Содержание
- 2. Chapter 2
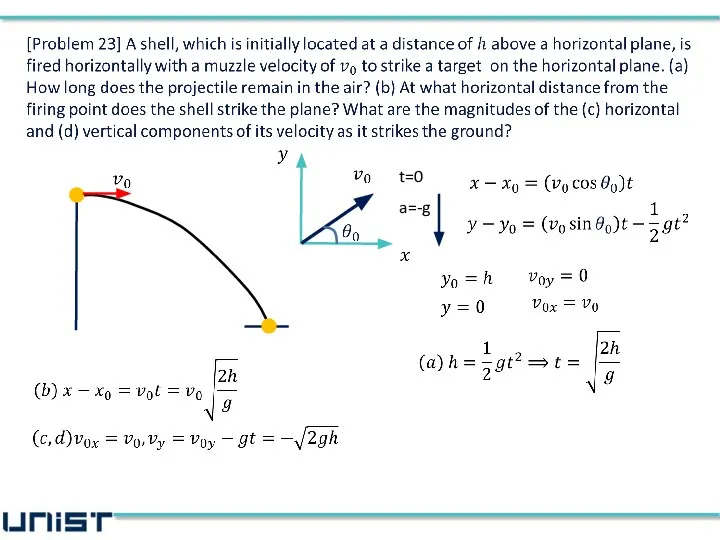
- 3. [Problem 29] A car moving at a constant velocity of 46 m/s passes a traffic cop
- 4. [Problem 29] A car moving at a constant velocity of 46 m/s passes a traffic cop
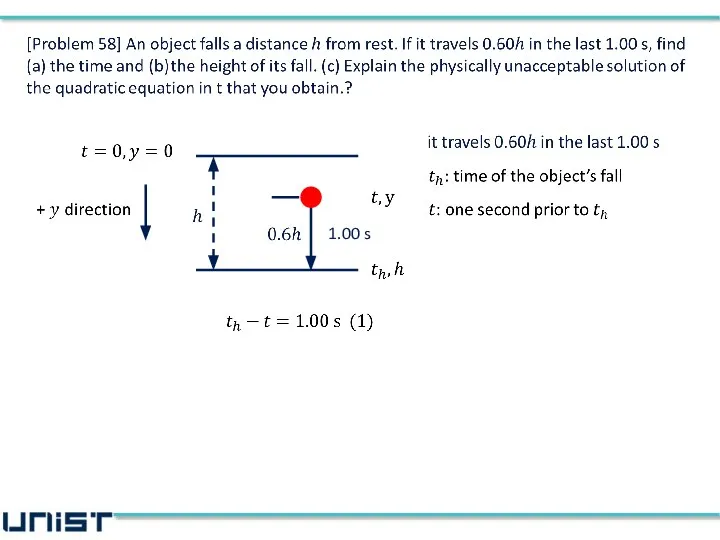
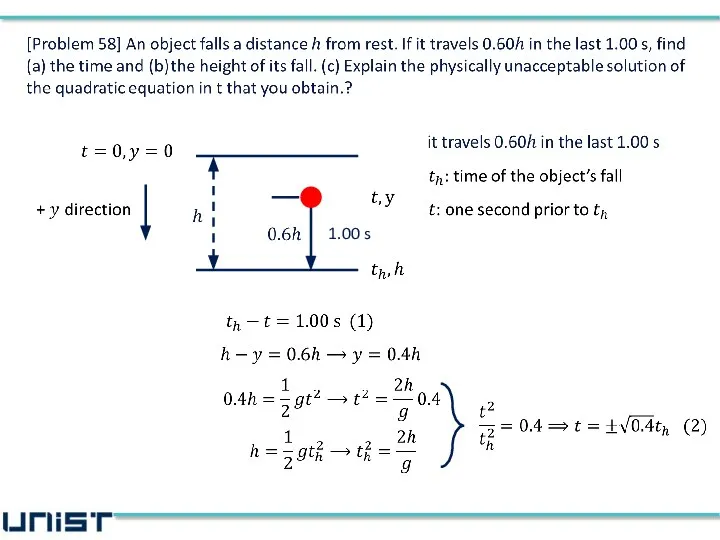
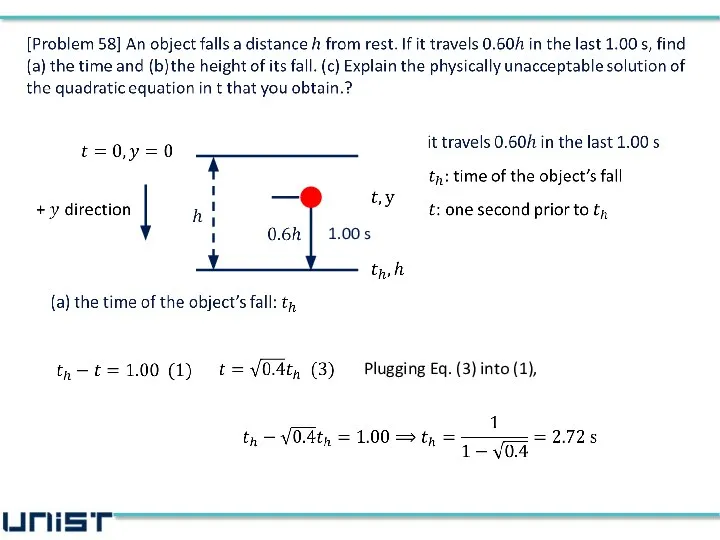
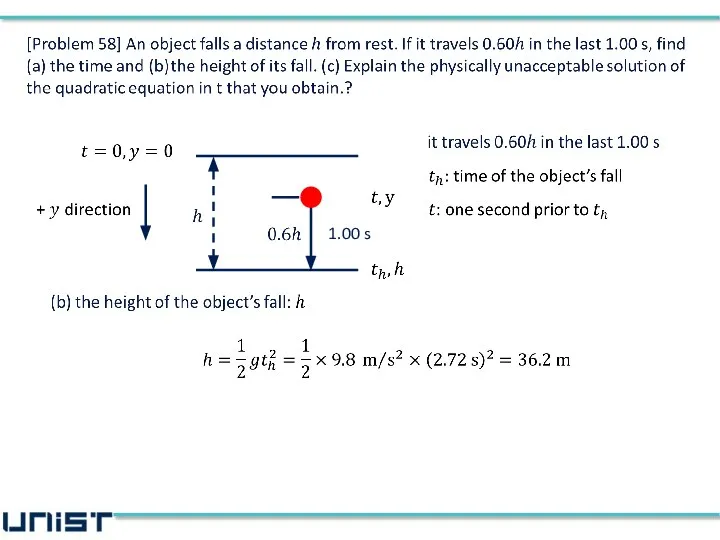
- 5. [Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If it travels 0.60h in the
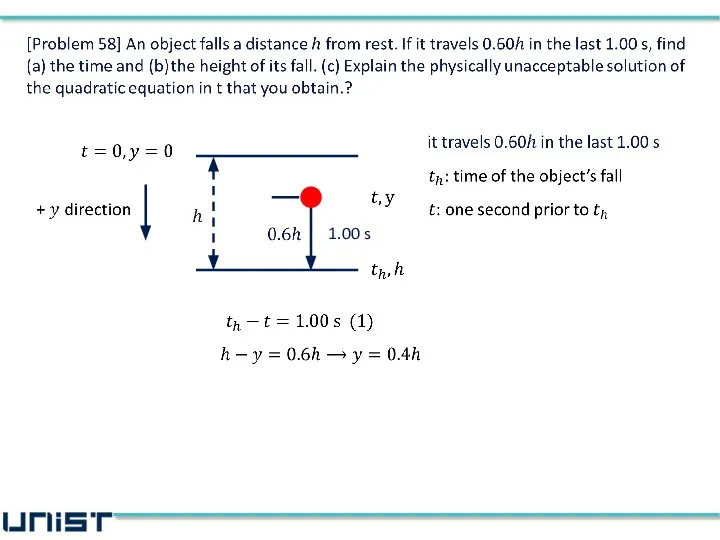
- 6. [Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If it travels 0.60h in the
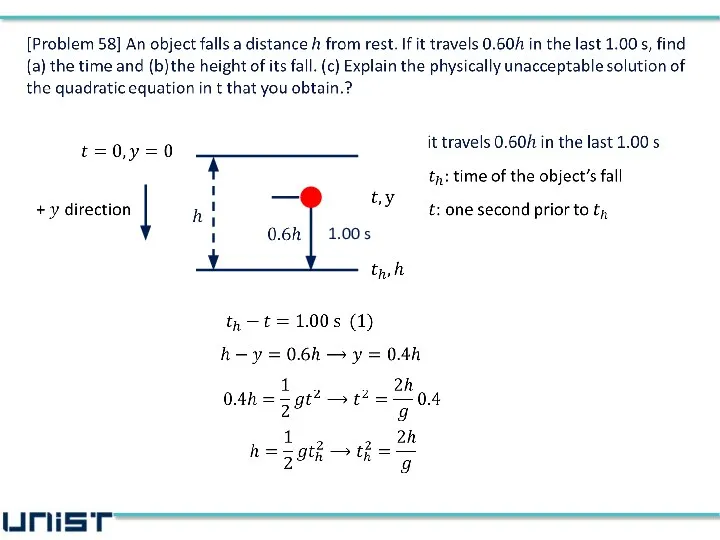
- 7. [Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If it travels 0.60h in the
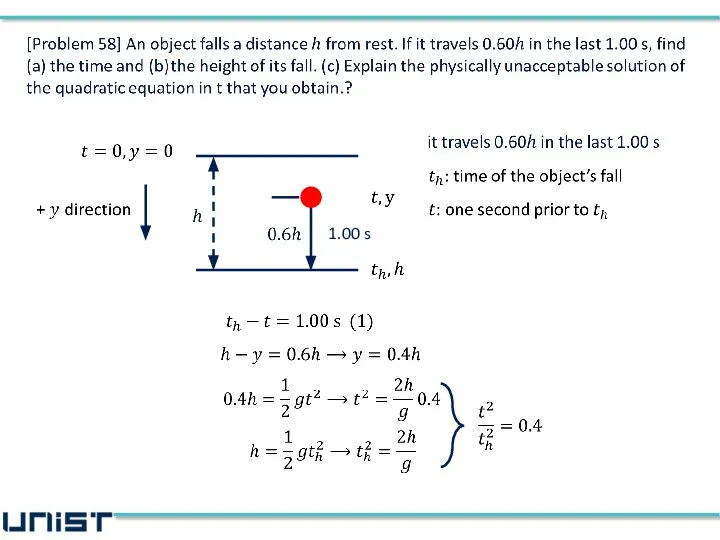
