Содержание
- 2. Memory loss Dementia Cognitive impairment or memory loss Onset: insidious Duration: irreversible Chronic Permanent Amnesia Memory
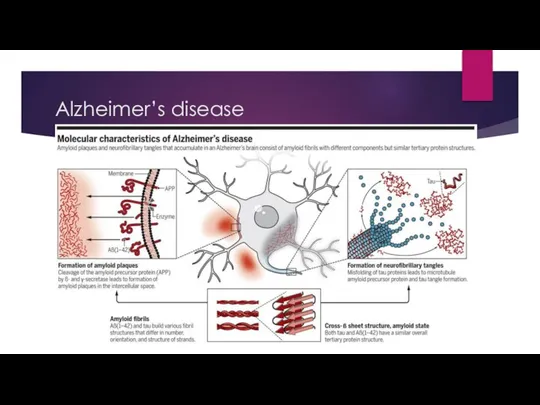
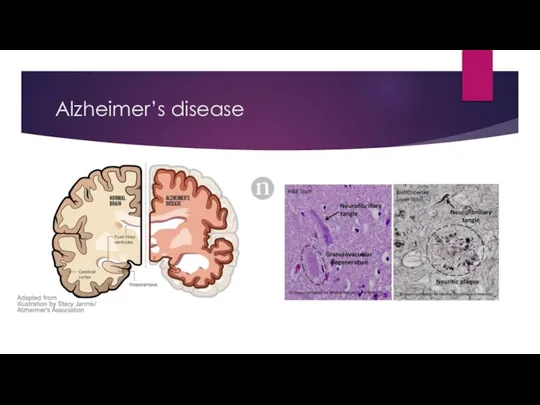
- 4. Alzheimer’s disease
- 5. Alzheimer’s disease
- 6. Alzheimer’s disease
- 7. Alzheimer’s disease Sporadic and Familial (PSEN-1 or PSEN-2 mutation and trisomy 21) Symptoms: short-term memory loss->
- 8. Pick’s disease
- 9. Pick’s disease Frontotemporal degeneration Behavior and personality change goes first (remain memory) Then dementia, aphasia, parkinsonian
- 10. Lewy-body dementia
- 11. Lewy-Body dementia Early symptoms: difficulty focusing, poor memory, visual hallucination, disorganized speech and depression Later symptoms:
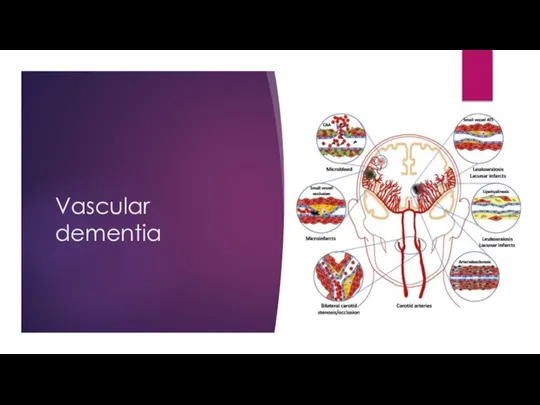
- 12. Vascular dementia
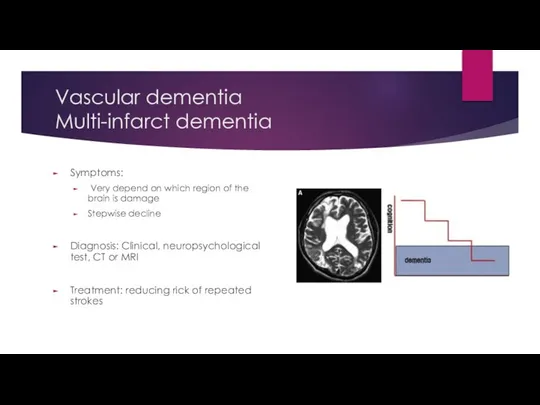
- 13. Vascular dementia Multi-infarct dementia Symptoms: Very depend on which region of the brain is damage Stepwise
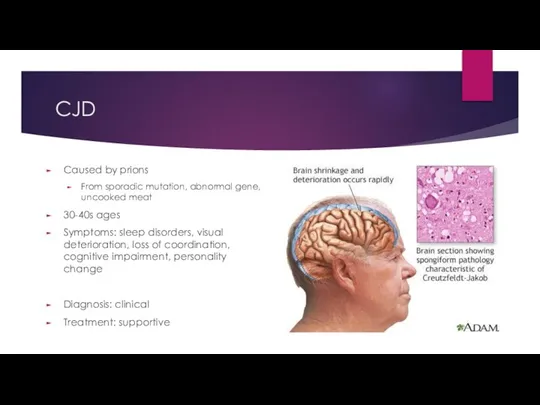
- 14. CJD
- 15. CJD Caused by prions From sporadic mutation, abnormal gene, uncooked meat 30-40s ages Symptoms: sleep disorders,
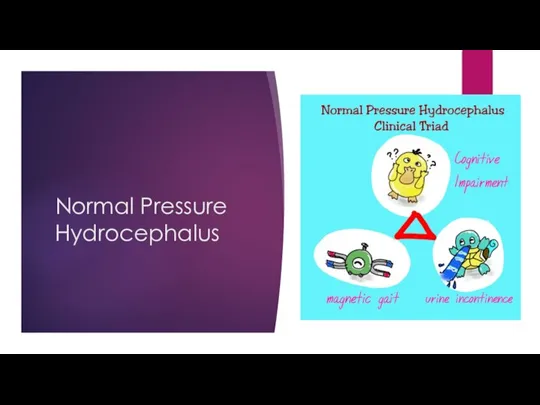
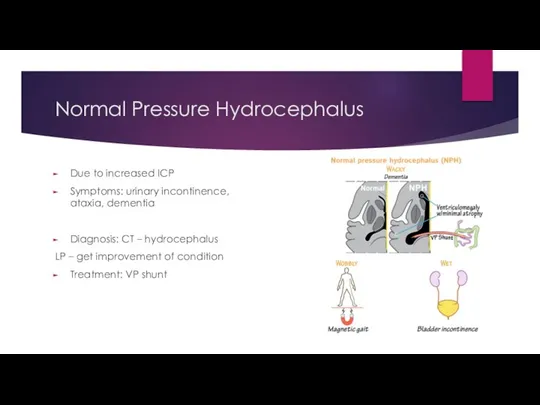
- 16. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
- 17. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Due to increased ICP Symptoms: urinary incontinence, ataxia, dementia Diagnosis: CT – hydrocephalus
