Содержание
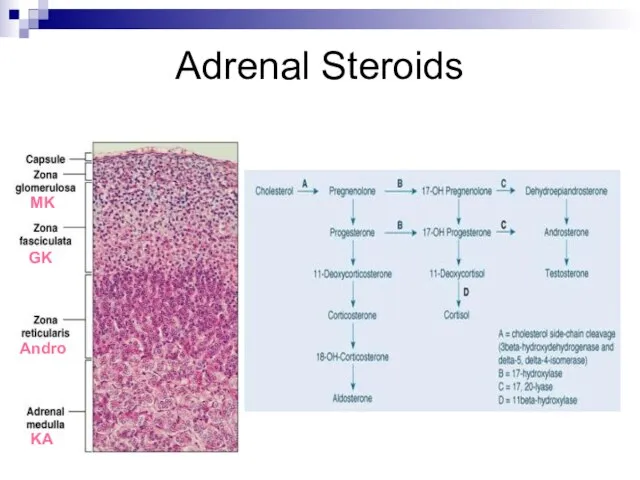
- 2. Adrenal Steroids MK GK Andro KA
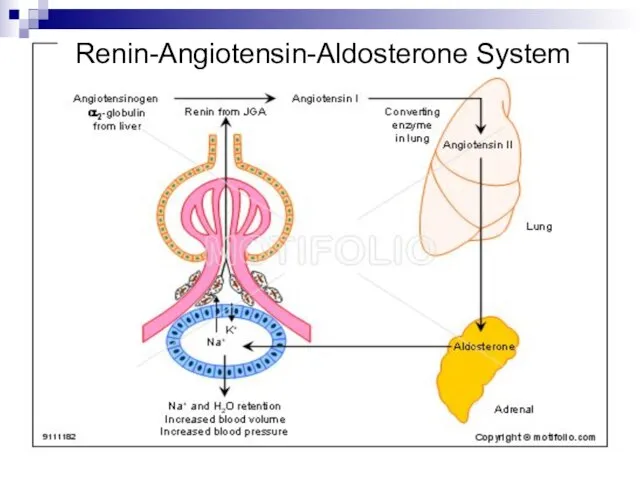
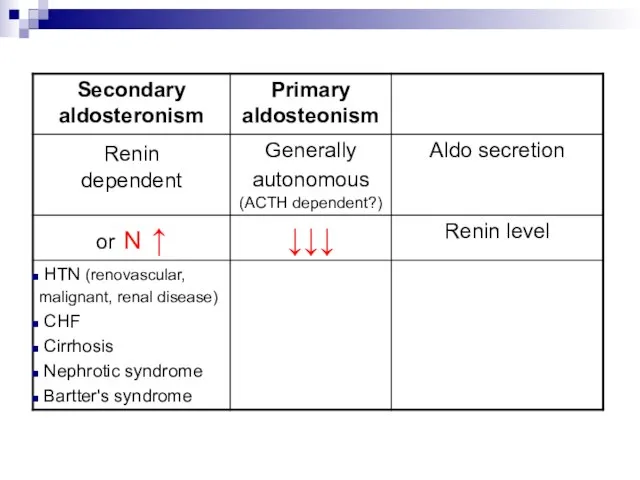
- 3. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
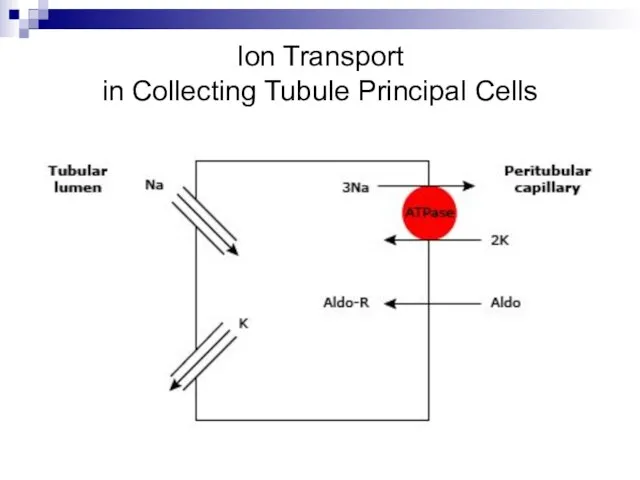
- 4. Ion Transport in Collecting Tubule Principal Cells
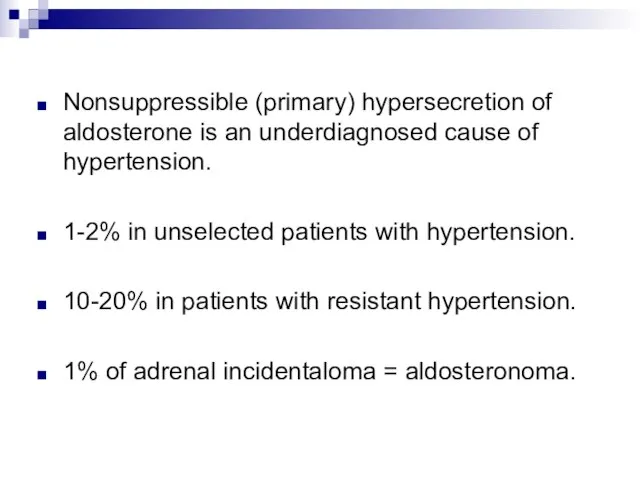
- 5. Nonsuppressible (primary) hypersecretion of aldosterone is an underdiagnosed cause of hypertension. 1-2% in unselected patients with
- 6. Resistant hypertension - failure to achieve goal blood pressure (BP) despite adherence to an appropriate three-drug
