Содержание
- 2. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems
- 3. How do competing on a global scale and promoting quality enhance competitive advantage? What is the
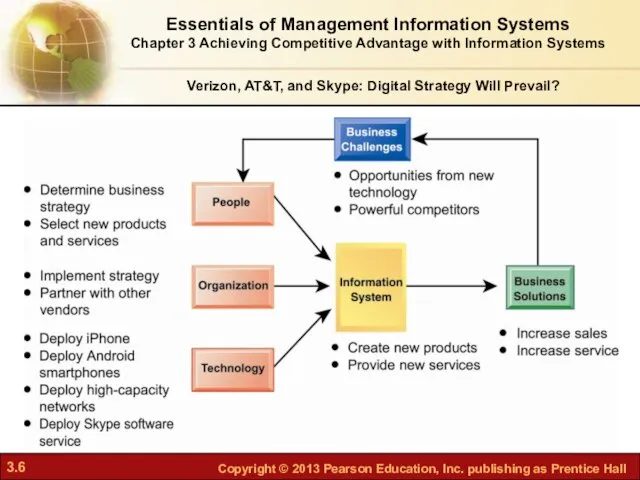
- 4. Verizon, AT&T, and Skype: Digital Strategy Will Prevail? Problem: Intense competition, difficult strategic decisions in arena
- 5. Cutting-edge technologies like the iPhone and fiber-optic networks offer Verizon and AT&T opportunities to gain an
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems Verizon, AT&T, and
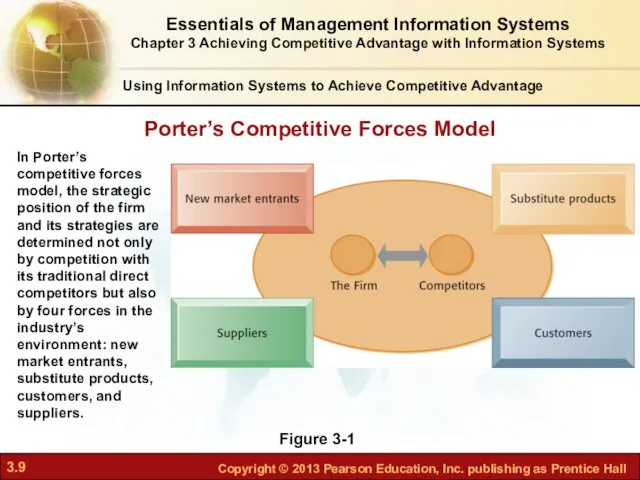
- 7. One way to understand competitive advantage Five competitive forces shape fate of firm Traditional competitors Competitors
- 8. Substitute products and services Substitutes customers can purchase if your prices too high E.g., Internet music
- 9. Figure 3-1 In Porter’s competitive forces model, the strategic position of the firm and its strategies
- 10. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Basic strategy: Align IT with business objectives 75
- 11. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Low-cost leadership Use information systems to achieve the
- 12. Using Information Systems to Achieve Competitive Advantage Supermarkets and large retail stores such as Walmart use
- 13. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Product differentiation Use information systems to enable new
- 14. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Focus on market niche Use information systems to
- 15. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Strengthen customer and supplier intimacy Strong linkages to
- 16. Interactive Session: Technology Technology Helps Starbucks Find New Ways to Compete Using Information Systems to Achieve
- 17. Information System Strategies for Dealing with Competitive Forces Some companies pursue several strategies at same time
- 18. Enables new products and services Encourages substitute products Lowers barrier to entry Changes balance of power
- 19. Highlights specific activities in a business where competitive strategies can best be applied and where information
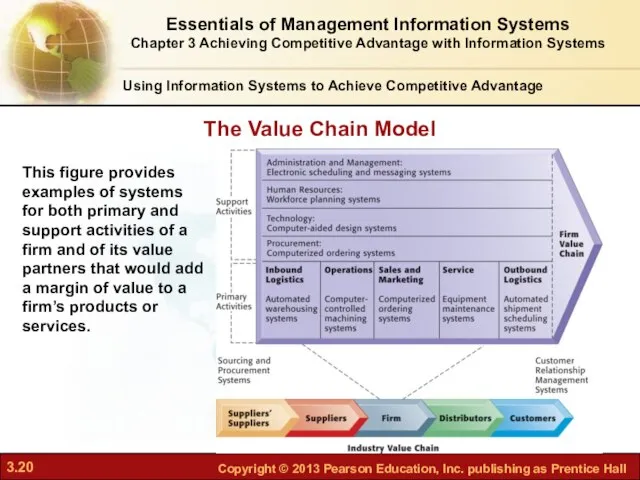
- 20. Using Information Systems to Achieve Competitive Advantage Figure 3-2 This figure provides examples of systems for
- 21. A firm’s value chain is linked to the value chains of its suppliers, distributors, and customers
