Содержание
- 4. Pain Localization: liver disease - right hypochondrium diseases of the BT- right hypochondrium, epigastrium diseases of
- 5. Pain The nature and intensity of pain - any, but biliary colic is more typical for
- 6. Pain Provocation: - The relationship with food intake is usually determined by the nature of the
- 7. Pain eponymous symptoms Murphy s. Eisenberg s. Mussi s. point Bergman point Boas BT diseases Punch
- 8. Kerte s.– pain in pancreas proection Kach s. – hypersensitivity p. Desjardins ∆ Shoffard p. Mayo-Robson
- 9. Conclusion: detailing the pain can help in the diagnosis, but the diagnostic significance may be. insufficient
- 10. Additional syndroms Gastric dyspepsia – nonspecific Biliary dyspepsia - reflects duodenal dyskinesia, not specific Small bowel
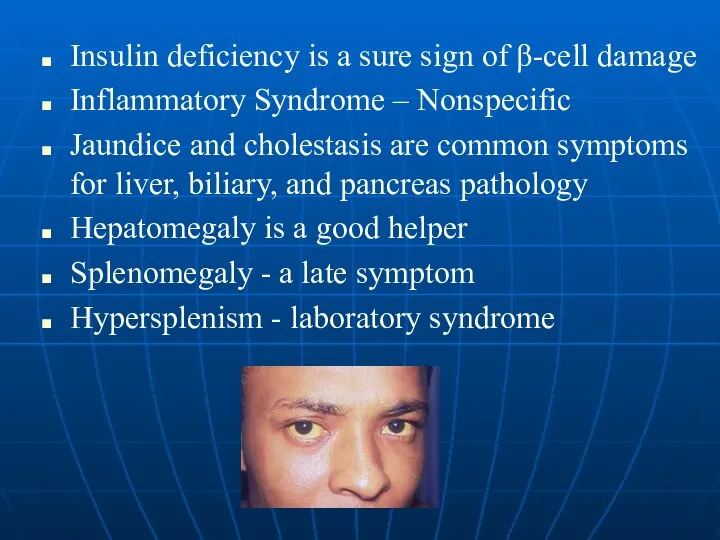
- 11. Insulin deficiency is a sure sign of β-cell damage Inflammatory Syndrome – Nonspecific Jaundice and cholestasis
- 12. Hepatocellular failure syndrome - significantly increases the likelihood of liver pathology, especially the presence of signs
- 13. Hepatocellular failure syndrome Teleangiectasia Jaundice Edema muscular atrophy hemorrhages (1972) vitamin K dependent clotting factors –
- 14. Portal Hypertension Syndrome is an accurate but late sign of probable liver disease The reason is
- 19. Lab test syndromes For L-B-P pathology - hyperbilirubinemia (conjugated, unconjugated, mixed) Inflammatory syndrome anemic cholestasis (ALP,
- 20. Lab test syndromes With liver diseases: HCFS (total protein, albumin, cholesterol, INR) Cytolysis (increase in AST,
- 21. For diseases of the pancreas: inflammatory-necrotic (amylase, lipase, trypsin in the blood) exocrine insufficiency = Malabsorption
- 22. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity Liver pathology exclusion of focal pathology, detection of ascites, hepato-splenomegaly, portal
- 23. Endoscopy Esophagus varices Duodenopapilloscopy
- 24. X-ray CT MRI PET
- 25. N liver
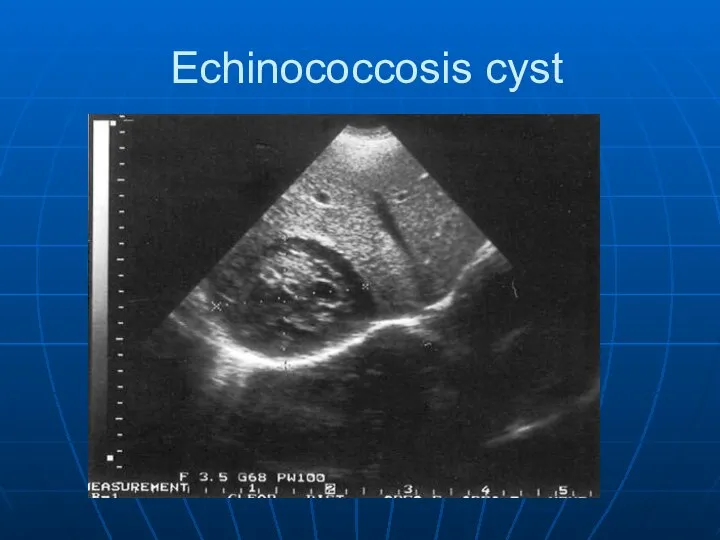
- 26. Echinococcosis cyst
- 27. uneven surface ascites High density
- 29. CT
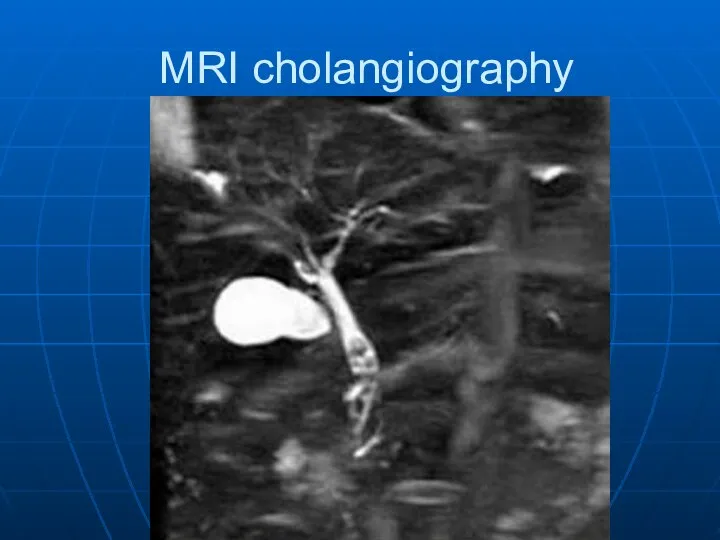
- 31. MRI cholangiography
- 34. Скачать презентацию



























 Изменения в организме женщины во время беременности
Изменения в организме женщины во время беременности Бронхиальная астма: современные подходы к диагностике и лечению
Бронхиальная астма: современные подходы к диагностике и лечению Оценка лабораторной диагностики сибирской язвы в объектах окружающей среды
