Содержание
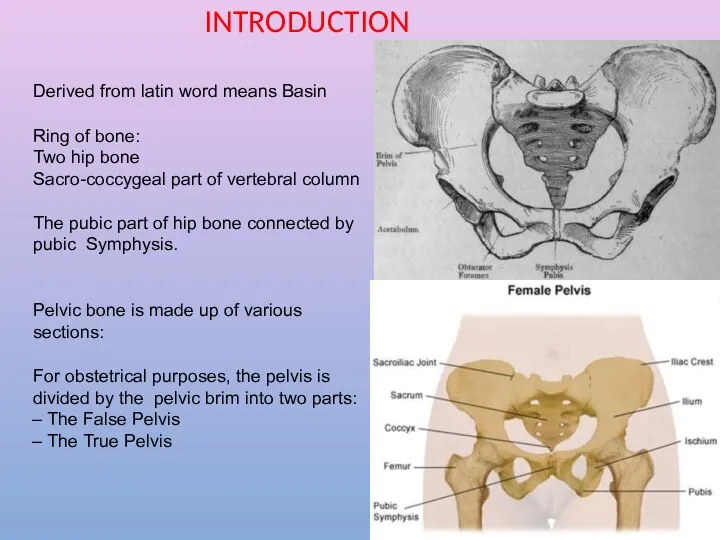
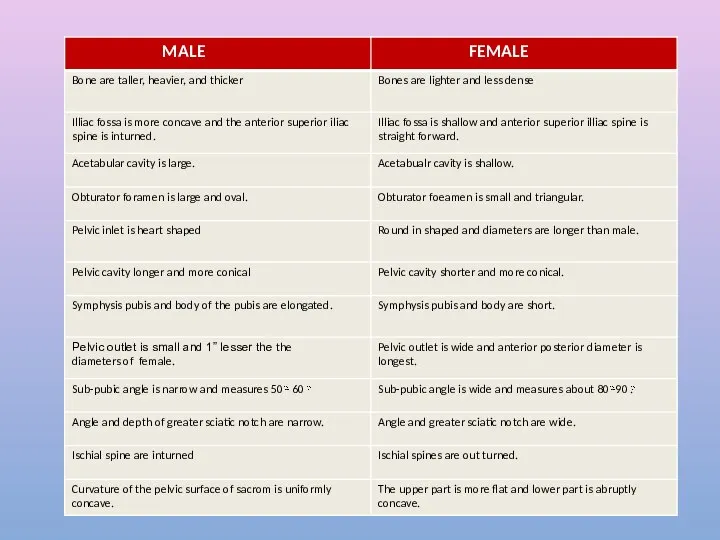
- 2. Derived from latin word means Basin Ring of bone: Two hip bone Sacro-coccygeal part of vertebral
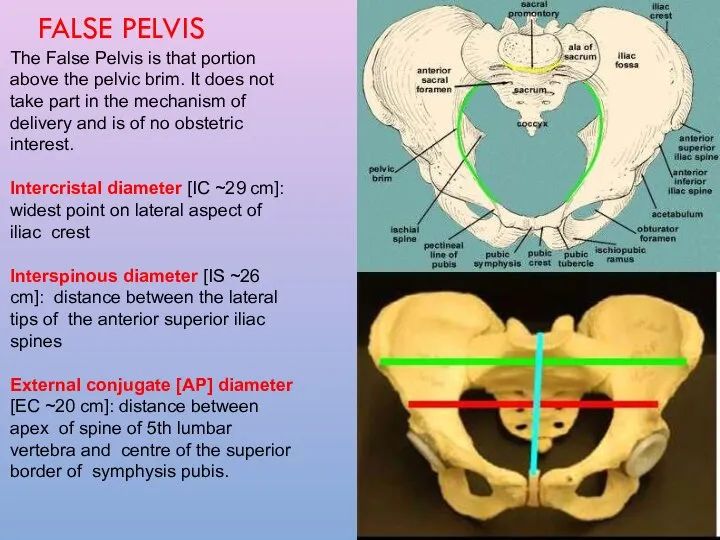
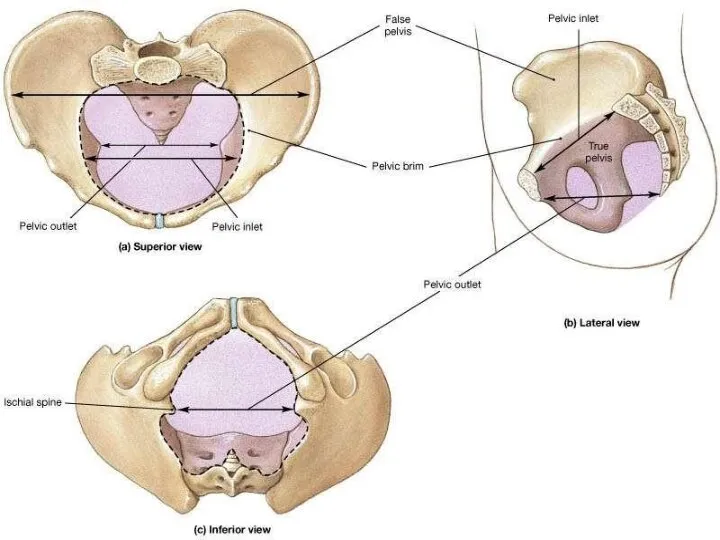
- 3. The False Pelvis is that portion above the pelvic brim. It does not take part in
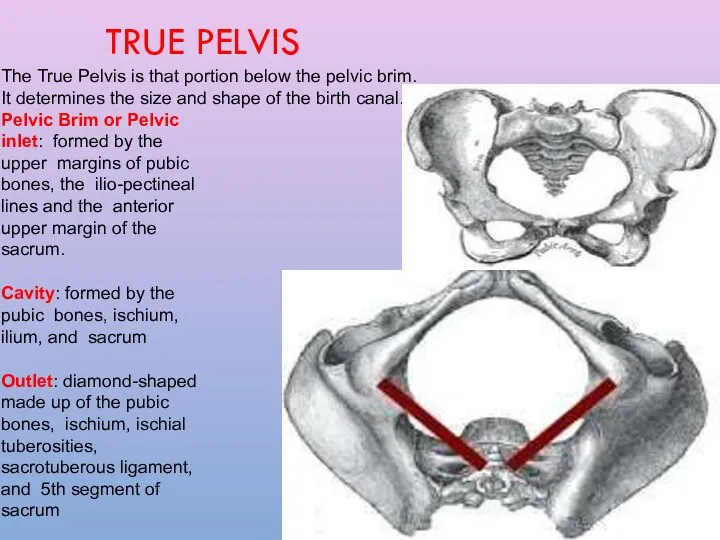
- 5. The True Pelvis is that portion below the pelvic brim. It determines the size and shape
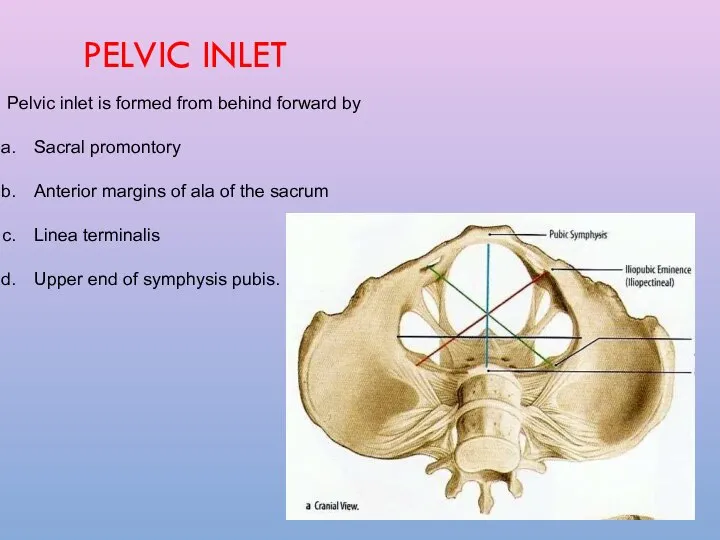
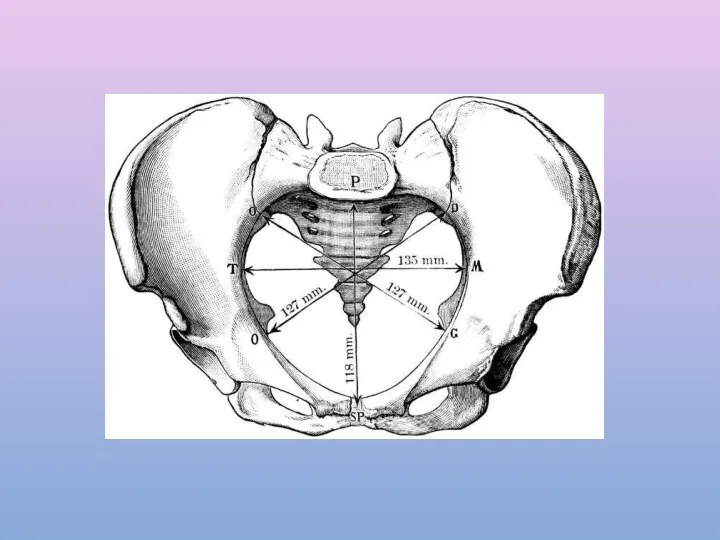
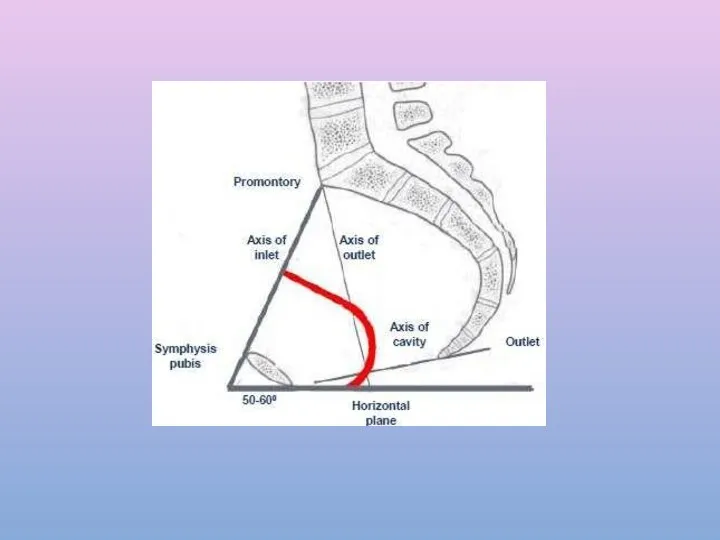
- 6. PELVIC INLET Pelvic inlet is formed from behind forward by Sacral promontory Anterior margins of ala
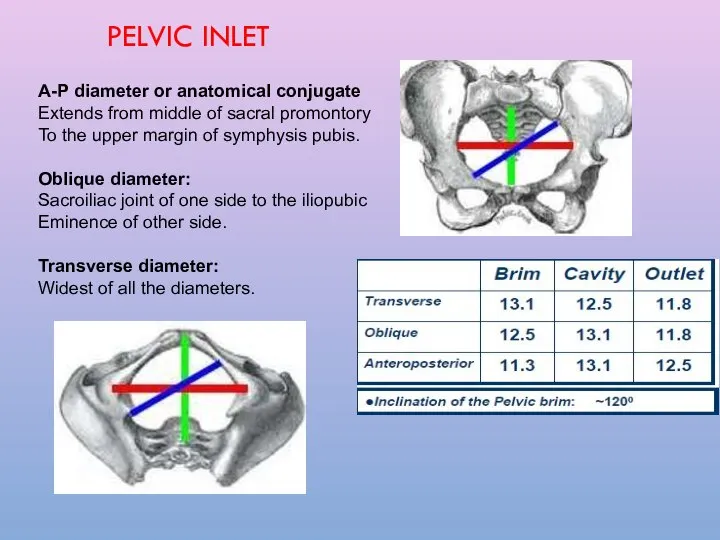