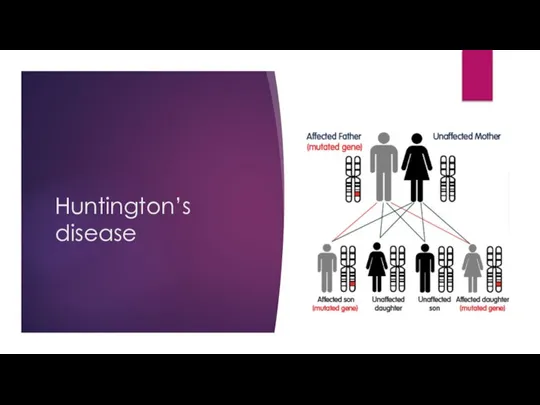
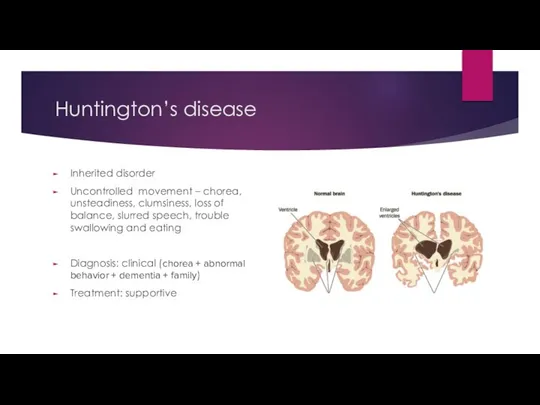
- 18. Huntington’s disease
- 19. Huntington’s disease Inherited disorder Uncontrolled movement – chorea, unsteadiness, clumsiness, loss of balance, slurred speech, trouble
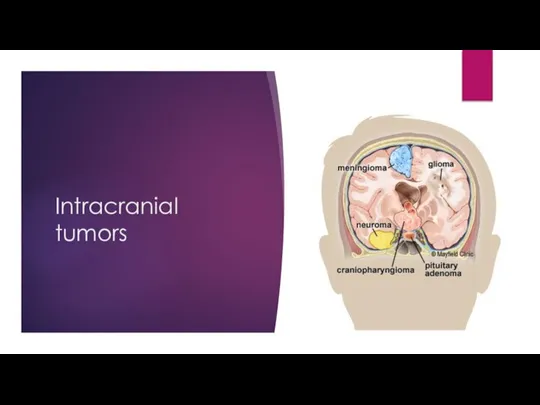
- 20. Intracranial tumors
- 21. Brain cancer Primary 30%(singular) and secondary 70%(multiple lesions) Symptoms: focal neurologic deficit, seizure, headache worse in
- 22. Glioblastoma Multiforme Adults Highly malignant tumor Product of parenchyma and tends to cross the corpus callosum
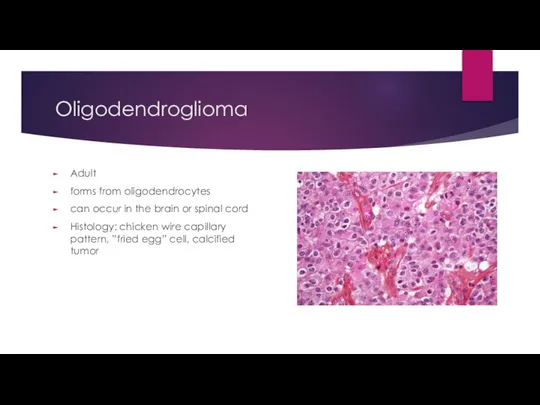
- 23. Oligodendroglioma Adult forms from oligodendrocytes can occur in the brain or spinal cord Histology: chicken wire
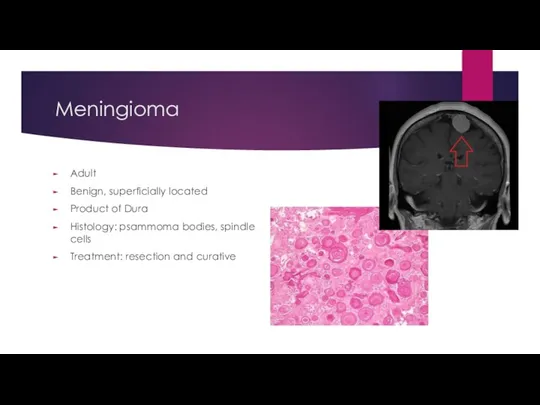
- 24. Meningioma Adult Benign, superficially located Product of Dura Histology: psammoma bodies, spindle cells Treatment: resection and
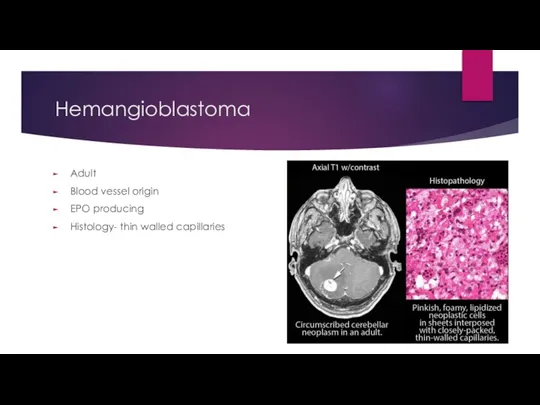
- 25. Hemangioblastoma Adult Blood vessel origin EPO producing Histology- thin walled capillaries
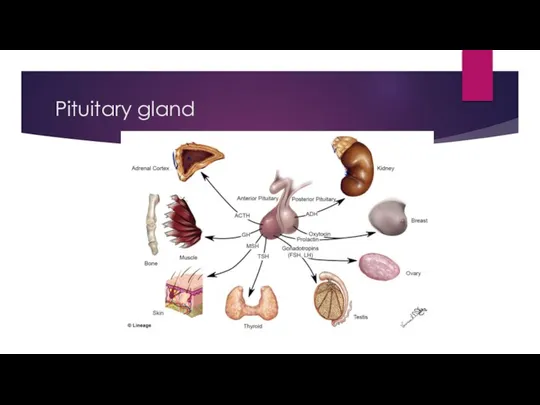
- 26. Pituitary gland
- 27. Pituitary Adenoma Prolactinoma Premenopausal females: Hypogonadism, oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, galactorrhea Males: Decrease libido, impotence, infertility Dx:
- 28. Acromegaly
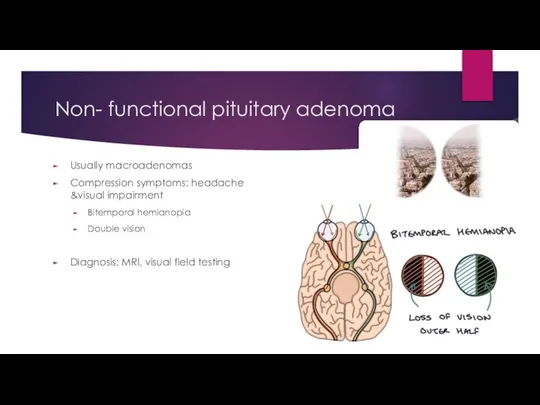
- 29. Non- functional pituitary adenoma Usually macroadenomas Compression symptoms: headache &visual impairment Bitemporal hemianopia Double vision Diagnosis:
