Содержание
- 2. Pyramid and its elements Definition Main formulas Problems Examples Truncated pyramid
- 3. A convex polyhedron with one face a convex polygon (the base) and the vertices of the
- 4. A right-regular pyramid is one in which the base is a regular polygon and the remaining
- 5. A regular tetrahedron has equilateral triangles as its faces, and so all its edges have the
- 6. A pyramid which angles between lateral faces and base are equal
- 7. A pyramid which angles between edges and base are equal
- 8. The elements of pyramid Base Vertex Edge Lateral face
- 9. h - height m - apothem l – lateral edge r – inscribed radius R –
- 10. The examples of Pyramid in real life
- 11. Pyramid of life
- 12. The comparison of world’s pyramids
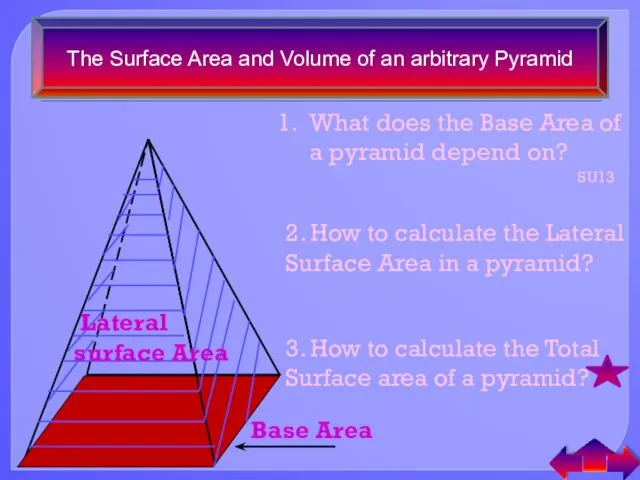
- 13. The Surface Area and Volume of an arbitrary Pyramid Base Area Lateral surface Area What does
- 14. Volume of a pyramid: Lateral Surface Area of a right-regular pyramid: (m-apothem): Tetrahedron (a solid figure
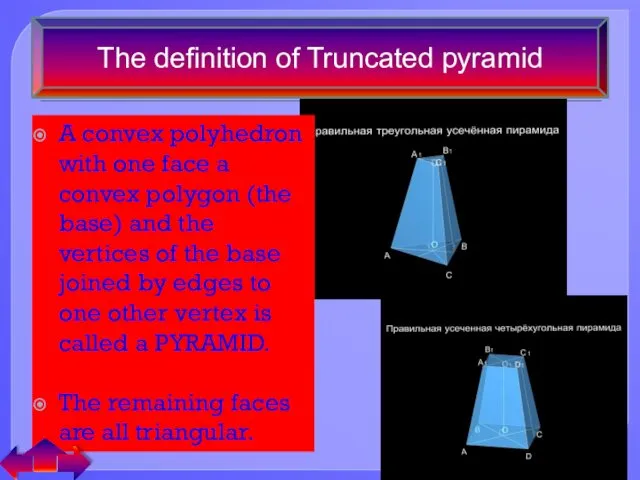
- 15. The definition of Truncated pyramid A convex polyhedron with one face a convex polygon (the base)