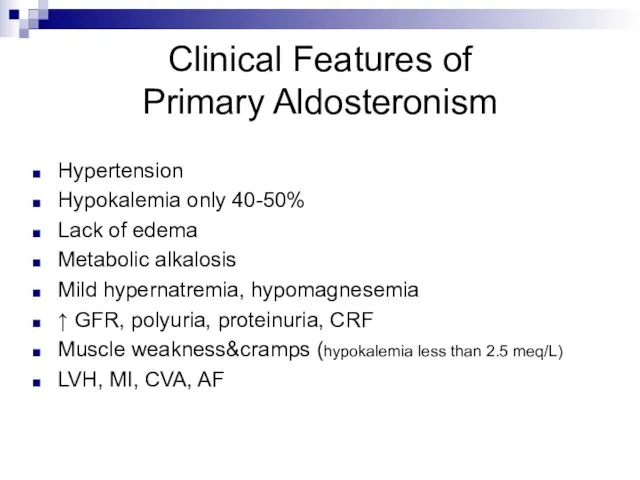
- 8. Clinical Features of Primary Aldosteronism Hypertension Hypokalemia only 40-50% Lack of edema Metabolic alkalosis Mild hypernatremia,
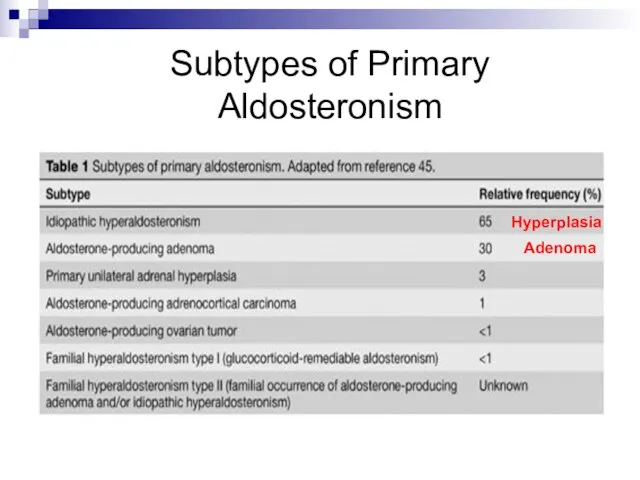
- 9. Subtypes of Primary Aldosteronism Adenoma Hyperplasia
- 11. Screening for Primary Aldosteronism severe hypertension (>160/100 mmHg) or drug-resistant hypertension HTN and spontaneous or diuretic-induced
- 12. Screening (cont.) Plasma Aldosterone-to-Renin ratio mid-morning, after the patient has been up for at least 2