- 22. Using Information Systems to Achieve Competitive Advantage Figure 3-3 The value web is a networked system
- 23. Synergies: When output of some units can be used as inputs to other units When two
- 24. Core competency: Activities for which firm is world-class leader E.g., world’s best miniature parts designer, best
- 25. Network-based strategies: Network economics: Marginal costs of adding another participant are near zero, whereas marginal gain
- 26. Disruptive technologies: Technologies with disruptive impact on industries and businesses, rendering existing products, services and business
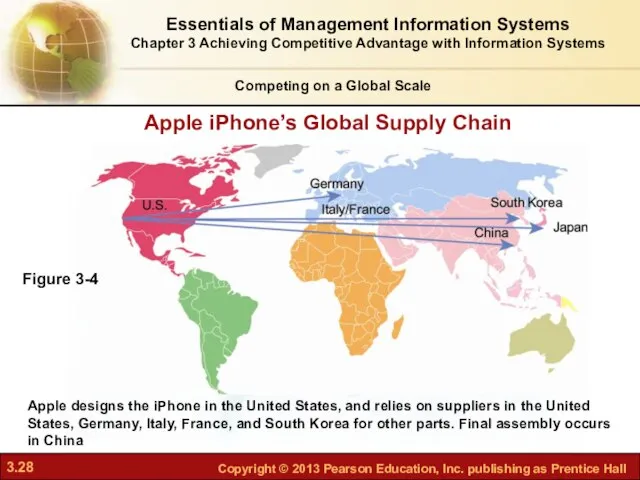
- 27. Prior to the Internet, competing globally was only an option for huge firms able to afford
- 28. Apple iPhone’s Global Supply Chain Competing on a Global Scale Apple designs the iPhone in the
- 29. Global Business and System Strategies Competing on a Global Scale Domestic exporters Heavy centralization of corporate
- 30. Global System Configurations Competing on a Global Scale Centralized systems: All development and operation at domestic
- 31. Global Business Organization Systems Configurations Competing on a Global Scale Figure 3-5 The large Xs show
- 32. What Is Quality? Competing on Quality and Design Producer perspective: Conformance to specifications and absence of
- 33. Reduce cycle time and simplify production process Benchmarking Use customer demands to improve products and services
- 34. Computer-aided design (CAD) systems improve the quality and precision of product design by performing much of
- 35. Technology alone is often not enough to make companies more efficient, competitive, or quality oriented Organizational
- 36. Steps in BPM Identify processes for change Analyze existing processes Design new process Implement new process
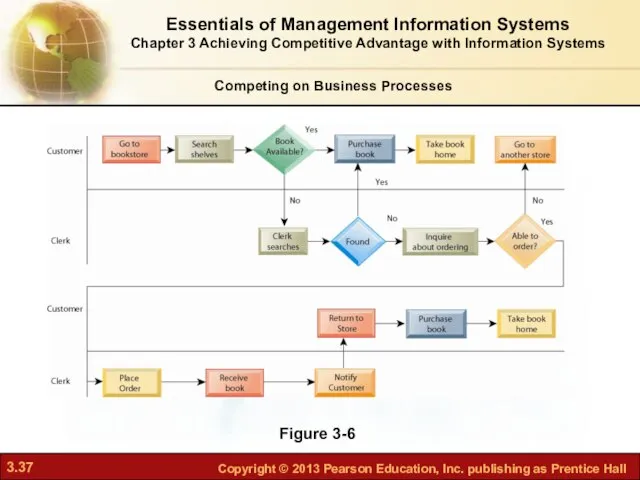
- 37. Figure 3-6 Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems
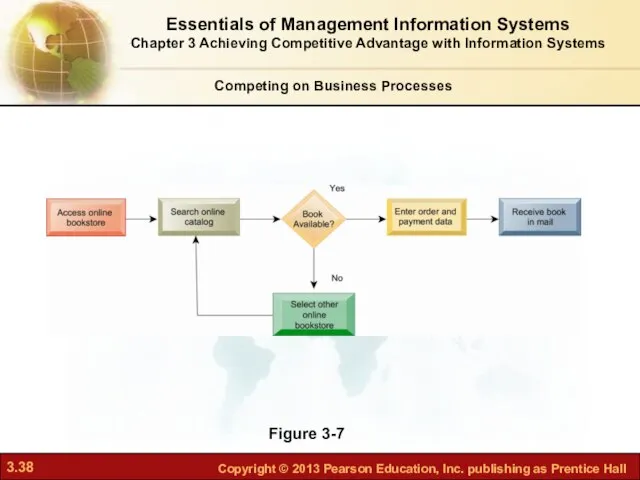
- 38. Figure 3-7 Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 3 Achieving Competitive Advantage with Information Systems
- 39. Interactive Session: Organizations Burton Snowboards Speeds Ahead with Nimble Business Processes Read the Interactive Session and
- 40. A radical form of fast change Not continuous improvement, but elimination of old processes, replacement with
