Содержание
- 2. Interactive Case studies Summary of specific surgical conditions
- 3. What is a neonate? What is preterm? What is term?
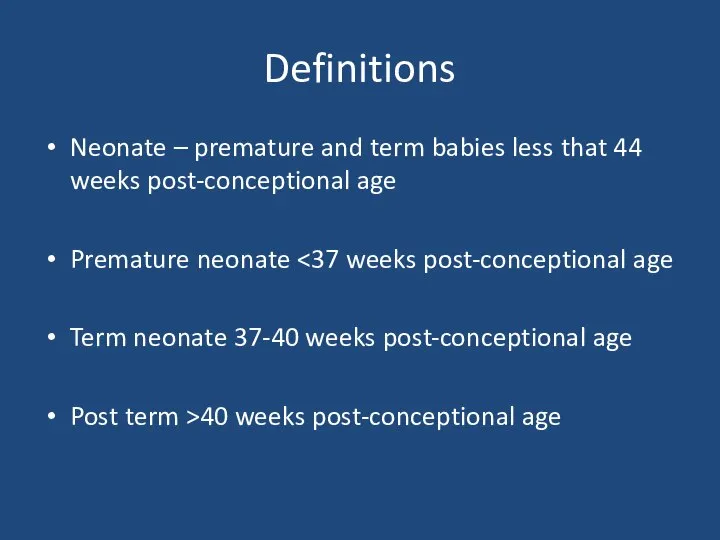
- 4. Definitions Neonate – premature and term babies less that 44 weeks post-conceptional age Premature neonate Term
- 5. History and Symptoms
- 6. History and Symptoms Gestation Weight Antenatal history Colour of vomit Frequency of vomit Bowel opening Saliva?
- 7. Physical Findings
- 8. Physical findings Observations Erythema and bruising Distended Scaphoid abdomen Mass Anus – site, size and patency
- 9. Investigations Plain AXR/CXR Upper/Lower GI contrast Abdominal USS
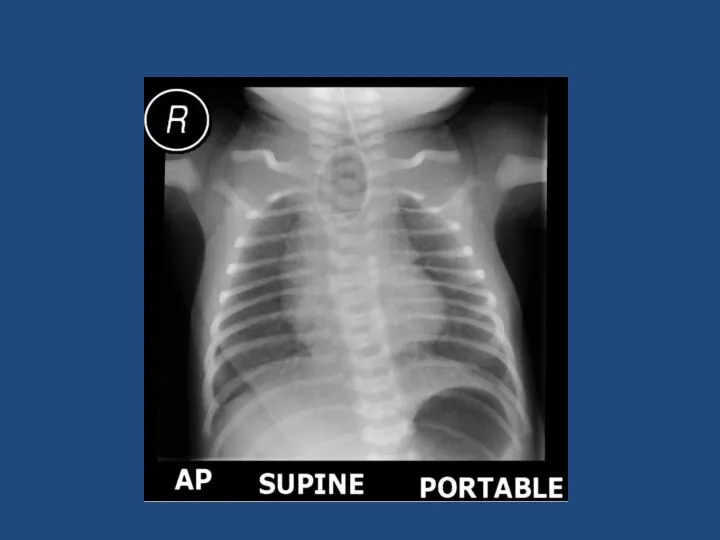
- 10. Case 1 Term neonate 1 day old Vomiting Relevant points in history Relevant examination findings Differential
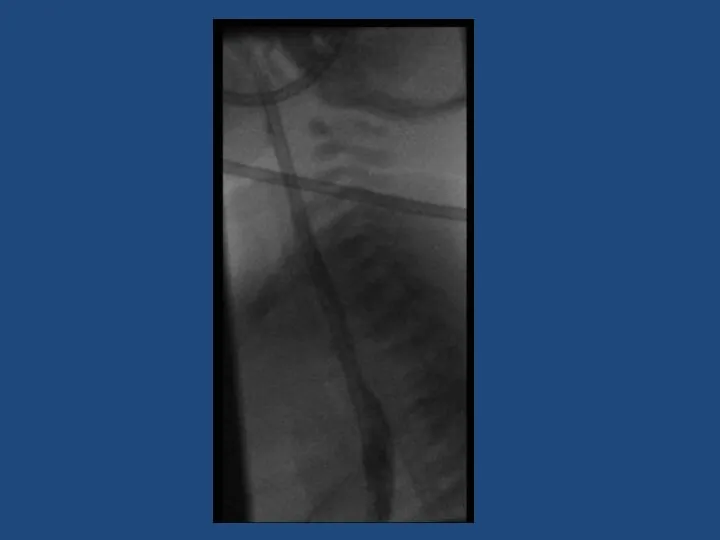
- 12. Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula 1 in 3500 liveborn births Antenatal Polyhydramnios, absent stomach, associated anomalies
