Содержание
- 2. Lecture Objectives Introduce the idea of and rationale for Bayesian perspective and Bayesian VARs Understand the
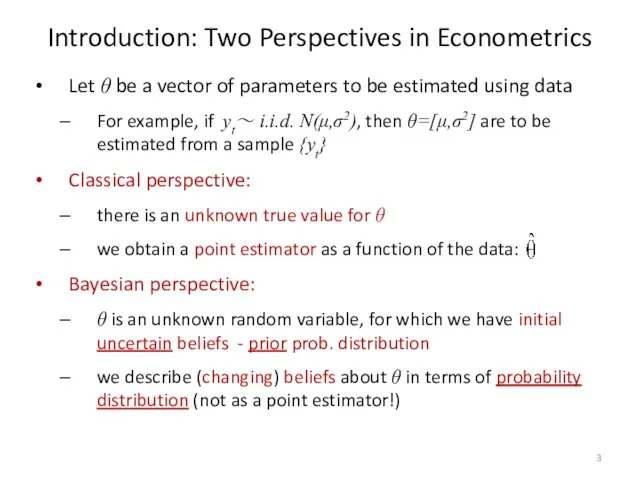
- 3. Introduction: Two Perspectives in Econometrics Let θ be a vector of parameters to be estimated using
- 4. Outline Why a Bayesian Approach to VARs? Brief Introduction to Bayesian Econometrics Analytical Examples Estimating a
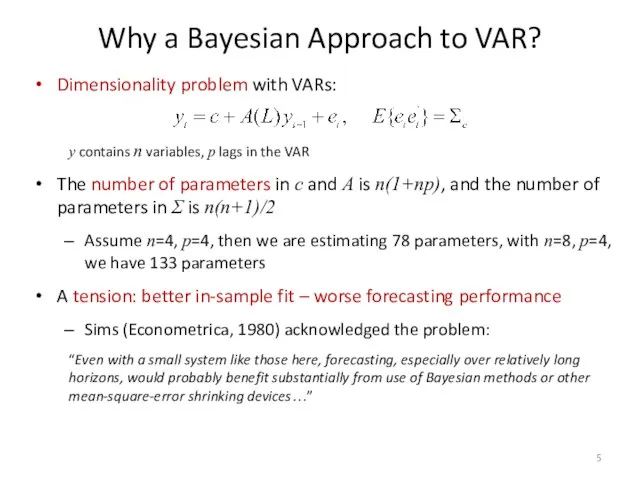
- 5. Why a Bayesian Approach to VAR? Dimensionality problem with VARs: y contains n variables, p lags
- 6. Usually, only a fraction of estimated coefficients are statistically significant parsimonious modeling should be favored What
- 7. Combining information: prior and posterior Bayesian coefficient estimates combine information in the prior with evidence from
- 8. Shrinkage There are many approaches to reducing over-parameterization in VARs A common idea is shrinkage Incorporating
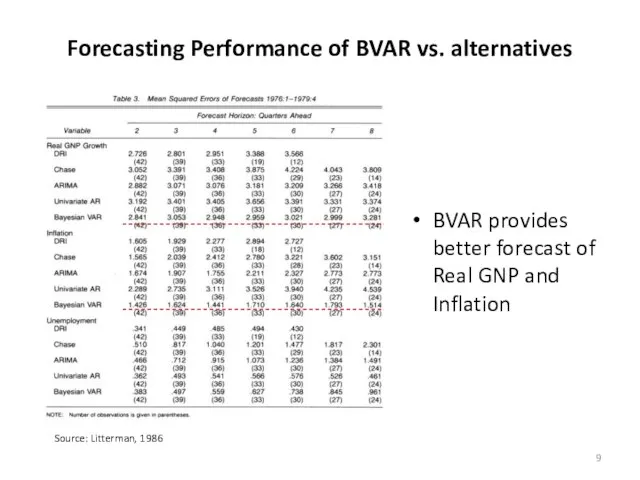
- 9. Forecasting Performance of BVAR vs. alternatives Source: Litterman, 1986 BVAR provides better forecast of Real GNP
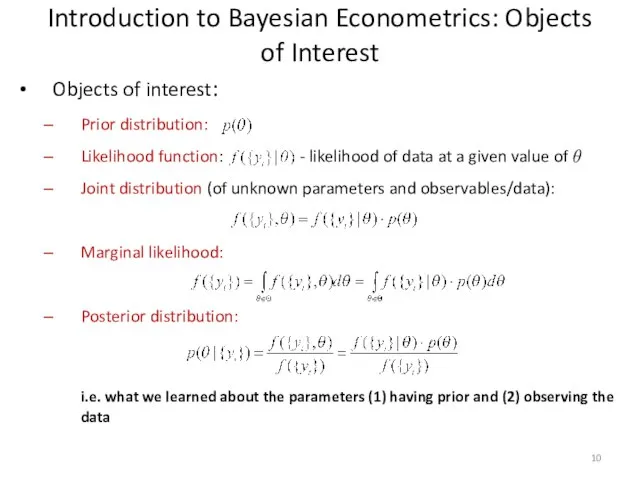
- 10. Introduction to Bayesian Econometrics: Objects of Interest Objects of interest: Prior distribution: Likelihood function: - likelihood
- 11. Bayesian Econometrics: Objects of Interest (2) The marginal likelihood… …is independent of the parameters of the
- 12. Bayesian Econometrics: maximizing criterion For practical purposes, it is useful to focus on the criterion: Traditionally,
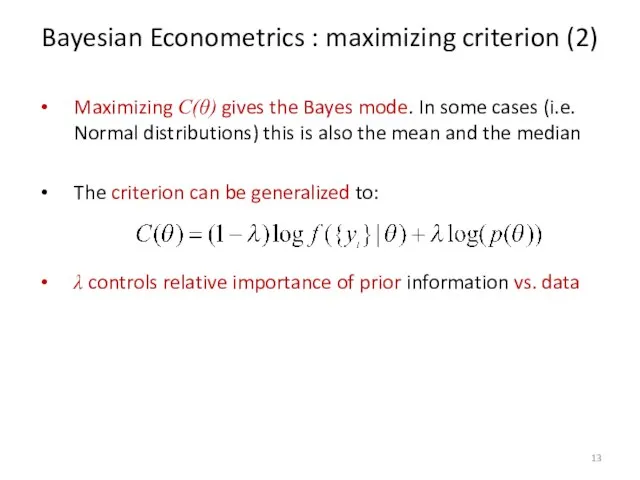
- 13. Bayesian Econometrics : maximizing criterion (2) Maximizing C(θ) gives the Bayes mode. In some cases (i.e.
