Содержание
- 2. Agents Stimulating the Appetite: 1. Bitters: Wormwood tincture – Tinctura Absinthii - vial 25 ml: PO
- 3. Wormwood tincture contains glycoside Absinthian and Ethereal Oil composed of Terpenes and a camphor isomer Absenthol.
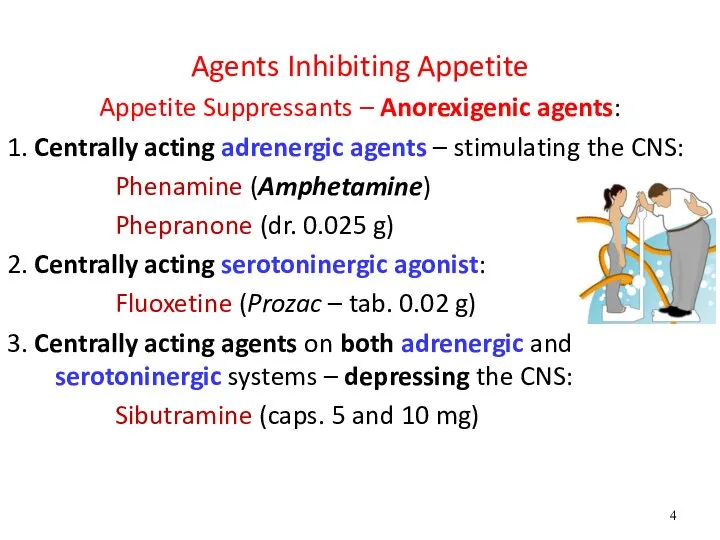
- 4. Agents Inhibiting Appetite Appetite Suppressants – Anorexigenic agents: 1. Centrally acting adrenergic agents – stimulating the
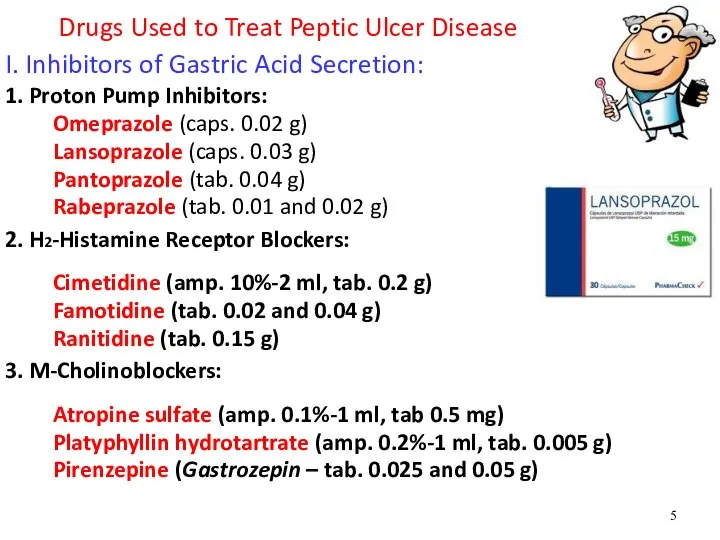
- 5. Drugs Used to Treat Peptic Ulcer Disease I. Inhibitors of Gastric Acid Secretion: 1. Proton Pump
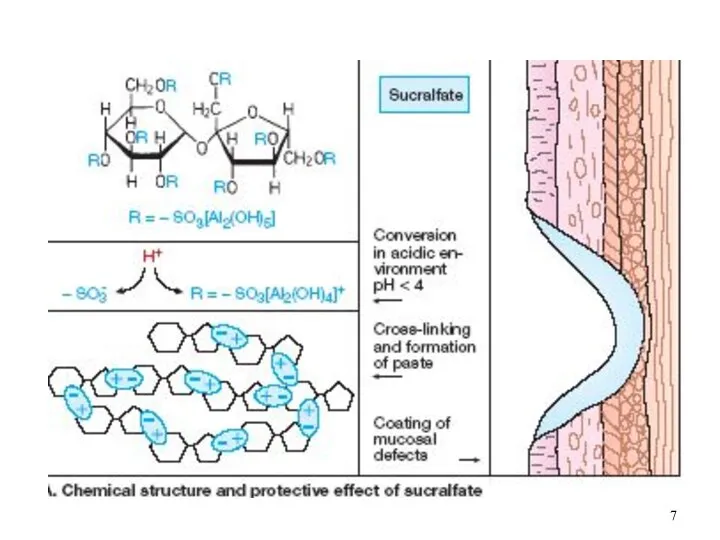
- 6. II. Gastroprotectors: 1. Producing Mechanical Defense of Mucous Coat: Sucralfate (Venter – tab. 0.5 g) Bismuth
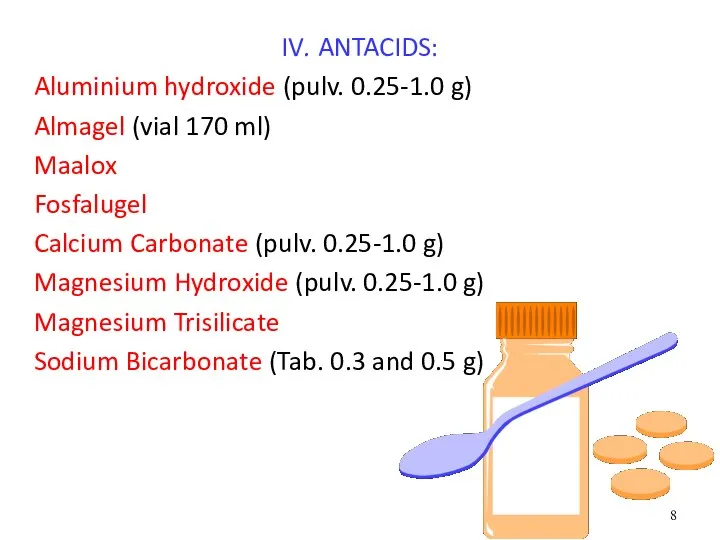
- 8. IV. ANTACIDS: Aluminium hydroxide (pulv. 0.25-1.0 g) Almagel (vial 170 ml) Maalox Fosfalugel Calcium Carbonate (pulv.
- 9. V. Myogenic Spasmolytics: No-spa – amp. 2% solution -2 ml, Tab. 0.04 g (40 mg) Papaverine