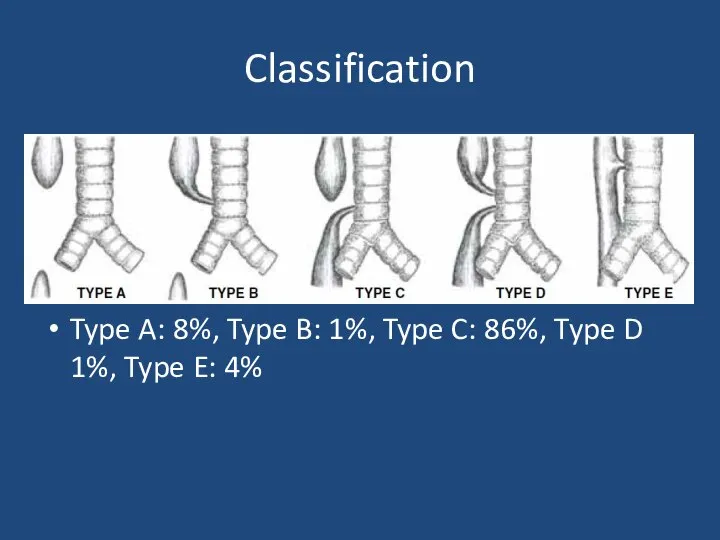
- 13. Classification Type A: 8%, Type B: 1%, Type C: 86%, Type D 1%, Type E: 4%
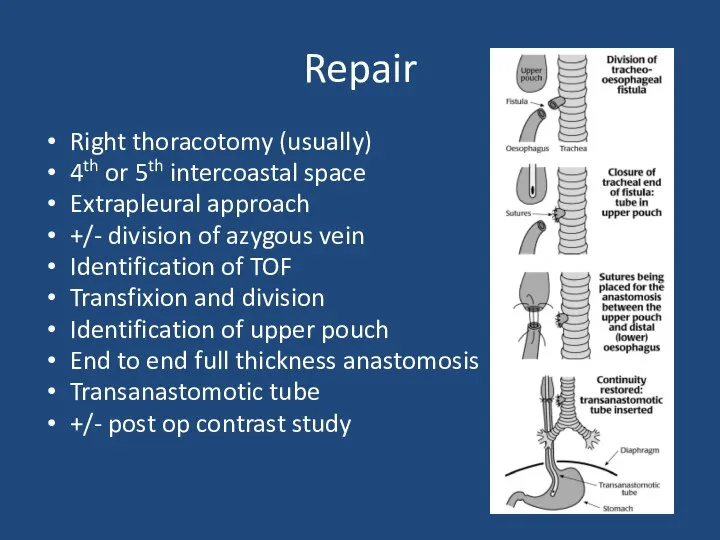
- 14. Repair Right thoracotomy (usually) 4th or 5th intercoastal space Extrapleural approach +/- division of azygous vein
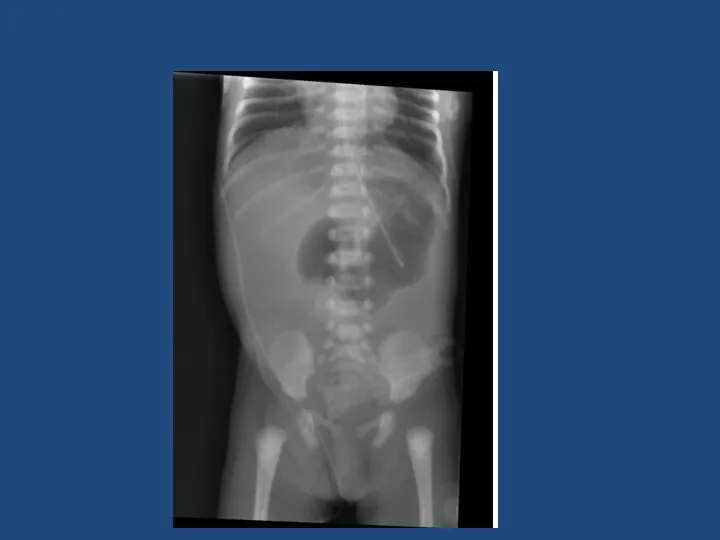
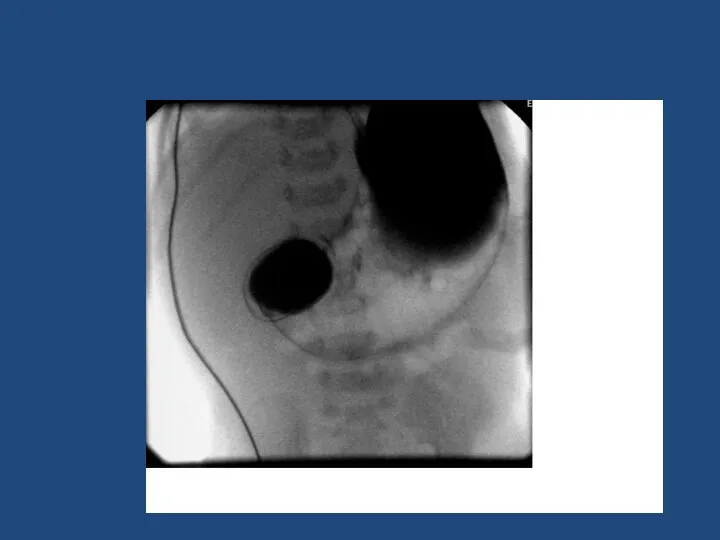
- 18. Duodenal Atresia 1 in 5000 Antenatal diagnosis – ‘double bubble’ Associated with Trisomy 21 - 30%,
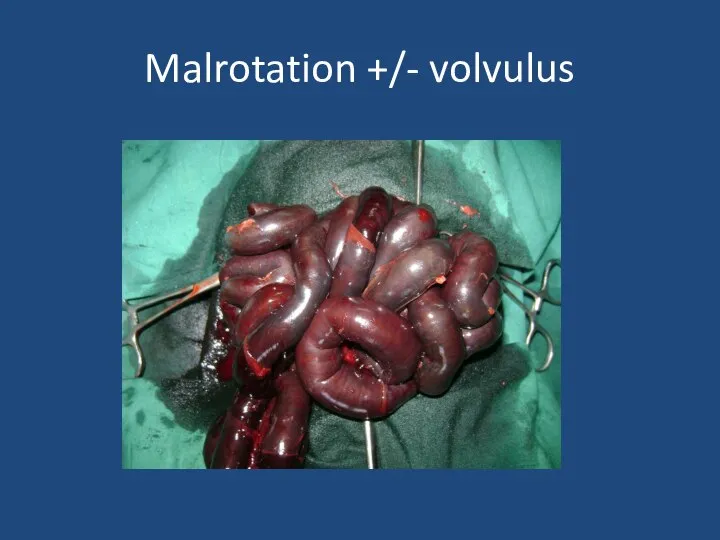
- 20. Malrotation +/- volvulus
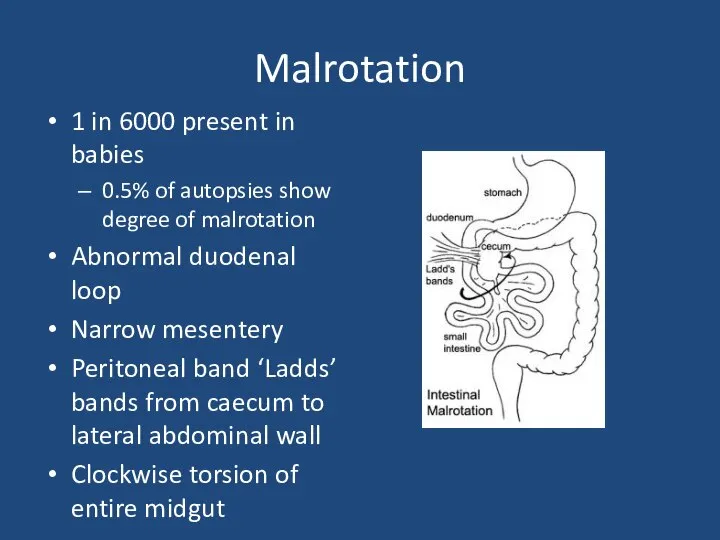
- 21. Malrotation 1 in 6000 present in babies 0.5% of autopsies show degree of malrotation Abnormal duodenal
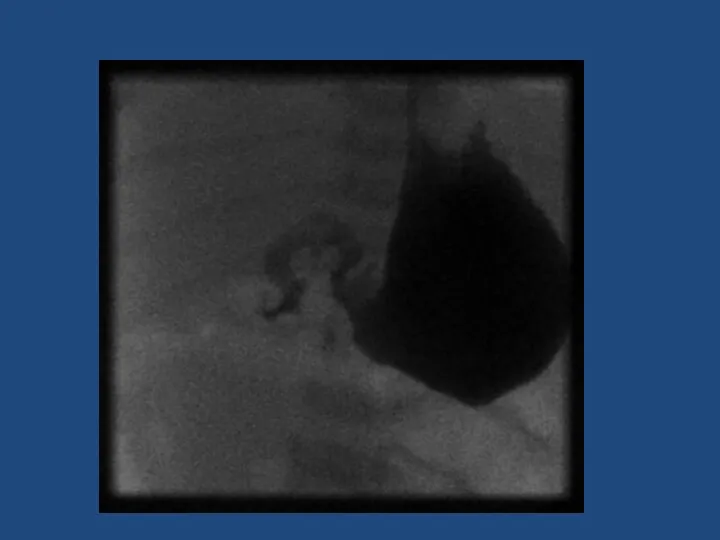
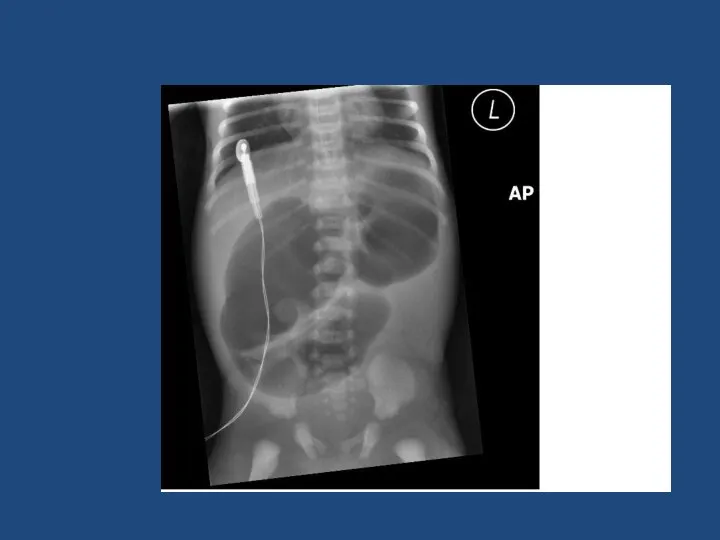
- 22. Malrotation + volvulus SURGICAL EMERGENCY Bilious vomiting in neonate Upper GI contrast to diagnose Emergency laparotomy
