Содержание
- 2. Plan: 1/ Constitutional monarchy vs parliamentary democracy The basic legal documents in the UK The governing
- 3. The System of government The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy
- 4. The UK is constitutional monarchy. This means that the official head of state is the monarch,
- 5. Legal documents Magna Carta – the Great Charter - 1215 Petition of Rights – 1628- the
- 6. A monarch is trained from Birth for the position of Head of State and even when
- 7. The Queen is the personification of the State. The Queen is the head of the executive
- 8. THE QUEEN'S WORKING DAY The Queen has many different duties to perform every day: investitures, ceremonies,
- 9. THE QUEEN'S CEREMONIAL DUTIES the State Opening of Parliament, Audiences with new ambassadors the presentation of
- 10. THE ROYAL FAMILY MEMBERS OF THE ROYAL FAMILY
- 11. Queen Elizabeth II is a descendent of the Saxon king, Egbert. ????? She is the 63d
- 12. The Queen's children
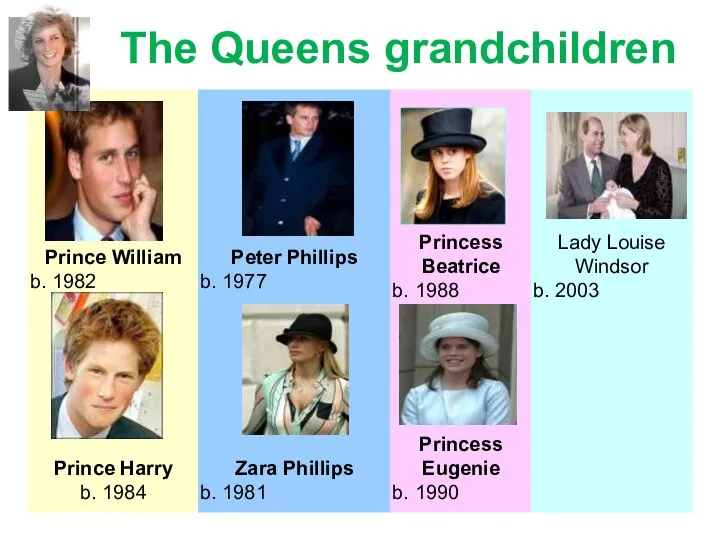
- 13. The Queens grandchildren
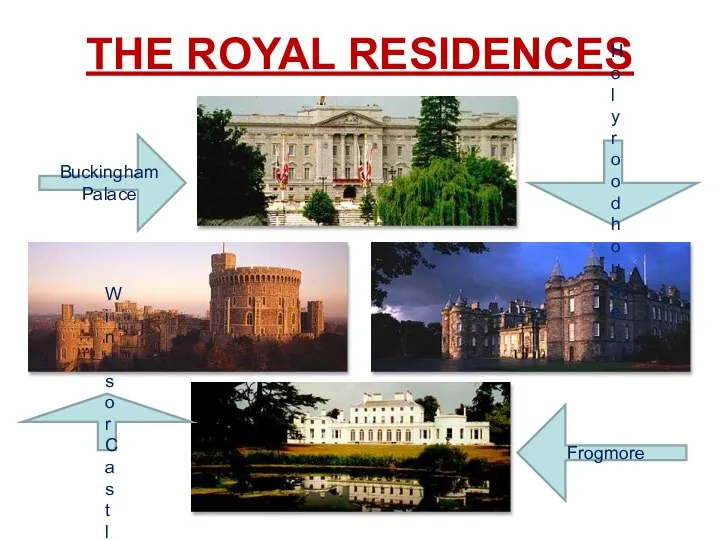
- 14. THE ROYAL RESIDENCES Buckingham Palace Holy rood house Frogmore Windsor Castle
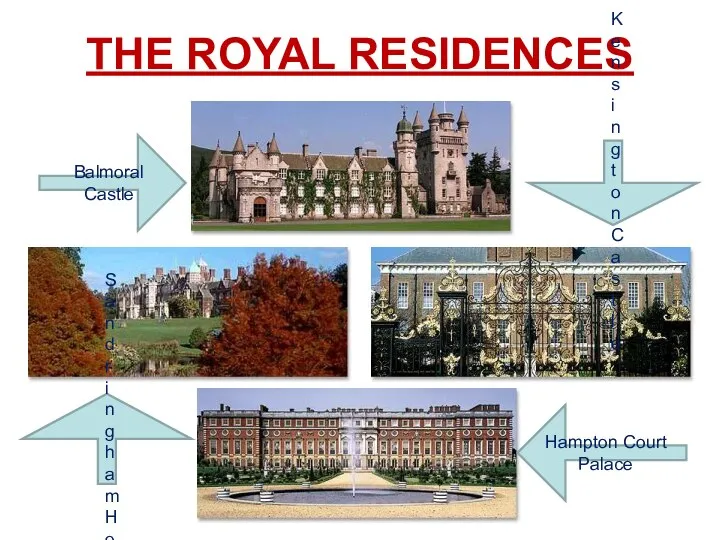
- 15. THE ROYAL RESIDENCES Balmoral Castle Kensington Castle Sand ringham House Hampton Court Palace
- 17. The organs of government in the United Kingdom are the legislature; the executive power; the judiciary.