- 14. Analytical Examples Let’s work on some analytical examples: Sample mean Linear regression model
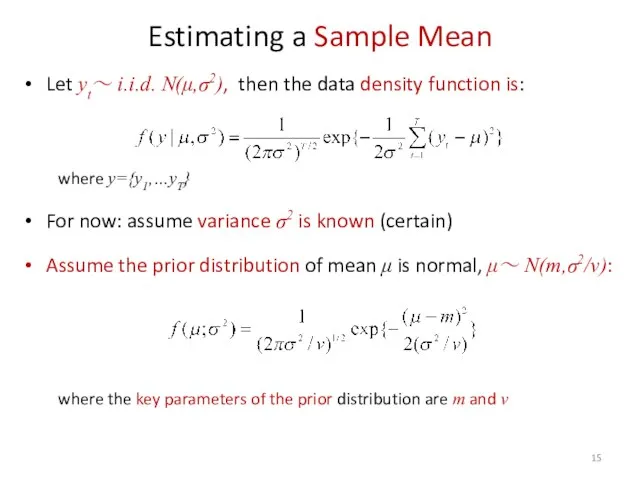
- 15. Estimating a Sample Mean Let yt~ i.i.d. N(μ,σ2), then the data density function is: where y={y1,…yT}
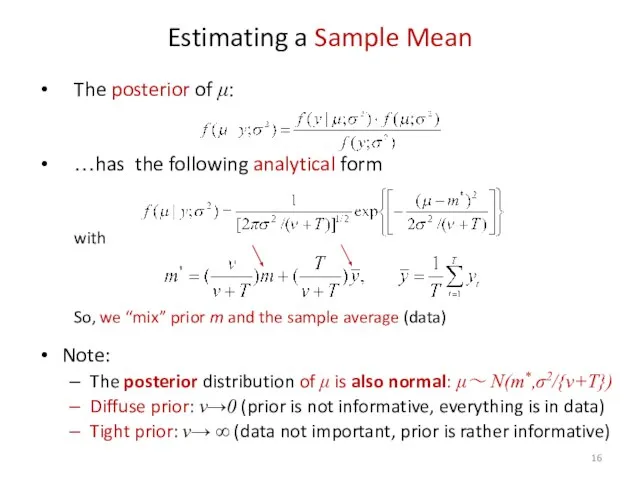
- 16. Estimating a Sample Mean The posterior of μ: …has the following analytical form with So, we
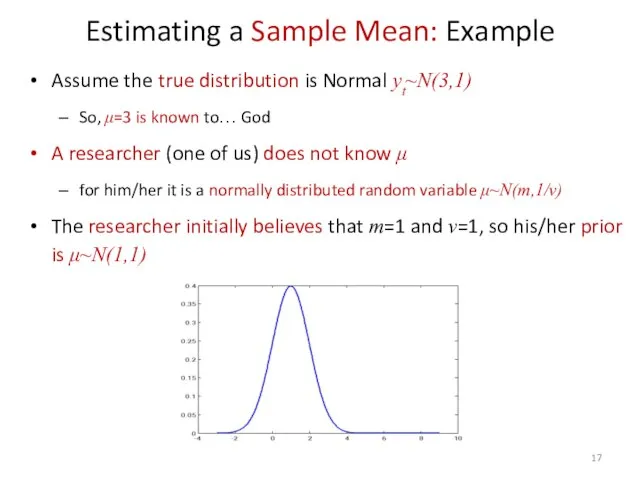
- 17. Estimating a Sample Mean: Example Assume the true distribution is Normal yt~N(3,1) So, μ=3 is known
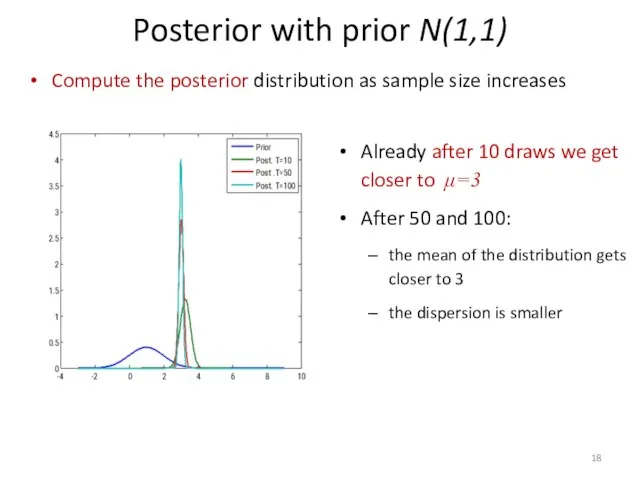
- 18. Compute the posterior distribution as sample size increases Posterior with prior N(1,1) Already after 10 draws
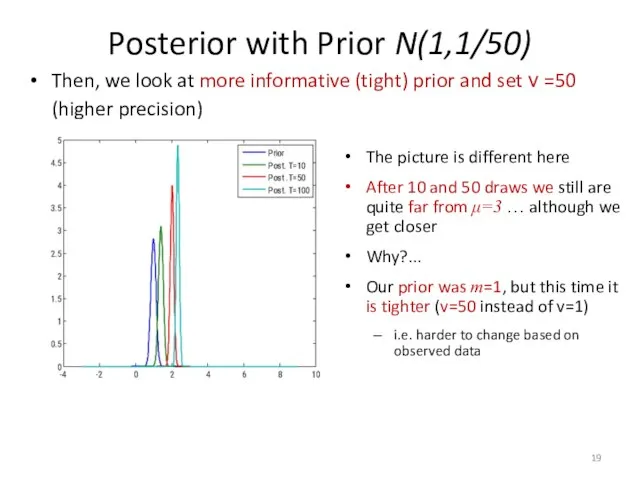
- 19. Then, we look at more informative (tight) prior and set ν =50 (higher precision) Posterior with
- 20. Examples: Regression Model I Linear Regression model: where ut~ i.i.d. N(0,σ2) Assume: β is random and
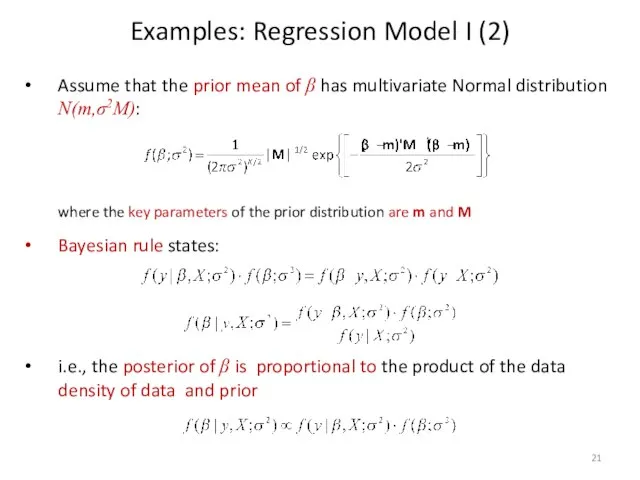
- 21. Assume that the prior mean of β has multivariate Normal distribution N(m,σ2M): where the key parameters
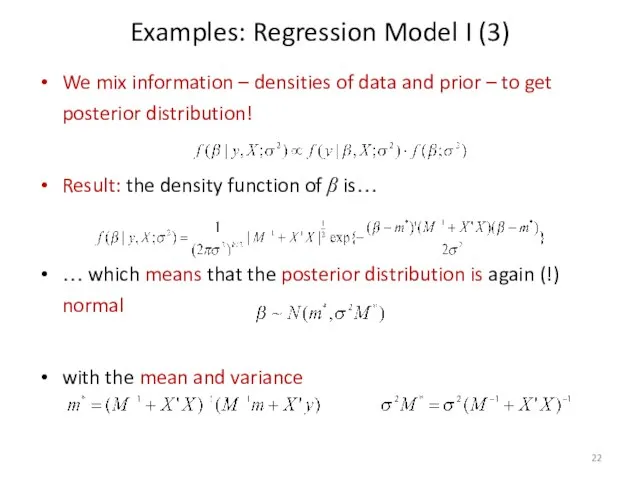
- 22. Examples: Regression Model I (3) We mix information – densities of data and prior – to
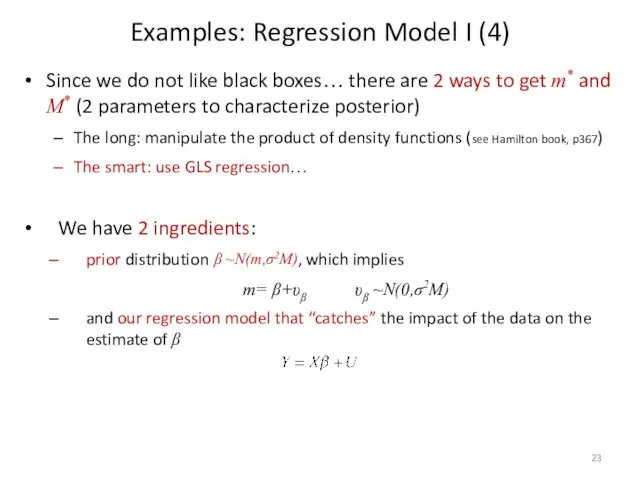
- 23. Since we do not like black boxes… there are 2 ways to get m* and M*
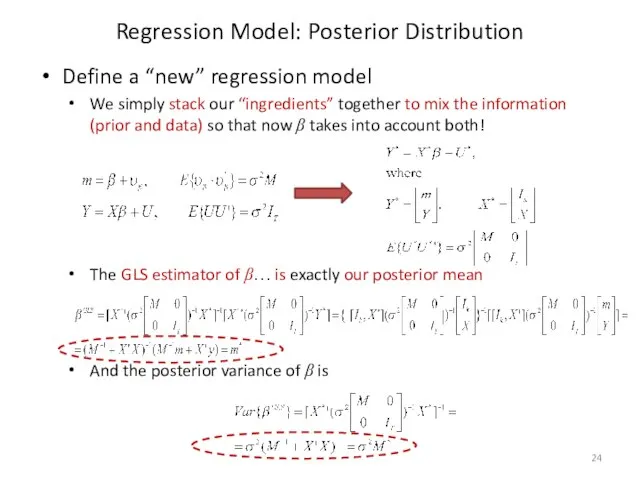
- 24. Define a “new” regression model We simply stack our “ingredients” together to mix the information (prior