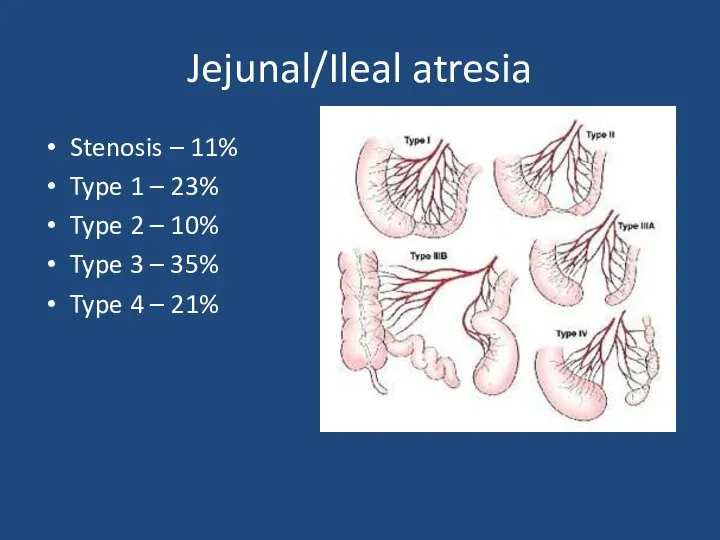
- 24. Jejunal/Ileal atresia Stenosis – 11% Type 1 – 23% Type 2 – 10% Type 3 –
- 25. Jejunal/ileal atresia 1 in 5000 births Aetiology – antenatal vascular compromise May have short bowel Resection
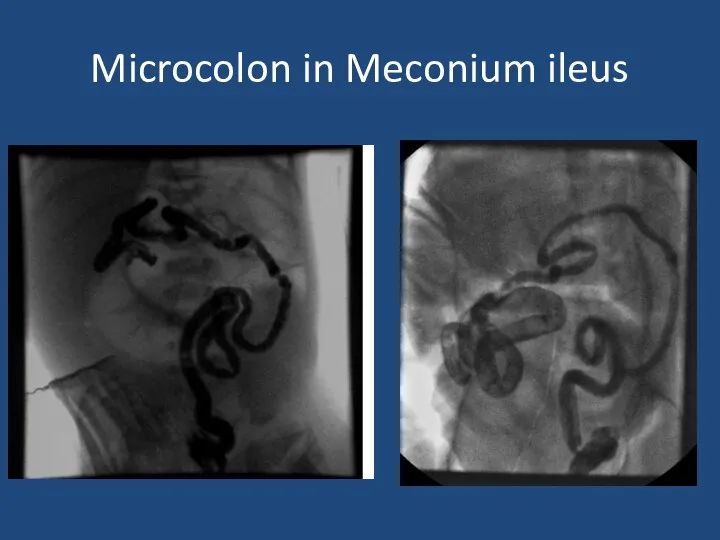
- 26. Meconium Ileus CF – 1 in 2500 births ~16% of babies with CF Inspissated sticky meconium
- 27. Microcolon in Meconium ileus
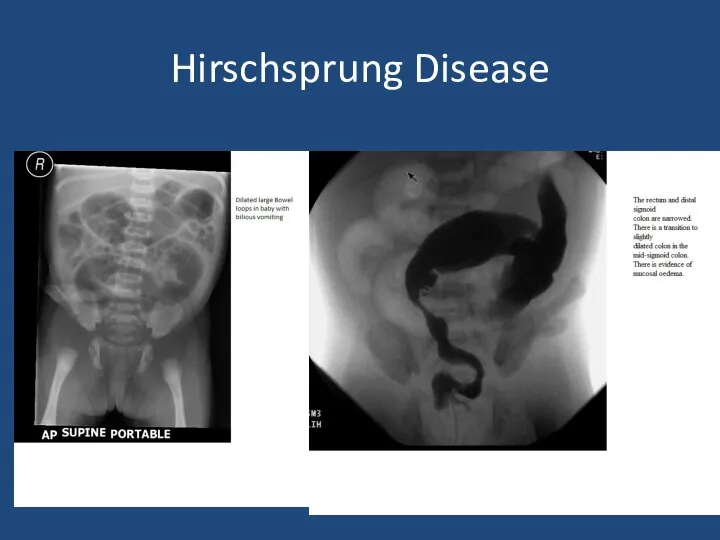
- 28. Hirschsprung Disease
- 29. Hirschsprung Disease 1 in 5000 births M:F 4:1 Associated with Trisomy 21 Delayed passage of meconium
- 30. Hirschsprung Disease Aganglionosis of bowel Variable failure of neural crest cell migration Rectosigmoid – 75% Long
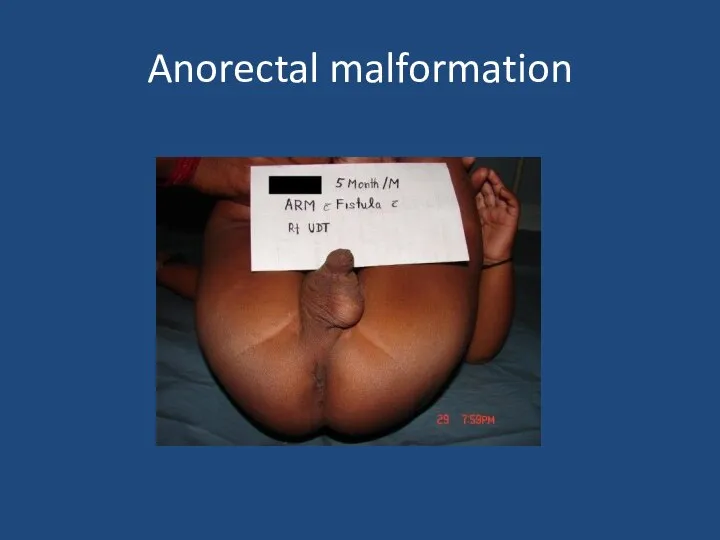
- 31. Anorectal malformation
- 32. Anorectal malformation 1 in 4000 births Management depends on level of ARM Primary anoplasty for low
