Содержание
- 3. In the adrenergic synapses the transmission is mediated by noradrenaline or norepinephrine (NE). The biosynthesis of
- 4. Noradrenaline (NE), dopamine and adrenaline are called catecholamines. In presynaptic endings noradrenaline is in a free
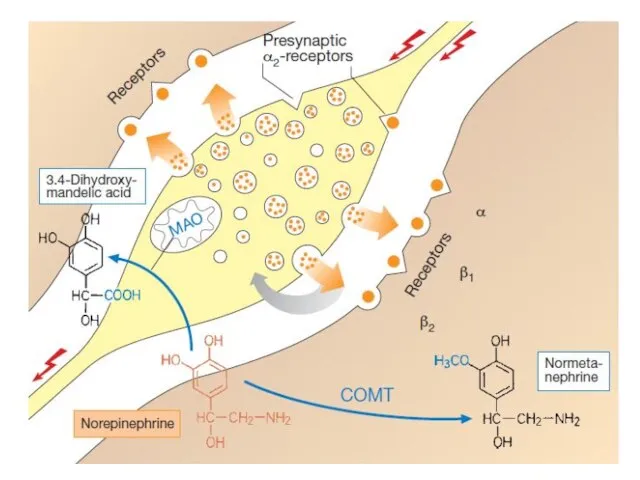
- 6. The action of NE on receptors is short-term. It is mainly caused by the swift uptake
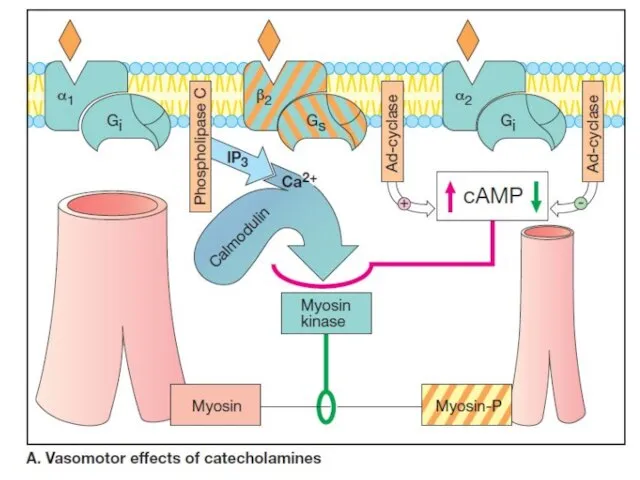
- 7. The main α-adrenoreceptors include α1 and α2R. Adrenoreceptors α1 have postsynaptic localization and α2R are located
- 8. Among β-R there are also post-, pre-, and extrasynaptic receptors. Presynaptic β2-R perform positive reverse feedback,
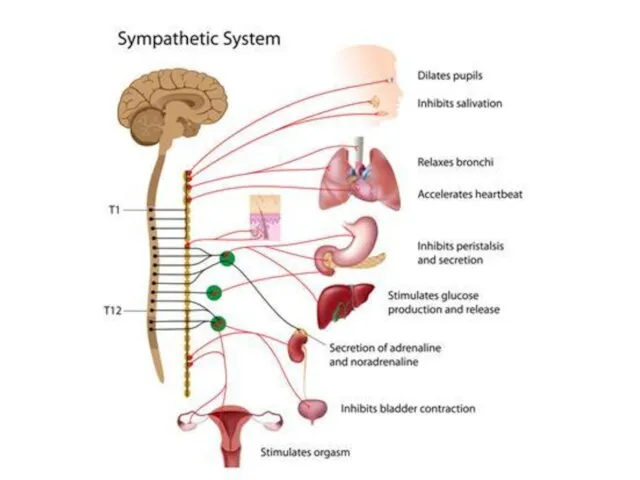
- 10. The main effects associated with the stimulation of post-and extrasynaptic adrenoreceptors α1 - adrenoreceptors: Constriction of
- 11. α2 –adrenoceptor (extrasynaptic): Vasoconstriction; Increased platelet aggregation; Decrease in insulin secretion.
