Содержание
- 2. T-cells can be distinguished from other lymphocyte types, such as B cells and NK cells by
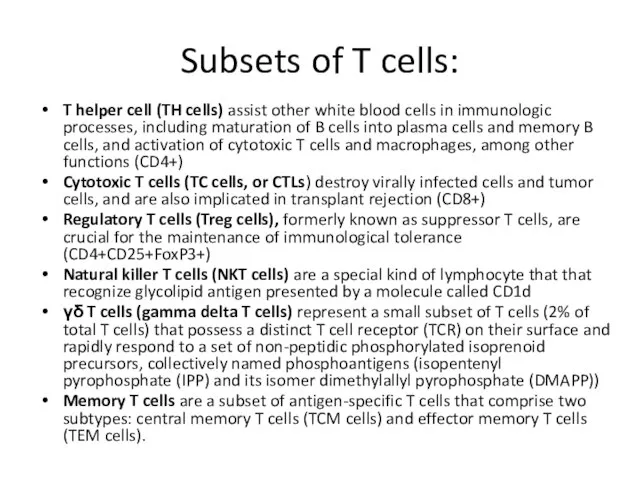
- 3. Subsets of T cells: T helper cell (TH cells) assist other white blood cells in immunologic
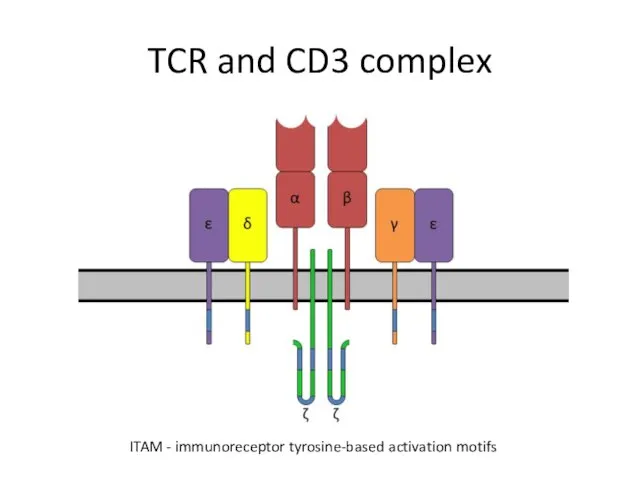
- 4. TCR and CD3 complex ITAM - immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs
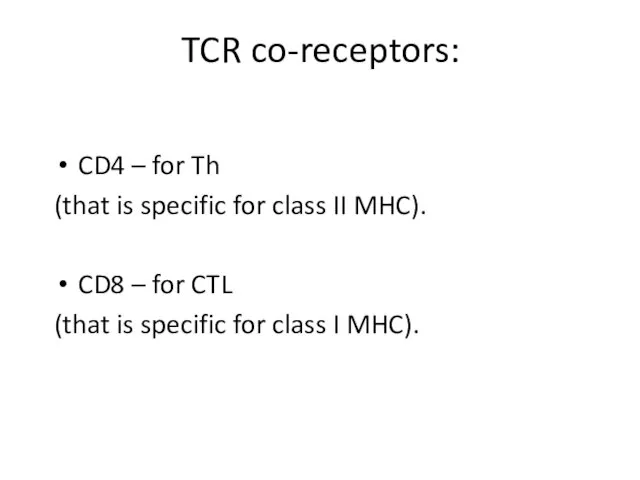
- 5. TCR co-receptors: CD4 – for Th (that is specific for class II MHC). CD8 – for
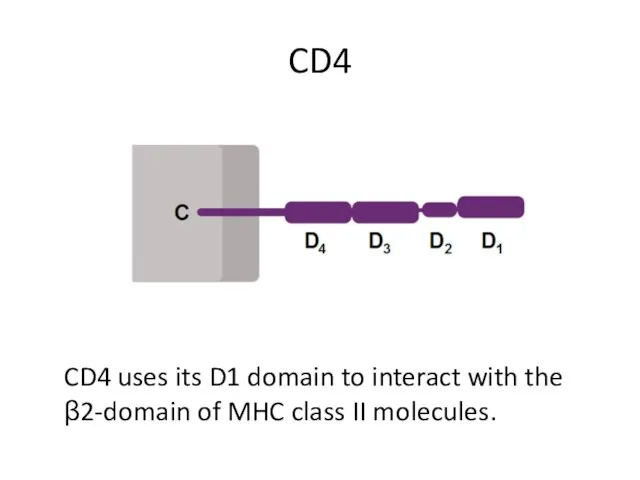
- 6. CD4 CD4 uses its D1 domain to interact with the β2-domain of MHC class II molecules.