- 33. Case 2 3 week old term baby Relevant points in history Relevant examination findings Differential diagnosis
- 34. Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis 1-4:1000, M:F 4:1 Overgrowth of pyloric muscle Gastric outlet obstruction Increasing non-bilious
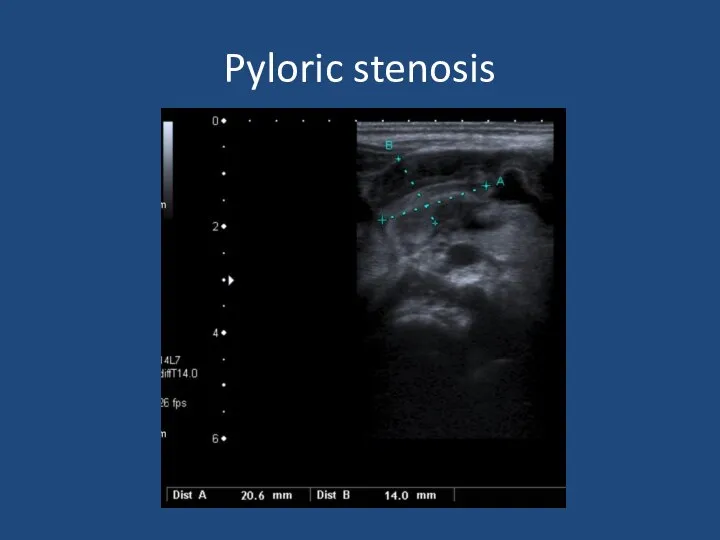
- 35. Pyloric stenosis
- 36. Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Diagnosis – palpable mass on ‘test feed’ USS Pyloric length >16mm Single
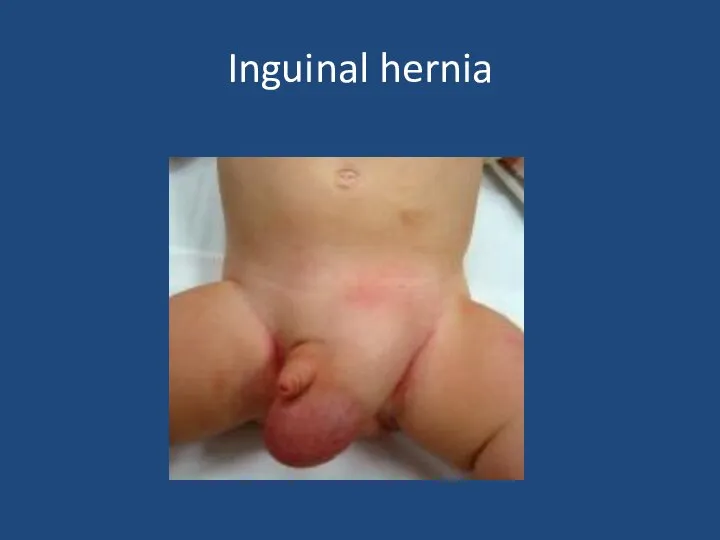
- 37. Inguinal hernia
- 38. Inguinal hernia Usually can reduce If truly incacerated – emergency exploration Otherwise if premature baby or
- 39. Case 3 Preterm neonate – bilious vomiting Born 27 weeks gestation Weight 1 kg 1 week
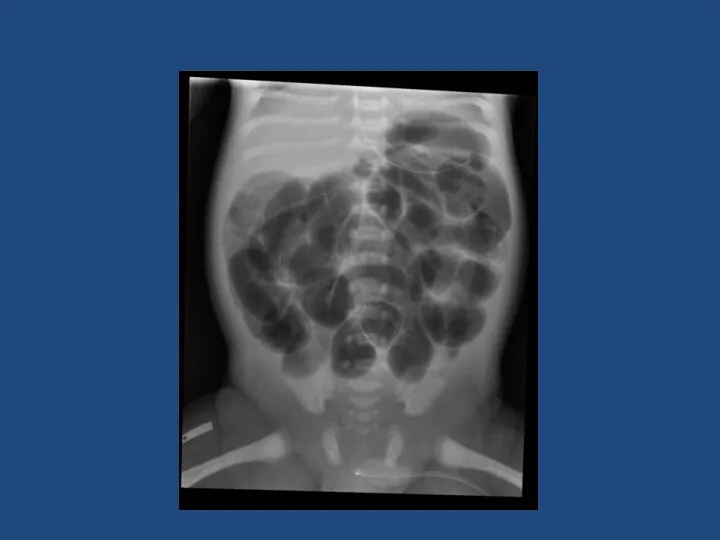
- 43. Necrotising Enterocolitis 90% in preterm 10% in term babies ~5% of all babies admitted to Neonatal
- 44. Necrotising Enterocolitis Surgery indicated for: Worsening clinical condition despite maximal supportive therapy Perforation Laparotomy Assess extent
