Содержание
- 2. Money and interest rates Lecture 8 Foundations of Economics
- 3. Outline The meaning and function of money The role of banks and central bank The supply
- 4. Teaching the Terms Commodity money Fiat money Representative money Liquidity
- 5. Problems with barter Inefficient Time consuming Difficult to satisfy wants and needs consistently
- 6. Functions of Money
- 7. Sources of Money’s Value Commodity Money – medium of exchange has intrinsic value Representative money –
- 8. Characteristics of Money Portable Durable Divisible Uniform Limited Acceptable
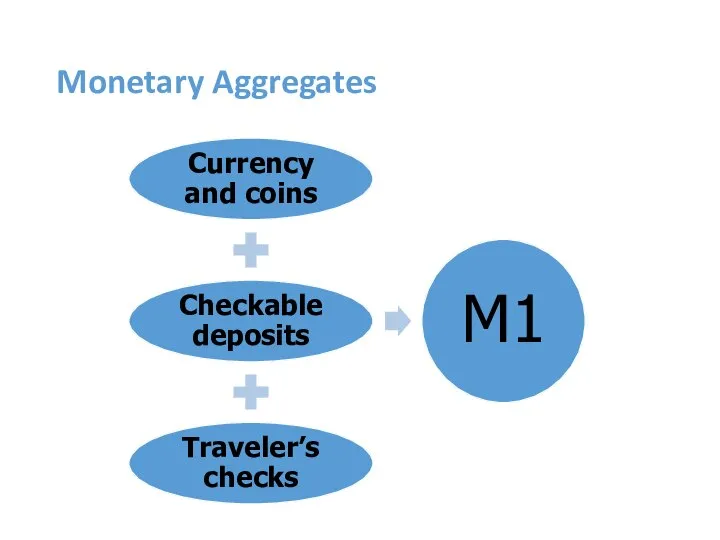
- 9. Monetary Aggregates
- 10. Two Definitions of the Money Supply, December 2017
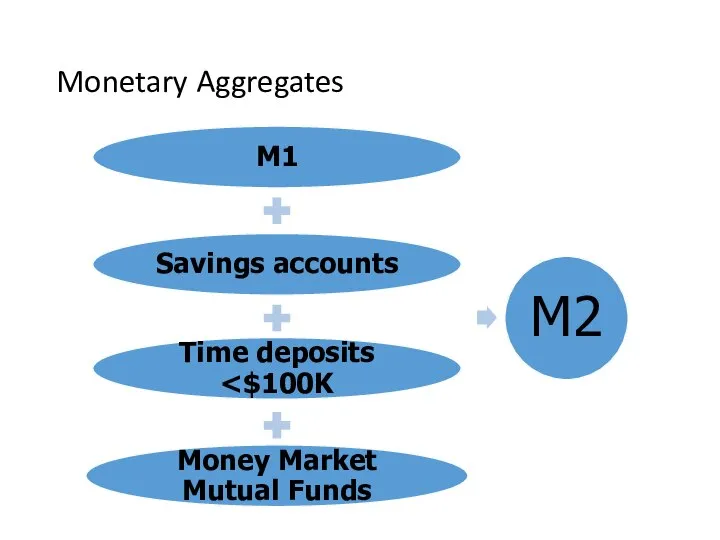
- 11. Monetary Aggregates
- 12. Two Definitions of the Money Supply, December 2017
- 13. Liquidity Ability to convert an asset to a medium of exchange without loss of value Factors
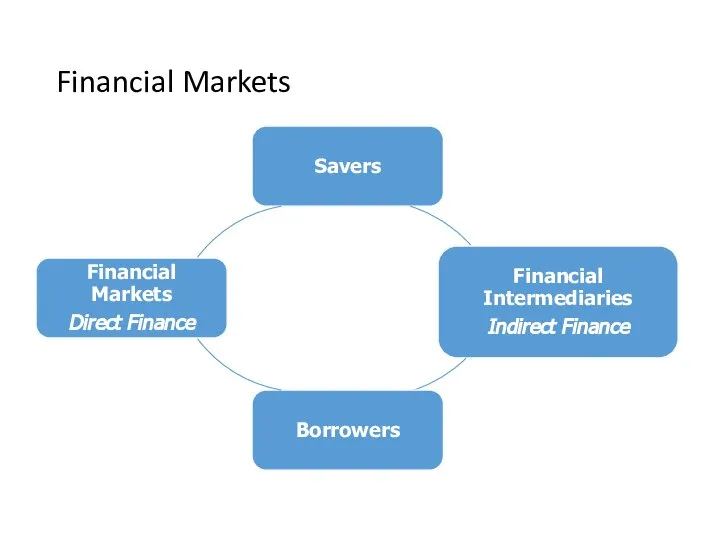
- 15. Financial Markets
- 16. Types of Financial Intermediaries Banks, savings and loans, credit unions Mutual funds Life insurance companies Pension
- 17. The Banking System How banking evolved From using gold as commodity money To goldsmiths who issued
- 18. Features of fractional reserve banking Bank profitability Banks are in business to earn profits Interest on
- 19. The Banking System Principles of bank management: Profit vs. Safety How do banks maintain a reputation
- 20. The Banking System Banking - inherently risky business Safe only by cautious and prudent management But
- 22. The Origins of the Money Supply Bankers books Asset An item of value owned Liability Item
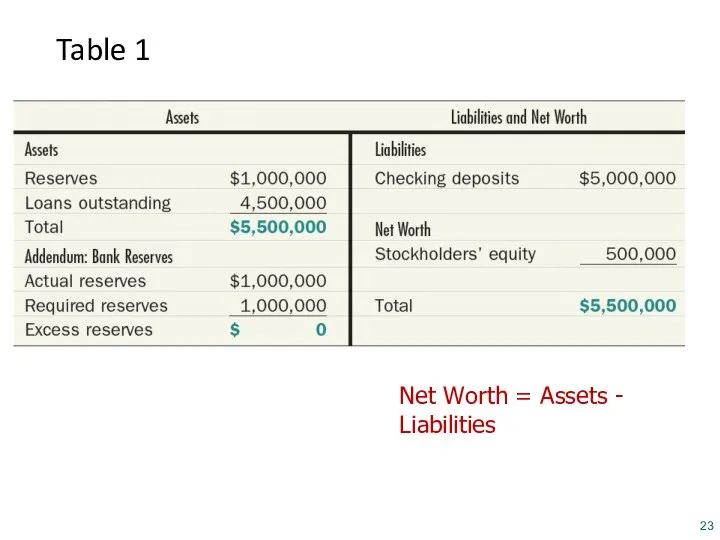
- 23. Table 1 Balance Sheet of Bank-a-Mythica, December 31, 2014 Net Worth = Assets - Liabilities
- 24. Bank Assets Cash and operational balances in the central bank Short-term loans Market loans Bills of
- 25. Bank Liabilities = Deposits Sight deposits Time deposits Certificates of deposit (CDs) Sale and repurchase agreements