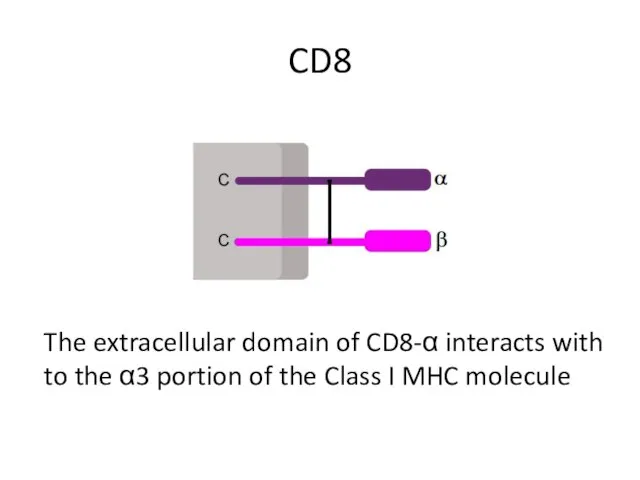
- 7. CD8 The extracellular domain of CD8-α interacts with to the α3 portion of the Class I
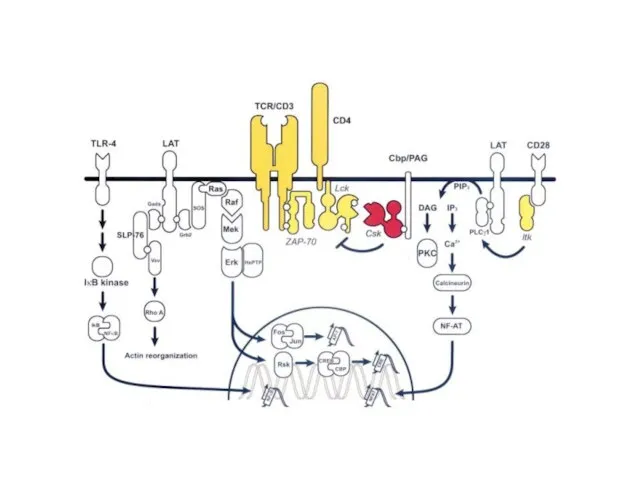
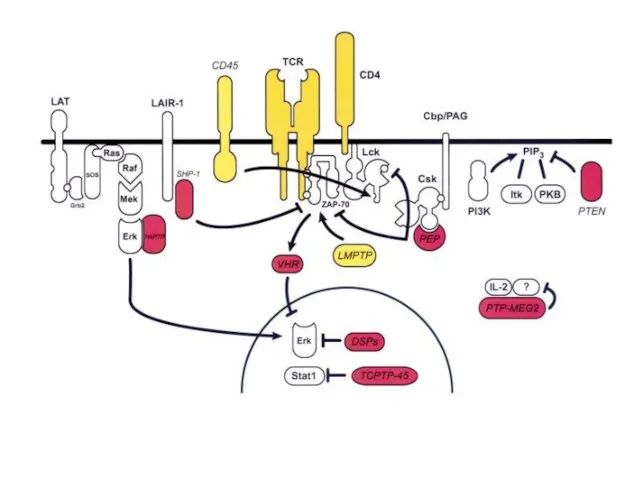
- 8. T-cell activation The mechanism by which a T-cell elicits this response upon contact with its unique
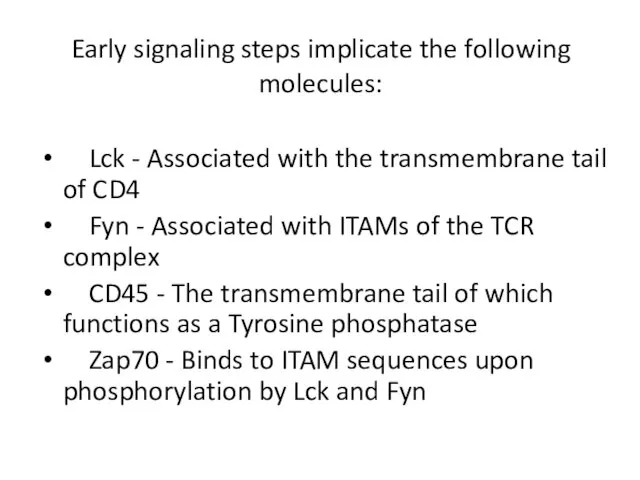
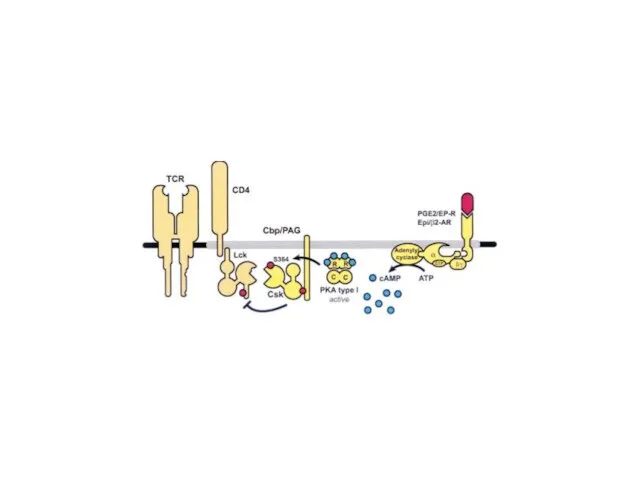
- 9. Early signaling steps implicate the following molecules: Lck - Associated with the transmembrane tail of CD4
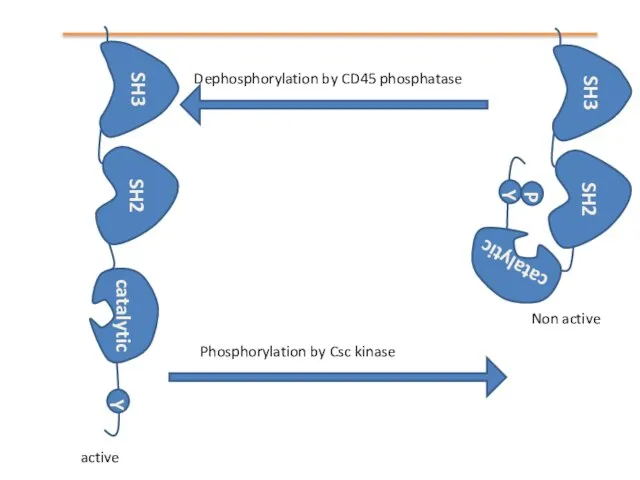