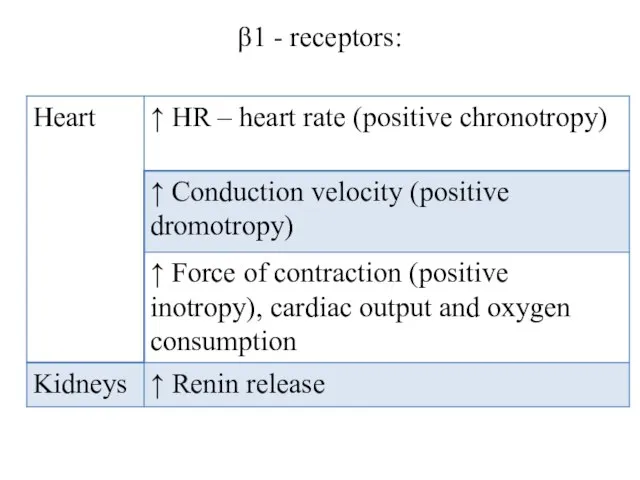
- 12. β1 - receptors:
- 13. β2 - receptors: Dilation of vessels of the skeletal muscles, liver, coronary; Decrease in muscle tone
- 15. Classification Drugs of presynaptic action, affecting release and storage of NE or sympathomimetics or adrenomimetics of
- 16. α and β adrenomimetics: Epinephrine, Norepinephrine; α1: Phenylephrine; α2: Naphazoline, Xylometazoline, Oxymetazoline; β1, 2: Isoprenaline; β1:
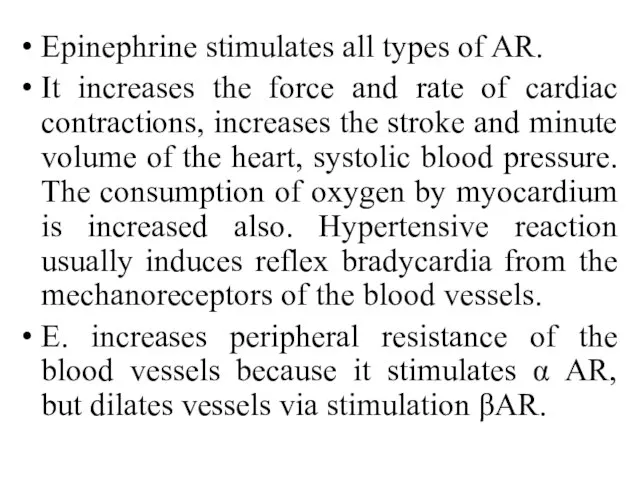
- 17. Epinephrine stimulates all types of AR. It increases the force and rate of cardiac contractions, increases
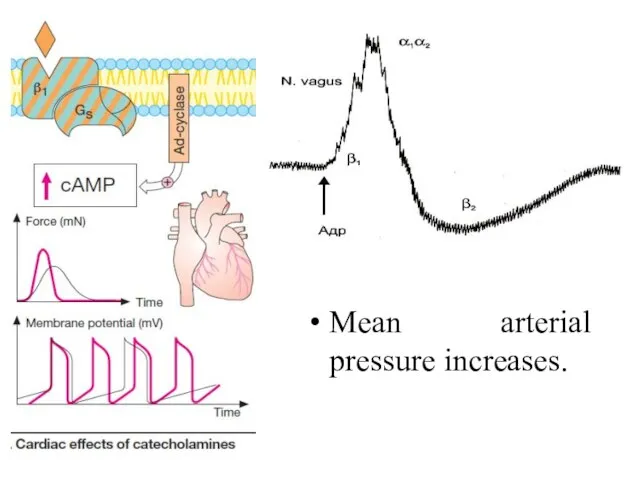
- 18. Mean arterial pressure increases.
- 19. E. relaxes smooth muscles of bronchi, eliminates bronchospasm. E. reduces the secretion of the bronchial glands,
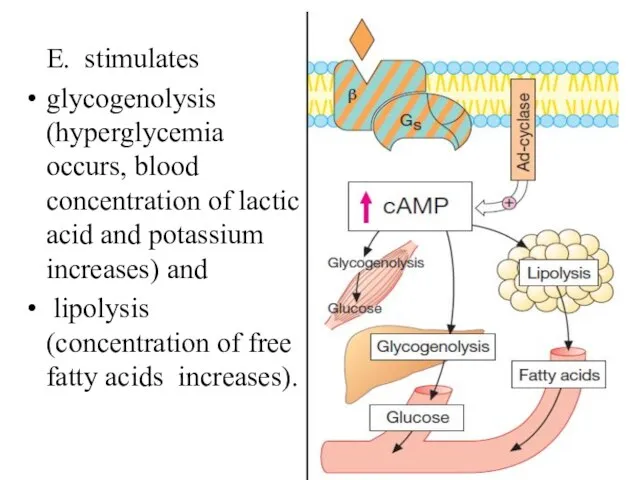
- 20. E. stimulates glycogenolysis (hyperglycemia occurs, blood concentration of lactic acid and potassium increases) and lipolysis (concentration
- 21. Local effects: E. dilates the pupils (mydriasis) due to the contraction of the radial muscles of
- 22. Duration of action: intravenously - 5-10 min., subcutaneous injections - up to 30 minutes. Indications for
- 23. Side effects: headache, fear, anxiety, tremor, vomiting, tachycardia, extrasystoles.