- 13. Confirmation of the Diagnosis Oral sodium loading 24-h urine Na excretion >200 meq Urine Aldo excretion>12
- 15. Imaging CT scan MRI Adrenal venous sampling Iodocholesterol scintigraphy
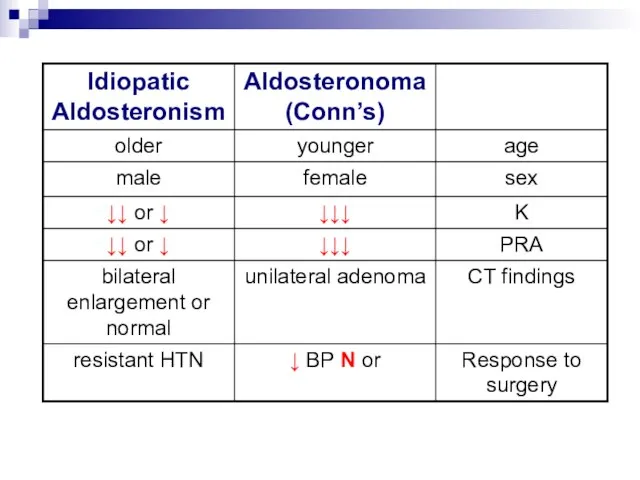
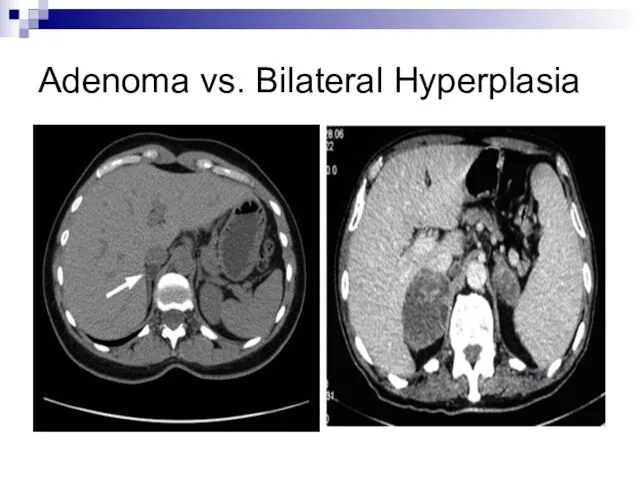
- 16. Adenoma vs. Bilateral Hyperplasia
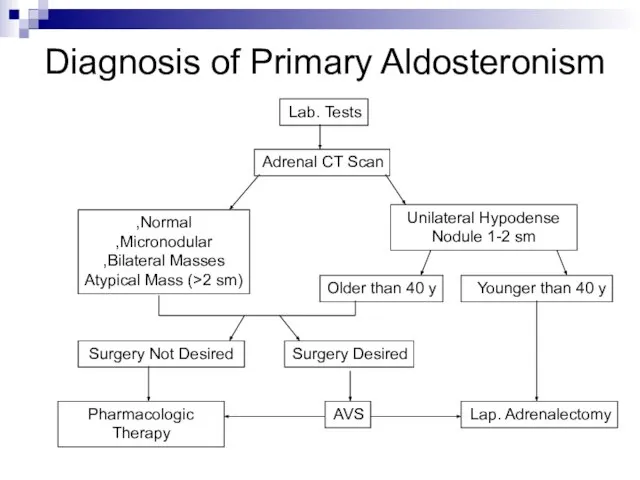
- 17. Diagnosis of Primary Aldosteronism Lab. Tests Adrenal CT Scan Unilateral Hypodense Nodule 1-2 sm Normal, Micronodular,
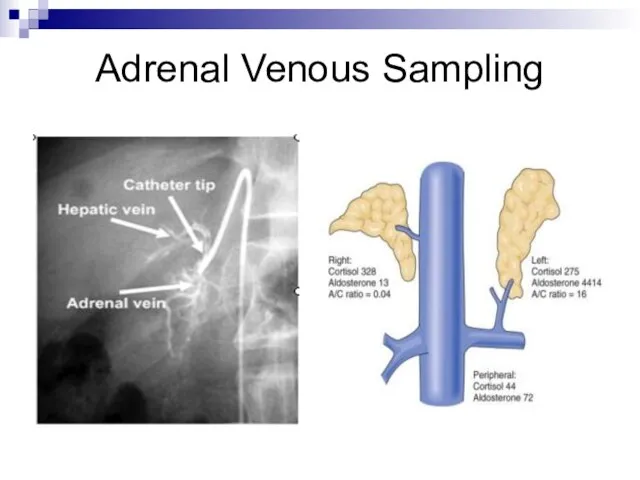
- 18. Adrenal Venous Sampling
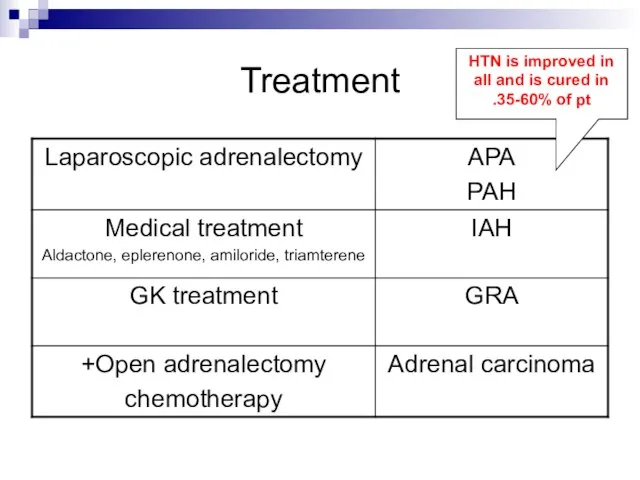
- 19. Treatment HTN is improved in all and is cured in 35-60% of pt.