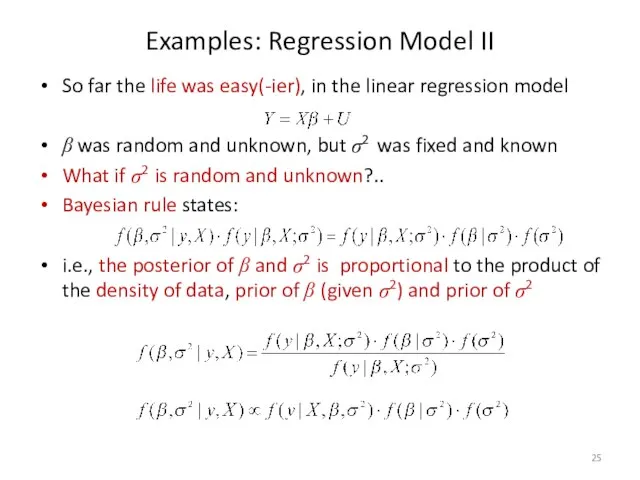
- 25. Examples: Regression Model II So far the life was easy(-ier), in the linear regression model β
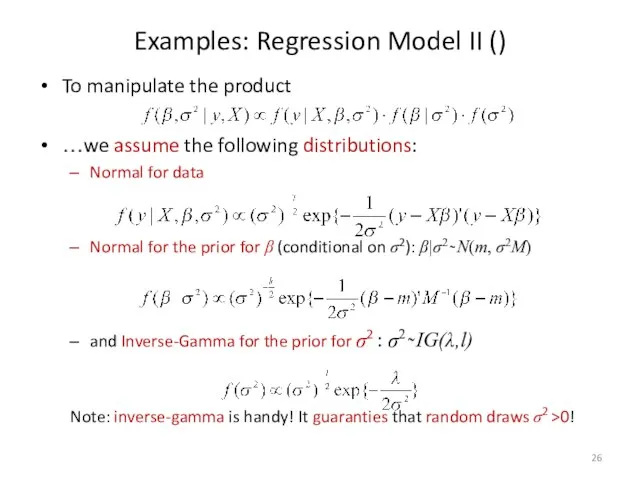
- 26. Examples: Regression Model II () To manipulate the product …we assume the following distributions: Normal for
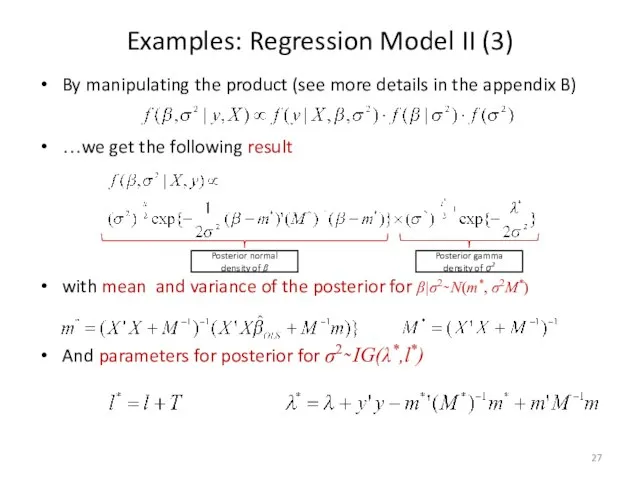
- 27. Examples: Regression Model II (3) By manipulating the product (see more details in the appendix B)
- 28. Priors: summary In the above examples we dealt with 2 types of prior distributions of our
- 29. Bayesian VARs Linear Regression examples will help us to deal with our main object – Bayesian
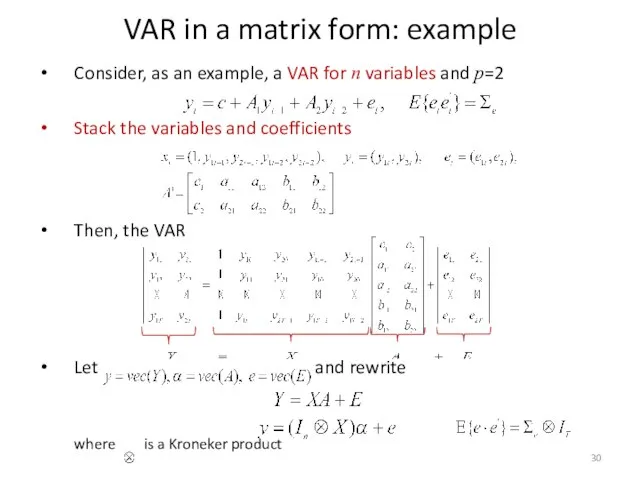
- 30. VAR in a matrix form: example Consider, as an example, a VAR for n variables and
- 31. How to Estimate a BVAR: Case 1 Prior Consider Case 1 prior for a VAR: coefficients
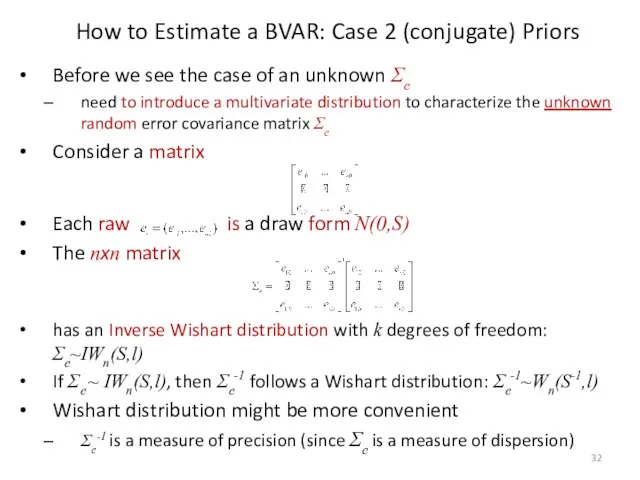
- 32. Before we see the case of an unknown Σe need to introduce a multivariate distribution to
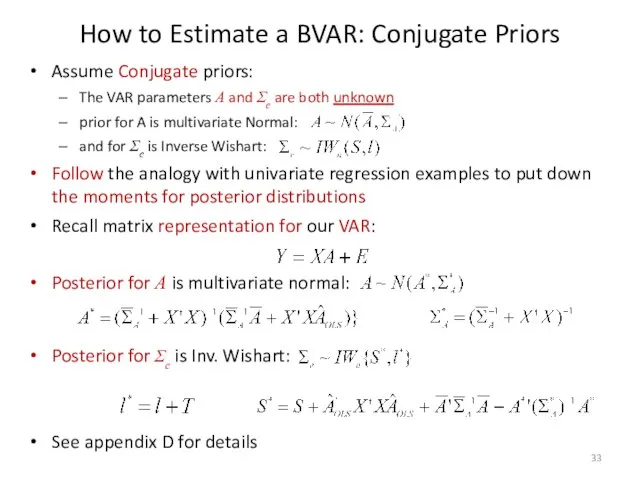
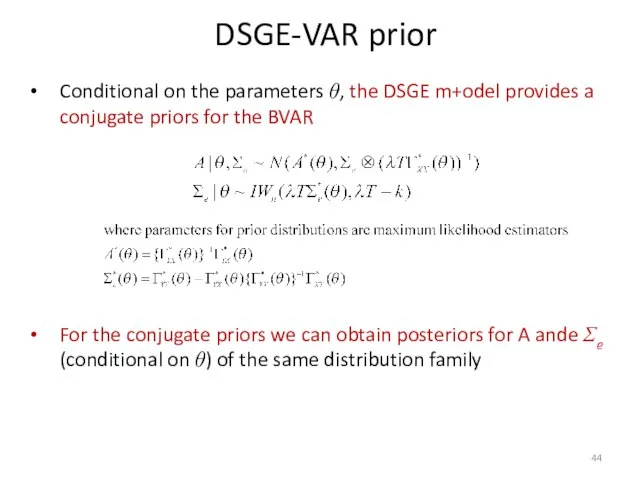
- 33. How to Estimate a BVAR: Conjugate Priors Assume Conjugate priors: The VAR parameters A and Σe
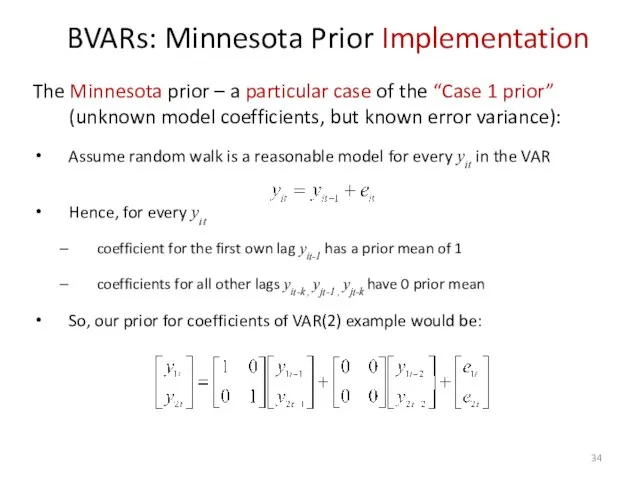
- 34. BVARs: Minnesota Prior Implementation The Minnesota prior – a particular case of the “Case 1 prior”
- 35. The Minnesota prior The prior variance for the coefficient of lag k in equation i for
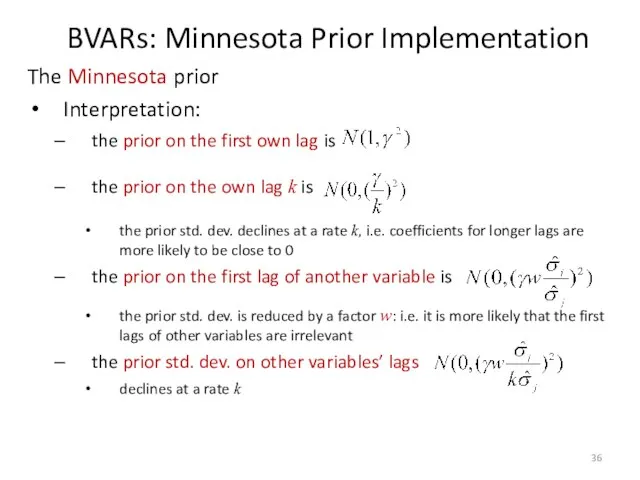
