Содержание
- 2. PDD Processing Raw pressure transmitted (Annular and Bore as GENERIC Variables – Units PSI Variables Tagged
- 3. PDD Applications The sleeve with two O rings can be changed at the rig site to
- 4. PDD Piezo resistive sensor
- 5. PDD Piezo resistive sensor
- 6. PDD Applications Real-time downhole hydraulics monitor Real-time ECD monitoring and management Annulus cuttings overload detection Washout
- 7. Managed Pressure Drilling Managing the annular hydraulic pressure profile within the allowed pressure window Well control
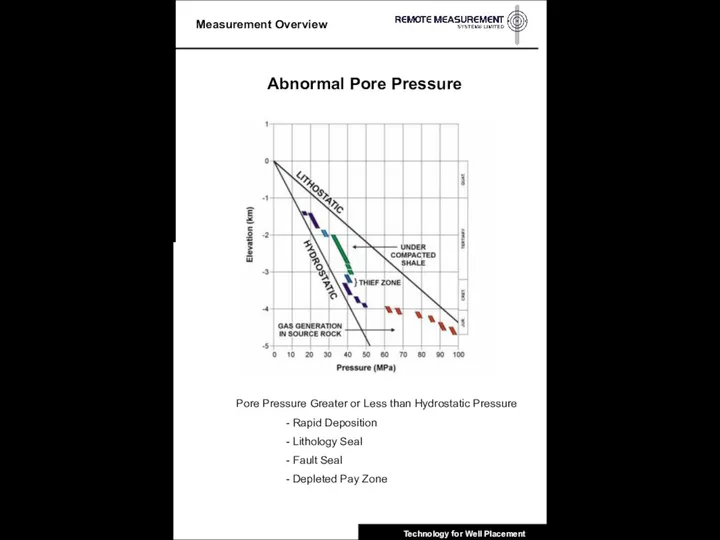
- 8. Abnormal Pore Pressure Pore Pressure Greater or Less than Hydrostatic Pressure - Rapid Deposition - Lithology
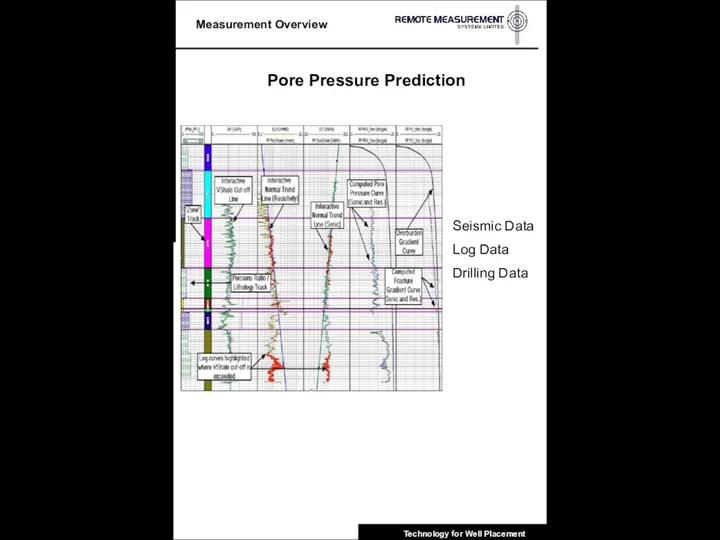
- 9. Pore Pressure Prediction Seismic Data Log Data Drilling Data
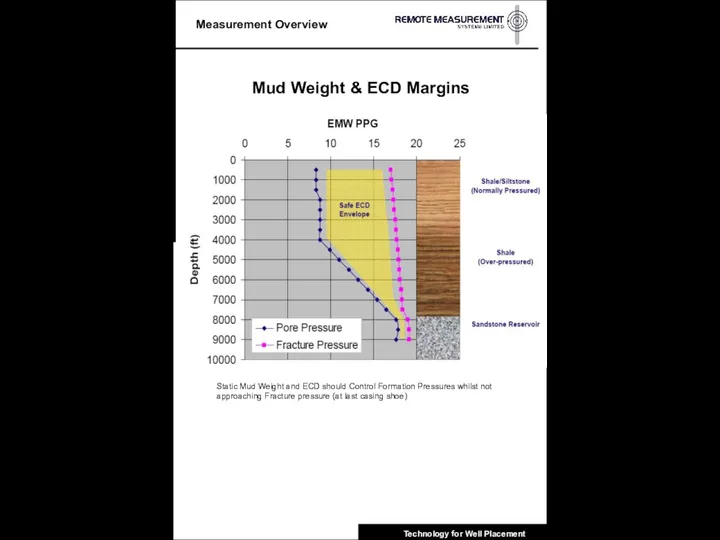
- 10. Mud Weight & ECD Margins Static Mud Weight and ECD should Control Formation Pressures whilst not
- 11. Failure to Control Pressure Shale Caving Borehole Rugosity Tight Spots Well Collapse Well Kicks Blow Out
- 12. ECD – Effective Circulating Density EMW = {PDD Pann (psi) / TVD (m) x 1.421} Mud
- 14. Скачать презентацию








 Анимация схемы тяги ЭТ-2М низковольтная
Анимация схемы тяги ЭТ-2М низковольтная Методика проектирования детского игрового пространства в жилой среде
Методика проектирования детского игрового пространства в жилой среде Первоначальная подготовка работников Обеспечивающих подразделений АО Авиакомпания Россия в рамках СУБП
Первоначальная подготовка работников Обеспечивающих подразделений АО Авиакомпания Россия в рамках СУБП Система керування вихідною потужністю електроприводу постійного струму газоперекачувального агрегату
Система керування вихідною потужністю електроприводу постійного струму газоперекачувального агрегату Центробежные насосы
Центробежные насосы Духовное краеведение Подмосковья. К игумену земли русской Сергию Радонежскому