- 10. Lck (lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) and Fyn are members of the Src family of tyrosine kinases.
- 11. Src (pronounced "sarc" as it is short for sarcoma) is a proto-oncogene encoding a tyrosine kinase
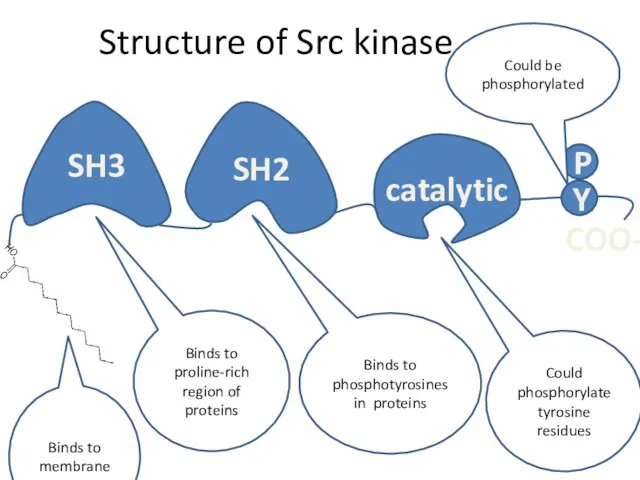
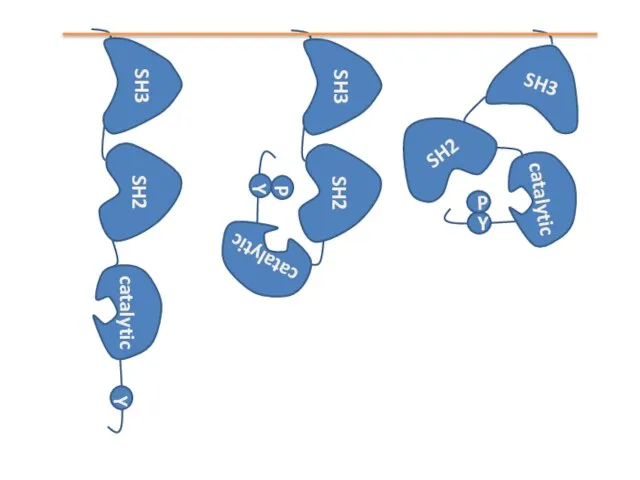
- 12. Structure of Src kinase P Binds to proline-rich region of proteins Binds to phosphotyrosines in proteins
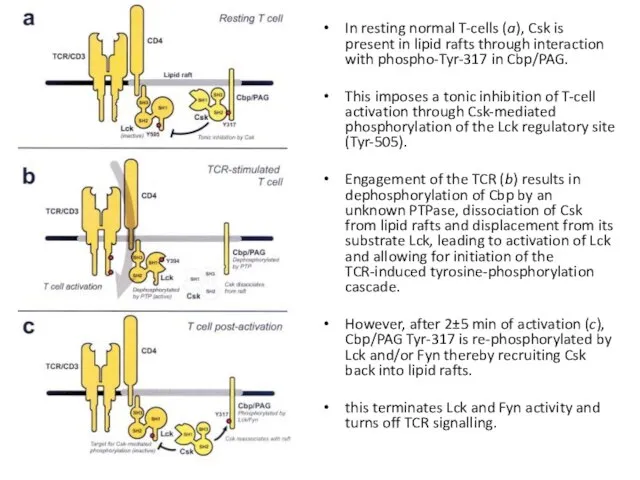
- 15. In resting normal T-cells (a), Csk is present in lipid rafts through interaction with phospho-Tyr-317 in
- 16. SH2 and SH3 domains were found in several other protein families Kinases Phosphatases Phospholipases Adaptor proteins