- 10. H2-antagonists Cimetidine, Ranitidine, Famotidine - inhibit (by 90%) basal, food-stimulated, and nocturnal secretion of gastric acid
- 11. Cimetidine has Endocrine effects and acts as a Nonsteroidal Antiandrogen Endocrine effects: Gynecomastia - abnormal overdevelopment
- 12. OMEPRAZOLE is the prototype of substituted benzimidazoles, which inhibit the final step in gastric acid secretion
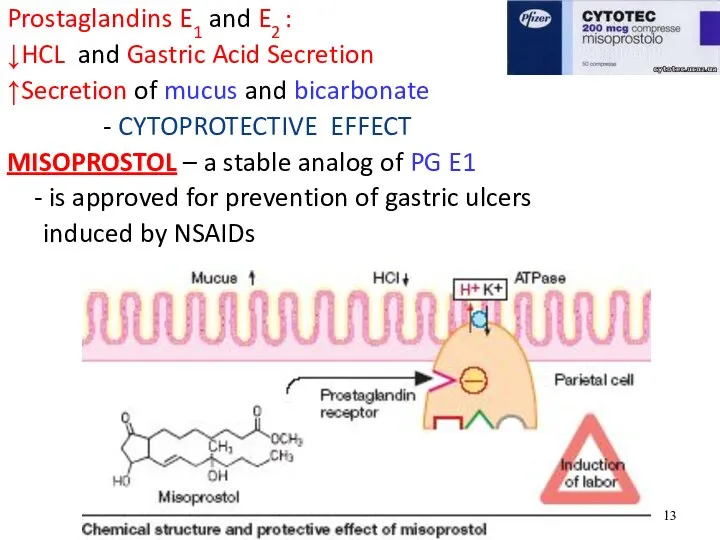
- 13. Prostaglandins E1 and E2 : ↓HCL and Gastric Acid Secretion ↑Secretion of mucus and bicarbonate -
- 14. ANTACIDS are weak bases that react with gastric acid to form water and a salt, thereby
- 15. Emetic Agents - are the drugs that produce vomiting. They may be classified as: 1. Centrally
- 16. Antiemetic Agents Metoclopramide – Tab. 5 mg, amp. 0.5%-2 ml inhibits D2 receptors in the brain’s
- 17. Corticosteroids: Dexamethasone Methylprednisolone are effective against Emetogenic Chemotherapy. Their antiemetic mechanism may involve blockade of PGs.
