Содержание
- 2. Newton’s Contributions Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of
- 3. Newton’s First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest and
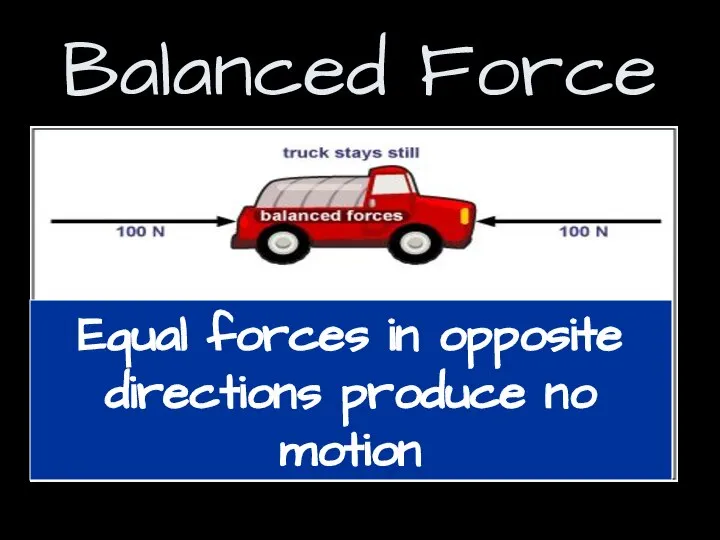
- 4. Balanced Force Equal forces in opposite directions produce no motion
- 5. Unbalanced Forces Unequal opposing forces produce an unbalanced force causing motion
- 6. If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why don’t moving objects keep moving forever?
- 7. Newton’s First Law (law of inertia) MASS is the measure of the amount of matter in
- 8. Newton’s First Law (law of inertia) INERTIA is a property of an object that describes how
- 9. 1st Law Unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, this golf ball would sit on the
- 10. There are four main types of friction: Sliding friction: ice skating Rolling friction: bowling Fluid friction
- 11. 1st Law Once airborne, unless acted on by an unbalanced force (gravity and air – fluid
- 12. Inertia
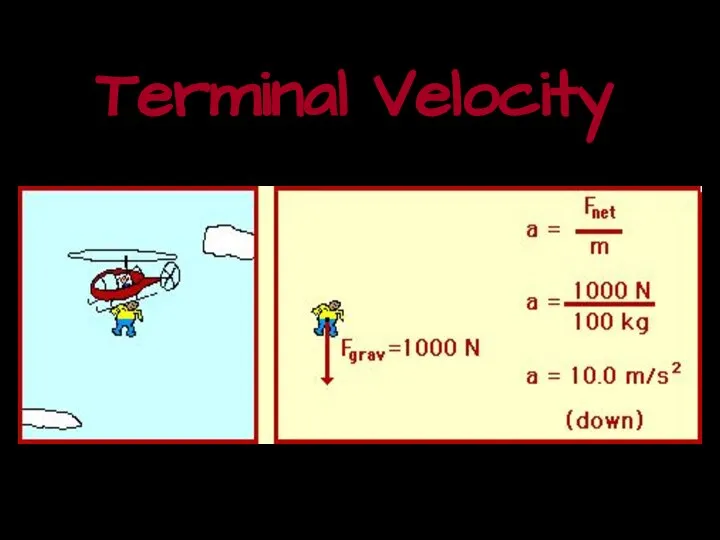
- 13. Terminal Velocity
- 14. Newton’s Second Law Force equals mass times acceleration. F = ma
- 15. Newton’s Second Law Force = Mass x Acceleration Force is measured in Newton ACCELERATION of GRAVITY(Earth)
- 16. Newton’s Second Law WEIGHT is a measure of the force of ___________ on the mass of
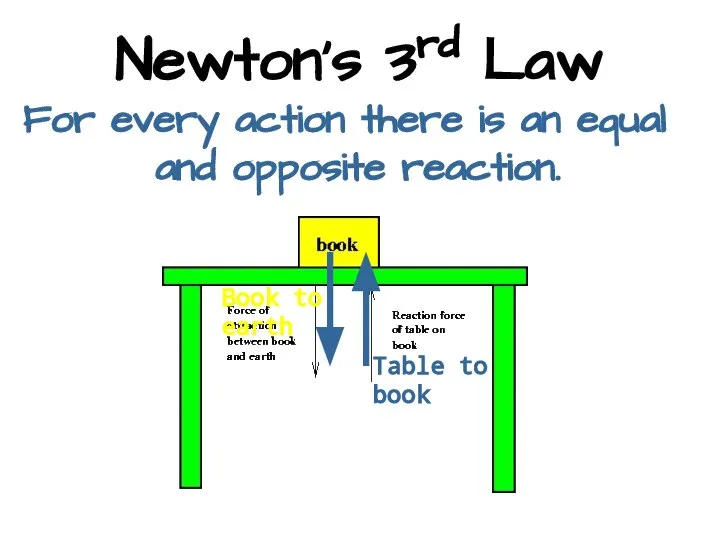
- 17. Newton’s Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- 18. Newton’s 3rd Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Book to earth
- 19. Newton’s Third Law A bug with a mass of 5 grams flies into the windshield of
- 20. Newton’s Third Law The force would be the same. Force (bug)= m x A Force (bus)=
- 21. Action: earth pulls on you Reaction: you pull on earth Action and Reaction on Different Masses
- 22. Action: tire pushes on road Reaction: road pushes on tire
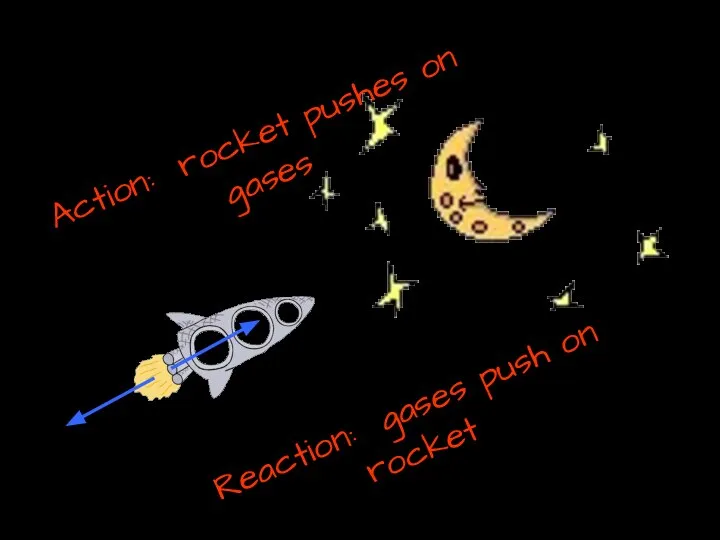
- 23. Action: rocket pushes on gases Reaction: gases push on rocket
- 24. Consider hitting a baseball with a bat. If we call the force applied to the ball
- 25. What Laws are represented?