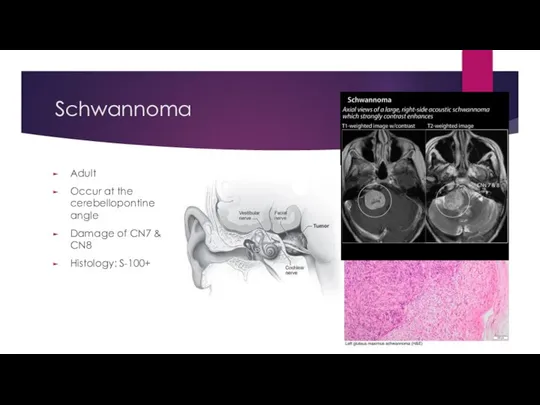
- 30. Schwannoma Adult Occur at the cerebellopontine angle Damage of CN7 & CN8 Histology: S-100+
- 31. Childhood tumors Infratentorial tumors Pilocytic Astrocytoma From Astrocytes Rosenthal Fibers Medulloblastoma From embryonic stem cells and
- 33. Скачать презентацию














 Aditivi alimentari
Aditivi alimentari Свойства вакцины Гам-КОВИД-Вак (Спутник V)
Свойства вакцины Гам-КОВИД-Вак (Спутник V) ИВЛ и НМС детям
ИВЛ и НМС детям Всемирный день борьбы со СПИДом
Всемирный день борьбы со СПИДом Общие вопросы фармакологии
Общие вопросы фармакологии Кафедра общей и клинической фармакологии
Кафедра общей и клинической фармакологии Лекарственные формы с антибиотиками
Лекарственные формы с антибиотиками Schistosomiasis (bilharziasis)
Schistosomiasis (bilharziasis) Нарушение функции кишечника
Нарушение функции кишечника Фармакология. Средства, влияющие на систему крови
Фармакология. Средства, влияющие на систему крови Проблема виникнення і розв’язання конфліктів у сім’ї
Проблема виникнення і розв’язання конфліктів у сім’ї Адамның тұқым қуалайтын патологиясындағы тұқым қуалаушылық пен ортаның ролі
Адамның тұқым қуалайтын патологиясындағы тұқым қуалаушылық пен ортаның ролі Влияния алкоголя на женский организм
Влияния алкоголя на женский организм Түбірі қалыптаспаған уақытша және тұрақты тістердегі периодонтиттерді емдеу
