Содержание
- 2. Classifying Cultures U.S. anthropologist Edward T. Hall (1976) divided cultures according to their ways of communicating,
- 3. Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory Between 1967 and 1973, a large survey study regarding national values differences
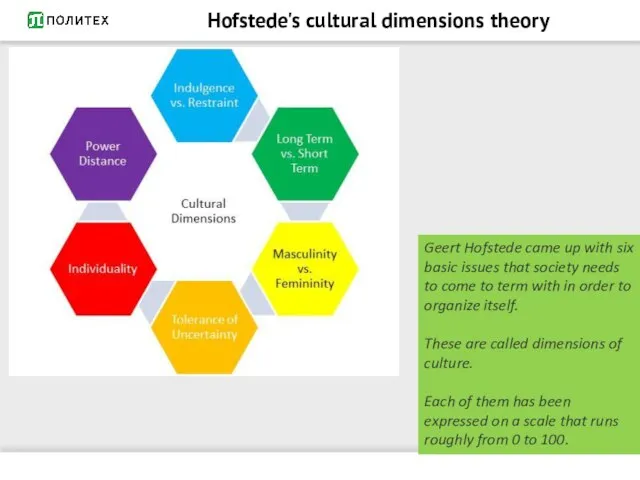
- 4. Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory Geert Hofstede came up with six basic issues that society needs to
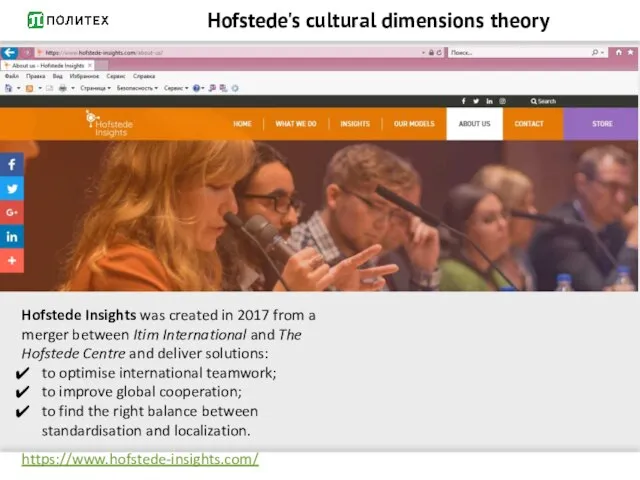
- 5. Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory Hofstede Insights was created in 2017 from a merger between Itim International
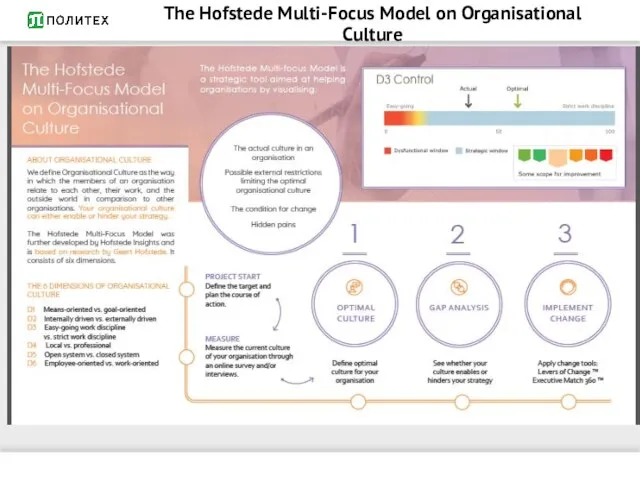
- 7. The Hofstede Multi-Focus Model on Organisational Culture
- 8. Task 1 “Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory ” 1. Analyze and discuss the materials. 2. Prepare the
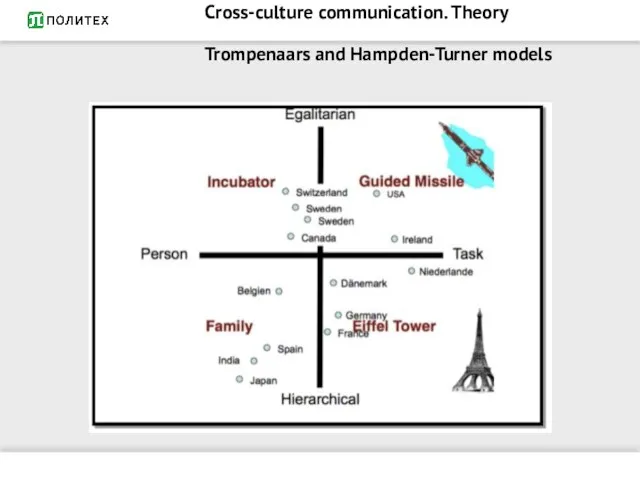
- 10. Cross-culture communication. Theory Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner models
- 11. Cross-culture communication. Theory Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner models
- 12. Cross-culture communication. Theory http://www2.thtconsulting.com/
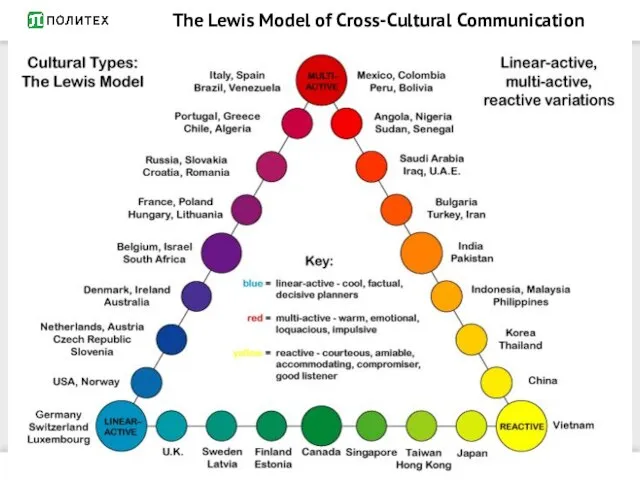
- 17. The Lewis Model of Cross-Cultural Communication
- 18. Communication
- 19. Communication https://www.crossculture.com/
- 21. Скачать презентацию













 Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности школьников в рамках взаимодействия школа - ВУЗ - церковь
Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности школьников в рамках взаимодействия школа - ВУЗ - церковь Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности. Проектная деятельность в начальной школе
Аттестационная работа. Программа внеурочной деятельности. Проектная деятельность в начальной школе Этический кодекс преподавателя и студента СевГУ
Этический кодекс преподавателя и студента СевГУ Специальность 19.02.10 Технология продукции общественного питания. Квалификация Техник-технолог
Специальность 19.02.10 Технология продукции общественного питания. Квалификация Техник-технолог Психолого-педагогическое просвещение участников образовательных отношений
Психолого-педагогическое просвещение участников образовательных отношений Технология интерактивного обучения
Технология интерактивного обучения Подзаголовок слайда