- 36. The Minnesota prior Interpretation: the prior on the first own lag is the prior on the
- 37. BVARs: Minnesota Prior Implementation
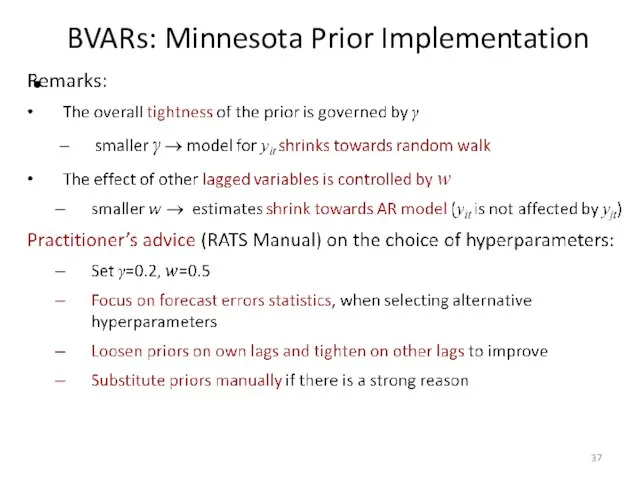
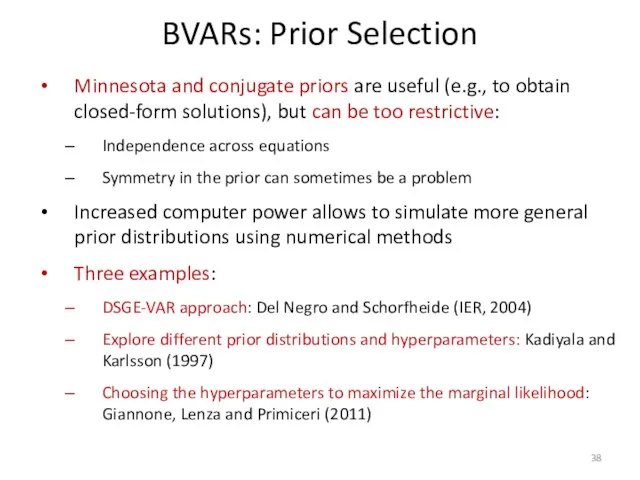
- 38. BVARs: Prior Selection Minnesota and conjugate priors are useful (e.g., to obtain closed-form solutions), but can
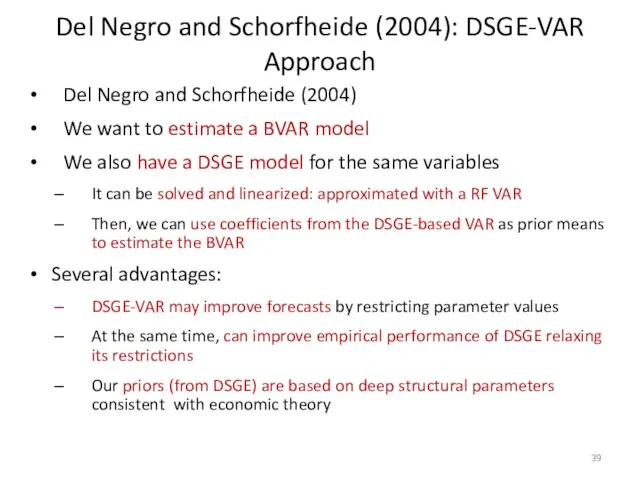
- 39. Del Negro and Schorfheide (2004): DSGE-VAR Approach Del Negro and Schorfheide (2004) We want to estimate
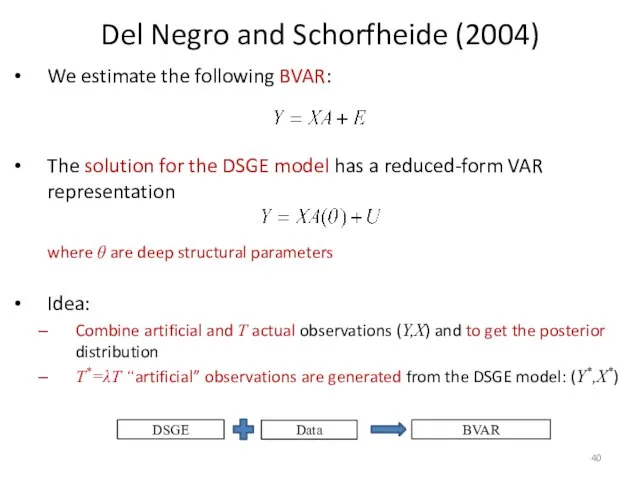
- 40. Del Negro and Schorfheide (2004) We estimate the following BVAR: The solution for the DSGE model
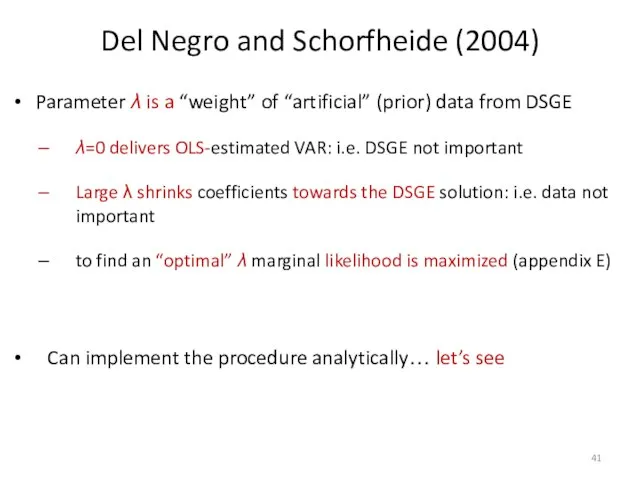
- 41. Del Negro and Schorfheide (2004) Parameter λ is a “weight” of “artificial” (prior) data from DSGE
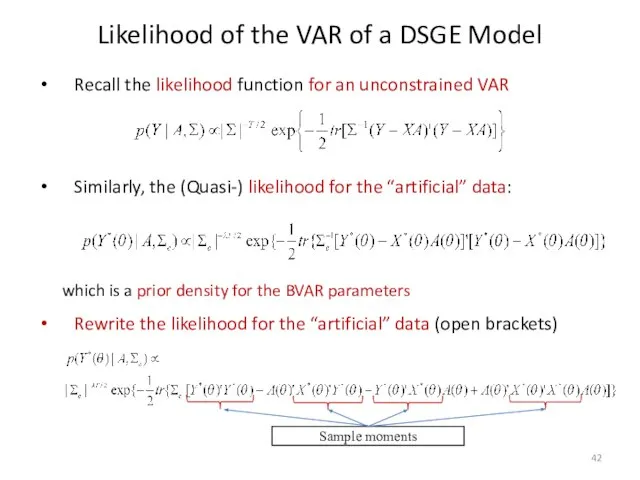
- 42. Likelihood of the VAR of a DSGE Model Recall the likelihood function for an unconstrained VAR
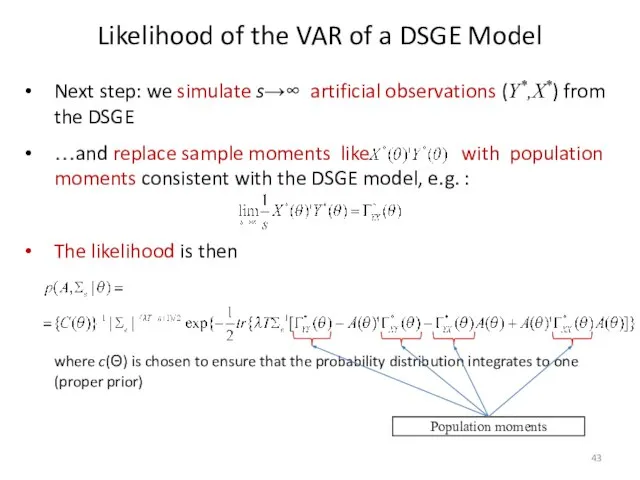
- 43. Next step: we simulate s→∞ artificial observations (Y*,X*) from the DSGE …and replace sample moments like
- 44. Conditional on the parameters θ, the DSGE m+odel provides a conjugate priors for the BVAR For
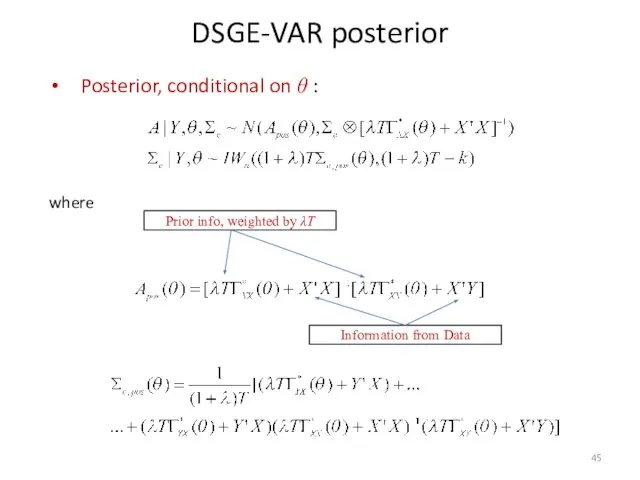
- 45. DSGE-VAR posterior Posterior, conditional on θ : where Prior info, weighted by λT Information from Data
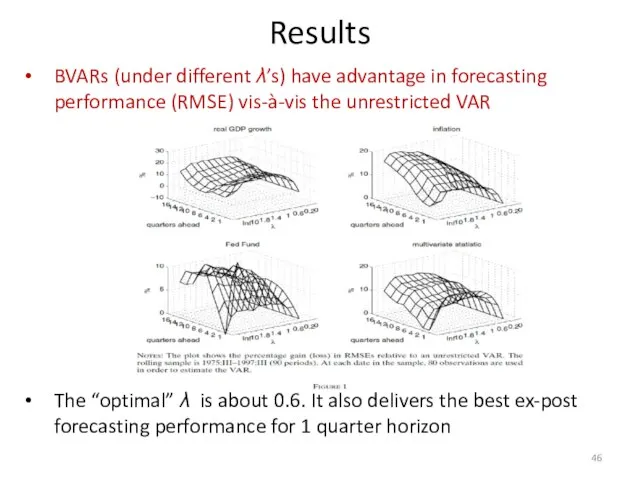
- 46. BVARs (under different λ’s) have advantage in forecasting performance (RMSE) vis-à-vis the unrestricted VAR The “optimal”
