Содержание
- 2. RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS Respiratory infections are diseases that transmitted mainly by airborne way and by dust. At
- 3. MOST IMPORTANT PATHOGENS The most important pathogens of respiratory infections are pathogenic cocci, which is an
- 4. COCCI A coccus (plural cocci) is any bacterium or archaeon that has a spherical, ovoid, or
- 6. STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTION Staphylococcal infection is a collective concept that unites infectious diseases caused by staphylococci. It
- 7. STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTION Staphylococcus can take part in mixed purulent processes of the maxillofacial area, stand out
- 8. STAPHYLOCOCCUS Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive round bacteria that form in grape-like clusters Aerobes or
- 9. STAPHYLOCOCCUS Staphylococci belong to the department of Firmicutes, this family. Micrococaceae, genus Staphylococcus. The genus includes
- 10. Staphylococcus aureus (Gram stain) http://www.meteoweb.eu/2016/03/il-diabete-aumenta-il-rischio-di-contrarre-gravi-infezioni-del-sangue/649580/
- 11. Staphylococcus epidermidis (Gram stain)
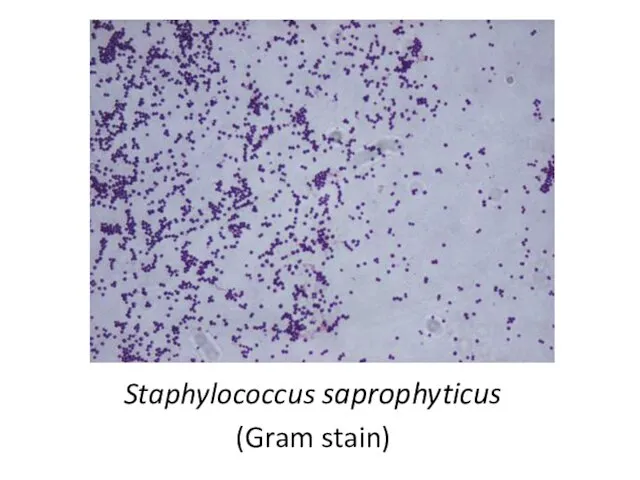
- 12. Staphylococcus saprophyticus (Gram stain)
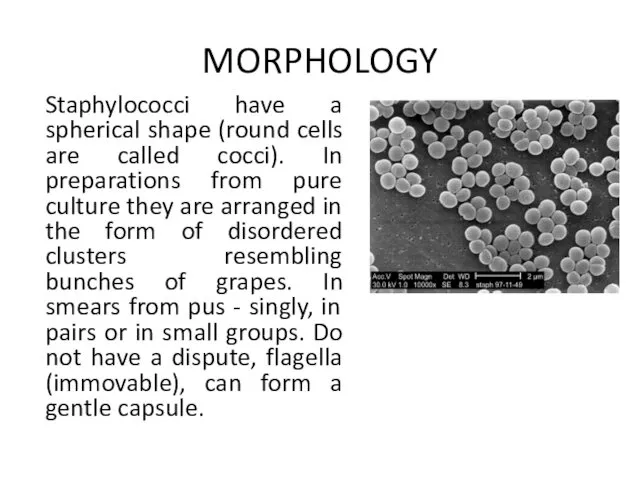
- 13. Staphylococci have a spherical shape (round cells are called cocci). In preparations from pure culture they
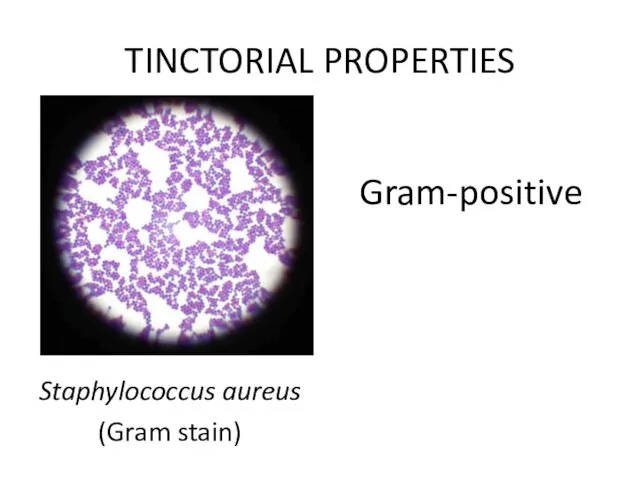
- 14. Staphylococcus aureus (Gram stain) TINCTORIAL PROPERTIES Gram-positive
- 15. CULTURAL PROPERTIES OF S. AUREUS Facultative anaerobes Are not demanding for nutrient media On dense media
- 17. BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES Saccharolytic: ferment 5 carbohydrates of Hiss's medium to acid Proteolytic: ferment proteins with the
- 18. STAPHYLOCOCCUS ANTIGENIC STRUSTURE Staphylococci have about 30 antigens: proteins, polysaccharides, teichoic acids; many extracellular substances that
- 19. FACTORS OF PATHOGENICITY Exotoxin (released outside, outside the cell), consisting of several fractions: hemolysin (destroys erythrocytes),
- 20. RESISTANCE Staphylococci are resistant to external environment, but sensitive to des. solutions, especially to diamond green,
- 21. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Staphylococci are ubiquitous and are often found in normal human microflora (carriers).