- 27. Скачать презентацию




















 Сила трения. Вездесущее, мешающее, необходимое
Сила трения. Вездесущее, мешающее, необходимое Тепловое излучение
Тепловое излучение Презентация по физике "КВАНТОВІ ГЕНЕРАТОРИ. ПРИНЦИП ДІЇ ТА ЗАСТОСУВАННЯ" - скачать
Презентация по физике "КВАНТОВІ ГЕНЕРАТОРИ. ПРИНЦИП ДІЇ ТА ЗАСТОСУВАННЯ" - скачать  Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по физике Шагаем в мир электротехники
Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по физике Шагаем в мир электротехники Термодинамиканың 2-заңы
Термодинамиканың 2-заңы Двигатель внутреннего сгорания
Двигатель внутреннего сгорания ЯМР спектроскопия
ЯМР спектроскопия Тема урока Сообщающиеся сосуды Школа №13 8 класс Васильева М.В. 2008 год
Тема урока Сообщающиеся сосуды Школа №13 8 класс Васильева М.В. 2008 год Бензиновые и дизельные двигатели. Преимущества и недостатки в сравнении
Бензиновые и дизельные двигатели. Преимущества и недостатки в сравнении Колориметр фотоэлектрический концентрационный КФК-2МП
Колориметр фотоэлектрический концентрационный КФК-2МП Ядерный реактор
Ядерный реактор Источники света
Источники света Мікроскопи. Техніка мікроскопування
Мікроскопи. Техніка мікроскопування Расчет свободной энергии с помощью молекулярной динамики
Расчет свободной энергии с помощью молекулярной динамики Деятельность РМО учителей физики в 2013-2014 учебном году: цифры и факты
Деятельность РМО учителей физики в 2013-2014 учебном году: цифры и факты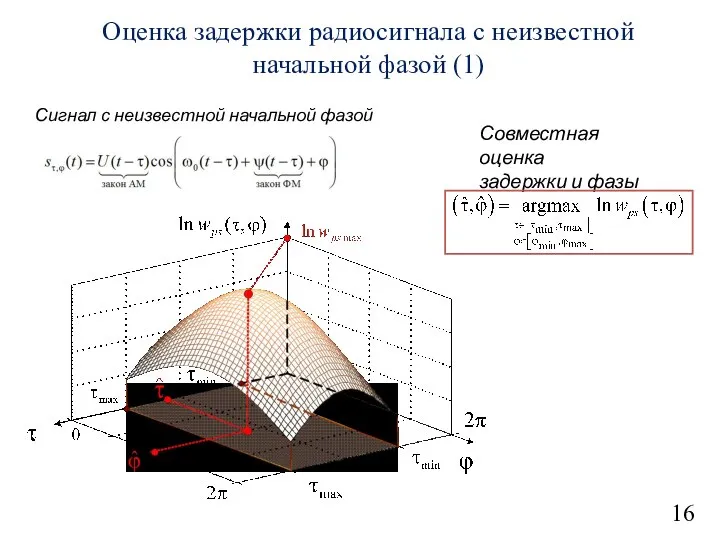 Оценка задержки радиосигнала с неизвестной начальной фазой
Оценка задержки радиосигнала с неизвестной начальной фазой Вага тіла, що рухається з прискоренням
Вага тіла, що рухається з прискоренням Проводниковые материалы
Проводниковые материалы Силы в механике
Силы в механике Законы Ньютона Три закона, лежащие в основе классической механики
Законы Ньютона Три закона, лежащие в основе классической механики Контроль параметрів радіовипромінювання. Радіоперешкоди
Контроль параметрів радіовипромінювання. Радіоперешкоди Гальванометр. Виды и применение
Гальванометр. Виды и применение Прямолинейное равноускоренное движение. Ускорение
Прямолинейное равноускоренное движение. Ускорение Тепловые излучения и фотоны
Тепловые излучения и фотоны Терморезистор
Терморезистор Закон электромагнитной индукции. (Лекция 4)
Закон электромагнитной индукции. (Лекция 4) Равновесие при радиоактивном распаде. (Лекция 2)
Равновесие при радиоактивном распаде. (Лекция 2) Первое начало термодинамики. Температура. (Лекция 3)
Первое начало термодинамики. Температура. (Лекция 3)