- 26. Banks and Money Creation In general If the required reserve ratio = m Money multiplier =
- 28. Monetary Policy and interest rates Government (through independent agency) regulates money supply to maintain stability During
- 29. The Central Bank Functions: Issue notes Bank to the government Bank to banks Bank to overseas
- 30. The Need for Monetary Policy During an economic boom Banks expand money supply Undesirable momentum to
- 31. Money supply The supply of money is to be determined by the Central Bank (exogenous). Therefore
- 32. Money Demand Quantity of money demanded is the amount of wealth that the individuals choose to
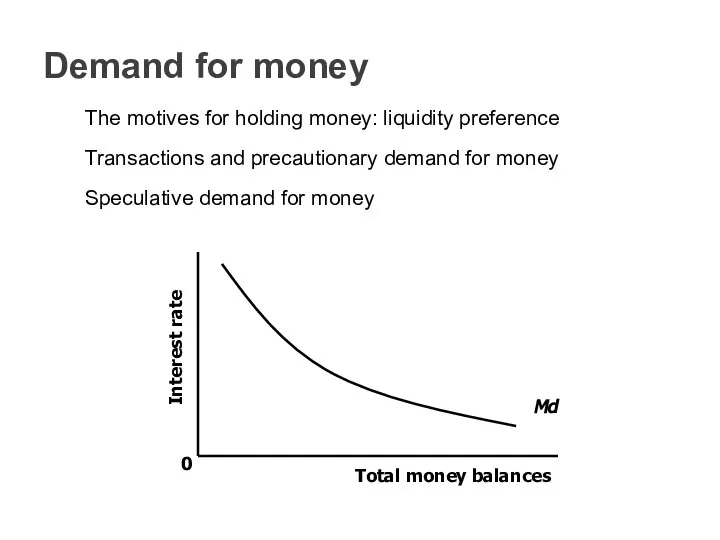
- 33. Demand for money The motives for holding money: liquidity preference Transactions and precautionary demand for money
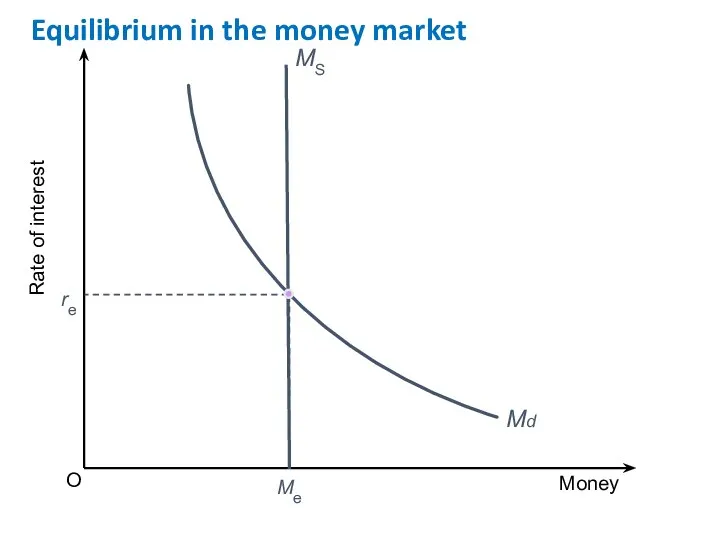
- 34. O Rate of interest Money re Me Equilibrium in the money market
- 37. Скачать презентацию



























 Квартира нашей мечты
Квартира нашей мечты Комплексная оценка финансового состояния компании
Комплексная оценка финансового состояния компании Vvodny_kurs_na_samostoyatelnoe_izuchenie_2
Vvodny_kurs_na_samostoyatelnoe_izuchenie_2 Фінансові піраміди
Фінансові піраміди Глобальные изменения в работе бухгалтеров в IV квартале 2020 года и начале 2021 года
Глобальные изменения в работе бухгалтеров в IV квартале 2020 года и начале 2021 года Кредитная политика коммерческого банка при кредитовании юридических лиц на примере ОАО Лето Банк
Кредитная политика коммерческого банка при кредитовании юридических лиц на примере ОАО Лето Банк Внебюджетное финансирование образования
Внебюджетное финансирование образования Расчет доходности операций с векселями
Расчет доходности операций с векселями Финансовая грамотность
Финансовая грамотность Банковское регулирование и банковский надзор. Лекция 13
Банковское регулирование и банковский надзор. Лекция 13 Имущество предприятия. Управление активами. (Тема 4)