- 8. [Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If it travels 0.60h in the
- 9. [Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If it travels 0.60h in the
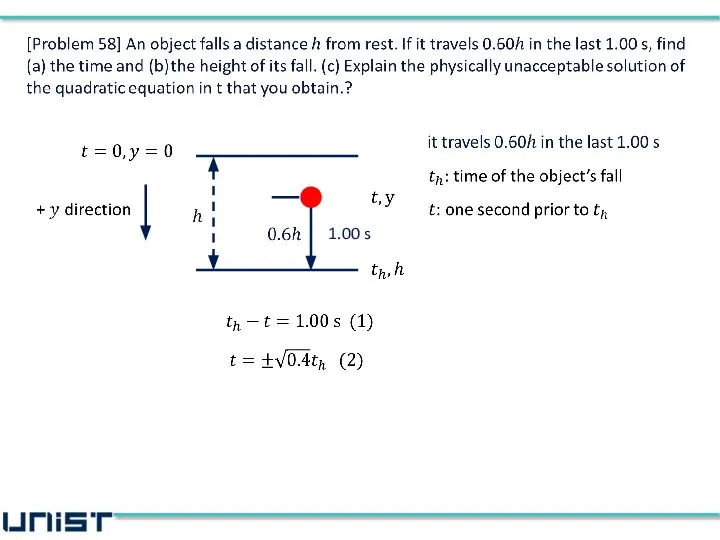
- 10. 1.00 s
- 11. 1.00 s
- 12. 1.00 s
- 13. 1.00 s
- 14. 1.00 s
- 15. 1.00 s
- 16. 1.00 s
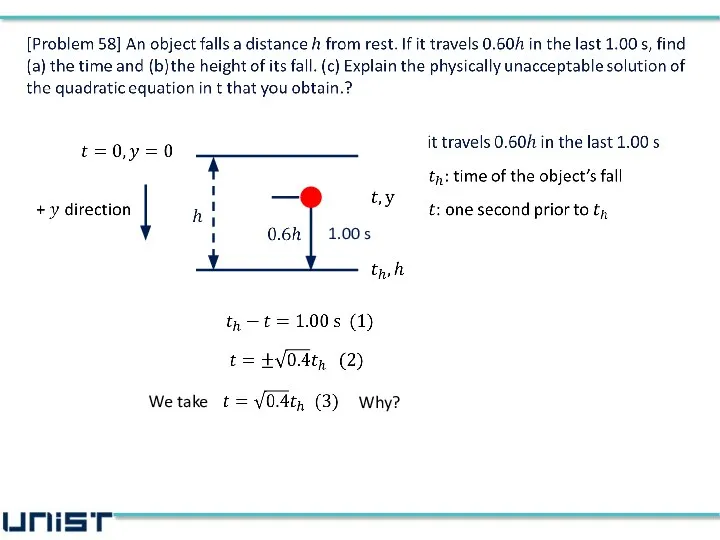
- 17. We take Why? 1.00 s
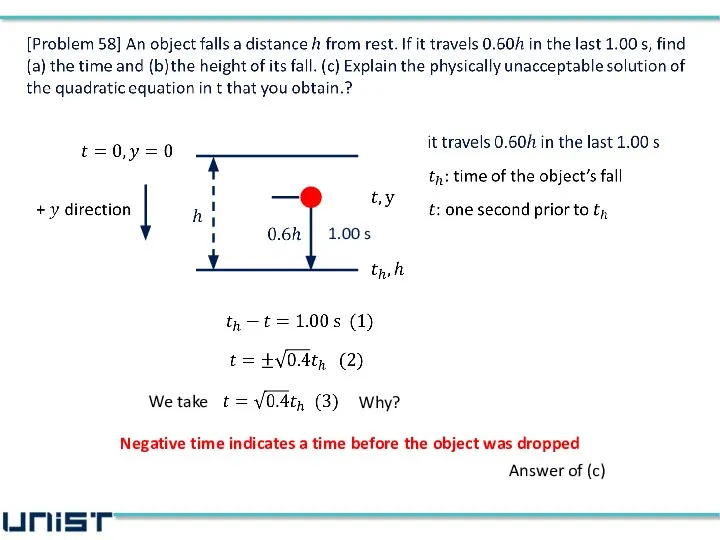
- 18. We take Why? Negative time indicates a time before the object was dropped Answer of (c)
- 19. Plugging Eq. (3) into (1), 1.00 s
- 20. 1.00 s
- 21. Chapter 4
- 24. Chapter 5
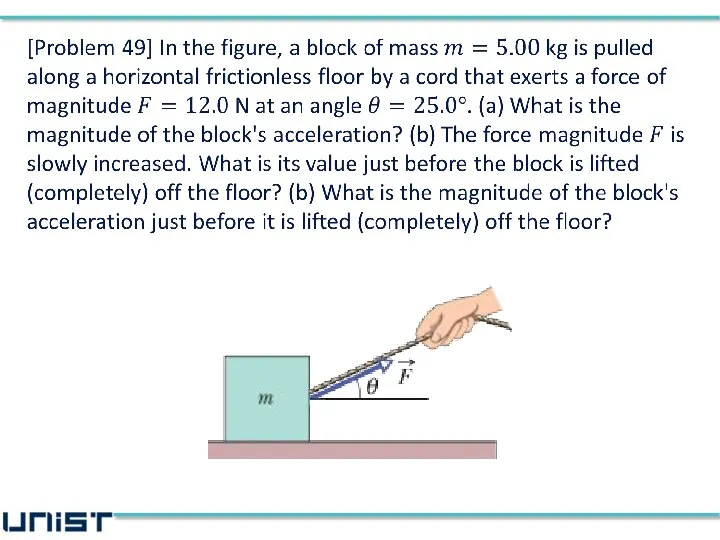
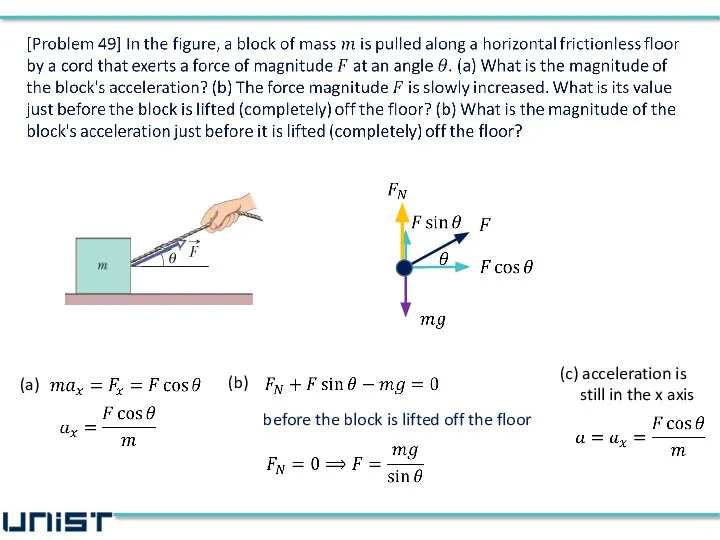
- 26. (a) (b) before the block is lifted off the floor (c) acceleration is still in the
- 27. [Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block