Духовное краеведение Подмосковья. К игумену земли русской Сергию Радонежскому Услуги Росреестра по Свердловской области, предоставляемые в электронном виде
Услуги Росреестра по Свердловской области, предоставляемые в электронном виде Kobieta
Kobieta Резюме. Чайка Срегей Игоревич
Резюме. Чайка Срегей Игоревич Используя шаблон программы из 1-го задания и метод Replace замените строку Здравствуй, мир! на Мои друзья:
Используя шаблон программы из 1-го задания и метод Replace замените строку Здравствуй, мир! на Мои друзья: Составление меню на завтрак
Составление меню на завтрак КББЖ
КББЖ Экспериментирование как средство развития познавательной активности детей среднего дошкольного возраста
Экспериментирование как средство развития познавательной активности детей среднего дошкольного возраста Итоговое повторение курса информатики за 8 класс
Итоговое повторение курса информатики за 8 класс Профиль муниципалитета
Профиль муниципалитета Мастер отделочных строительных работ. Обойные работы
Мастер отделочных строительных работ. Обойные работы Vienna at night
Vienna at night 20141122_konkursnaya_prgramma
20141122_konkursnaya_prgramma Бюджет для граждан Краснотуранского района на 2014 год и план 2015-2016 годов
Бюджет для граждан Краснотуранского района на 2014 год и план 2015-2016 годов Как выбрать теплый пол
Как выбрать теплый пол Анастасия Бондарик
Анастасия Бондарик Рождество Христово
Рождество Христово Каркасы с деревянными балками
Каркасы с деревянными балками Профилактика конфликтов
Профилактика конфликтов Образ города в изобразительном творчестве
Образ города в изобразительном творчестве Збережемо першоцвіти!
Збережемо першоцвіти! Периферийные устройства персонального компьютера
Периферийные устройства персонального компьютера Основные понятия и определения делопроизводства
Основные понятия и определения делопроизводства