- 46. Скачать презентацию























 Ультразвук в клинической диагностике глаз и орбиты
Ультразвук в клинической диагностике глаз и орбиты Ортодонтия. Тістем дегеніміз орталық окклюзия жағдайында тістердің түйісуі
Ортодонтия. Тістем дегеніміз орталық окклюзия жағдайында тістердің түйісуі Недоверие и страх системы ОСМС
Недоверие и страх системы ОСМС Влияние антибиотиков на микрофлору
Влияние антибиотиков на микрофлору Сүйек кемігі
Сүйек кемігі Хронические гепатиты, циррозы печени
Хронические гепатиты, циррозы печени Хроническая сердечная недостаточность
Хроническая сердечная недостаточность Сахар и сахарозаменители
Сахар и сахарозаменители Вредное влияние алкоголя, курения и наркотиков в период эмбрионального развития
Вредное влияние алкоголя, курения и наркотиков в период эмбрионального развития Профилактика и ранняя диагностика онкологических заболеваний
Профилактика и ранняя диагностика онкологических заболеваний Уход за пациентами пожилого возраста в стационаре и дома
Уход за пациентами пожилого возраста в стационаре и дома Наркомани. Наркотические средства
Наркомани. Наркотические средства Особенности первичной позитивной профилактики аддиктивного поведения в образовательных учреждениях
Особенности первичной позитивной профилактики аддиктивного поведения в образовательных учреждениях Основные правила рационального питания
Основные правила рационального питания Классный час на тему: Глаза - главные помощники человека. Гигиена зрения. Забота о глазах
Классный час на тему: Глаза - главные помощники человека. Гигиена зрения. Забота о глазах Правила оказания первой помощи при ранениях
Правила оказания первой помощи при ранениях Сознание. Свойства сознания
Сознание. Свойства сознания Методы обследования больного: субъективные и объективные
Методы обследования больного: субъективные и объективные Гистологиялық препараттардың электрондық нұсқасы