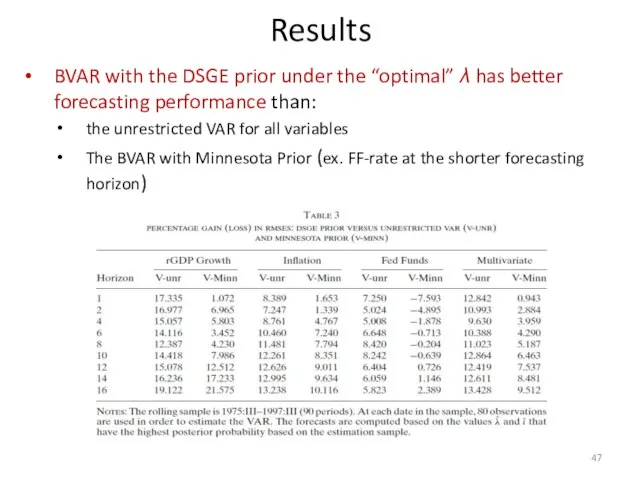
- 47. BVAR with the DSGE prior under the “optimal” λ has better forecasting performance than: the unrestricted
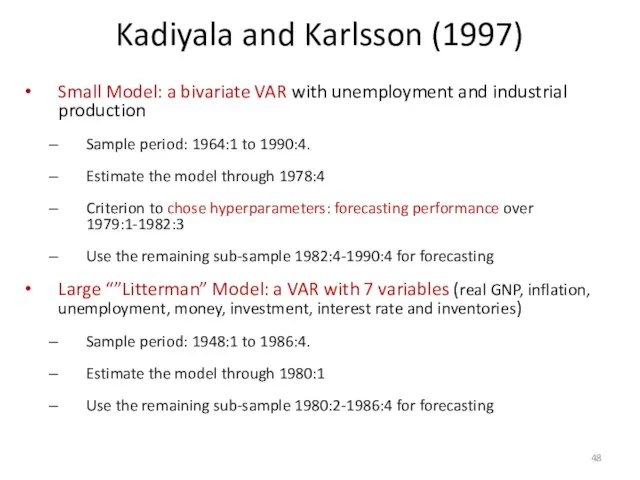
- 48. Kadiyala and Karlsson (1997) Small Model: a bivariate VAR with unemployment and industrial production Sample period:
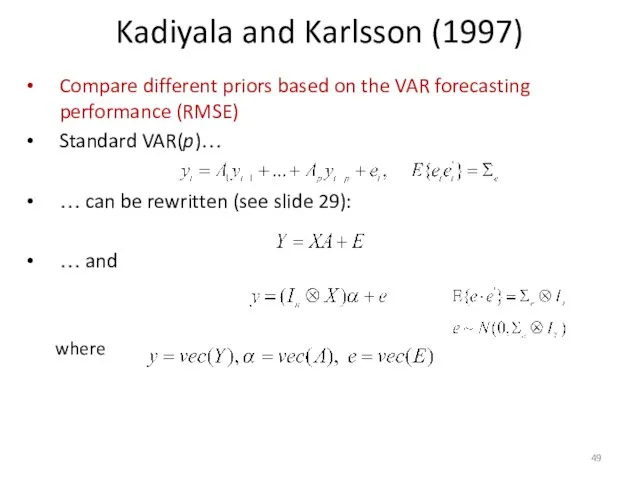
- 49. Kadiyala and Karlsson (1997) Compare different priors based on the VAR forecasting performance (RMSE) Standard VAR(p)…
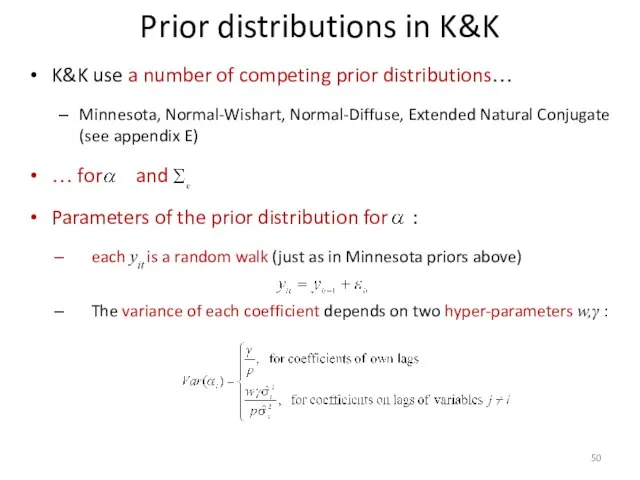
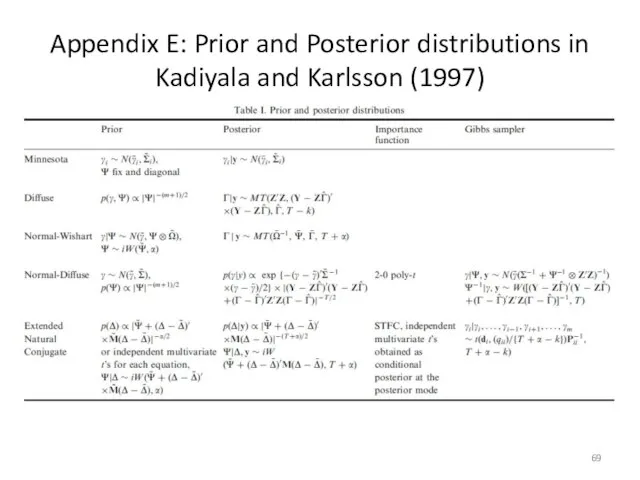
- 50. Prior distributions in K&K K&K use a number of competing prior distributions… Minnesota, Normal-Wishart, Normal-Diffuse, Extended
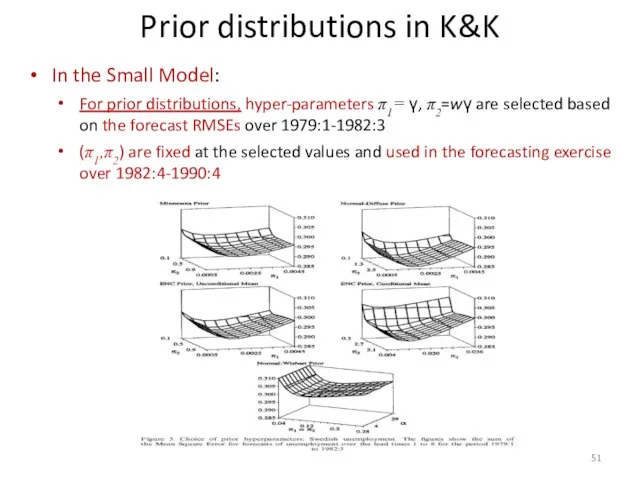
- 51. Prior distributions in K&K In the Small Model: For prior distributions, hyper-parameters π1= γ, π2=wγ are
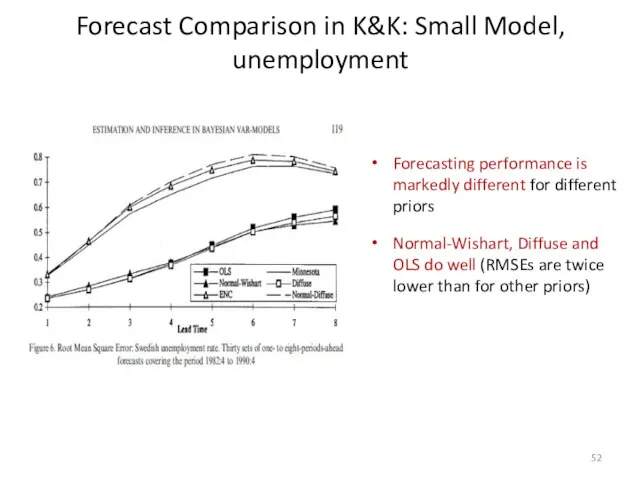
- 52. Forecast Comparison in K&K: Small Model, unemployment Forecasting performance is markedly different for different priors Normal-Wishart,
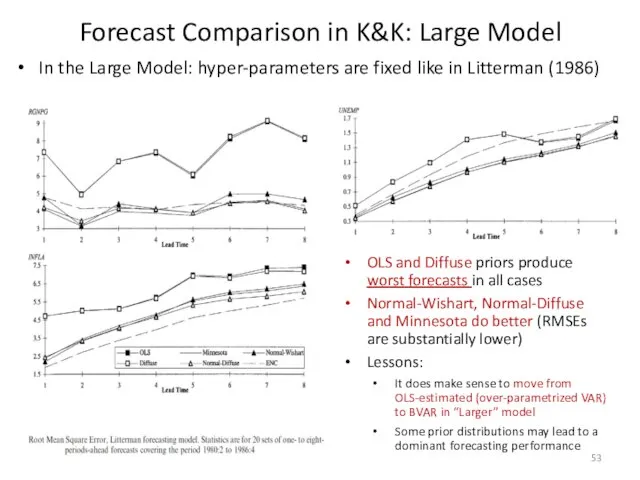
- 53. Forecast Comparison in K&K: Large Model OLS and Diffuse priors produce worst forecasts in all cases
- 54. Giannone, Lenza and Primiceri (2011) Use three VARs to compare forecasting performance Small VAR: GDP, GDP
- 55. Giannone, Lenza and Primiceri (2011) The marginal likelihood is obtained by integrating out the parameters of
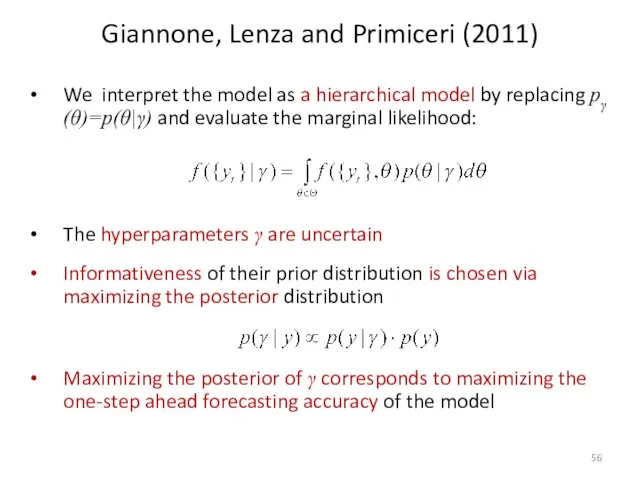