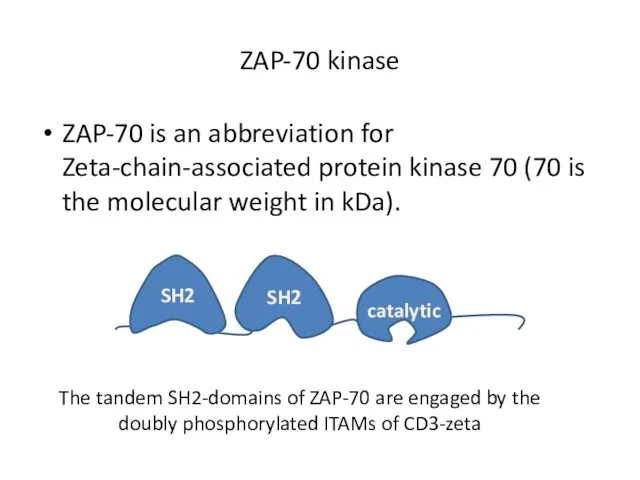
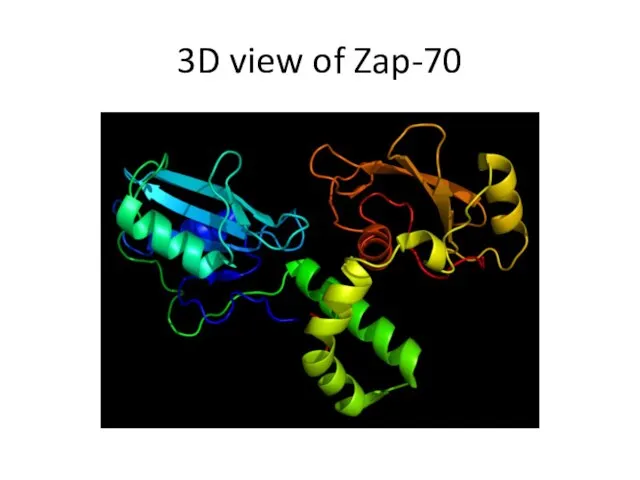
- 17. ZAP-70 kinase ZAP-70 is an abbreviation for Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70 (70 is the molecular weight
- 18. 3D view of Zap-70
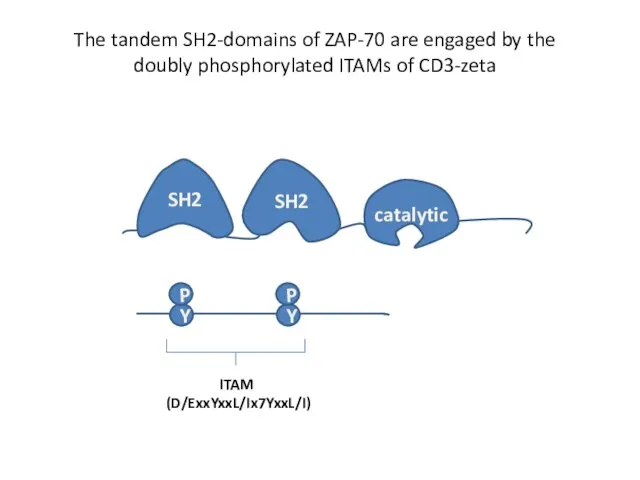
- 19. The tandem SH2-domains of ZAP-70 are engaged by the doubly phosphorylated ITAMs of CD3-zeta Y P
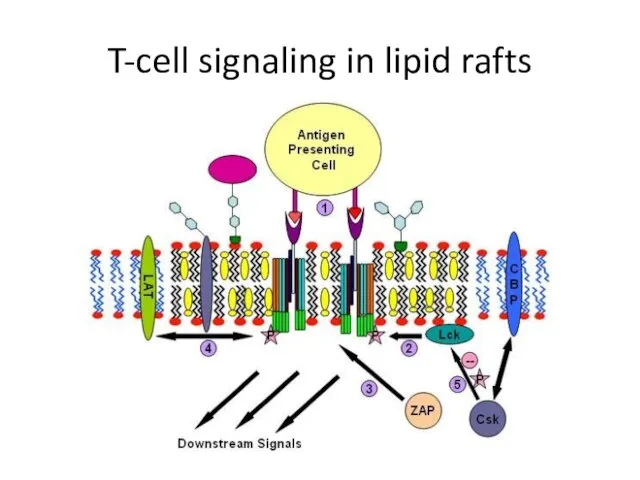
- 20. ZAP-70 could phosphorylate the transmembrane protein LAT (linker of activated T cells). LAT localizes to lipid
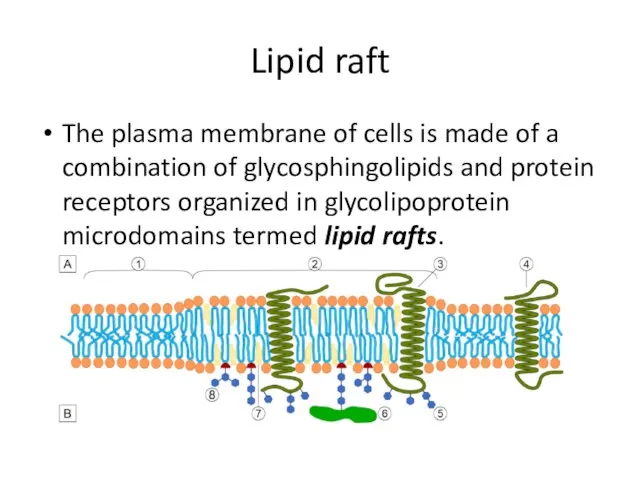
