Содержание
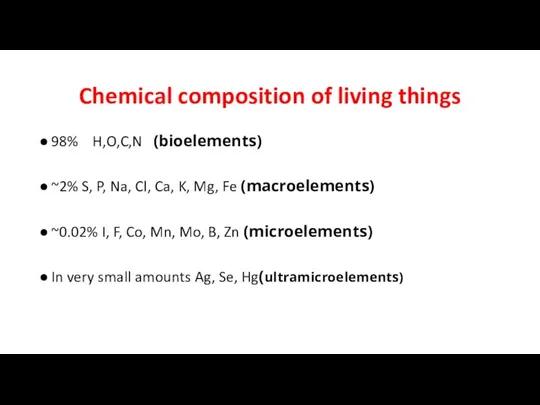
- 2. Chemical composition of living things 98% H,O,C,N (bioelements) ~2% S, P, Na, Cl, Ca, K, Mg,
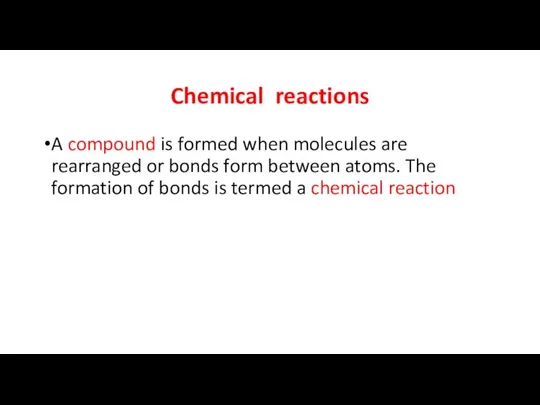
- 3. Chemical reactions A compound is formed when molecules are rearranged or bonds form between atoms. The
- 4. Types of reaction Oxidation - reduction (redox) reactions Anabolic - catabolic reactions Hydrolysis - dehydration synthesis
- 5. Oxidation - reduction (redox) reactions A chemical reaction involves physical changes to all the reactants involved.
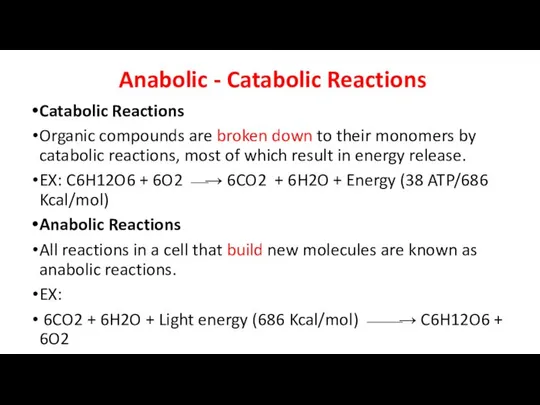
- 6. Anabolic - Catabolic Reactions Catabolic Reactions Organic compounds are broken down to their monomers by catabolic
- 8. Скачать презентацию


 Конструкционные функциональные волокнистые композиты
Конструкционные функциональные волокнистые композиты Металлы и сплавы. История цивилизаций
Металлы и сплавы. История цивилизаций Многоатомные спирты. Фенол.
