Содержание
- 2. Testing Previous Knowledge 29/03/2017 Sonali The concepts/terms learnt: Factors of production Factor Incomes Derived demand Employer/
- 3. Lesson Objectives 29/03/2017 Sonali The students will be able to Understand the nature of factors of
- 4. 29/03/2017 Sonali Activity 1 (5.51 min)
- 5. Class Discussion 29/03/2017 Sonali Nature of Factors of Production. Income earned by each factor
- 6. Reflection 29/03/2017 Sonali 1. What did you learn today? 2. Where are you going to use
- 7. Unit: 11.4A 29/03/2017 Sonali LABOUR MARKET Lesson 2-3 WEEK 1
- 8. Lesson Objectives 29/03/2017 Sonali The students will be able to Explain the peculiarity of resource markets,
- 9. Group Division GROUP 1: GROUP 2: GROUP 3: GROUP 4: KAZAKH LABOUR MARKET MINING
- 10. Activity 2-Critical Thinking (25 min) GROUP WORK- PRESENTATION : GROUP DISCUSSION Preparation Time: 10 min Presentation:
- 11. Class Discussion 29/03/2017 Sonali Nature of Kazakhstan’s Labour markets
- 12. Reflection What did you learn today ? Чему вы научились сегодня?
- 13. Unit: 11.4A-2 29/03/2017 Sonali Demand & Supply of labour WEEK 2 Lesson 4-6
- 14. Lesson Objectives 29/03/2017 Sonali The students will be able to Analyse the factors affecting the demand
- 15. 29/03/2017 Sonali
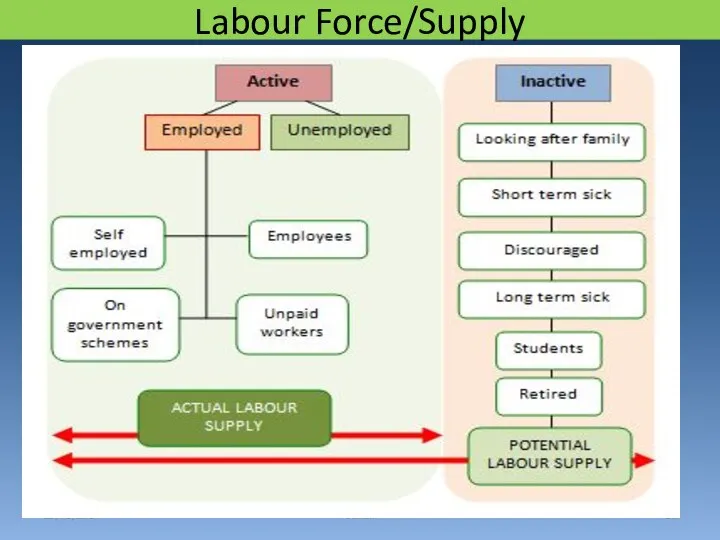
- 16. Labour Force/Supply 29/03/2017 Sonali
- 17. Demand for Labour 29/03/2017 Sonali Labour demand is a derived demand The demand for an additional
- 18. 29/03/2017 Sonali
- 19. 29/03/2017 Sonali Supply for Labour Labour force Population of working age Participation rate = unemployment rate
- 20. WAGE RATE DETERMINATION 29/03/2017 Sonali Equilibrium Wage Rate Demand for Labour = Supply of Labour New
- 21. Changes in equilibrium Wage rate 29/03/2017 Sonali
- 22. Elasticity of Demand and Supply of labour 29/03/2017 Sonali ELASTIC INELASTIC
- 23. 29/03/2017 Sonali
- 25. Скачать презентацию





















 Суспільне відтворення, його типи і показники
Суспільне відтворення, його типи і показники Требования ФГОС высшего образования по направлению подготовки 40.03.01 юриспруденция (уровень бакалавриата). Тема 1
Требования ФГОС высшего образования по направлению подготовки 40.03.01 юриспруденция (уровень бакалавриата). Тема 1 Издержки производства, доходы предприятия
Издержки производства, доходы предприятия Иностранный капитал в России. Структура, динамика, проблемы
Иностранный капитал в России. Структура, динамика, проблемы Общественный сектор. Экономика общественного сектора
Общественный сектор. Экономика общественного сектора Донецк - мой город
Донецк - мой город Финансы организаций. Финансы некоммерческих организаций. (Тема 3.7)
Финансы организаций. Финансы некоммерческих организаций. (Тема 3.7) Жаһандану процесіне сипаттама
Жаһандану процесіне сипаттама Презентация Размер трудовой пенсии по старости; основные понятия, применяемые при определении размера трудовой пенсии по старост
Презентация Размер трудовой пенсии по старости; основные понятия, применяемые при определении размера трудовой пенсии по старост Дальневосточный молодежный форум «Амур»
Дальневосточный молодежный форум «Амур» Анализ временных рядов. Аналитические и алгоритмические тренды. Сезонность
Анализ временных рядов. Аналитические и алгоритмические тренды. Сезонность Проблема импортозамещения в условиях экономических санкций
Проблема импортозамещения в условиях экономических санкций Развитые страны. Общая характеристика
Развитые страны. Общая характеристика Введение в «Макроэкономику»
Введение в «Макроэкономику» Что такое рынок. Спрос. Рынок как лучший администратор
Что такое рынок. Спрос. Рынок как лучший администратор Трудовые ресурсы предприятия
Трудовые ресурсы предприятия Сельское хозяйство Исландии
Сельское хозяйство Исландии Оптимальное налогообложение
Оптимальное налогообложение Глобальні пріоритети міжнародних стратегій економічного розвитку: сталість, конкурентоспроможність, макроекономічна стійкість
Глобальні пріоритети міжнародних стратегій економічного розвитку: сталість, конкурентоспроможність, макроекономічна стійкість Занятость и безработица. Рынок труда
Занятость и безработица. Рынок труда О.Замулин Уроки Фелпса - для мира и для России
О.Замулин Уроки Фелпса - для мира и для России Анализ временных рядов. Аналитические и алгоритмические тренды. Сезонность
Анализ временных рядов. Аналитические и алгоритмические тренды. Сезонность Понятие основных фондов предприятия
Понятие основных фондов предприятия Концепция устойчивого развития
Концепция устойчивого развития Презентация Новый курс Франклина Рузвельда
Презентация Новый курс Франклина Рузвельда Экономическая эффективность
Экономическая эффективность Виды движения предметов труда
Виды движения предметов труда Основные проблемы экономического развития общества. (Тема 2)
Основные проблемы экономического развития общества. (Тема 2)