- 21. Lipid raft The plasma membrane of cells is made of a combination of glycosphingolipids and protein
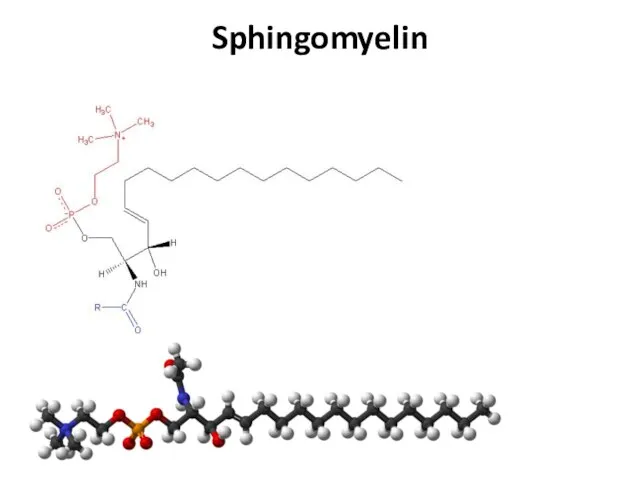
- 22. Sphingomyelin
- 23. T-cell signaling in lipid rafts
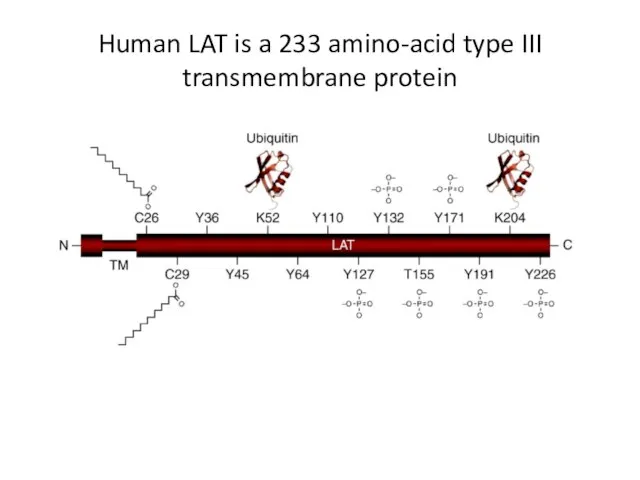
- 24. Human LAT is a 233 amino-acid type III transmembrane protein
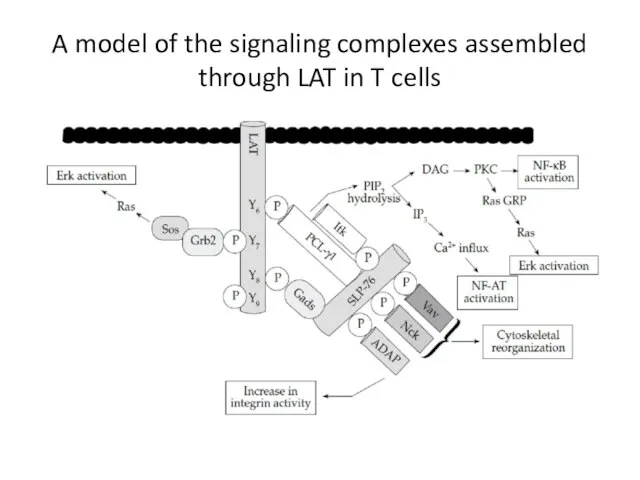
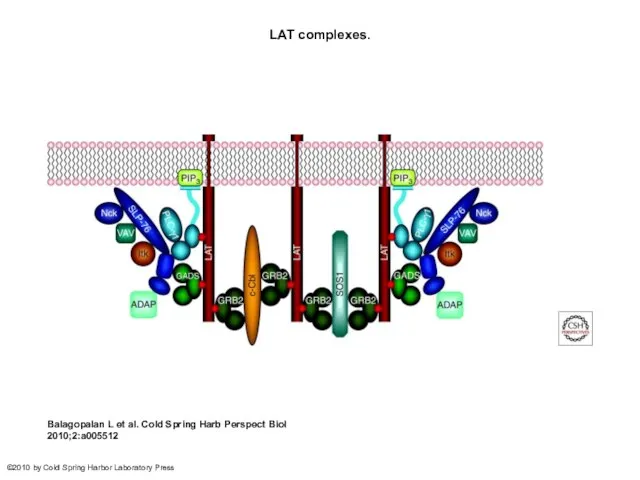
- 25. A model of the signaling complexes assembled through LAT in T cells
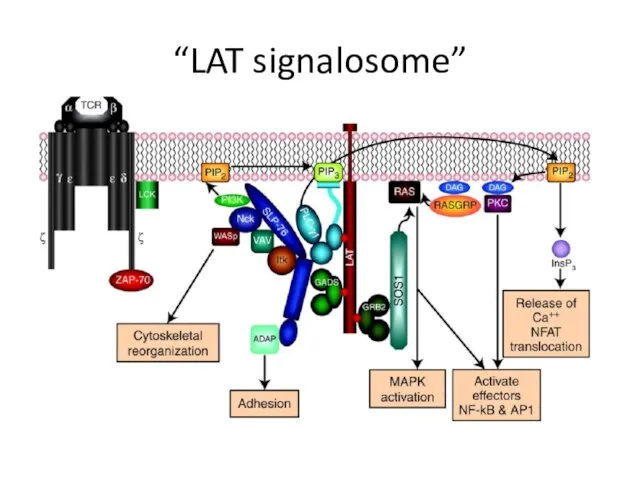
- 26. “LAT signalosome”