- 28. [Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block
- 29. [Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block
- 30. [Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that loop over frictionless pulleys. Block
- 31. Chapter 6
- 32. [Problem 10] In the figure, a block of weight W experiences two applied forces, each of
- 33. W/2 W/2 W/4 W [Problem 10] In the figure, a block of weight W experiences two
- 34. W/2 W/2 W/4 W [Problem 10] In the figure, a block of weight W experiences two
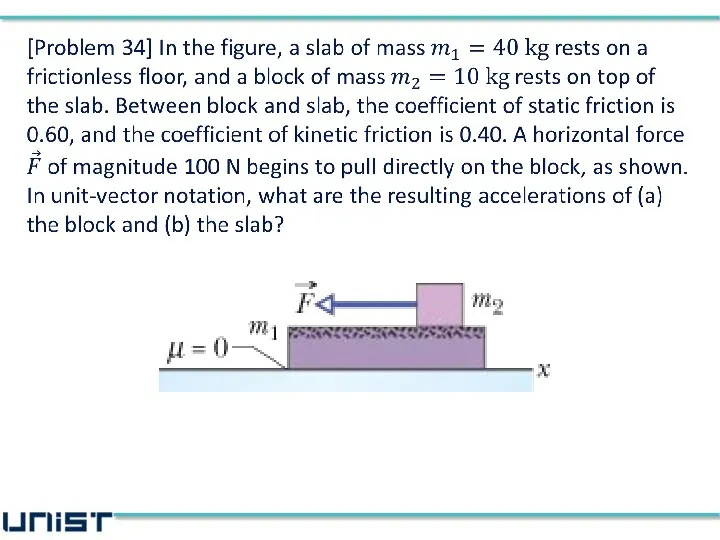
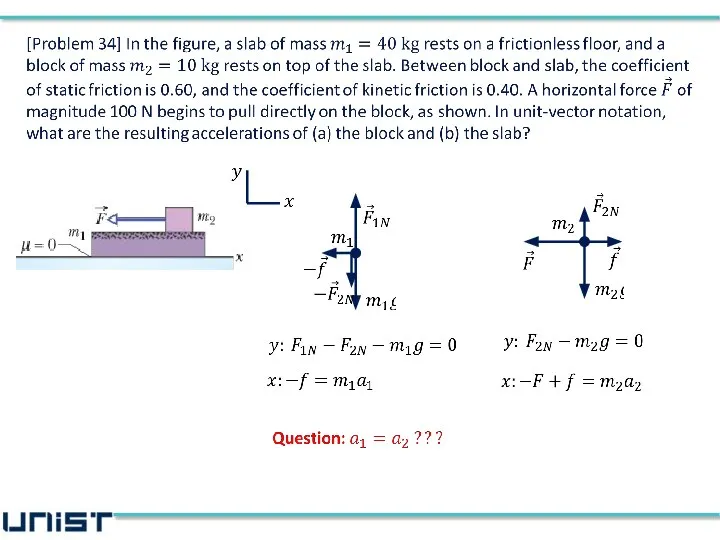
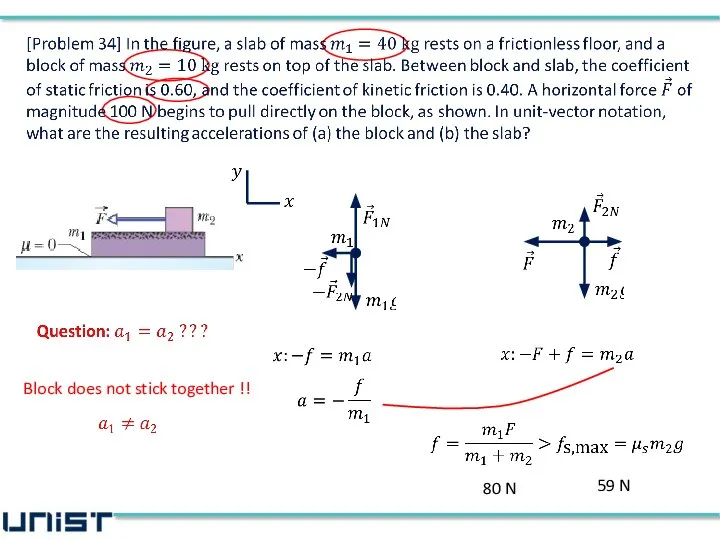
- 37. Block does not stick together !! 80 N 59 N
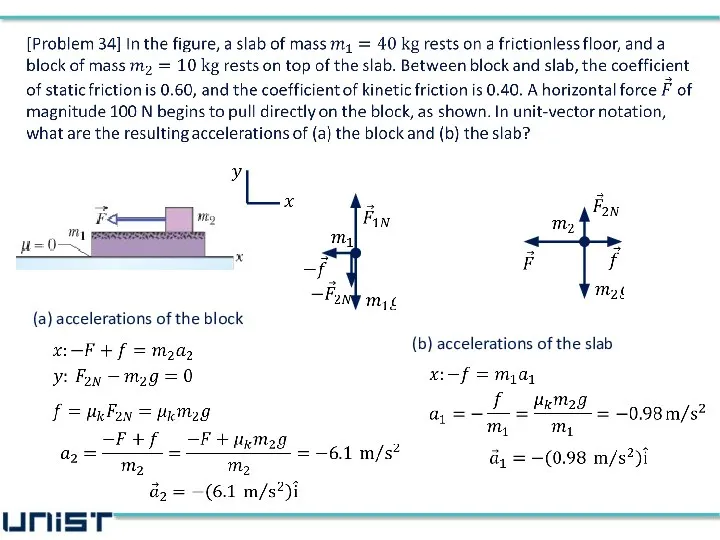
- 38. (a) accelerations of the block (b) accelerations of the slab
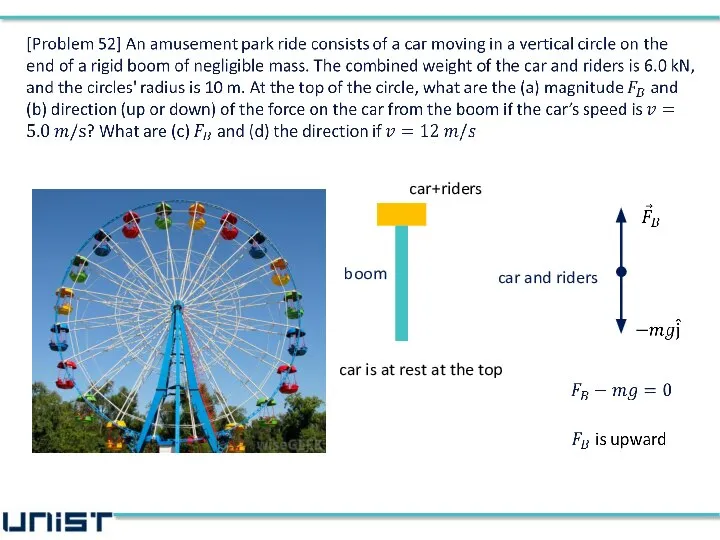