- 56. Giannone, Lenza and Primiceri (2011) We interpret the model as a hierarchical model by replacing pγ(θ)=p(θ|γ)
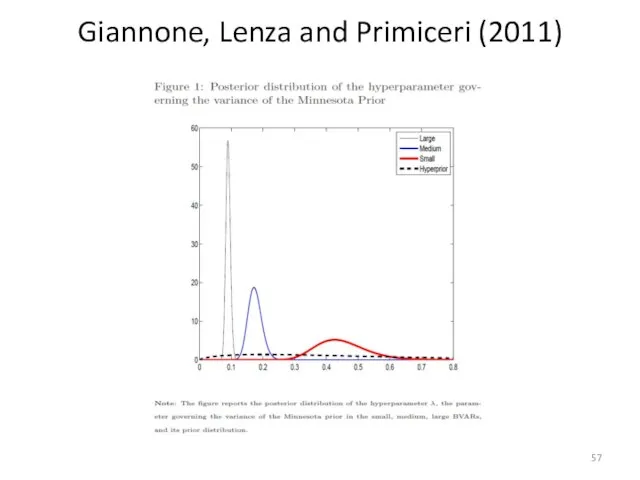
- 57. Giannone, Lenza and Primiceri (2011)
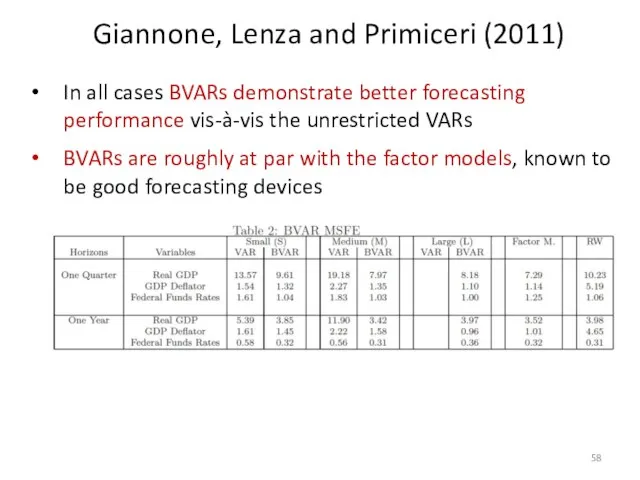
- 58. In all cases BVARs demonstrate better forecasting performance vis-à-vis the unrestricted VARs BVARs are roughly at
- 59. Conclusions BVARs is a useful tool to improve forecasts This is not a “black box” posterior
- 60. Thank You!
- 61. Appendix A: Remarks about the marginal likelihood Remarks about the marginal likelihood: If we have M1,….MN
- 62. Appendix A: Remarks about the marginal likelihood Remarks about the marginal likelihood: Predict the first observation
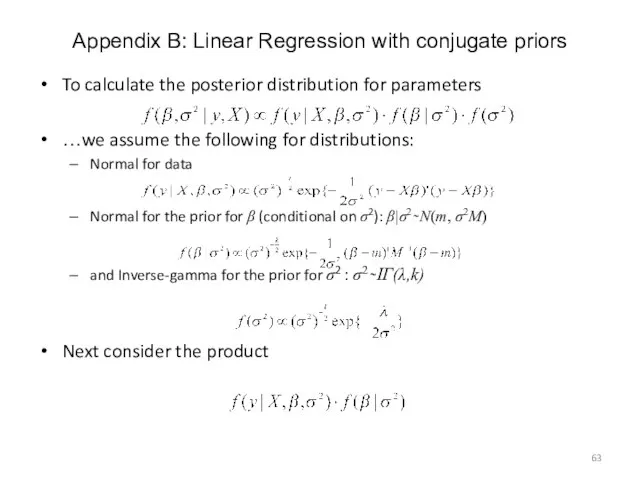
- 63. Appendix B: Linear Regression with conjugate priors To calculate the posterior distribution for parameters …we assume
- 64. Rearranging the expressions under the exponents we have the following: where Further denote … and rewrite
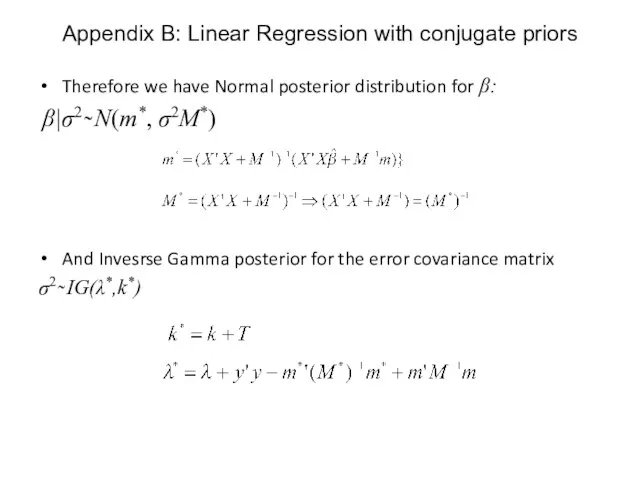
- 65. Therefore we have Normal posterior distribution for β: β|σ2 ̴ N(m*, σ2M*) And Invesrse Gamma posterior
- 66. Appendix C: How to Estimate a BVAR, Case 1 prior Use GLS estimator for the regression
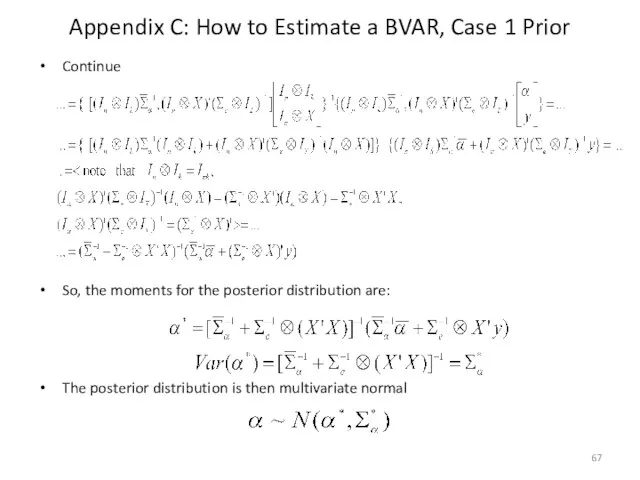
- 67. Appendix C: How to Estimate a BVAR, Case 1 Prior Continue So, the moments for the
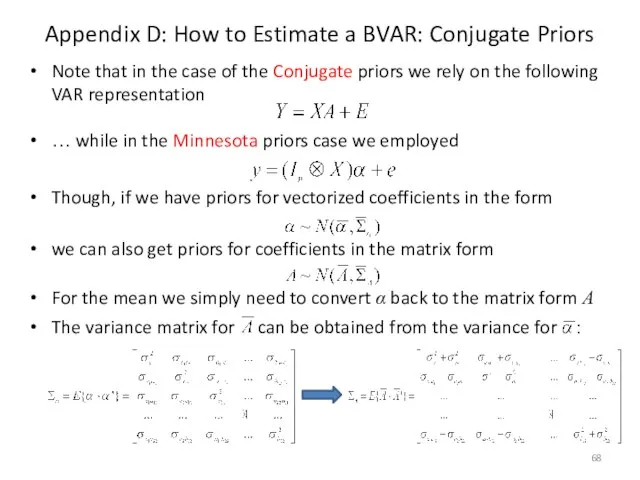
- 68. Appendix D: How to Estimate a BVAR: Conjugate Priors Note that in the case of the