Многоатомные спирты. Фенол. Из чего оно сделано молоко
Из чего оно сделано молоко Алканы. Состав, строение, свойства и химические превращения. Экологические последствия. Синтезы генетическая связь
Алканы. Состав, строение, свойства и химические превращения. Экологические последствия. Синтезы генетическая связь Проблемы и меры по защите окружающей среды ПМР
Проблемы и меры по защите окружающей среды ПМР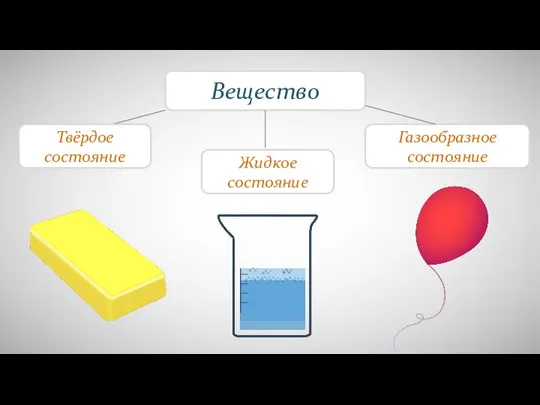 Различия в молекулярном строении газов, жидкостей и твердых тел
Различия в молекулярном строении газов, жидкостей и твердых тел Презентация по химии Введение в биоорганическую химию
Презентация по химии Введение в биоорганическую химию  160198375
160198375 Методы контроля и анализа веществ
Методы контроля и анализа веществ Чистые вещества и смеси
Чистые вещества и смеси Приборы для измерения температуры
Приборы для измерения температуры Химические реакции. Реакции по фазовому составу
Химические реакции. Реакции по фазовому составу Викторина. Дмитрий Иванович Менделеев
Викторина. Дмитрий Иванович Менделеев Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity Фолиевая кислота
Фолиевая кислота  Менделєєв Дмитро Іванович Роботу виконав: Учень 11 - Б класу Вдовіченко І. Вчитель інформатики: Трибко О.Б.
Менделєєв Дмитро Іванович Роботу виконав: Учень 11 - Б класу Вдовіченко І. Вчитель інформатики: Трибко О.Б.  Щелочноземельные металлы
Щелочноземельные металлы Воронежская область п.г.т. Анна, МОУ Аннинская средняя общеобразовательная школа №1 Выполнила: учитель химии высшей квалифика
Воронежская область п.г.т. Анна, МОУ Аннинская средняя общеобразовательная школа №1 Выполнила: учитель химии высшей квалифика Углеводы: простые и сложные. Строение, свойства и биологическая роль
Углеводы: простые и сложные. Строение, свойства и биологическая роль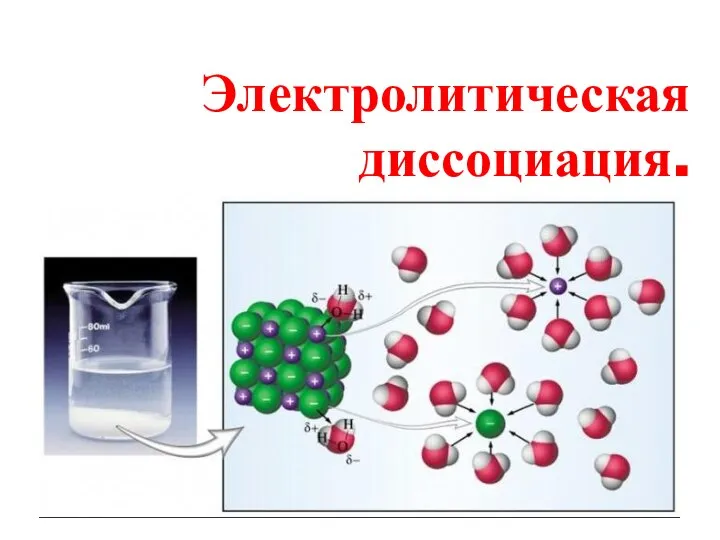 Электролитическая диссоциация
Электролитическая диссоциация Опал
Опал Презентация по Химии "Глюкоза - альдегідоспирт" - скачать смотреть бесплатно
Презентация по Химии "Глюкоза - альдегідоспирт" - скачать смотреть бесплатно Лекарственные растения и сырье, содержащие гликозиды. (Лекция 7)
Лекарственные растения и сырье, содержащие гликозиды. (Лекция 7) Защитные покрытия поверхности металла от коррозии
Защитные покрытия поверхности металла от коррозии Автомобильные бензины и дизельное топливо
Автомобильные бензины и дизельное топливо Адсорбционные равновесия и процессы на подвижных и неподвижных границах раздела
Адсорбционные равновесия и процессы на подвижных и неподвижных границах раздела Степень диссоциации. 9 класс
Степень диссоциации. 9 класс