Содержание
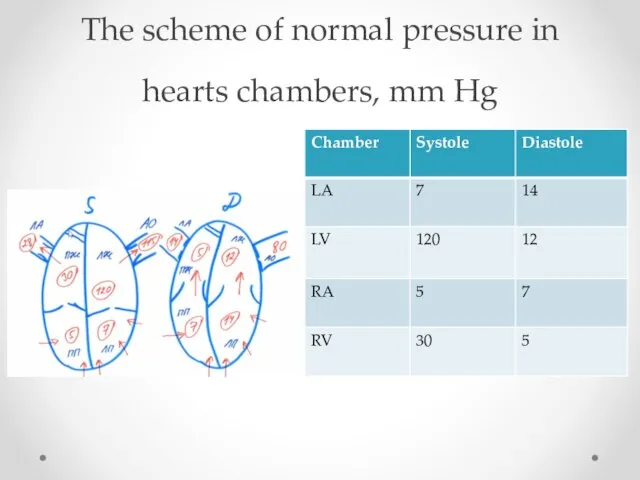
- 3. The scheme of normal pressure in hearts chambers, mm Hg
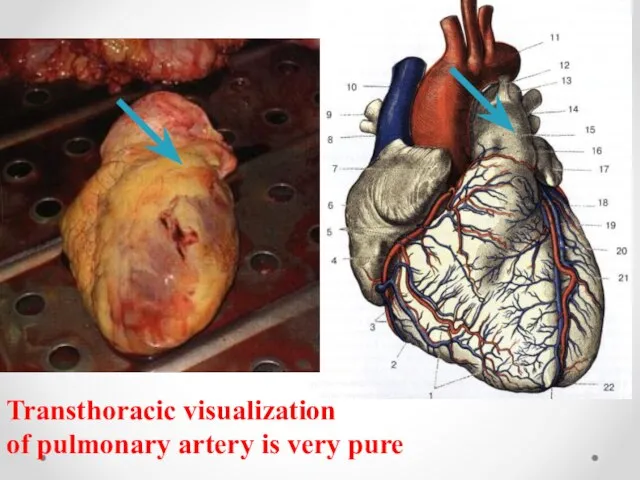
- 4. c Transthoracic visualization of pulmonary artery is very pure
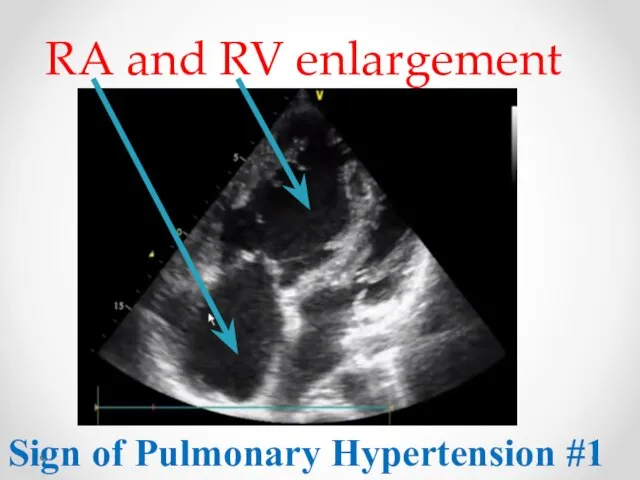
- 5. RA and RV enlargement Sign of Pulmonary Hypertension #1
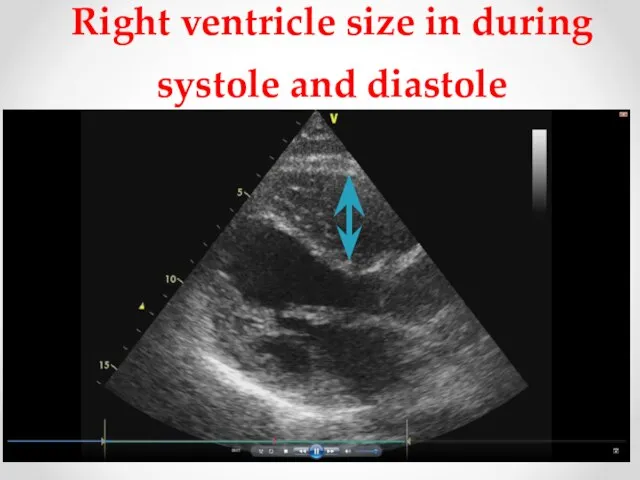
- 6. Right ventricle size in during systole and diastole
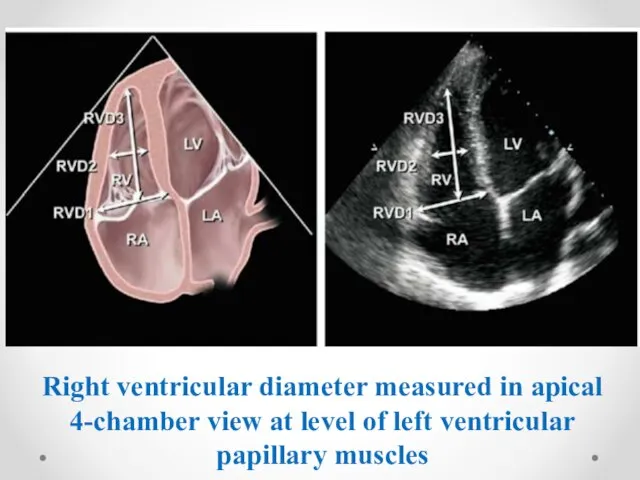
- 7. Right ventricular diameter measured in apical 4-chamber view at level of left ventricular papillary muscles
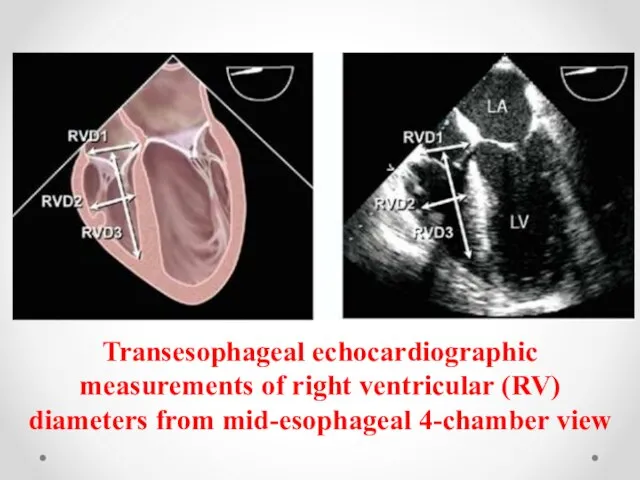
- 8. Transesophageal echocardiographic measurements of right ventricular (RV) diameters from mid-esophageal 4-chamber view
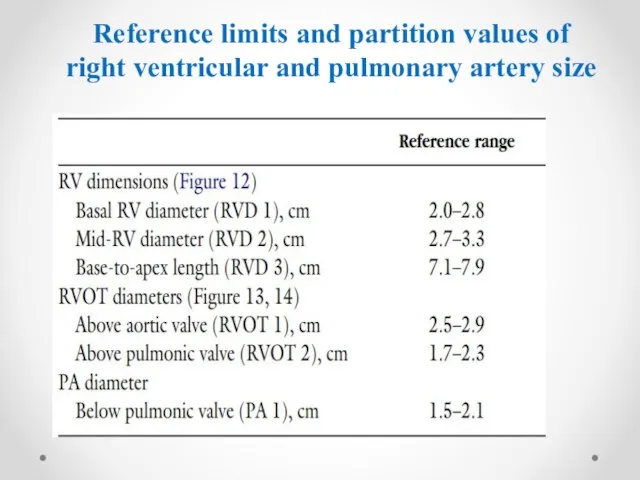
- 9. Reference limits and partition values of right ventricular and pulmonary artery size
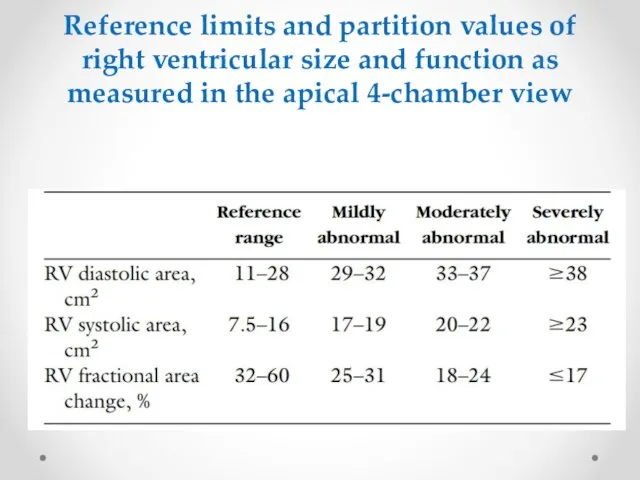
- 10. Reference limits and partition values of right ventricular size and function as measured in the apical