- 69. Appendix E: Prior and Posterior distributions in Kadiyala and Karlsson (1997)
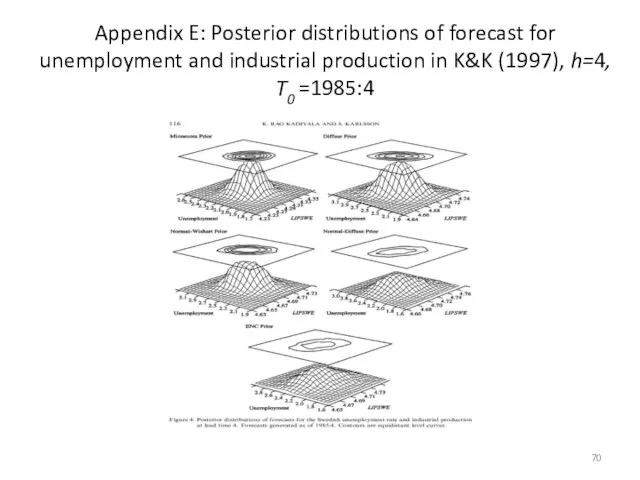
- 70. Appendix E: Posterior distributions of forecast for unemployment and industrial production in K&K (1997), h=4, T0
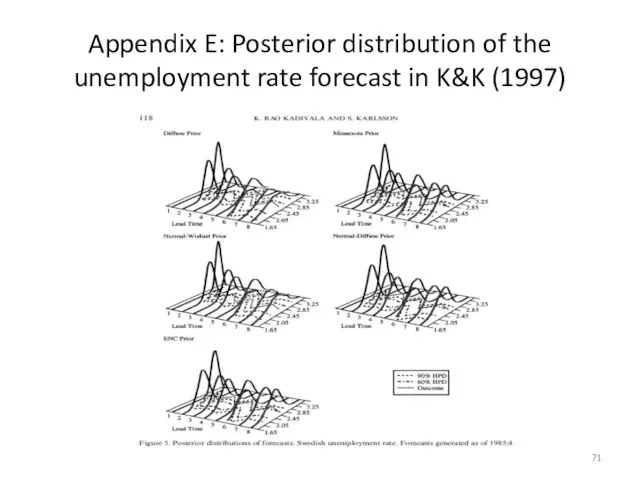
- 71. Appendix E: Posterior distribution of the unemployment rate forecast in K&K (1997)
- 73. Скачать презентацию




















 Упрощение выражений. 5 класс
Упрощение выражений. 5 класс Обыкновенные дроби. Игра "Счастливый случай"
Обыкновенные дроби. Игра "Счастливый случай" Математические основы построения экспертной модели при расплывчатости границ между смежными рангами пожара
Математические основы построения экспертной модели при расплывчатости границ между смежными рангами пожара Мультимедийное пособие «Функция»
Мультимедийное пособие «Функция» Исторические комбинаторные задачи. 6 - 8 классы
Исторические комбинаторные задачи. 6 - 8 классы Математика XIX ст. Жан Батист Жозеф Фур'є
Математика XIX ст. Жан Батист Жозеф Фур'є Теорема Пифагора
Теорема Пифагора Понятие модели. Способы представления моделей. (Лекция 4)
Понятие модели. Способы представления моделей. (Лекция 4) Состав чисел в приделах 10. Закрепление
Состав чисел в приделах 10. Закрепление Площадь и объем
Площадь и объем Сочетания. Формирование умений и навыков
Сочетания. Формирование умений и навыков Равные выражения. Сравниваем выражения
Равные выражения. Сравниваем выражения Угол между векторами. Скалярное произведение векторов