Гистологиялық препараттардың электрондық нұсқасы Вірус Зіка
Вірус Зіка Взгляд косметолога на акне и качество кожи лица
Взгляд косметолога на акне и качество кожи лица Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии в акушерской практике
Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии в акушерской практике Профессиональное выгорание педагогов-психологов
Профессиональное выгорание педагогов-психологов Детский церебральный паралич. Клинические симптомы
Детский церебральный паралич. Клинические симптомы Пуринергиялық синапстарда қозудың берілуіне әсер ететін дәрілер
Пуринергиялық синапстарда қозудың берілуіне әсер ететін дәрілер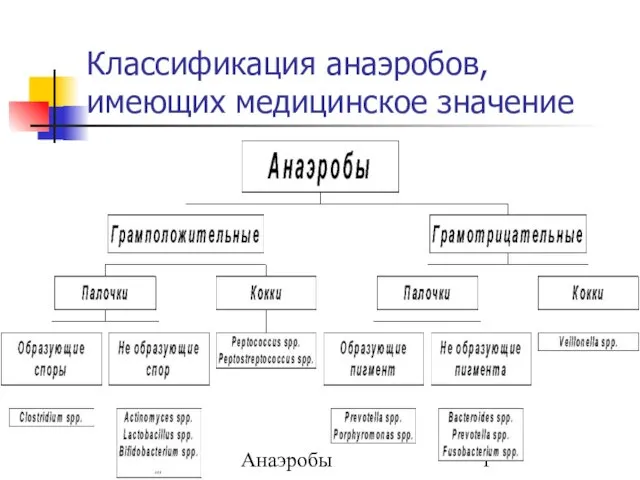 Классификация анаэробов, имеющих медицинское значение
Классификация анаэробов, имеющих медицинское значение Виды медицинского страхования
Виды медицинского страхования Когнитивная психология
Когнитивная психология