Оценка лабораторной диагностики сибирской язвы в объектах окружающей среды Отеки. Определение понятия. Механизм развития. Виды отеков
Отеки. Определение понятия. Механизм развития. Виды отеков История развития Всероссийской службы медицины катастроф (ВСМК). Определение, задачи и основные принципы организации помощи
История развития Всероссийской службы медицины катастроф (ВСМК). Определение, задачи и основные принципы организации помощи Органы мочевыделительной системы
Органы мочевыделительной системы Безопасность медицинского персонала при оказании помощи больным
Безопасность медицинского персонала при оказании помощи больным Торлы құрылым және оның организмдегі орны, лимбикалық жүйе
Торлы құрылым және оның организмдегі орны, лимбикалық жүйе Пиелонефрит. Этиология пиелонефрита
Пиелонефрит. Этиология пиелонефрита Лікувальні стратегії остеоартриту: чи можливі альтернативні рішення?
Лікувальні стратегії остеоартриту: чи можливі альтернативні рішення? Системные васкулиты
Системные васкулиты Иммунная система организма. Антигены
Иммунная система организма. Антигены Свертывание крови. Гемостаз
Свертывание крови. Гемостаз АФО новорожденного ребенка
АФО новорожденного ребенка Исследование мокроты
Исследование мокроты Эритроциттегі глюкоза-6-фосфатдегидрогеназа ферменті тапшылығына байланысты туындайтын гемолиздік анемия
Эритроциттегі глюкоза-6-фосфатдегидрогеназа ферменті тапшылығына байланысты туындайтын гемолиздік анемия Эндокринные средства (гормоны и их антагонисты)
Эндокринные средства (гормоны и их антагонисты) Кровозамінні перфузійні розчини
Кровозамінні перфузійні розчини Характеристика нозологических групп обучающихся
Характеристика нозологических групп обучающихся Эмоциональные тона. Поведение, реакции, эмоции
Эмоциональные тона. Поведение, реакции, эмоции Анализ системного воспалительного ответа при применении различных методик искусственного кровообращения
Анализ системного воспалительного ответа при применении различных методик искусственного кровообращения Сестринский уход при объемных процессах центральной нервной системы. Эпилепсия. Судорожный синдром
Сестринский уход при объемных процессах центральной нервной системы. Эпилепсия. Судорожный синдром Регуляция двигательной системы ортезами. Мануальная медицина
Регуляция двигательной системы ортезами. Мануальная медицина Клинический случай
Клинический случай Первая помощь при огнестрельных ранениях
Первая помощь при огнестрельных ранениях Работа мышц
Работа мышц Жатыр миомасы
Жатыр миомасы ВИЧ-инфекция и беременность
ВИЧ-инфекция и беременность