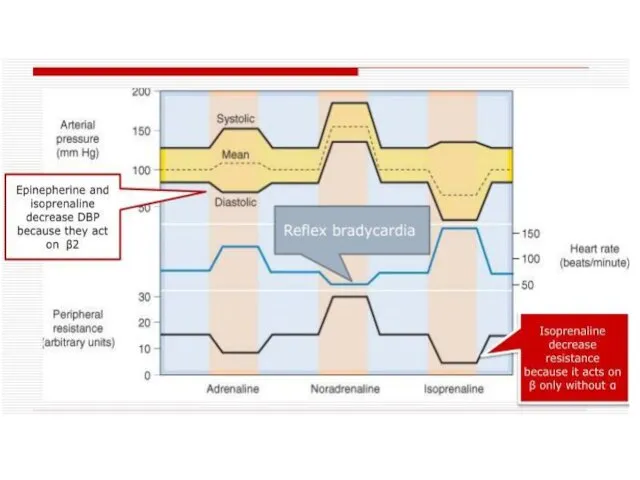
- 24. Norepinephrine stimulates predominantly α-adrenergic receptors and to a small extent β-AR. It causes severe vasospasm and
- 26. Norepinephrine can not be administered subcutaneously due to the possibility of necrosis. It is contraindicated in
- 27. Phenylephrine stimulates α1-AR but acts weaker than norepinephrine. It increases arterial pressure and causes reflex bradycardia.
- 28. Indications for the use: relief and prevention of shock and collapse, to potentiate the action and
- 29. Naphazoline, Oxymetazoline and Xylometazoline constrict the vessels of the nasal mucosa, reduce inflammatory response, exudation. They
- 31. Isoprenaline stimulates all types of β-AR. It stimulates β1-AR of the heart and increases the force
- 33. The drug facilitates atrioventricular conduction and increases heart automatism.
- 34. I. decreases the tone of bronchi, muscles of gastrointestinal tract; causes hyperglycaemia. Indications for use: bronchial
- 35. Salbutamol, fenoterol, salmeterol stimulate B2-AR. They expand the bronchi and are used for the prevention and
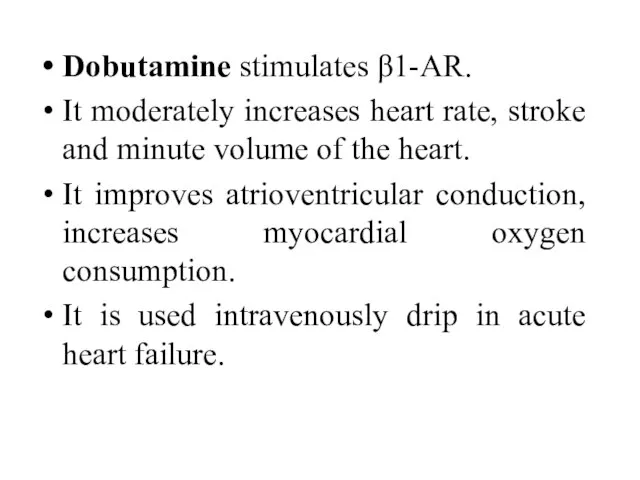
- 37. Dobutamine stimulates β1-AR. It moderately increases heart rate, stroke and minute volume of the heart. It
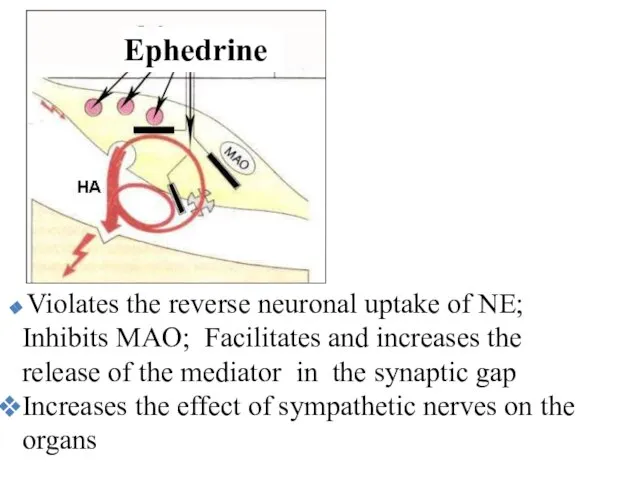
- 39. Violates the reverse neuronal uptake of NE; Inhibits MAO; Facilitates and increases the release of the
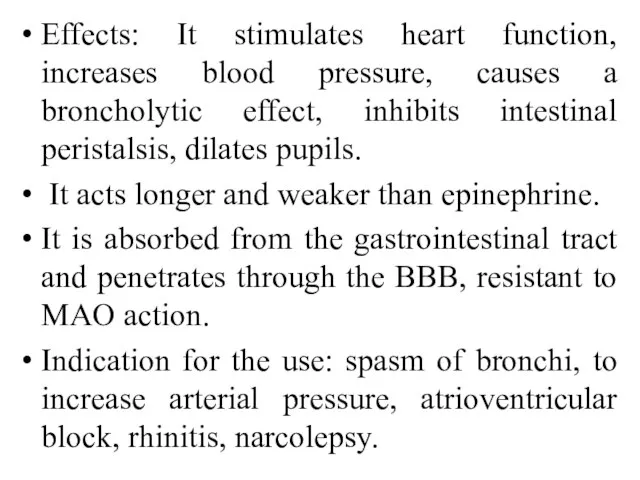
- 40. Effects: It stimulates heart function, increases blood pressure, causes a broncholytic effect, inhibits intestinal peristalsis, dilates
- 41. Side effects: tachyphylaxis with frequent use (reduction in norepinephrine storage in the varicosities), tachycardia, increased blood
- 44. Скачать презентацию


























 Сальмонеллезный сепсис. Клинический случай
Сальмонеллезный сепсис. Клинический случай Морфофункциональная организация ствола мозга
Морфофункциональная организация ствола мозга ОРВИ
ОРВИ Действующие химические вещества в лекарственных растениях