- 22. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Staphylococcal infections are called plague of the 20th century, i.e. they are
- 23. PATHOGENESIS AND CLINIC OF DISEASES Entrance gate - any organ and any fabric; Staphylococci penetrate through
- 24. PATHOGENESIS AND CLINIC OF DISEASES Staphylococci cause more than 100 nosological forms of diseases. They affect
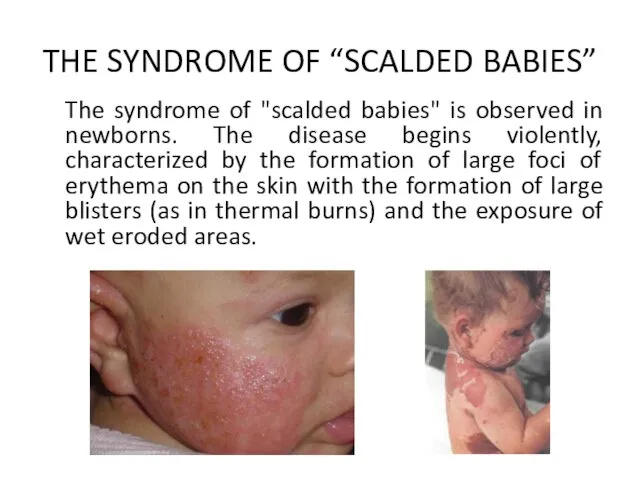
- 25. THE SYNDROME OF “SCALDED BABIES” The syndrome of "scalded babies" is observed in newborns. The disease
- 26. THE TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME The toxic shock syndrome was first recorded in 1980 in women aged
- 27. FOOD POISONING Food poisoning is manifested by vomiting, watery diarrhea within 2 to 6 hours after
- 28. AN ALLERGY TO STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS It is often develops an allergy to staphylococcal toxins, which leads
- 29. PYODERMA Pyoderma means any skin disease that is pyogenic (has pus) Most common isolated organism was
- 30. WHITLOW A whitlow or felon is an infection of the tip of the finger A whitlow
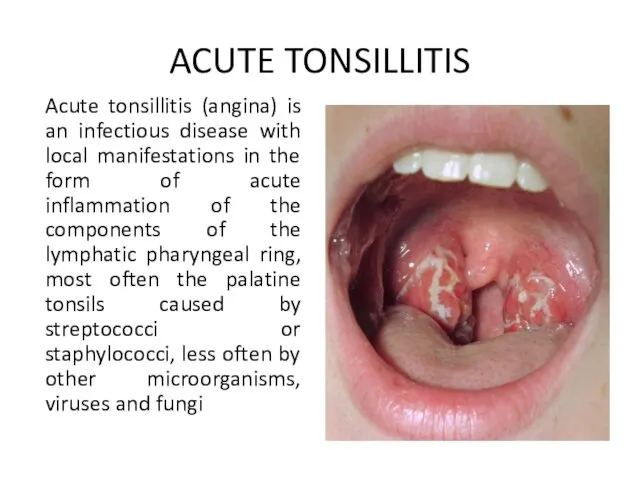
- 31. ACUTE TONSILLITIS Acute tonsillitis (angina) is an infectious disease with local manifestations in the form of
- 32. DIAGNOSIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Materials to be examined: pus, wounds liquor, sputum, blood, vomit, food Bacterioscopic,
- 33. DIAGNOSIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Bacterioscopic method prepare a smear from pus, Gram staining and microscopy; in
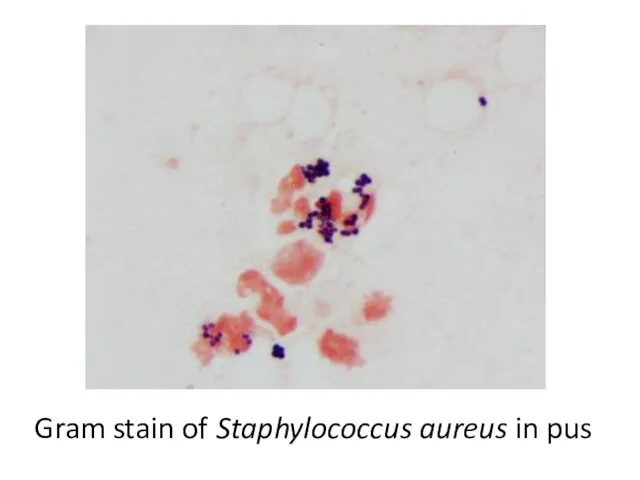
- 34. Gram stain of Staphylococcus aureus in pus
- 35. DIAGNOSIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Bacteriological method Isolate a pure culture by sowing the material on nutrient
- 36. DIAGNOSIS OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS Bioprobe (food poisoning) infection of small suckling kittens, who get vomiting and
- 37. TREATMENT Apply broad-spectrum antibiotics, semisynthetic penicillins (methicillin, oxacillin), sulfonamide preparations It is necessary to determine the
- 39. Скачать презентацию






























 Ролевые и деловые игры
Ролевые и деловые игры Клінічні випадки Завдання
Клінічні випадки Завдання Үй жұмысын тексеру. Есеп шығару
Үй жұмысын тексеру. Есеп шығару Инновационные технологии в ортодонтии