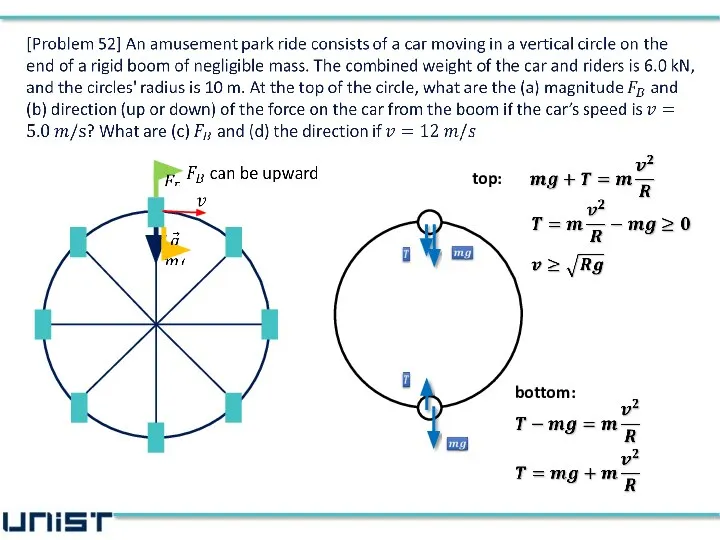
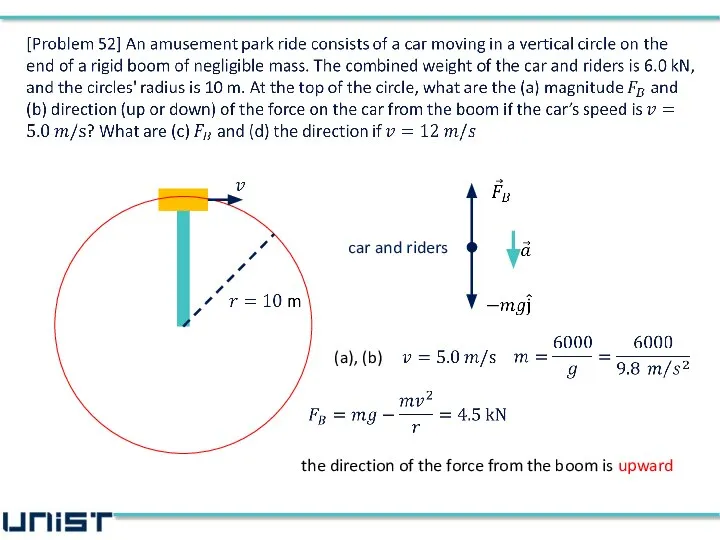
- 40. boom car is at rest at the top car and riders car+riders
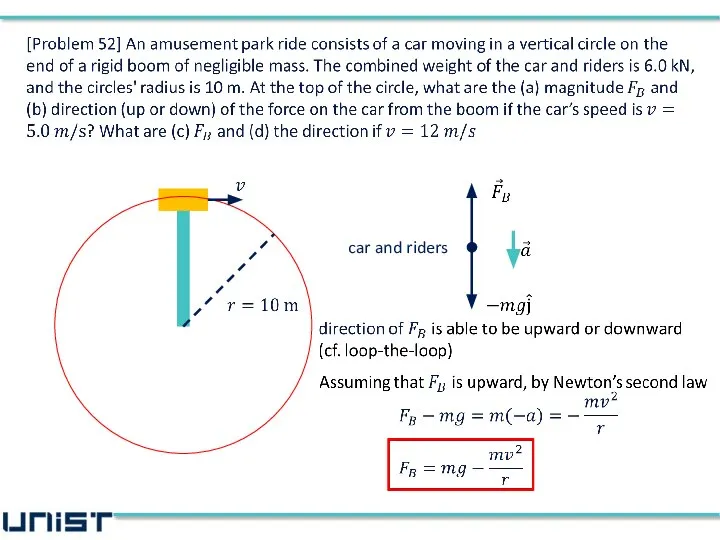
- 47. car and riders
- 48. car and riders (a), (b) the direction of the force from the boom is upward
- 50. Скачать презентацию

![[Problem 29] A car moving at a constant velocity of 46](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-2.jpg)
![[Problem 29] A car moving at a constant velocity of 46](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-3.jpg)
![[Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-4.jpg)
![[Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-5.jpg)
![[Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-6.jpg)
![[Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-7.jpg)