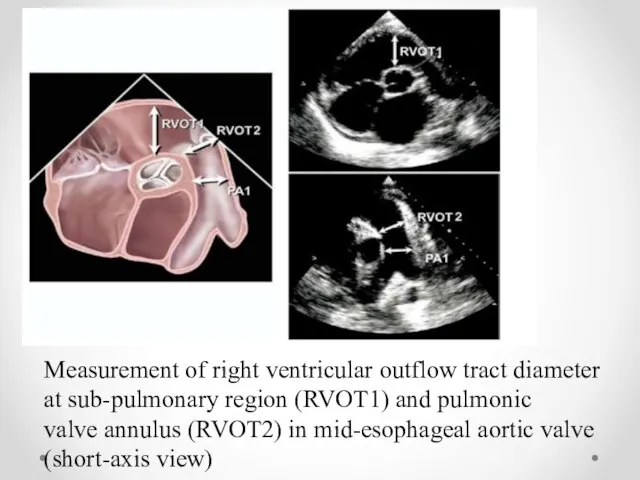
- 11. Measurement of right ventricular outflow tract diameter at sub-pulmonary region (RVOT1) and pulmonic valve annulus (RVOT2)
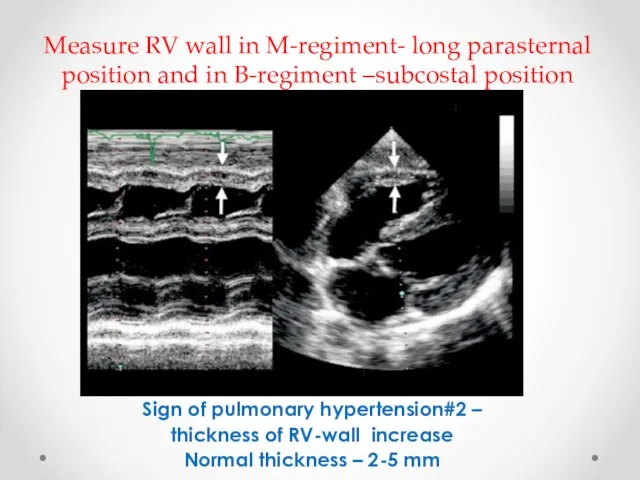
- 12. Measure RV wall in M-regiment- long parasternal position and in B-regiment –subcostal position Sign of pulmonary
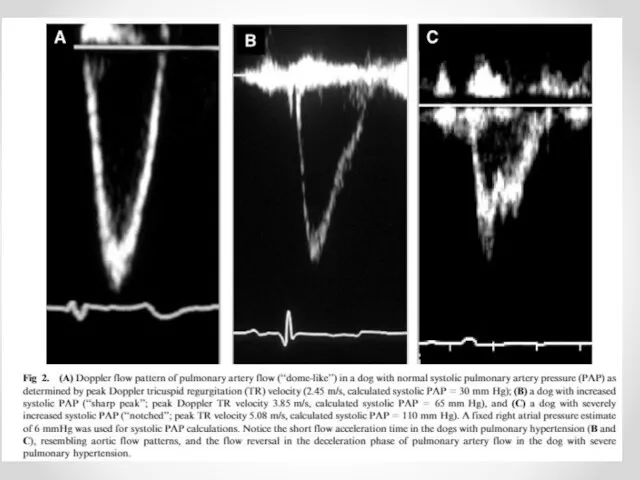
- 13. Variants of Pulmonary arteries pressure calculating AT/ET connection= middle pulmonary pressure Equation of Kitabatake Calculation by
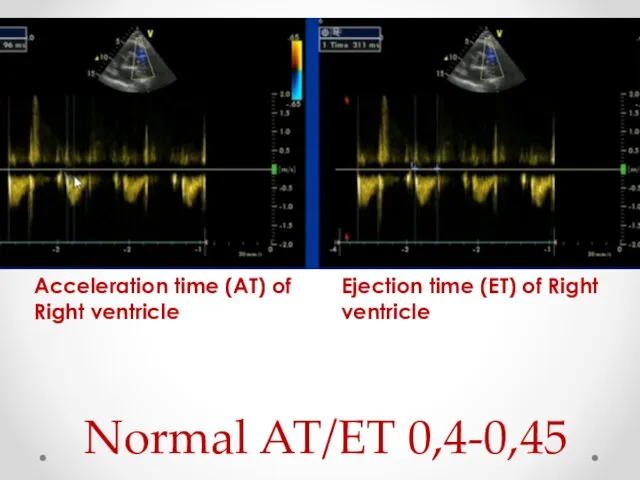
- 14. Acceleration time (AT) of Right ventricle Ejection time (ET) of Right ventricle Normal AT/ET 0,4-0,45
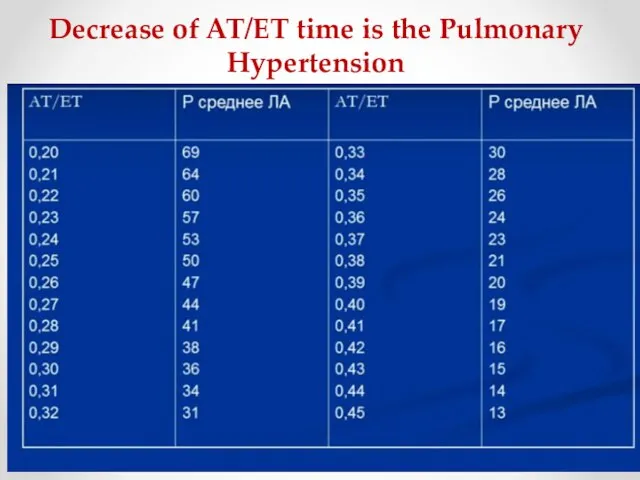
- 15. Decrease of AT/ET time is the Pulmonary Hypertension
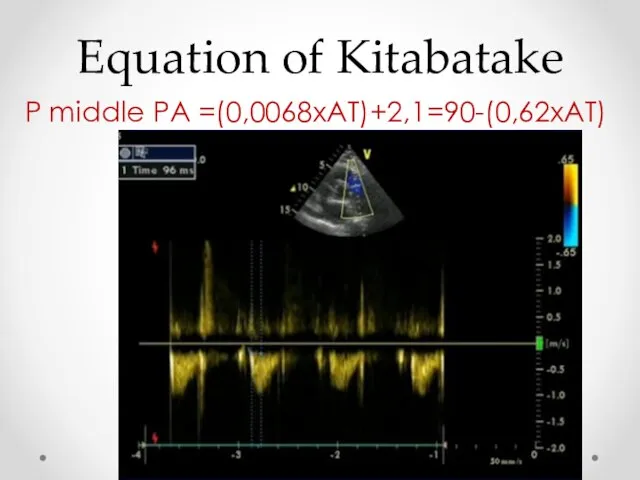
- 17. Equation of Kitabatake P middle PA =(0,0068хАТ)+2,1=90-(0,62хАТ)
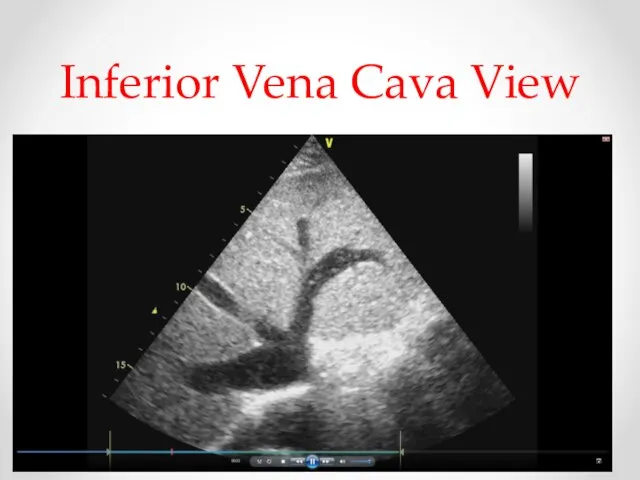
- 18. The diameter of the Inferior vena cava (IVC) and the percent decrease in the diameter during