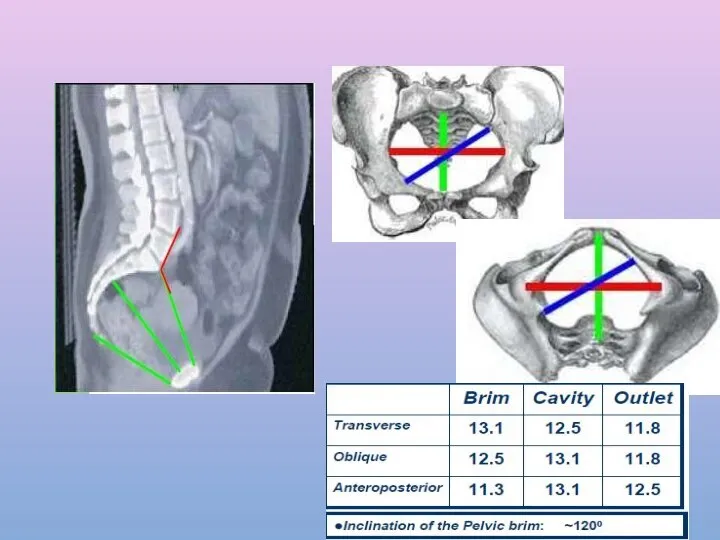
- 8. A-P diameter or anatomical conjugate Extends from middle of sacral promontory To the upper margin of
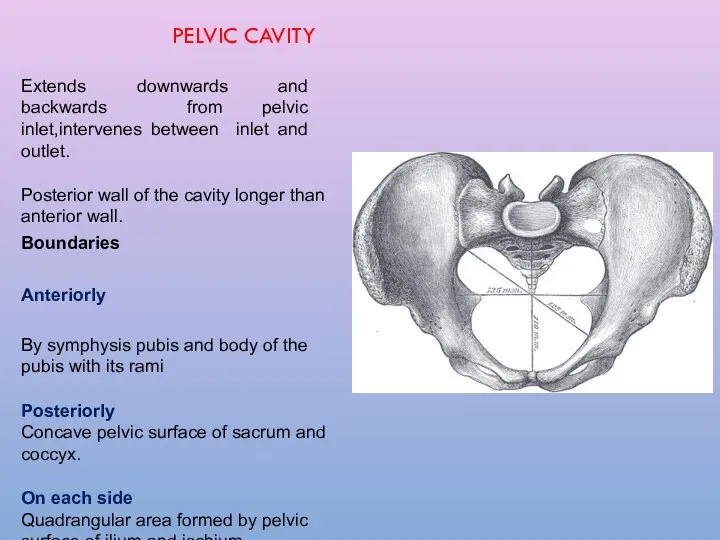
- 10. PELVIC CAVITY Extends downwards and backwards from pelvic inlet,intervenes between inlet and outlet. Posterior wall of
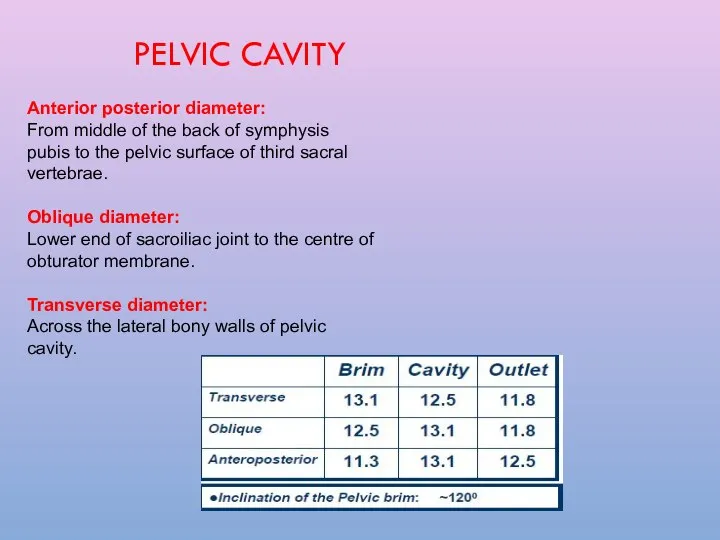
- 11. PELVIC CAVITY Anterior posterior diameter: From middle of the back of symphysis pubis to the pelvic
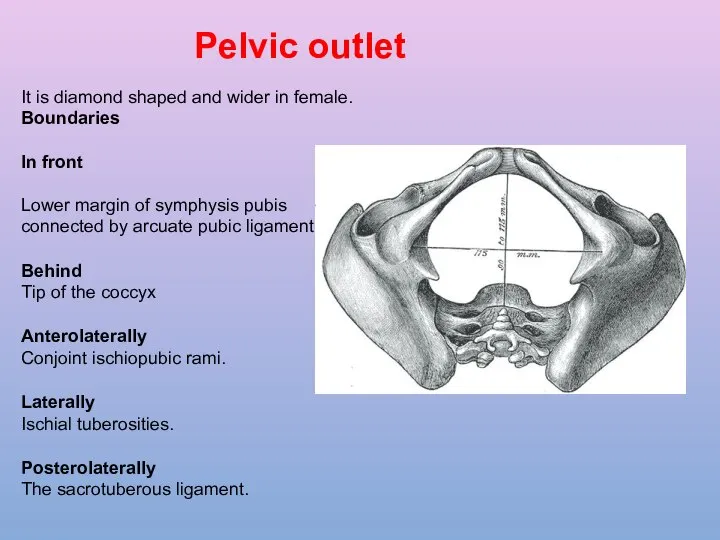
- 12. . Pelvic outlet It is diamond shaped and wider in female. Boundaries In front Lower margin
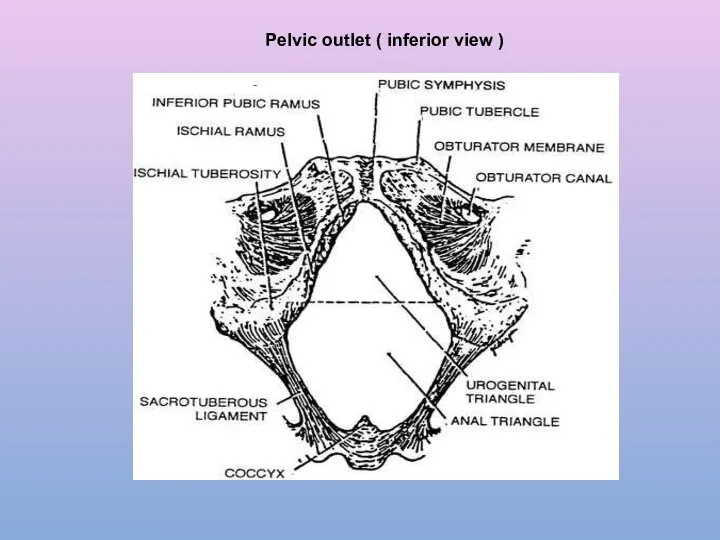
- 13. Pelvic outlet ( inferior view )
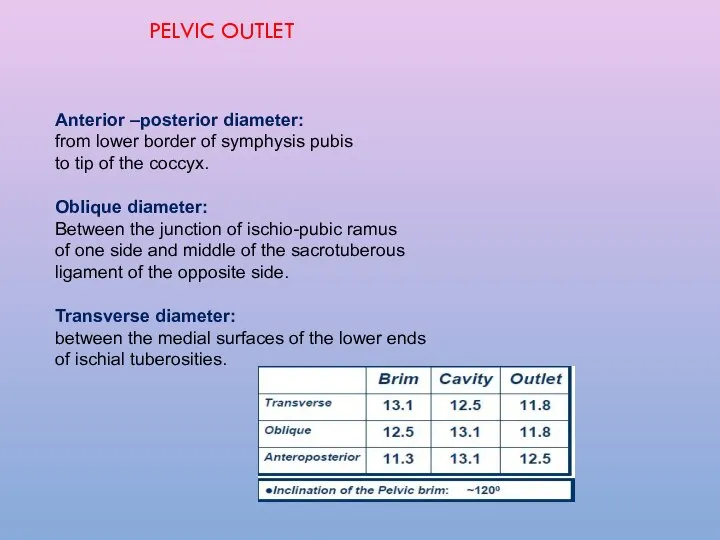
- 14. PELVIC OUTLET Anterior –posterior diameter: from lower border of symphysis pubis to tip of the coccyx.