- 21. Скачать презентацию





 Рекламная деятельность как творческий процесс
Рекламная деятельность как творческий процесс Отраженные и фантомные боли. Зоны Захарьина-Геда
Отраженные и фантомные боли. Зоны Захарьина-Геда ООО Завод Медсинтез Организация комплексного производства субстанции и готовых лекарственных форм генноинженерного инсулина человека
ООО Завод Медсинтез Организация комплексного производства субстанции и готовых лекарственных форм генноинженерного инсулина человека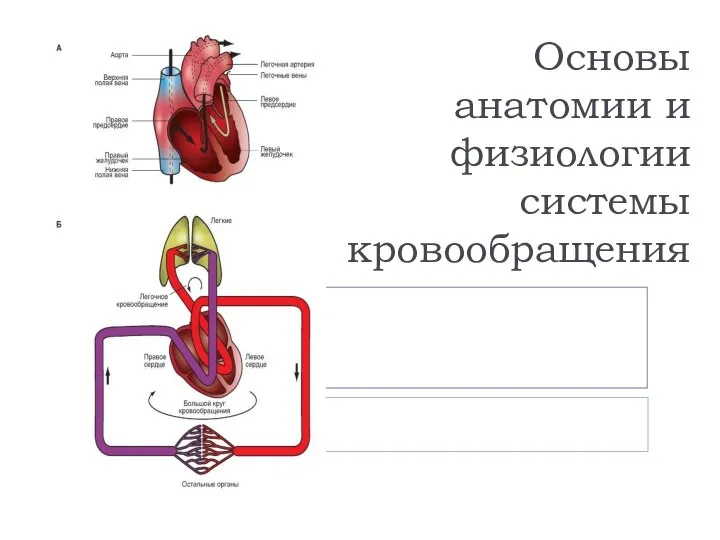 Основы анатомии и физиологии системы кровообращения
Основы анатомии и физиологии системы кровообращения Неспецифический язвенный колит
Неспецифический язвенный колит Классификация, мониторирование, лечение бронхиальной астмы у детей
Классификация, мониторирование, лечение бронхиальной астмы у детей Гемолитическая болезнь плода
Гемолитическая болезнь плода Опухоли из эпителия. Рак отдельных локализаций (молочной железы, матки)
Опухоли из эпителия. Рак отдельных локализаций (молочной железы, матки) Регенерация костной ткани. Основные принципы лечения переломов
Регенерация костной ткани. Основные принципы лечения переломов Diseases of the endocrine system
Diseases of the endocrine system Функциональная анатомия артерий и вен головы и шеи
Функциональная анатомия артерий и вен головы и шеи Ультразвуковая диагностика цереброваскулярных заболеваний
Ультразвуковая диагностика цереброваскулярных заболеваний Патофизиология эндокринной системы
Патофизиология эндокринной системы Международный день толерантности
Международный день толерантности Осложнения после удаления зуба
Осложнения после удаления зуба Острая ревматическая лихорадка. Хроническая ревматическая болезнь сердца
Острая ревматическая лихорадка. Хроническая ревматическая болезнь сердца Улыбка. Улыбка? Улыбка!!!
Улыбка. Улыбка? Улыбка!!! Биохимия опухолевой ткани
Биохимия опухолевой ткани Отделение кардиохирургии и интенсивной терапии ГБУЗ ДГКБ №13 им .Н.Ф. Филатова. ДЗМ. Десять лет работы командой
Отделение кардиохирургии и интенсивной терапии ГБУЗ ДГКБ №13 им .Н.Ф. Филатова. ДЗМ. Десять лет работы командой Создание лекарственных средств
Создание лекарственных средств Бронхиты у детей
Бронхиты у детей Использование партограммы
Использование партограммы Ішкі секреция бездері
Ішкі секреция бездері Физиология беременности и перинатальная охрана плода. Особенности наблюдения беременных женщин в женской консультации
Физиология беременности и перинатальная охрана плода. Особенности наблюдения беременных женщин в женской консультации Қан аурулары
Қан аурулары РА 2 часть 2 исправ.pptx
РА 2 часть 2 исправ.pptx Ведение пациентов с острым коронарным синдромом. Руководство по реваскуляризации миокарда,
Ведение пациентов с острым коронарным синдромом. Руководство по реваскуляризации миокарда, Организация деятельности страховых представителей 3 уровня. Пилотный проект в Ставропольском крае
Организация деятельности страховых представителей 3 уровня. Пилотный проект в Ставропольском крае