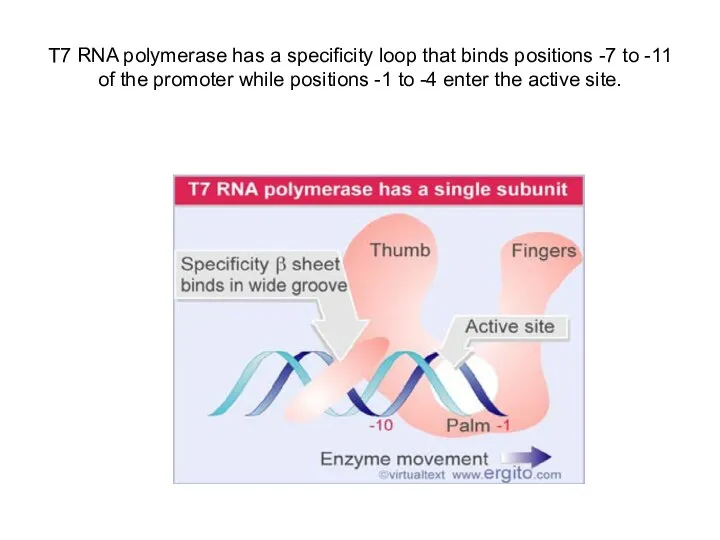
T7 RNA polymerase has a specificity loop that binds positions -7
T7 RNA polymerase has a specificity loop that binds positions -7
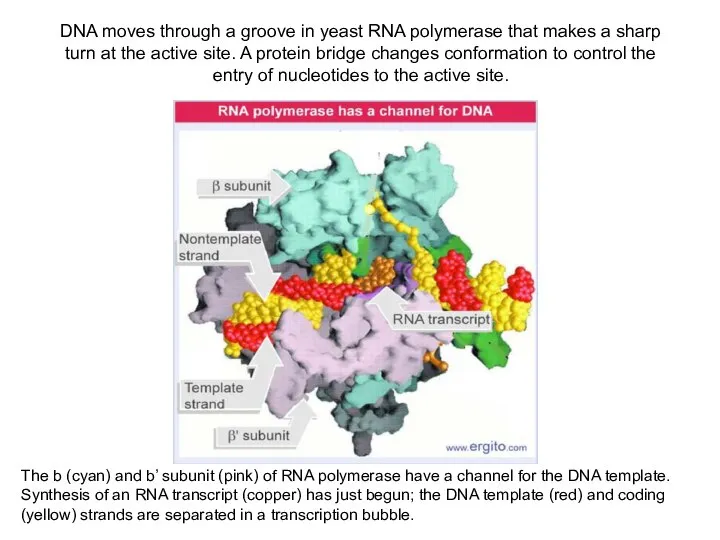
DNA moves through a groove in yeast RNA polymerase that makes
DNA moves through a groove in yeast RNA polymerase that makes
The b (cyan) and b’ subunit (pink) of RNA polymerase have a channel for the DNA template. Synthesis of an RNA transcript (copper) has just begun; the DNA template (red) and coding (yellow) strands are separated in a transcription bubble.
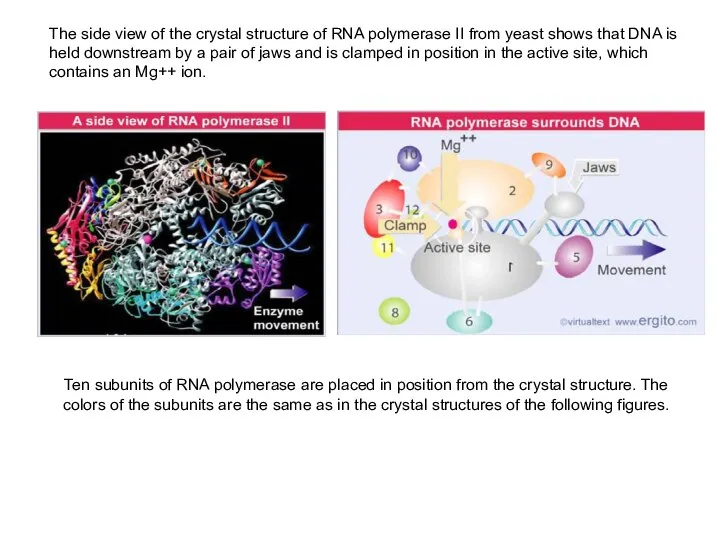
Ten subunits of RNA polymerase are placed in position from the
Ten subunits of RNA polymerase are placed in position from the
The side view of the crystal structure of RNA polymerase II from yeast shows that DNA is
held downstream by a pair of jaws and is clamped in position in the active site, which contains an Mg++ ion.