![[Problem 58] An object falls a distance h from rest. If](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-8.jpg)




![[Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-26.jpg)
![[Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-27.jpg)
![[Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-28.jpg)
![[Problem 67] The figure shows three blocks attached by cords that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-29.jpg)

![[Problem 10] In the figure, a block of weight W experiences](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-31.jpg)
![W/2 W/2 W/4 W [Problem 10] In the figure, a block](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-32.jpg)
![W/2 W/2 W/4 W [Problem 10] In the figure, a block](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/1469113/slide-33.jpg)


 Перестановки. Лекция 23
Перестановки. Лекция 23 Степень с целым показателем
Степень с целым показателем Среднее арифметическое. 5 класс
Среднее арифметическое. 5 класс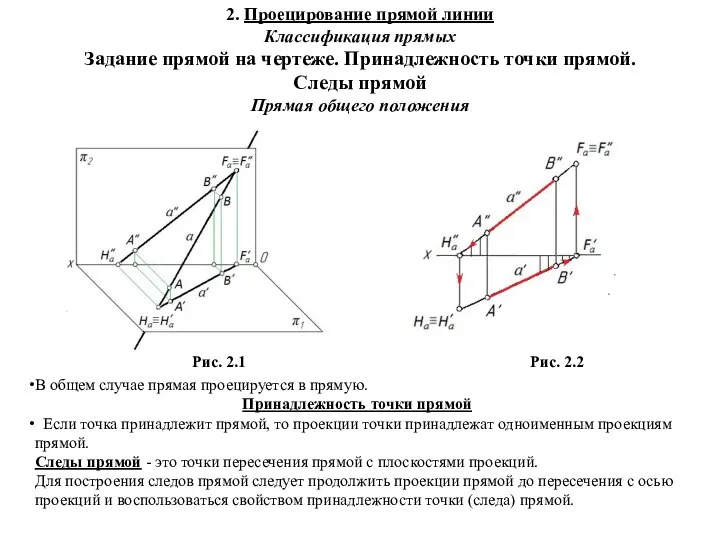 Предмет начертательной геометрии. Проецирование прямой линии. Классификация прямых. Задание прямой на чертеже. (Лекция 2)
Предмет начертательной геометрии. Проецирование прямой линии. Классификация прямых. Задание прямой на чертеже. (Лекция 2) Призмы и антипризмы
Призмы и антипризмы Пересечение поверхностей
Пересечение поверхностей Понятие логарифма
Понятие логарифма Проверка деления с остатком
Проверка деления с остатком Совместные действия с обыкновенными и десятичными дробями
Совместные действия с обыкновенными и десятичными дробями Координатная плоскость. Алгебра 7 класс