Түбірі қалыптаспаған уақытша және тұрақты тістердегі периодонтиттерді емдеу Комп'ютерна залежність - ознаки, стадії, причини виникнення та профілактика. Селфіманія - хвороба чи спосіб самовираження
Комп'ютерна залежність - ознаки, стадії, причини виникнення та профілактика. Селфіманія - хвороба чи спосіб самовираження Инфекция кожи и подкожной клетчатки
Инфекция кожи и подкожной клетчатки Мікроелементози жуйних
Мікроелементози жуйних Воспалительные заболевания внутренних женских половых органов
Воспалительные заболевания внутренних женских половых органов Препараты, спасающие жизнь после инфаркта миокарда
Препараты, спасающие жизнь после инфаркта миокарда Роды
Роды Хронические расстройства питания у детей. Дистрофии, паратрофии
Хронические расстройства питания у детей. Дистрофии, паратрофии Обезболивание родов
Обезболивание родов Синдром дыхательной недостаточности. Клиническая и лабораторная характеристика ДН
Синдром дыхательной недостаточности. Клиническая и лабораторная характеристика ДН Сестринский процесс при сахарном диабете у детей
Сестринский процесс при сахарном диабете у детей Генетические основы болезней. Наследственные дефекты неферментных белков
Генетические основы болезней. Наследственные дефекты неферментных белков Принципы системы оздоровления
Принципы системы оздоровления Дифференциальная диагностика заболеваний, протекающих с лихорадкой
Дифференциальная диагностика заболеваний, протекающих с лихорадкой Пластикалық хирургияның негіздері мен қалыптасу
Пластикалық хирургияның негіздері мен қалыптасу