Имущество предприятия. Управление активами. (Тема 4) Инструкция по заполнению кредитной заявки
Инструкция по заполнению кредитной заявки Базовые показателикорпоративных финансов
Базовые показателикорпоративных финансов Анализ рисков проекта
Анализ рисков проекта Учет оплаты неотработанного времени. Оплата отпуска
Учет оплаты неотработанного времени. Оплата отпуска Привлечение ресурсов для СО НКО
Привлечение ресурсов для СО НКО Оценка общей культурной ситуации в Москве. Финансирование культурной сферы жизни
Оценка общей культурной ситуации в Москве. Финансирование культурной сферы жизни Банкротство, санация и ликвидация предприятия. (Тема 5)
Банкротство, санация и ликвидация предприятия. (Тема 5) Содействие в создании кадрового потенциала учителей, методистов образовательных организаций в области финансовой грамотности
Содействие в создании кадрового потенциала учителей, методистов образовательных организаций в области финансовой грамотности Преимущества приобретения транспорта в лизинг перед покупкой за наличный расчет и в кредит
Преимущества приобретения транспорта в лизинг перед покупкой за наличный расчет и в кредит Оборотные средства предприятия
Оборотные средства предприятия Роль управленческого учета
Роль управленческого учета Податок на додану вартість
Податок на додану вартість Семейная ипотека с государственной поддержкой. Льготная ипотечная программа со ставкой 6% для семей с детьми
Семейная ипотека с государственной поддержкой. Льготная ипотечная программа со ставкой 6% для семей с детьми Методика исчисления налога на прибыль организаций и порядок заполнения налоговой декларации и налоговых расчетов
Методика исчисления налога на прибыль организаций и порядок заполнения налоговой декларации и налоговых расчетов Понятие о счетах бухгалтерского учета и их строение
Понятие о счетах бухгалтерского учета и их строение Ринок кредитних ресурсів. Роль банків
Ринок кредитних ресурсів. Роль банків Банковские карты, кэшбэк, денежные переводы
Банковские карты, кэшбэк, денежные переводы