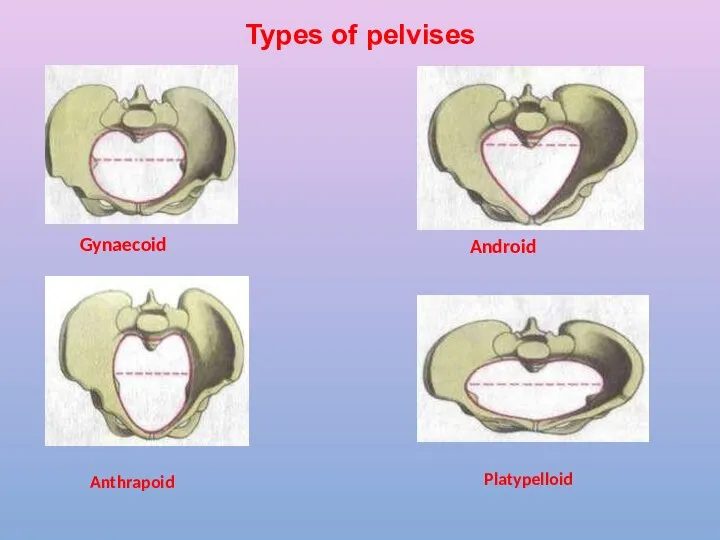
- 16. Types of pelvises Gynaecoid Anthrapoid Android Platypelloid
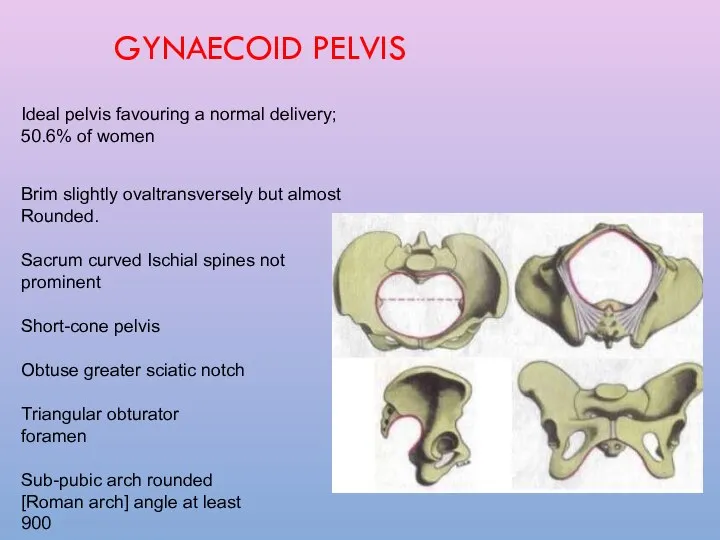
- 17. GYNAECOID PELVIS Ideal pelvis favouring a normal delivery; 50.6% of women Brim slightly ovaltransversely but almost
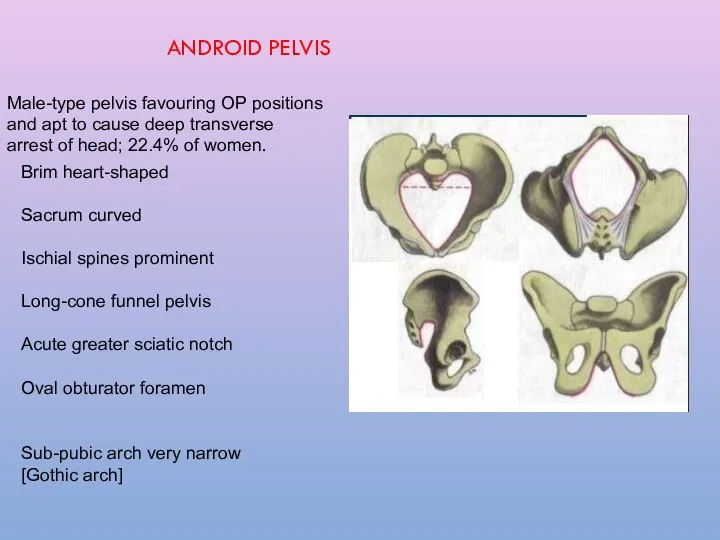
- 18. Male-type pelvis favouring OP positions and apt to cause deep transverse arrest of head; 22.4% of
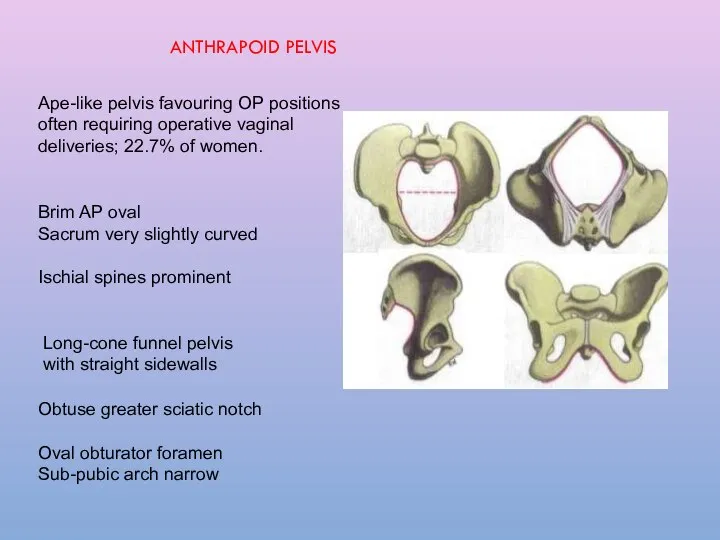
- 19. Ape-like pelvis favouring OP positions often requiring operative vaginal deliveries; 22.7% of women. Brim AP oval
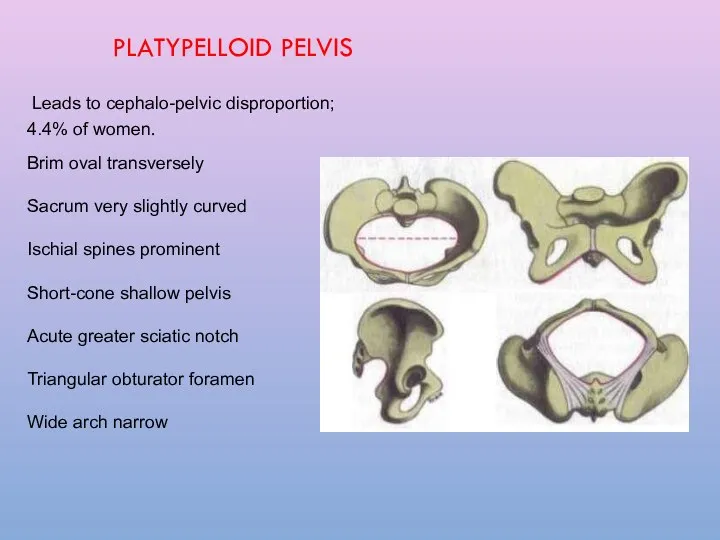
- 20. PLATYPELLOID PELVIS Leads to cephalo-pelvic disproportion; 4.4% of women. Brim oval transversely Sacrum very slightly curved