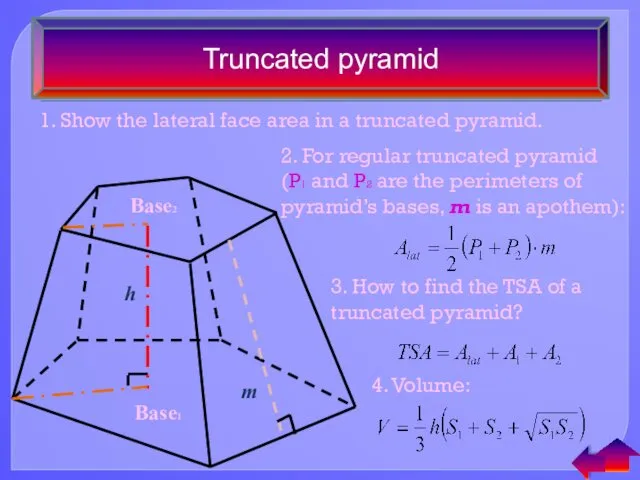
- 16. Truncated pyramid 1. Show the lateral face area in a truncated pyramid. 2. For regular truncated
- 17. Problems 3D examples Problem #1 Problem #2 Problem #3 Problem #4 Problem #5 Problem #6 Problem
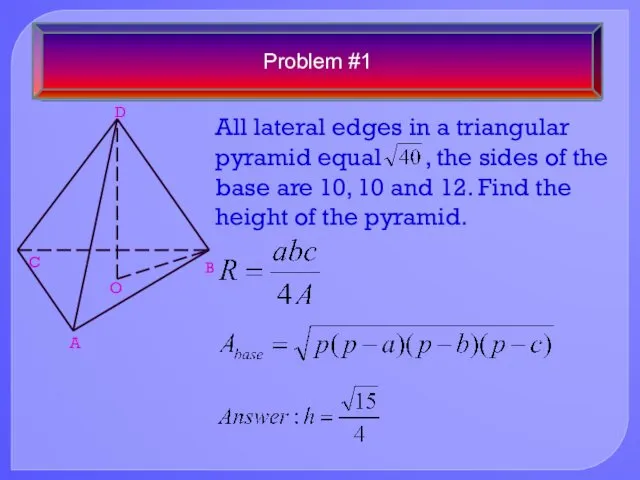
- 18. Problem #1 All lateral edges in a triangular pyramid equal , the sides of the base
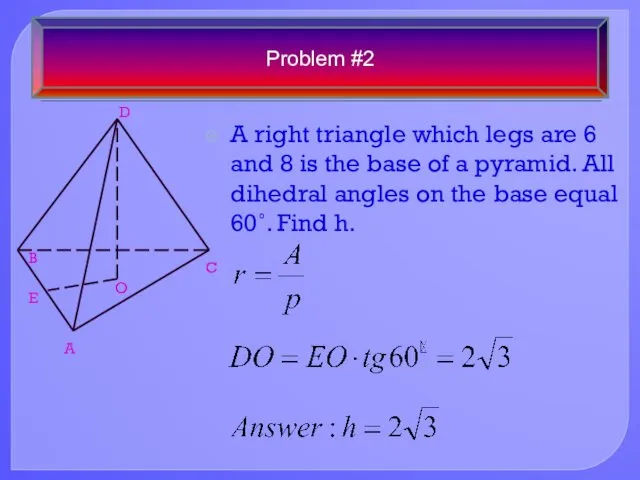
- 19. A right triangle which legs are 6 and 8 is the base of a pyramid. All
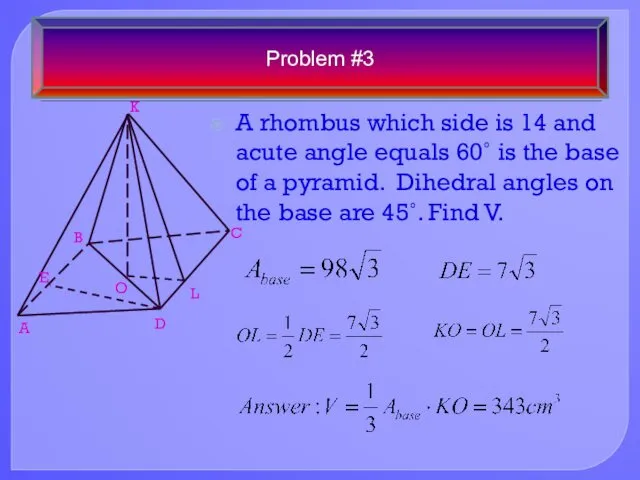
- 20. A rhombus which side is 14 and acute angle equals 60˚ is the base of a
- 21. Prism and its elements Definition Main formulas Problems Examples
- 22. Examples
- 23. A convex polyhedron with two “end” faces that are congruent convex polygons lying in parallel planes
- 24. A right-regular prism is one in which the two end faces are regular polygons and the
- 25. The types of Prism. Parallelepiped A parallelepiped is a prism in which the two end faces
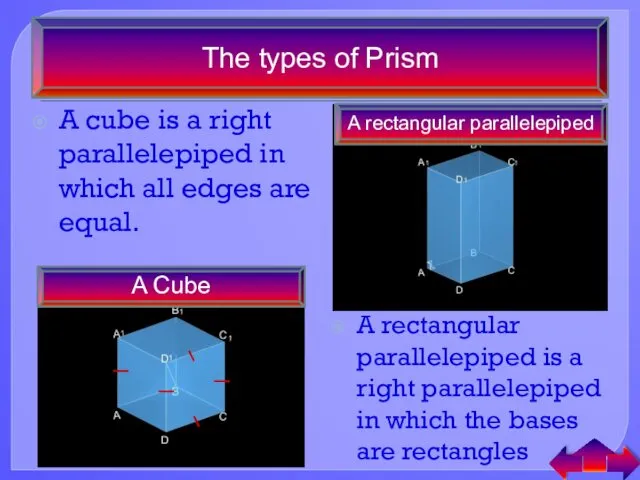
- 26. The types of Prism A cube is a right parallelepiped in which all edges are equal.