Подзаголовок слайда Применение ИКТ на уроке математики
Применение ИКТ на уроке математики Військова академія (м. Одеса)
Військова академія (м. Одеса) Как составить кластер
Как составить кластер Psychological-pedagogical conditions of using a training in emotional competence for development of students
Psychological-pedagogical conditions of using a training in emotional competence for development of students ОГЭ-2018: что нужно знать
ОГЭ-2018: что нужно знать Аттестационная работа. Планирование работы начальной школы, параллель 4-ых классов, в области проектной деятельности
Аттестационная работа. Планирование работы начальной школы, параллель 4-ых классов, в области проектной деятельности Организация проектной и учебно-исследовательской деятельности обучающихся
Организация проектной и учебно-исследовательской деятельности обучающихся Темы выступлений. Общелингвистическая концепция В. Гумбольдта
Темы выступлений. Общелингвистическая концепция В. Гумбольдта Аттестационная работа. Проектная и исследовательская деятельность в Забайкальском краевом училище культуры
Аттестационная работа. Проектная и исследовательская деятельность в Забайкальском краевом училище культуры Основы разработки проекта
Основы разработки проекта День Российской науки 8 февраля
День Российской науки 8 февраля Самообразование студентов
Самообразование студентов Аттестационная работа. Педагогический проект Творческие лаборатории
Аттестационная работа. Педагогический проект Творческие лаборатории Инклюзивное образование
Инклюзивное образование Білімі туралы құжат
Білімі туралы құжат Государственная итоговая аттестация обучающихся 9-ых классов 2021-2022 учебный год
Государственная итоговая аттестация обучающихся 9-ых классов 2021-2022 учебный год Кружки онлайн. Вместе с детьми, но не вместо детей
Кружки онлайн. Вместе с детьми, но не вместо детей Модель эффективного взаимодействия учитель — ученик при работе над проектом
Модель эффективного взаимодействия учитель — ученик при работе над проектом Методология и методы научного исследования
Методология и методы научного исследования Система образования в России. Противоречия и проблемы современного образования
Система образования в России. Противоречия и проблемы современного образования Аттестация аспиранта 2 - го года обучения (шаблон)
Аттестация аспиранта 2 - го года обучения (шаблон)