- 19. Inferior Vena Cava View
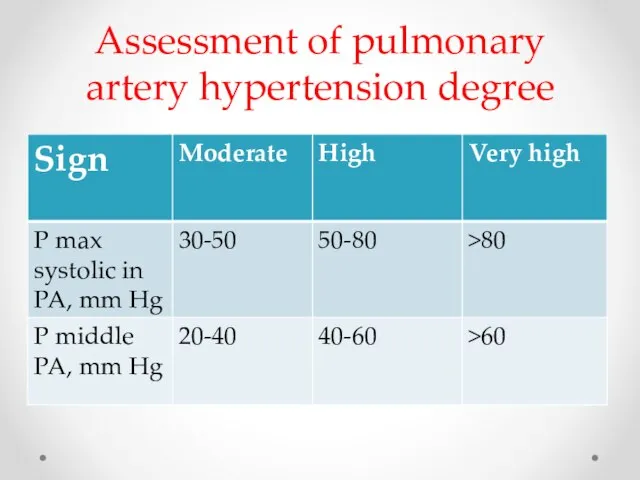
- 20. Assessment of pulmonary artery hypertension degree
- 22. Скачать презентацию


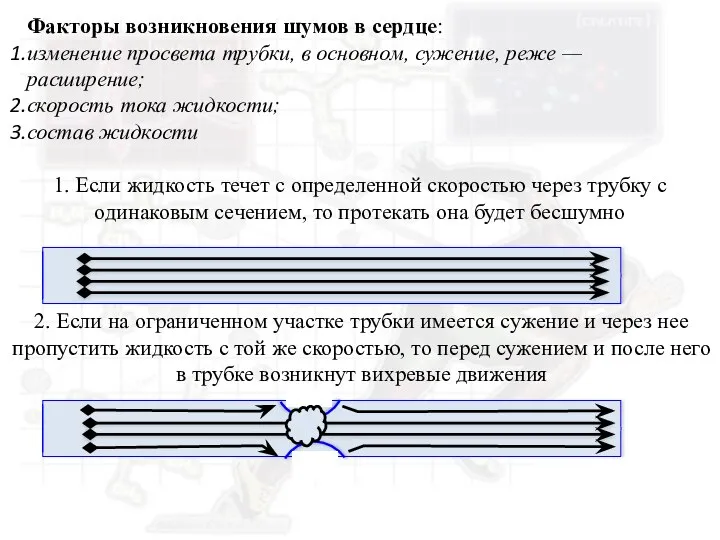 Факторы возникновения шумов в сердце
Факторы возникновения шумов в сердце Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция)
Инфекции, передающиеся парентеральным путем (вирусные гепатиты В,С,Д, ВИЧ-инфекция) Амбулаторлы хирургия
Амбулаторлы хирургия Углеводы. Классификация углеводов
Углеводы. Классификация углеводов Пищеварение у детей
Пищеварение у детей Общая распространенность нарушений функционирования, жизнедеятельности и здоровья у реконвалисцентов COVID-19: результаты
Общая распространенность нарушений функционирования, жизнедеятельности и здоровья у реконвалисцентов COVID-19: результаты Понятие заикание
Понятие заикание Сестринский уход за детьми при рахите, спазмофилии
Сестринский уход за детьми при рахите, спазмофилии Тифлит как осложнение острого аппендицита