Координатная плоскость. Алгебра 7 класс Эталоны и их классификация. (Лекция 3)
Эталоны и их классификация. (Лекция 3) Четвертое измерение
Четвертое измерение Тест по теме: "Векторы в пространстве. Сложение и вычитание векторов. Умножение вектора на число". Вариант 2
Тест по теме: "Векторы в пространстве. Сложение и вычитание векторов. Умножение вектора на число". Вариант 2 Площадь треугольника
Площадь треугольника Метод координат
Метод координат Прямоугольные треугольники
Прямоугольные треугольники Задача двух тел. Уравнения движения в задаче двух тел
Задача двух тел. Уравнения движения в задаче двух тел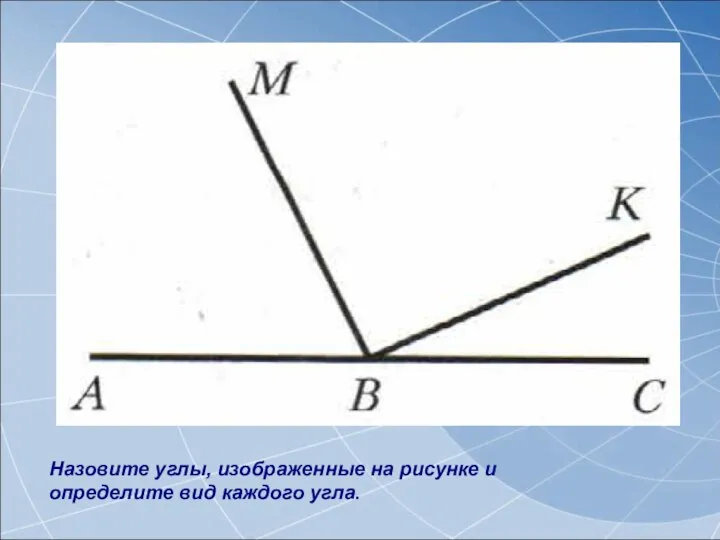 Виды треугольников. 5 класс
Виды треугольников. 5 класс Пространственные фигуры. Площадь, объем
Пространственные фигуры. Площадь, объем ЛИНЕЙНАЯ ФУНКЦИЯ» Презентация по алгебре для 7 класса