- 18. ANTIDIARRHEALS Loperamide - is widely used to control acute and chronic diarrhea. It is phenylpiperidine derivative
- 19. Classification of Cholagogic Agents I. Agents Stimulating Bile Formation: 1. Agents Containing Bile Acids: Allochol, Cholenzyme
- 20. Cholosas (vial 300 g) is a syrup prepared from condensed rosehip liquid extract and sugar. It
- 21. Hepatoprotectors Lipoic Acid [Thioctic acid]: Tab. 12 mg, amp. 0.5% - 2 ml Legalon (Silymarin): Dr.
- 22. Agents Used in Disturbances of the Excretory Function of Pancreas I. For Substitute Therapy: Pancreatin (Creon)
- 23. 2. Inhibitors of the Proteolytic Enzymes of Pancreas - are used mainly for patients with HYPERSECRETION
- 24. Orlistat is a pancreatic Lipase inhibitor, preventing the breakdown of dietary fat to fatty acids and
- 25. LAXATIVES I. Irritant Laxatives – Purgatives, Cathartics 1. Small Bowel Irritant Purgative: Vegetable oils: Castor Oil
- 26. CASTOR OIL (Oleum Ricini) a small bowel irritant, is a colourless glutinous oil obtained from the
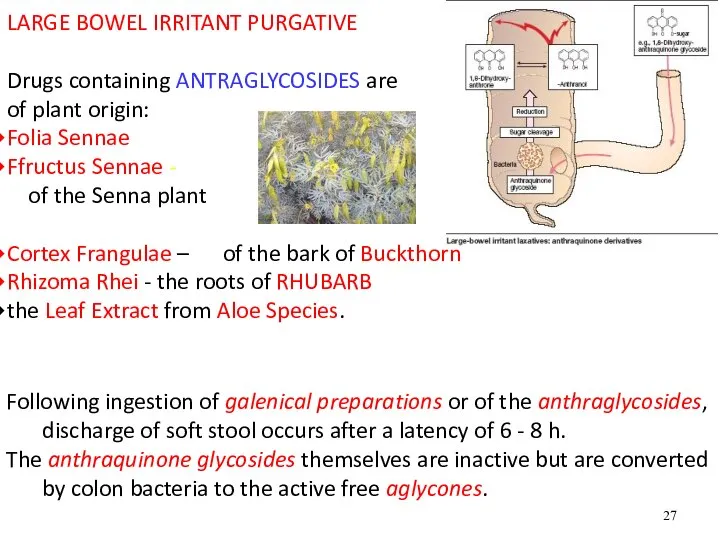
- 27. LARGE BOWEL IRRITANT PURGATIVE Drugs containing ANTRAGLYCOSIDES are of plant origin: Folia Sennae Ffructus Sennae -
- 28. Bisacodyl (tab. 5 mg; rectal supp. 10 mg) is rapidly converted by intestinal enzymes and gut
- 30. Скачать презентацию













![Hepatoprotectors Lipoic Acid [Thioctic acid]: Tab. 12 mg, amp. 0.5% -](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/646298/slide-20.jpg)





 Возможности магнитно-резонансной томографии в диагностике височно-нижнечелюстного сустава
Возможности магнитно-резонансной томографии в диагностике височно-нижнечелюстного сустава Хроническая сердечная недостаточность
Хроническая сердечная недостаточность Туберкулез глаз
Туберкулез глаз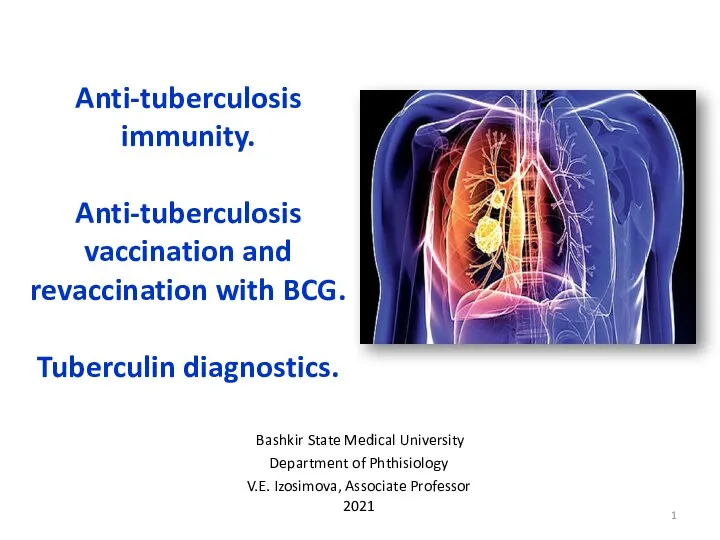 Лекция 2
Лекция 2 Болезни органов дыхания
Болезни органов дыхания MEN синдром
MEN синдром Жанұя денсаулығын нығайту,жанұяны жоспарлау
Жанұя денсаулығын нығайту,жанұяны жоспарлау Әйелдер консультациясы және отбасын жоспарлау орталықтарында жас ата – аналар мектебінің жұмысына есеп жазу