- 27. LAT complexes. Balagopalan L et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010;2:a005512 ©2010 by Cold Spring
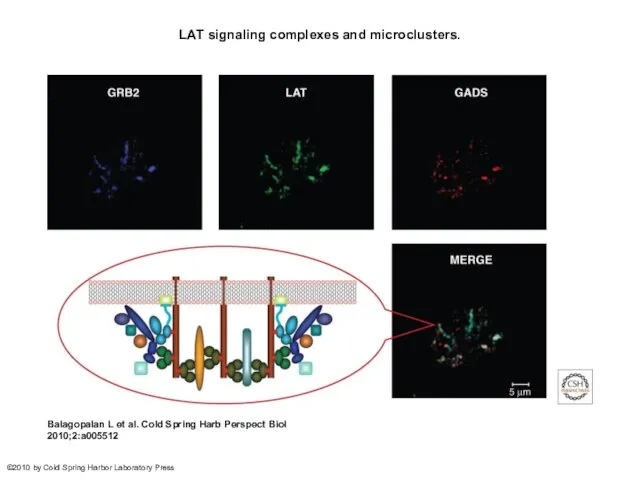
- 28. LAT signaling complexes and microclusters. Balagopalan L et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010;2:a005512 ©2010
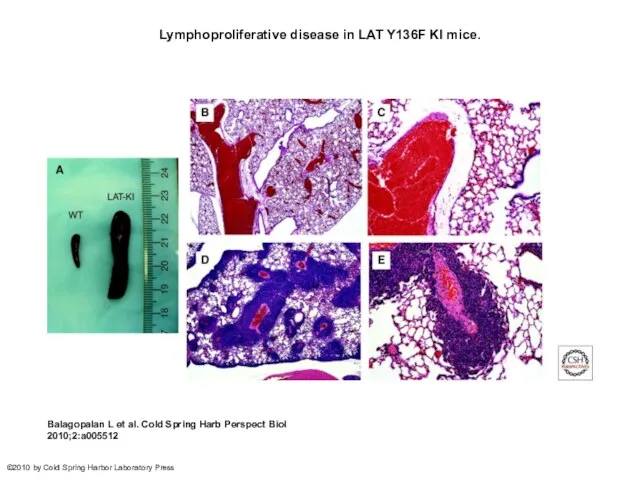
- 29. Lymphoproliferative disease in LAT Y136F KI mice. Balagopalan L et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol
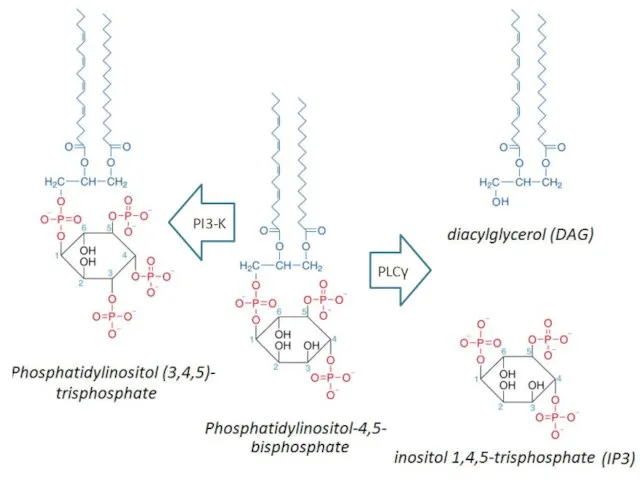
- 30. PLCγ PI3-K
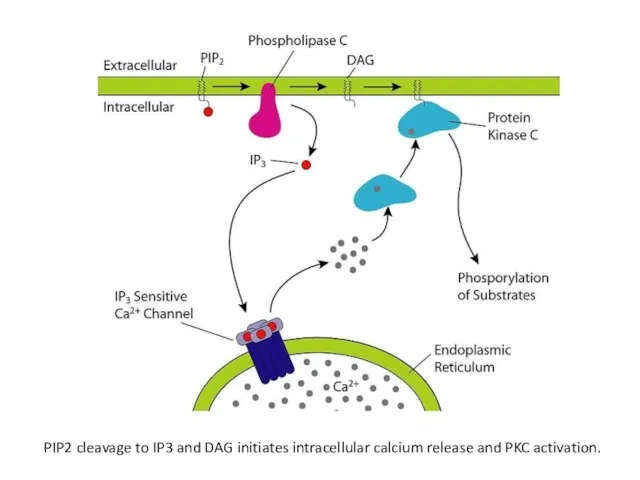
- 31. PIP2 cleavage to IP3 and DAG initiates intracellular calcium release and PKC activation.