ЛИНЕЙНАЯ ФУНКЦИЯ» Презентация по алгебре для 7 класса  Познайте мир логических задач. Математика и логика неразделимы
Познайте мир логических задач. Математика и логика неразделимы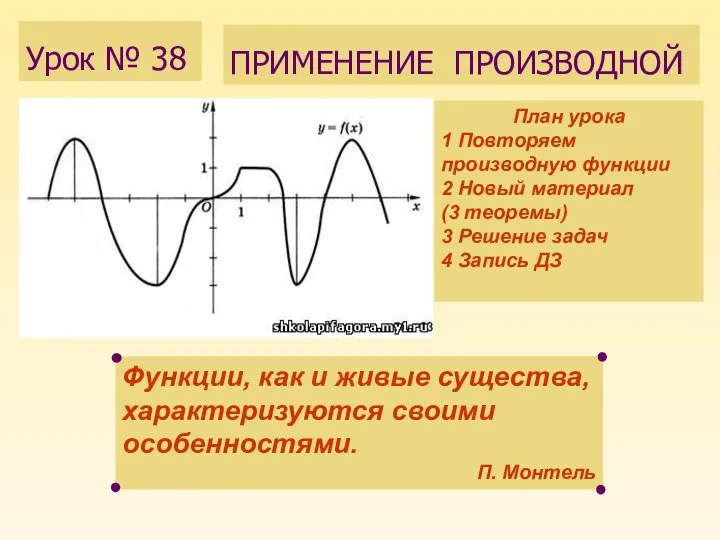 Правила дифференцирования
Правила дифференцирования Числовой отрезок
Числовой отрезок Бирелгән почмакка тигез почмакны циркуль һәм линейка ярдәмендә ничек төзергә
Бирелгән почмакка тигез почмакны циркуль һәм линейка ярдәмендә ничек төзергә Деление десятичных дробей на натуральное число
Деление десятичных дробей на натуральное число Задачи на дроби (3). 6 класс
Задачи на дроби (3). 6 класс Определение и признаки параллелограмма
Определение и признаки параллелограмма Таблица основных неопределенных интегралов
Таблица основных неопределенных интегралов