- 18. the legislature power belongs to Parliament which main function is law-making.
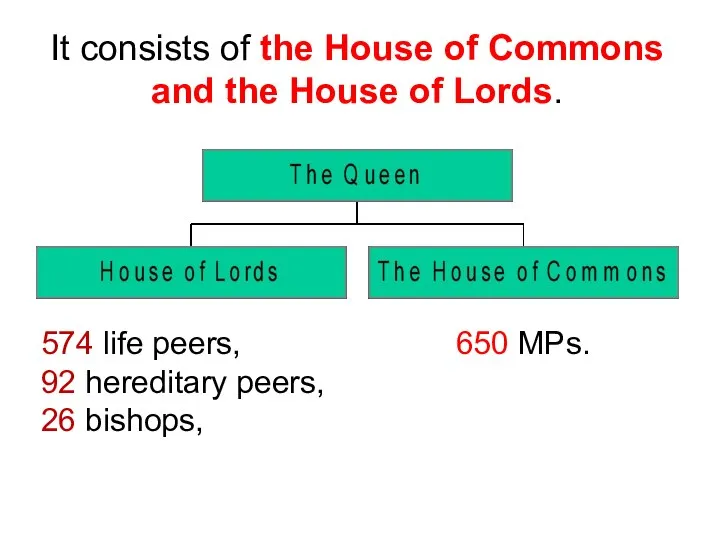
- 20. 574 life peers, 92 hereditary peers, 26 bishops, 650 MPs. It consists of the House of
- 21. The House of Lords 574 life peers, 92 hereditary peers, 26 bishops
- 22. The House of Commons is elected by an almost universal adult suffrage. There are at present
- 23. Erskine May: Parliamentary Practice The rules how to behave in Parliament No reading No violency
- 24. MPs are elected either at a general election or at a by-election following the death or
- 26. the executive power Is realized by: the Cabinet and other ministers of the Crown; Government departments;
- 27. The executive power of the Crown is exercised by the cabinet, headed by the prime minister.
- 28. Five last prime ministers since… 1974-1976 Harold Wilson 1976-1979 James Callaghan 1979-1990 Margaret Thatcher 1990-1997 John
- 29. Prime Minister First Lord of the Treasury Minister for the Civil Service David Cameron
- 30. Each member of the Cabinet is a minister responsible for a government department.
- 31. Chancellor of the Exchequer Responsibility Government spending Presents the Budget annually in March Lives at 11
- 32. Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs Responsibility Relations with other countries Philip Hammond
- 33. Secretary of State for Justice Lord Chancellor Michael Gove
- 34. Secretary of State for the Home Department Responsibility Internal relations The police Law and order Law
- 35. Secretary of State for Education Nicola Ann Morgan 1970 - Margaret Thatcher
- 36. The Cabinet meets at the Prime Minister’s house – number 10 Downing street.
- 37. The second largest party becomes the official opposition with its own leader and the Shadow Cabinet.