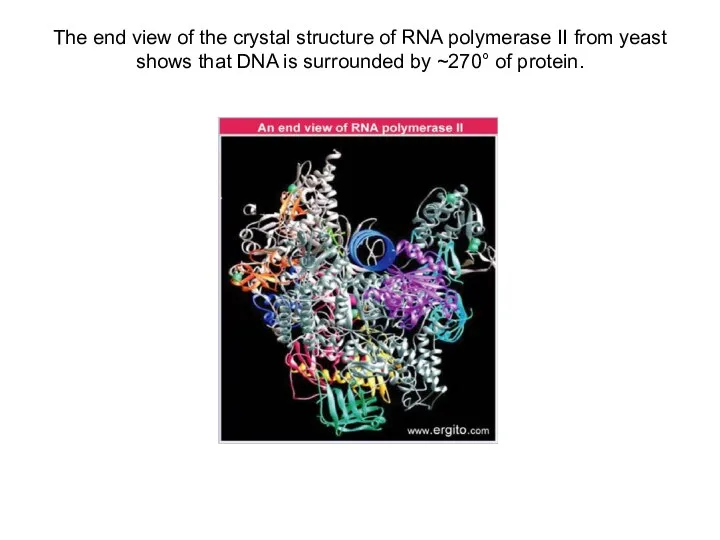
The end view of the crystal structure of RNA polymerase II
The end view of the crystal structure of RNA polymerase II
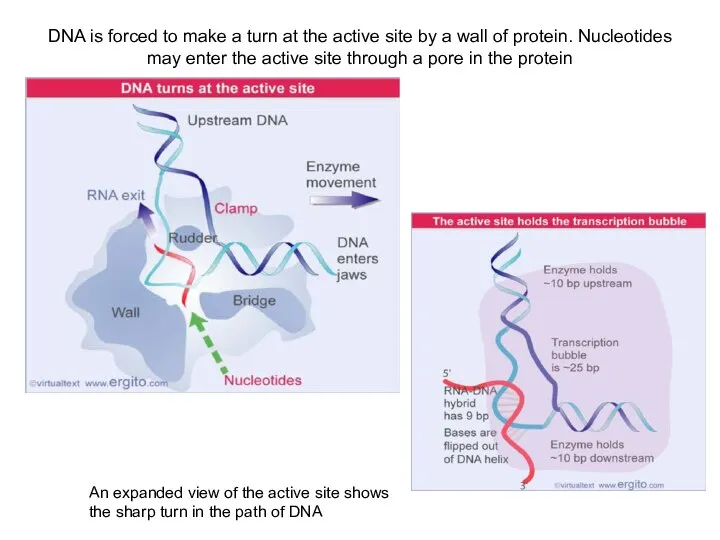
DNA is forced to make a turn at the active site
DNA is forced to make a turn at the active site
An expanded view of the active site shows the sharp turn in the path of DNA
 MY IDOLS
MY IDOLS Программирование виртуальной реальности с Alice и Java. (Лекция 1)
Программирование виртуальной реальности с Alice и Java. (Лекция 1) Общие положения по ОС в сухопутных войсках. Основы построения системы и узлов связи. (Тема 1.7)
Общие положения по ОС в сухопутных войсках. Основы построения системы и узлов связи. (Тема 1.7) Управленческий контроль
Управленческий контроль Человек и общество – 10 класс (профильный уровень) Учитель: Саетгареева Н.М.
Человек и общество – 10 класс (профильный уровень) Учитель: Саетгареева Н.М. Hoy vamos a aprender
Hoy vamos a aprender Конструктор та деструктор класу. Успадкування. Поліморфізм. Лекція 2. Об’єктно-орієнтоване програмування
Конструктор та деструктор класу. Успадкування. Поліморфізм. Лекція 2. Об’єктно-орієнтоване програмування Экономика и экономическая наука
Экономика и экономическая наука Выполнение курсового проекта
Выполнение курсового проекта Конфликтные ситуации.Управление конфликтами
Конфликтные ситуации.Управление конфликтами Jemaah Islamiayh (JI)
Jemaah Islamiayh (JI) Лекарственные средства и биологически активные добавки. Последствия их применения для спортсмена
Лекарственные средства и биологически активные добавки. Последствия их применения для спортсмена Презентация "Современные концепции менеджмента качества" - скачать презентации по Экономике
Презентация "Современные концепции менеджмента качества" - скачать презентации по Экономике Культура, традиции и быт чувашского народа
Культура, традиции и быт чувашского народа Культура Древнего Рима. Религия, обычаи, нравы, культура
Культура Древнего Рима. Религия, обычаи, нравы, культура Презентация на тему "Анатомо-физиологические, эмоциональные и психологические особенности детей младшего школьного возраста&qu
Презентация на тему "Анатомо-физиологические, эмоциональные и психологические особенности детей младшего школьного возраста&qu Преступления в сфере торговли товарами, содержащими объекты интеллектуальной Собственности
Преступления в сфере торговли товарами, содержащими объекты интеллектуальной Собственности  Автоматты реттеу заңдары
Автоматты реттеу заңдары Сущность и особенности функционирования валютных бирж на примере ММВБ Белоглазова юлия, Безнощук богдан, ДС-01
Сущность и особенности функционирования валютных бирж на примере ММВБ Белоглазова юлия, Безнощук богдан, ДС-01  Представление символьной информации. ASCII
Представление символьной информации. ASCII Организация педагогической деятельности музыкального руководителя в ДОУ в соответствии с ФГОС ДО Муниципальное бюджетное д
Организация педагогической деятельности музыкального руководителя в ДОУ в соответствии с ФГОС ДО Муниципальное бюджетное д Презентация "Православный храм II часть" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Православный храм II часть" - скачать презентации по МХК Диаграммы
Диаграммы Презентация Основные философские школы и течения антисциентизма в западной философии
Презентация Основные философские школы и течения антисциентизма в западной философии Презентация Должности государственной гражданской службы
Презентация Должности государственной гражданской службы  ДУХОВНО-НРАВСТВЕННОЕ ВОСПИТАНИЕ ПОДРАСТАЮЩЕГО ПОКОЛЕНИЯ КАК ГОСУДАРСТВЕННАЯ ПАРАДИГМА Викулов А.В., кандидат педагогических н
ДУХОВНО-НРАВСТВЕННОЕ ВОСПИТАНИЕ ПОДРАСТАЮЩЕГО ПОКОЛЕНИЯ КАК ГОСУДАРСТВЕННАЯ ПАРАДИГМА Викулов А.В., кандидат педагогических н Цилиндрические прямозубые передачи
Цилиндрические прямозубые передачи Тепловая инерция экодома
Тепловая инерция экодома