Әйелдер консультациясы және отбасын жоспарлау орталықтарында жас ата – аналар мектебінің жұмысына есеп жазу Антибиотики как особая группа лекарственных средств
Антибиотики как особая группа лекарственных средств Обмен углеводов. Биологическая роль углеводов
Обмен углеводов. Биологическая роль углеводов Защищенные аминопенициллины
Защищенные аминопенициллины Дезинфицирующие средства
Дезинфицирующие средства Моббинг и его профилактика
Моббинг и его профилактика Клинико-лабораторная характеристика энтеровирусных менингитов у детей
Клинико-лабораторная характеристика энтеровирусных менингитов у детей Гастроэзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь
Гастроэзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь Анатомия и физиология речевой системы
Анатомия и физиология речевой системы Химиотерапия
Химиотерапия Эпидемиология сахарного диабета. Типы, виды терапии, классификация лекарственных средств
Эпидемиология сахарного диабета. Типы, виды терапии, классификация лекарственных средств Инвазивные и неинвазивные методы диагностики
Инвазивные и неинвазивные методы диагностики Гигиена девочки до года
Гигиена девочки до года Некариозные поражения твердых тканей зубов
Некариозные поражения твердых тканей зубов Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция)
Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция) Классификация детей с нарушением слуха
Классификация детей с нарушением слуха Табиғи ошақтардың қалыптасу факторы мен жағдайы
Табиғи ошақтардың қалыптасу факторы мен жағдайы Медицинское сообщество и общество. Права пациента и правила биомедицинской этики (лекция №3)
Медицинское сообщество и общество. Права пациента и правила биомедицинской этики (лекция №3) Гигиена детей и подростков. Лекция № 10, 11
Гигиена детей и подростков. Лекция № 10, 11 Клиника интеллектуальных нарушений при микросоциальной педагогической запущенности
Клиника интеллектуальных нарушений при микросоциальной педагогической запущенности Теории детской и возрастной психологии
Теории детской и возрастной психологии