- 38. Political parties At present the main political groupings are the Conservative and Labour Parties and the
- 39. The Conservative Party often called the Tory Party, started as Royalists in the 17th century. It
- 40. The Liberal Party began its activities as anti-Royalists. The Liberals represented the trading and manufacturing class
- 41. The Labour Party was established at the beginning of the last century. It was set up
- 42. Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in Britain which existed from 1838 to 1858.
- 43. The People's Charter called for six reforms A vote for every man 21 years of age
- 44. The party that obtains the majority of seats in the House is called the Government, and
- 45. The Government is the party which has the majority in the Parliament and the Queen appoints
- 46. the judiciary determines common law and interprets statutes.
- 48. Скачать презентацию








































 Проектно-изыскательские организации
Проектно-изыскательские организации Предмет правовой статистики
Предмет правовой статистики  Технологические основы сварки сталей различных классов
Технологические основы сварки сталей различных классов Живопись Руси в XIV-XV вв. Знаменитые мастера.
Живопись Руси в XIV-XV вв. Знаменитые мастера.  Презентация "Проблема стиля и стилизации в изобразительном искусстве. Рисуем собаку" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Проблема стиля и стилизации в изобразительном искусстве. Рисуем собаку" - скачать презентации по МХК Logistica în distribuție (Aval)
Logistica în distribuție (Aval) Гибкие теплоизолированные трубы
Гибкие теплоизолированные трубы Партія «Об’єднання Самопоміч»
Партія «Об’єднання Самопоміч» Роль и место лингвострановедческого аспекта в системе обучения иностранному языку
Роль и место лингвострановедческого аспекта в системе обучения иностранному языку Учебная мотивация и ее развитие Клепикова Г.И. преподаватель психологи КГБОУ СПО «Енисейский педагогический колледж»
Учебная мотивация и ее развитие Клепикова Г.И. преподаватель психологи КГБОУ СПО «Енисейский педагогический колледж» Олена Пчілка – мати Лесі Українки, дитяча письменниця
Олена Пчілка – мати Лесі Українки, дитяча письменниця Семейная реликвия пишущая машинка «УНДЕРВУД»
Семейная реликвия пишущая машинка «УНДЕРВУД» ПРАВИЛЬНАЯ ОСАНКА-ЗАЛОГ ЗДОРОВЬЯ Подготовил учитель физической культуры МАОУ «Гимназия им. Н.В. Пушкова» Тайшина Татьяна Виталь
ПРАВИЛЬНАЯ ОСАНКА-ЗАЛОГ ЗДОРОВЬЯ Подготовил учитель физической культуры МАОУ «Гимназия им. Н.В. Пушкова» Тайшина Татьяна Виталь Редактирование страниц сайта компании PerfectCode
Редактирование страниц сайта компании PerfectCode Модель поведения потребителя Продукции COCA-COLA
Модель поведения потребителя Продукции COCA-COLA Конь против ферзя, слона и ладьи. Тренажеры. Часть 1
Конь против ферзя, слона и ладьи. Тренажеры. Часть 1 Культура Індії
Культура Індії Розборка ноутбука emashines
Розборка ноутбука emashines Презентация Требования к языку и оформлению студенческих научных работ
Презентация Требования к языку и оформлению студенческих научных работ Презентация "Знакомство с орнаментом" - скачать презентации по МХК
Презентация "Знакомство с орнаментом" - скачать презентации по МХК ИКТ в организации образовательного процесса Карамшук И.Н., старший преподаватель кафедры ФМО
ИКТ в организации образовательного процесса Карамшук И.Н., старший преподаватель кафедры ФМО Мастерская декоративно-прикладного творчества «Сувенир»
Мастерская декоративно-прикладного творчества «Сувенир» Архитектура Intel Core
Архитектура Intel Core Элементы горного рельефа
Элементы горного рельефа Презентация "Барокко"
Презентация "Барокко" Гигиена детей и подростков
Гигиена детей и подростков Формы и порядок проведения таможенного контроля
Формы и порядок проведения таможенного контроля Захворювання молочної залози укр
Захворювання молочної залози укр