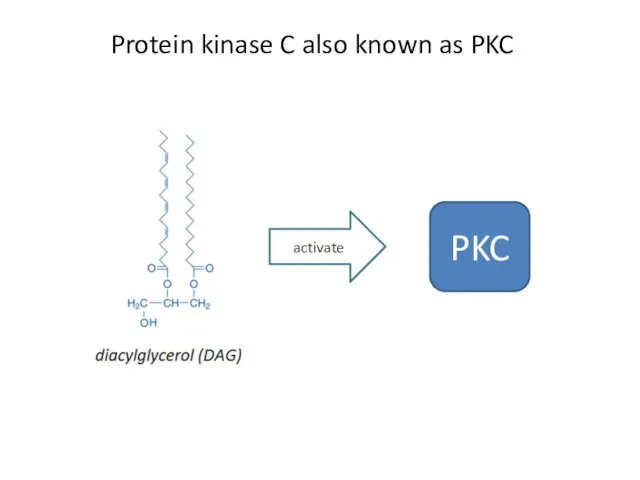
- 32. Protein kinase C also known as PKC activate PKC
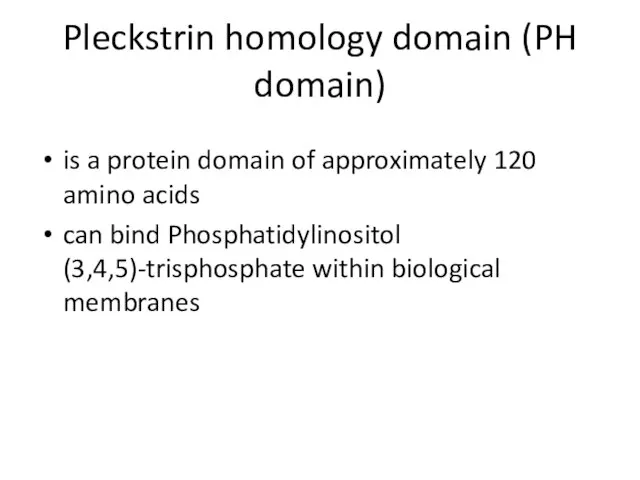
- 33. Pleckstrin homology domain (PH domain) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids can bind
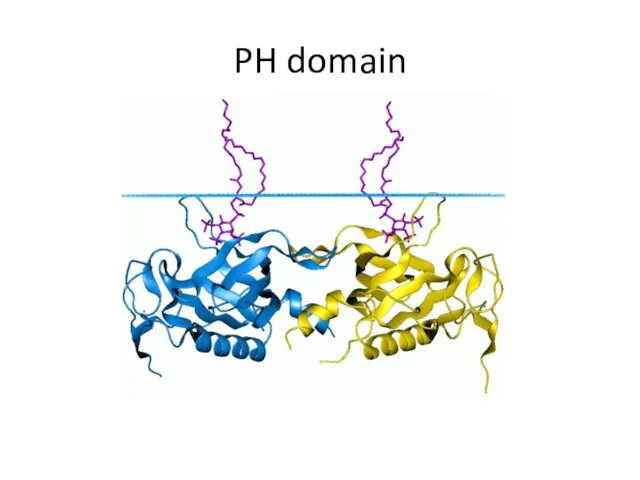
- 34. PH domain
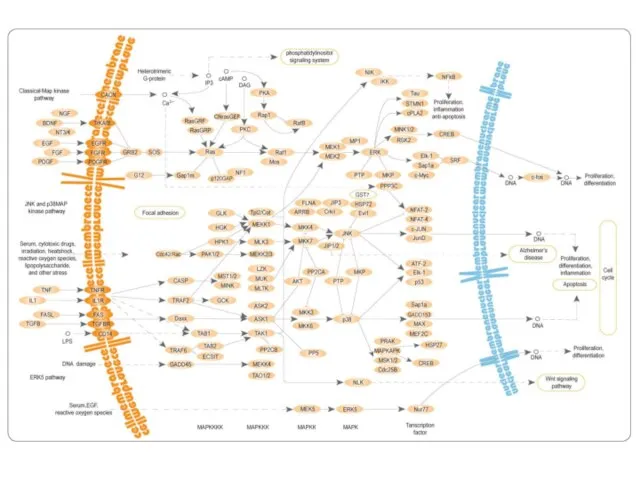
- 35. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases MAPKKK -> MAPKK -> MAPK -> Transcription factor
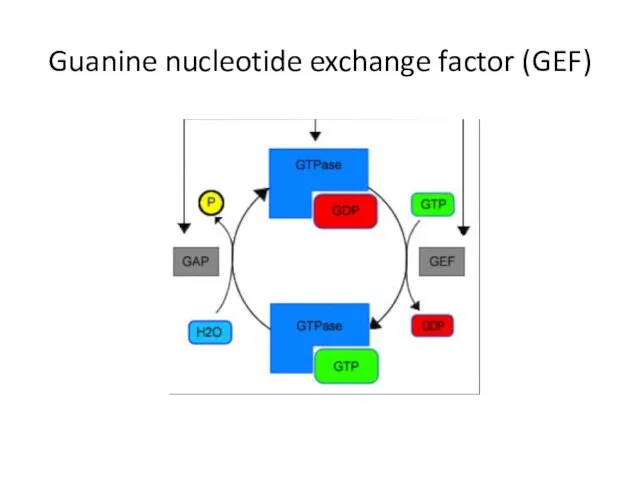
- 37. Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF)
- 42. Скачать презентацию






 Занятие 4. ЛР и ЛРС, содержащие эфирные масла (Apiaceae и Juniperus communis). Сырьевые источники камфоры
Занятие 4. ЛР и ЛРС, содержащие эфирные масла (Apiaceae и Juniperus communis). Сырьевые источники камфоры Иммунопатология
Иммунопатология Диффузные заболевания соединительной ткани: дерматологические аспекты
Диффузные заболевания соединительной ткани: дерматологические аспекты Клинический разбор пациента
Клинический разбор пациента Развитие потребностей младшего школьника
Развитие потребностей младшего школьника Кинопропаганда. Кино как средство информационно-психологической войны
Кинопропаганда. Кино как средство информационно-психологической войны Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов
Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов Нарушения функции почек
Нарушения функции почек Абдоминальный ишемический синдром
Абдоминальный ишемический синдром Земские врачи
Земские врачи Марафон «Энергия жизни». Часть 3 «Путь к мечте». Неделя 2