Инновационные технологии в ортодонтии Профессиональная деятельность медицинской сестры при черепно-мозговой травме
Профессиональная деятельность медицинской сестры при черепно-мозговой травме Осложнения анестезии
Осложнения анестезии Мужское здоровье
Мужское здоровье История развития психопатологии в зарубежный странах
История развития психопатологии в зарубежный странах Новый порядок проведения профилактического осмотра и диспансеризации в рамках Приказа Министерства здравоохранения РФ №124н
Новый порядок проведения профилактического осмотра и диспансеризации в рамках Приказа Министерства здравоохранения РФ №124н Основы эпидемиологии и иммунологии. Меры профилактики инфекционных заболеваний
Основы эпидемиологии и иммунологии. Меры профилактики инфекционных заболеваний Выделительная система
Выделительная система Жүрекің тәждік (коронарлық) жетіспеушілігінің диагностикасында коронарографияның, аортографияның, вентрикулографияның
Жүрекің тәждік (коронарлық) жетіспеушілігінің диагностикасында коронарографияның, аортографияның, вентрикулографияның Технология приготовления липосомальных форм лекарственных препаратов и их применение
Технология приготовления липосомальных форм лекарственных препаратов и их применение Движение без боли. Здоровье и молодость вместе с Devita
Движение без боли. Здоровье и молодость вместе с Devita Сочетание речевых средств и невербальных действий
Сочетание речевых средств и невербальных действий Туберкулез костей и суставов
Туберкулез костей и суставов Острый перитонит
Острый перитонит Потребностно-мотивационная сфера личности
Потребностно-мотивационная сфера личности Современные аспекты интенсивного лечения пострадавших с политравмой
Современные аспекты интенсивного лечения пострадавших с политравмой Психология преступных групп
Психология преступных групп Основные аспекты взаимодействия пищи и ЛС
Основные аспекты взаимодействия пищи и ЛС Сущность биосоциальной природы психики и поведения человека
Сущность биосоциальной природы психики и поведения человека Инфекционный процесс. Сепсис. ВИЧ - инфекция
Инфекционный процесс. Сепсис. ВИЧ - инфекция Структура приемного покоя детского стационара
Структура приемного покоя детского стационара Выявление туберкулёза согласно стратегии ДОТС
Выявление туберкулёза согласно стратегии ДОТС Общие правила транспортировки пострадавшего
Общие правила транспортировки пострадавшего Обзор эрготерапии
Обзор эрготерапии Наркотические анальгетики
Наркотические анальгетики