Содержание
- 2. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the
- 3. Urea’s names Urea has a lot name. For example: Carbamide, Carbony ldiamide and Carbonyldiamine.
- 4. More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release
- 5. Many soil bacteria possess the enzyme urease, which catalyzes conversion of urea to ammonia (NH3) or
- 7. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and
is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules (NH3) with a carbon dioxide (CO2) molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen and is an important raw material for the chemical industry.
Слайд 3
Urea’s names
Urea has a lot name. For example: Carbamide,
Carbony ldiamide and
Urea’s names
Urea has a lot name. For example: Carbamide, Carbony ldiamide and
Carbonyldiamine.
Слайд 4
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined
for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer.[5] Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has the lowest transportation costs per unit of nitrogen nutrient.
Слайд 5
Many soil bacteria possess the enzyme urease, which catalyzes conversion of urea to ammonia (NH3) or ammonium ion (NH4+) and
Many soil bacteria possess the enzyme urease, which catalyzes conversion of urea to ammonia (NH3) or ammonium ion (NH4+) and
bicarbonate ion (HCO3−).




 Решение задач на нахождение молекулярной формулы газообразного алкана
Решение задач на нахождение молекулярной формулы газообразного алкана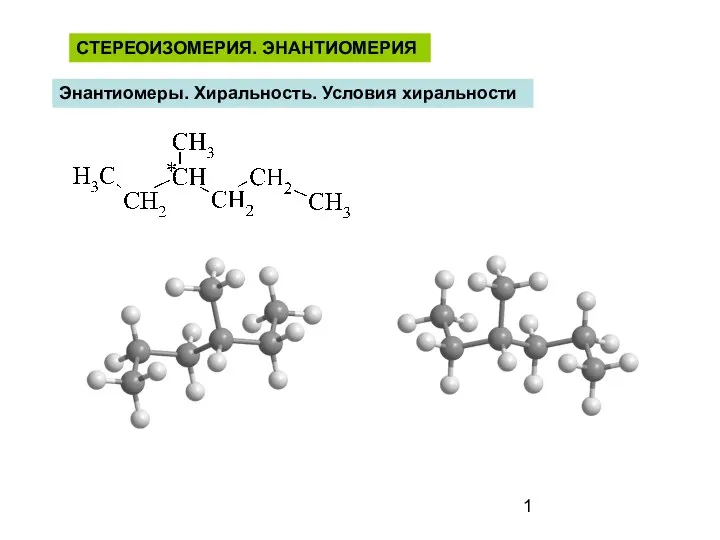 Стереоизомерия. Энантиомерия. Энантиомеры. Хиральность. Условия хиральности
Стереоизомерия. Энантиомерия. Энантиомеры. Хиральность. Условия хиральности Кислородсодержащие органические соединения
Кислородсодержащие органические соединения Кинетика химических реакций. Основные понятия и законы химической кинетики
Кинетика химических реакций. Основные понятия и законы химической кинетики Кристаллы. Виды
Кристаллы. Виды Фуллерен, его свойства, производство и применение
Фуллерен, его свойства, производство и применение Алканы. Строение алканов
Алканы. Строение алканов 6-я группа элементов. 9 класс
6-я группа элементов. 9 класс Презентация Углерод Carboneum происходит от лат. carbo — уголь.
Презентация Углерод Carboneum происходит от лат. carbo — уголь. Интересные свойства редких металлов
Интересные свойства редких металлов Химические реакции. по фазовому составу
Химические реакции. по фазовому составу Совместимость электродных материалов в новой электрохимической системе Li4Ti5O12/Li3V2(PO4)3 с традиционным электролитом для
Совместимость электродных материалов в новой электрохимической системе Li4Ti5O12/Li3V2(PO4)3 с традиционным электролитом для Рекомендации по подготовке учащихся к выполнению заданий различного уровня сложности ЕГЭ по химии
Рекомендации по подготовке учащихся к выполнению заданий различного уровня сложности ЕГЭ по химии Гидролиз
Гидролиз Презентация по Химии "Діопсид силікати" - скачать смотреть
Презентация по Химии "Діопсид силікати" - скачать смотреть  Дисперсные системы: общая характеристика и классификация
Дисперсные системы: общая характеристика и классификация Алюминий – металл будущего
Алюминий – металл будущего Анализ качества неорганических лекарственных средств количественно определяемых методами редоксиметрии
Анализ качества неорганических лекарственных средств количественно определяемых методами редоксиметрии Химические реакции. Закон сохранения массы веществ
Химические реакции. Закон сохранения массы веществ Видалення забруднень із поверхні тканини Виконали: Сидорова Анастасія Труба Альона
Видалення забруднень із поверхні тканини Виконали: Сидорова Анастасія Труба Альона  Общая характеристика металлов. Металлическая связь
Общая характеристика металлов. Металлическая связь Обобщение по теме: «Азот»( урок-сказка) Тайны царства Азота
Обобщение по теме: «Азот»( урок-сказка) Тайны царства Азота Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по химии экологическая химия
Аттестационная работа. Программа элективного курса по химии экологическая химия Железо и его соединения
Железо и его соединения Нітрати – токсичні речовини
Нітрати – токсичні речовини  Неорганическая химия 8 класс г. Азов школа №9 учитель: Карасёв Евгений Владимирович
Неорганическая химия 8 класс г. Азов школа №9 учитель: Карасёв Евгений Владимирович  Дисперсные системы. Свойства коллоидных растворов
Дисперсные системы. Свойства коллоидных растворов Строение твердых и жидких металлов. Зональная ликвация
Строение твердых и жидких металлов. Зональная ликвация