Угол между векторами. Скалярное произведение векторов Задачи на вероятность
Задачи на вероятность Примеры решения комбинаторных задач Примеры решения комбинаторных задач
Примеры решения комбинаторных задач Примеры решения комбинаторных задач  Функция y = x2 и её график
Функция y = x2 и её график Призма
Призма Преобразование графика функции
Преобразование графика функции חשבון רוקחי 4 תרגילים+תשובות
חשבון רוקחי 4 תרגילים+תשובות Различные способы решения систем двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными
Различные способы решения систем двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными Угол между плоскостями
Угол между плоскостями Число и цифра 4
Число и цифра 4 Деление обыкновенных дробей Математика, 6 класс
Деление обыкновенных дробей Математика, 6 класс Математика 4 класс Морозова Валентина Анатольевна учитель начальных классов МОУ Шевыряловская основная общеобразовательная шк
Математика 4 класс Морозова Валентина Анатольевна учитель начальных классов МОУ Шевыряловская основная общеобразовательная шк Прямая. Отрезок. Луч
Прямая. Отрезок. Луч Интерактивные тренинги по математике для подготовки к ЕГЭ
Интерактивные тренинги по математике для подготовки к ЕГЭ Презентация на тему Сравнение предметов Математика 1 класс
Презентация на тему Сравнение предметов Математика 1 класс Презентация по математике "Юным умникам и умницам" - скачать
Презентация по математике "Юным умникам и умницам" - скачать