Действующие химические вещества в лекарственных растениях Младенчество. Развитие от 0 до года
Младенчество. Развитие от 0 до года Многопрофильная клиника. Направления деятельности
Многопрофильная клиника. Направления деятельности Организация амбулаторно – поликлинической помощи населению в РК
Организация амбулаторно – поликлинической помощи населению в РК Патология эндокринной системы
Патология эндокринной системы Обеспечения безопасности пищевой продукции
Обеспечения безопасности пищевой продукции Агрессия детей: ее причины и предупреждение
Агрессия детей: ее причины и предупреждение Интерпретация гравидограмм
Интерпретация гравидограмм Массаж для подтяжки лица и активации лимфы
Массаж для подтяжки лица и активации лимфы Телемедицина
Телемедицина Контрацепция: защита женского здоровья и не только
Контрацепция: защита женского здоровья и не только Cахарный диабет и беременность
Cахарный диабет и беременность Питание детей дошкольного возраста
Питание детей дошкольного возраста Психобелсенді заттарды қабылдаумен байланысты экономикалық, әлеуметтік, ар-ождандық зардаптары
Психобелсенді заттарды қабылдаумен байланысты экономикалық, әлеуметтік, ар-ождандық зардаптары Оперативное лечение грыж
Оперативное лечение грыж Беременность и эпилепсия
Беременность и эпилепсия қызбааа.pptx
қызбааа.pptx Некроз. Смерть, признаки смерти. Посмертные изменения
Некроз. Смерть, признаки смерти. Посмертные изменения Лекция 2 диагностика, классификация
Лекция 2 диагностика, классификация Жедел гастрит
Жедел гастрит Профилактика синдрома эмоционального выгорания замещающих родителей
Профилактика синдрома эмоционального выгорания замещающих родителей Значение двигательной активности и физической культуры для здоровья человека
Значение двигательной активности и физической культуры для здоровья человека Причины возникновения заболеваний кожи
Причины возникновения заболеваний кожи Косыночные повязки
Косыночные повязки Семіотика уражень органів дихання у дітей. ГРЗ, бронхіти, пневмонії, плеврити. (Лекция 8)
Семіотика уражень органів дихання у дітей. ГРЗ, бронхіти, пневмонії, плеврити. (Лекция 8)