- 27. The types of Prism A quadrilateral prism A right-regular hexagonal prism Make the definitions of the
- 28. Prism and its elements
- 29. Surface area and Volume of a Prism
- 30. Cylinder and its elements Definition Main formulas Problems Examples
- 31. Examples
- 32. Examples
- 36. Скачать презентацию
























 Геометрический и механический смысл производной
Геометрический и механический смысл производной Две точки.Отрезок.
Две точки.Отрезок. Десятичные дроби на координатной прямой
Десятичные дроби на координатной прямой Неполные квадратные уравнения
Неполные квадратные уравнения Виды многогранников
Виды многогранников умножение дес др Основное
умножение дес др Основное Решение полного квадратного уравнения
Решение полного квадратного уравнения Сравнение чисел. 6 класс
Сравнение чисел. 6 класс Смешанные числа. Математический диктант
Смешанные числа. Математический диктант Тест по теме: "Объем прямой призмы и цилиндра"
Тест по теме: "Объем прямой призмы и цилиндра" Квадратичная функция
Квадратичная функция Численный анализ нелинейных моделей и теория Куна-Таккера (Лекция 5)
Численный анализ нелинейных моделей и теория Куна-Таккера (Лекция 5) Стенды "Сегодня на уроке"
Стенды "Сегодня на уроке" «Теорема Фалеса» 8 класс. Урок №9 по геометрии
«Теорема Фалеса» 8 класс. Урок №9 по геометрии Алгебра и начала анализа. 9-10 класс. Радианная мера углов и дуг
Алгебра и начала анализа. 9-10 класс. Радианная мера углов и дуг Cálculo numérico. Resolução de equações diferenciais ordinárias de 1a ordem. (Aula 9)
Cálculo numérico. Resolução de equações diferenciais ordinárias de 1a ordem. (Aula 9) Старинные единицы измерения
Старинные единицы измерения Время и его измерение
Время и его измерение Теорема сложения вероятностей совместных событий
Теорема сложения вероятностей совместных событий Правильные многогранники
Правильные многогранники Распредели предметы поровну. 2 класс
Распредели предметы поровну. 2 класс Системы линейных уравнений с двумя переменными
Системы линейных уравнений с двумя переменными Одночлены. Многочлен. Цифровой диктант
Одночлены. Многочлен. Цифровой диктант Интегралы, зависящие от параметра
Интегралы, зависящие от параметра Логарифмическая и обратные тригонометрические функции комплексного переменного
Логарифмическая и обратные тригонометрические функции комплексного переменного Урок математики в 4 классе Тема урока : «Деление многозначного числа на однозначное.» Учитель: Залалтдинова Л.Д.
Урок математики в 4 классе Тема урока : «Деление многозначного числа на однозначное.» Учитель: Залалтдинова Л.Д.  Тригонометрически уравнения
Тригонометрически уравнения Деление числа на произведение
Деление числа на произведение