Марафон «Энергия жизни». Часть 3 «Путь к мечте». Неделя 2 Операции на мозговом отделе головы
Операции на мозговом отделе головы Ларингеальная трубка
Ларингеальная трубка Армысыңдар менің бауырларым мен қарындастарым. Болашақ тигрлер ( жолбарыстар)
Армысыңдар менің бауырларым мен қарындастарым. Болашақ тигрлер ( жолбарыстар) Xəstəxanadaxili infeksiyalar və onlarla mübarizənin əsasları, əksepidemik tədbirlər
Xəstəxanadaxili infeksiyalar və onlarla mübarizənin əsasları, əksepidemik tədbirlər Қоршаған орта факторларының салдарлық итж дамуындағы маңызы
Қоршаған орта факторларының салдарлық итж дамуындағы маңызы Азбука витаминов плюс детские витамины для поддержки зрения. Строение зрительной системы
Азбука витаминов плюс детские витамины для поддержки зрения. Строение зрительной системы Мой профессиональный выбор
Мой профессиональный выбор Особенности эмоционально-волевой и личностной сфер при нарушениях слуха
Особенности эмоционально-волевой и личностной сфер при нарушениях слуха СРСП 3 Сайлауов Б.С. 2-067 ОМ
СРСП 3 Сайлауов Б.С. 2-067 ОМ Омыртқа туберкулезінің салыстырмалы диагностикасы
Омыртқа туберкулезінің салыстырмалы диагностикасы Быть хорошим соседом, это значит
Быть хорошим соседом, это значит Поражение ЦНС вирусами герпеса
Поражение ЦНС вирусами герпеса Себорея. Себорейный дерматит
Себорея. Себорейный дерматит Клеточные типичные патологические процессы
Клеточные типичные патологические процессы Обработка и кодирование сенсорной информации Сознание – следствие ощущения
Обработка и кодирование сенсорной информации Сознание – следствие ощущения Вирус геномы
Вирус геномы Педагогические конфликты
Педагогические конфликты