Тифлит как осложнение острого аппендицита Өндірістік улардың әсерінің жалпы заңдылықтары
Өндірістік улардың әсерінің жалпы заңдылықтары Наставничество как ответственная функция организатора сестринского дела
Наставничество как ответственная функция организатора сестринского дела Оказание доврачебной помощи пострадавшим
Оказание доврачебной помощи пострадавшим Наблюдение беременной в женской консультации при физиологической беременности
Наблюдение беременной в женской консультации при физиологической беременности Санитарное содержание предприятий ОП
Санитарное содержание предприятий ОП Вариативная анатомия сосудов головы и шеи
Вариативная анатомия сосудов головы и шеи Санаторно-курортная индустрия
Санаторно-курортная индустрия Хирургиялық аурулардың су-электірлік бұзылыстары және инфузионды терапияның принціпі
Хирургиялық аурулардың су-электірлік бұзылыстары және инфузионды терапияның принціпі Микробиология острых кишечных вирусных инфекций
Микробиология острых кишечных вирусных инфекций Новые коллекционные КФС Жемчужина Сербии, Варварин Ключ
Новые коллекционные КФС Жемчужина Сербии, Варварин Ключ Задержка психического развития
Задержка психического развития Методы простейшей физиотерапии
Методы простейшей физиотерапии Чума. Этиология
Чума. Этиология Виды дренажей
Виды дренажей Медицина мен денсаулық сақтаудағы дисперсиялық анализ. Дисперсиялық анализдің негізгі ұғымдары мен əдістемесі
Медицина мен денсаулық сақтаудағы дисперсиялық анализ. Дисперсиялық анализдің негізгі ұғымдары мен əдістемесі Рахит (от греч.rhahis — спинной хребет)
Рахит (от греч.rhahis — спинной хребет) lektsiya_11_svezhie_formy_vtorichnogo_tuberkuleza_ochagovaya_infiltrativnaya_kazeoznaya_pnevmoniya_tuberkuleznyiy_plevrit
lektsiya_11_svezhie_formy_vtorichnogo_tuberkuleza_ochagovaya_infiltrativnaya_kazeoznaya_pnevmoniya_tuberkuleznyiy_plevrit Диагностика определения уровня готовности ребенка к школе
Диагностика определения уровня готовности ребенка к школе Трансплантация лица
Трансплантация лица