- 42. Скачать презентацию

































 Итоговая игра Государственная и муниципальная служба
Итоговая игра Государственная и муниципальная служба Плетёные листья
Плетёные листья Квест два вуза: одна история
Квест два вуза: одна история Шануй батька і матір
Шануй батька і матір SIGGRAPH 2010
SIGGRAPH 2010 Электрическая мощность
Электрическая мощность Обращение дольщиков 2 очереди ЖК Домашний
Обращение дольщиков 2 очереди ЖК Домашний Загородная недвижимость. Особенности создания объектов загородной недвижимости
Загородная недвижимость. Особенности создания объектов загородной недвижимости Изготовление простого концевого углового столярного соединения УК-1. Учебная практика
Изготовление простого концевого углового столярного соединения УК-1. Учебная практика Мосты Новосибирска
Мосты Новосибирска Рациональное питание человека
Рациональное питание человека Газификация твердых топлив в мировой энергетике
Газификация твердых топлив в мировой энергетике Pravidla silničního provozu
Pravidla silničního provozu интегрция
интегрция Петушок из солёного теста и скорлупы
Петушок из солёного теста и скорлупы Прибор для измерения ОПФ объективов
Прибор для измерения ОПФ объективов Виды сфер и услуг
Виды сфер и услуг Внедрение программного комплекса Ankey SIEM NG в инфраструктуру предприятия ООО НПФ ИСБ
Внедрение программного комплекса Ankey SIEM NG в инфраструктуру предприятия ООО НПФ ИСБ Изучение взаимодействия пирокатехина с дифенилметанолом. Новые стерически экранированные о-бензохиноны
Изучение взаимодействия пирокатехина с дифенилметанолом. Новые стерически экранированные о-бензохиноны Прекрасное лето в Карелии
Прекрасное лето в Карелии Современные методы приготовления ХБИ и МКИ
Современные методы приготовления ХБИ и МКИ От Империи к Республике
От Империи к Республике СТО К ОДНОМУ для ЛА
СТО К ОДНОМУ для ЛА Повторительно-обобщающая викторина по физике _Своя игра (1)
Повторительно-обобщающая викторина по физике _Своя игра (1) Выбор и приобретение земельного участка под строительство жилого дома
Выбор и приобретение земельного участка под строительство жилого дома Headphones
Headphones Товароведная характеристика и экспертиза качества мясных полуфабрикатов различных производителей
Товароведная характеристика и экспертиза качества мясных полуфабрикатов различных производителей Парикмахерская
Парикмахерская