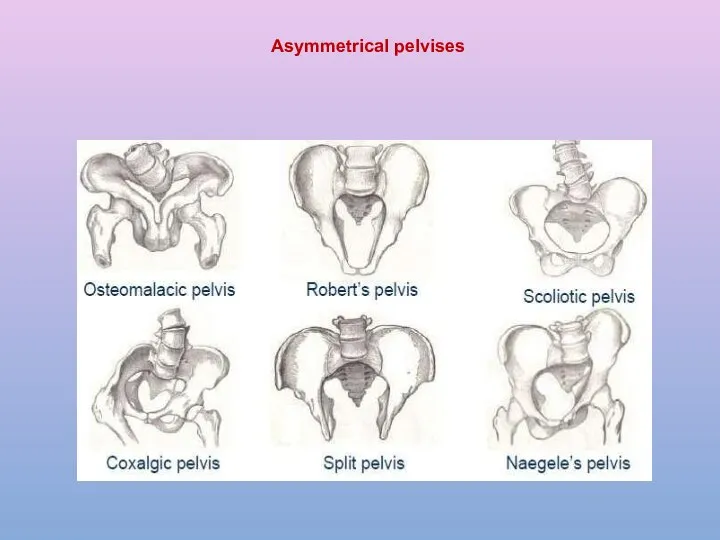
- 21. Asymmetrical pelvises
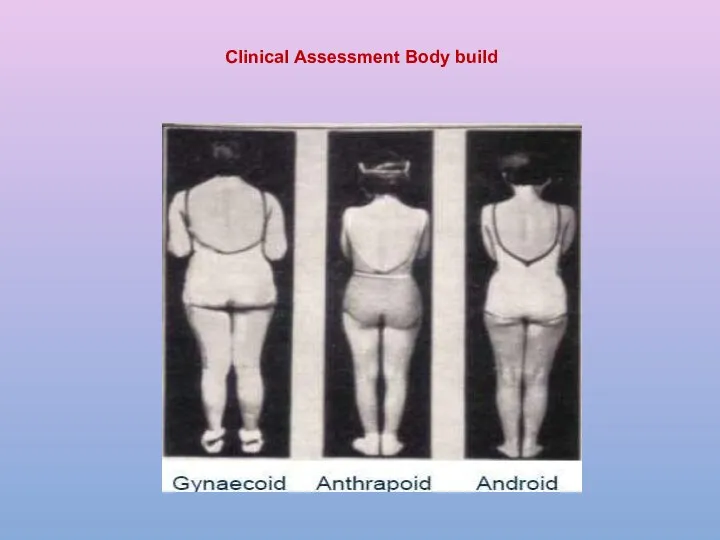
- 23. Clinical Assessment Body build
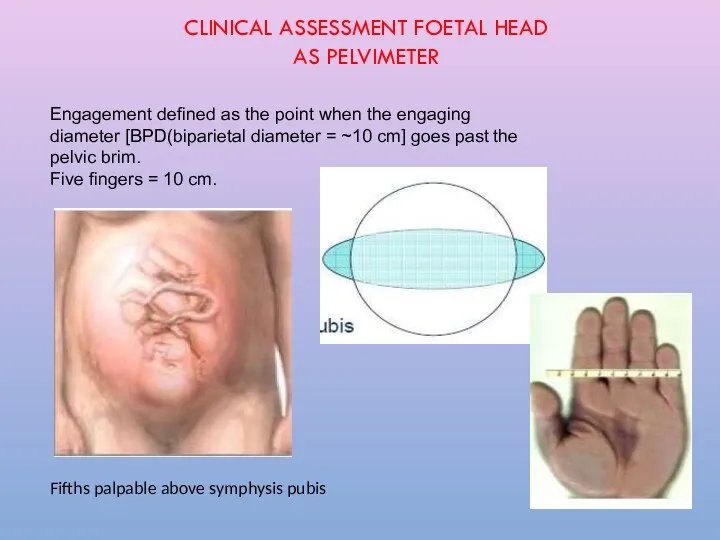
- 24. Engagement defined as the point when the engaging diameter [BPD(biparietal diameter = ~10 cm] goes past
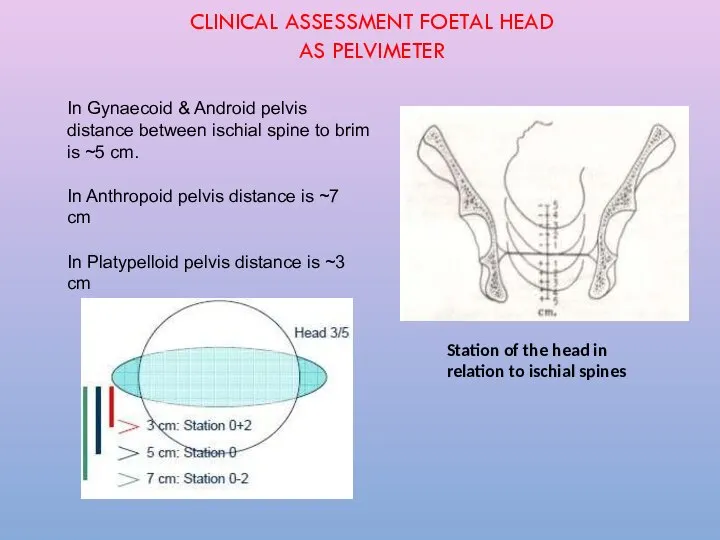
- 25. In Gynaecoid & Android pelvis distance between ischial spine to brim is ~5 cm. In Anthropoid
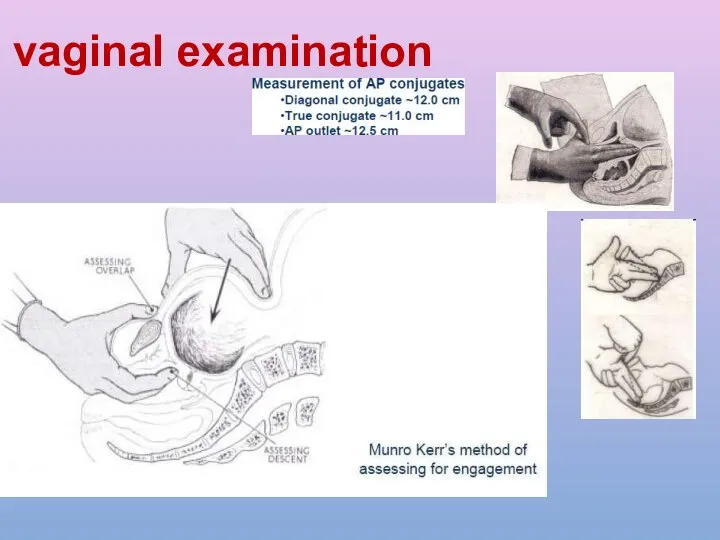
- 26. vaginal examination
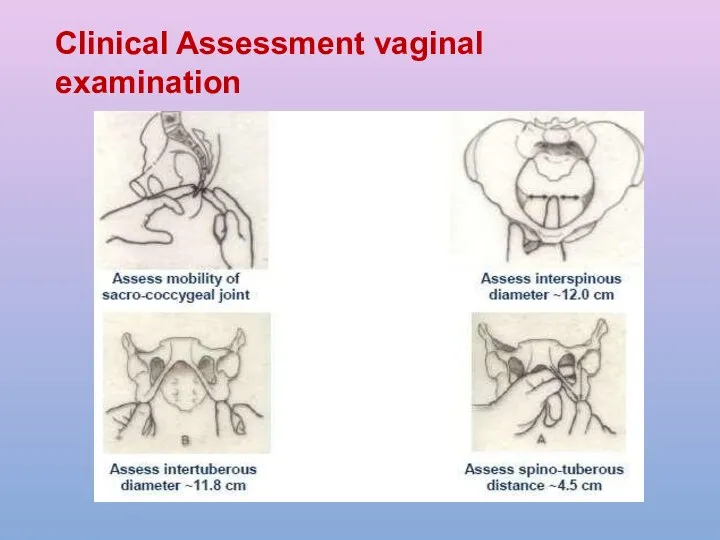
- 27. Clinical Assessment vaginal examination
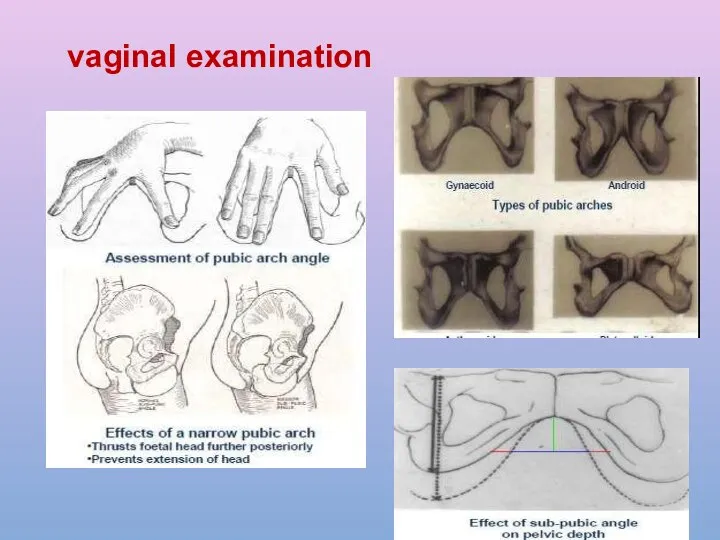
- 28. vaginal examination
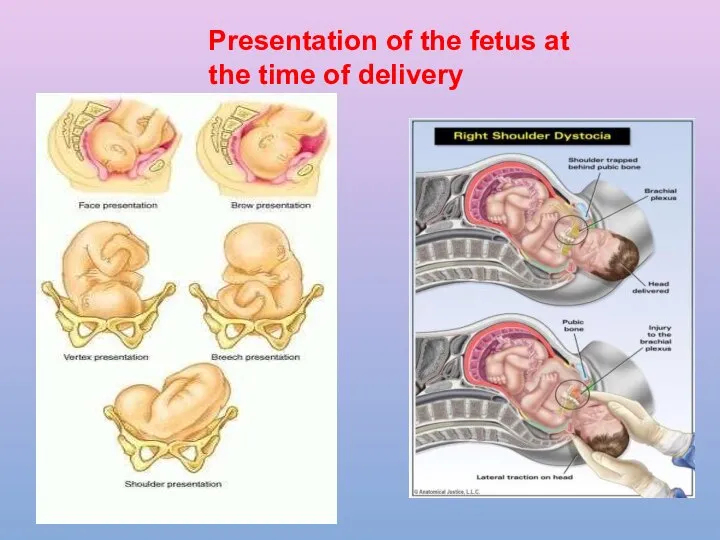
- 29. Presentation of the fetus at the time of delivery
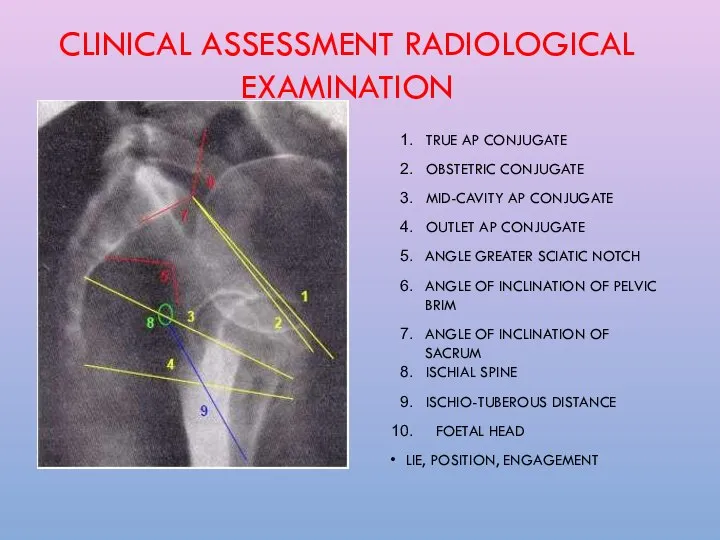
- 30. CLINICAL ASSESSMENT RADIOLOGICAL EXAMINATION TRUE AP CONJUGATE OBSTETRIC CONJUGATE MID-CAVITY AP CONJUGATE OUTLET AP CONJUGATE ANGLE
- 32. Скачать презентацию
 Острый панкреатит. Этиопатогенез. Клиника. Диагностика
Острый панкреатит. Этиопатогенез. Клиника. Диагностика Презентация по книге Л.В. Петрановской «Дитя двух семей»
Презентация по книге Л.В. Петрановской «Дитя двух семей» Иммунитет
Иммунитет Эффективность Линезолида (новый оксазолидинон) и ванкомицина для лечения резистентных грамположительных инфекций у детей
Эффективность Линезолида (новый оксазолидинон) и ванкомицина для лечения резистентных грамположительных инфекций у детей Аурухана ішілік инфекция
Аурухана ішілік инфекция Метод мозкового штурму. Фрірайтінг
Метод мозкового штурму. Фрірайтінг Современные исследования новых психоактивных веществ с целью возможного отнесения их к аналогам наркотических средств
Современные исследования новых психоактивных веществ с целью возможного отнесения их к аналогам наркотических средств Санаторий Asta Vita в посёлке Репино курортного района Санкт-Петербурга
Санаторий Asta Vita в посёлке Репино курортного района Санкт-Петербурга Желчнокаменная болезнь. Клиника, диагностика, лечение
Желчнокаменная болезнь. Клиника, диагностика, лечение Хирургическое лечение патологий пищевода и желудка
Хирургическое лечение патологий пищевода и желудка Введение в изучение органических лекарственных средств
Введение в изучение органических лекарственных средств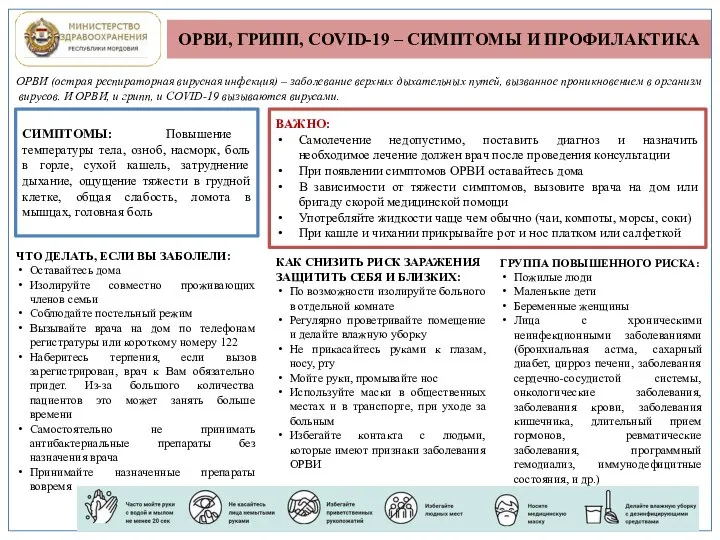 ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика
ОРВИ, грипп, covid-19 – симптомы и профилактика Рак слизистой оболочки полости рта
Рак слизистой оболочки полости рта Қарым-қатынастың әрекеттестік жағы
Қарым-қатынастың әрекеттестік жағы Противомикробные средства: антисептические и дезинфицирующие лекарственные средства
Противомикробные средства: антисептические и дезинфицирующие лекарственные средства Бас ми жарақаттары
Бас ми жарақаттары Стресс-ЭХОКГ
Стресс-ЭХОКГ Трофобластическая болезнь. Лекция 11
Трофобластическая болезнь. Лекция 11 VII Международный форум «Каждый ребенок достоин семьи. Программы раннего вмешательства»
VII Международный форум «Каждый ребенок достоин семьи. Программы раннего вмешательства» Жеке тұлға психологиясының қаралу,зерттелу аспектілері. Тұлға компоненттері
Жеке тұлға психологиясының қаралу,зерттелу аспектілері. Тұлға компоненттері Адамгершілік құндылықтардың мәні. Тұлғаның өзін-өзі тәрбиелеуі
Адамгершілік құндылықтардың мәні. Тұлғаның өзін-өзі тәрбиелеуі Дәлелді медицина және маркетинг
Дәлелді медицина және маркетинг Пневмония у детей
Пневмония у детей Гематология: лейкозы, геморрагические диатезы
Гематология: лейкозы, геморрагические диатезы Periconception endogenous and exogenous maternal sex steroid hormones and risk of asthma and allergy in offspring
Periconception endogenous and exogenous maternal sex steroid hormones and risk of asthma and allergy in offspring Деятельность, как способ существования людей
Деятельность, как способ существования людей Болезнь Паркинсона
Болезнь Паркинсона Атмосферное давление в медицине
Атмосферное давление в медицине