Содержание
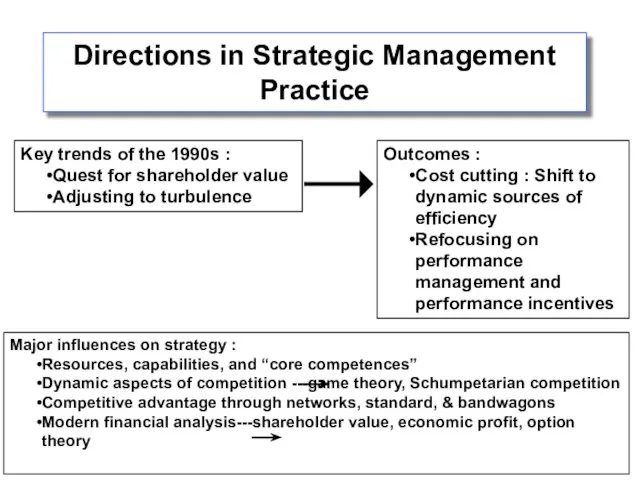
- 2. Directions in Strategic Management Practice Key trends of the 1990s : Quest for shareholder value Adjusting
- 3. New Directions in Strategic Thinking BEYOND DOWNSIZING Gains from cost cutting and downsizing largely exhausted Need
- 4. Knowledge Management and the Knowledge-Based View of the Firm KNOWLEDGE UTILIZATION Need to identify knowledge with
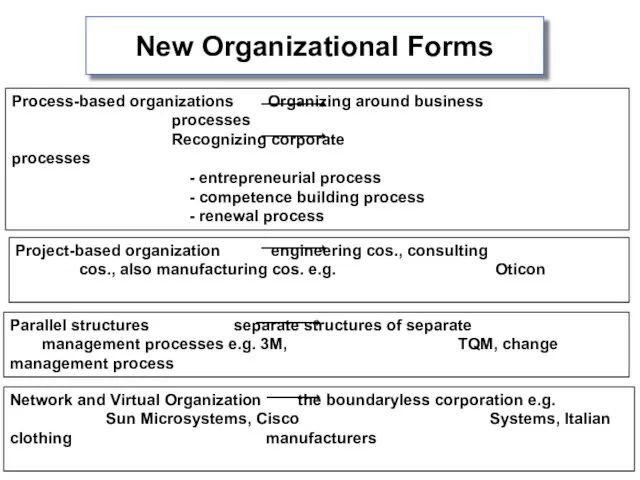
- 5. New Organizational Forms Process-based organizations Organizing around business processes Recognizing corporate processes - entrepreneurial process -
- 6. New Models of Leadership THE LEADERSHIP NEEDS OF ORGANIZATIONS The ability to: build confidence build enthusiasm
- 7. New Environment & Strategic Change Why are many companies surprised by changes in their industry environments?
- 8. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Managerial thinking and environmental change. Managers fail to anticipate
- 9. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness The problem of noticing. Interpretation of data. Limits in
- 10. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Failures in organizational learning also limit organizational adaptation and
- 11. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Lower-level learning Characterized by improvements in or refinements of
- 12. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Without higher-level learning, firms can fall into “competency traps.”
- 13. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Two factors influence the extent of higher-level learning: Higher-level
- 14. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Organizations can overcome the dangers of like-minded thinking in
- 15. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Power of industry influences in limiting organizational change. Industry
- 16. Factors that Contribute to Lack of Responsiveness Summary: 4 factors can limit responsiveness of managers to
- 17. Strategic Planning Processes Advantages of strategic planning: Allow firms to determine what needs to be done
- 18. Strategic Planning Processes Problems or limitations associated with strategic planning. Planning often fails to acknowledge the
- 19. Strategic Planning Processes (cont.) Planning data are often used -- incorrectly -- for evaluating the performance
- 21. Скачать презентацию
















 Организация как функция менеджмента
Организация как функция менеджмента Директ Кредит. Карьерный рост
Директ Кредит. Карьерный рост Раскрытие корпоративной информации
Раскрытие корпоративной информации Управление трудовыми ресурсами
Управление трудовыми ресурсами Развитие системы подбора и отбора персонала на предприятии
Развитие системы подбора и отбора персонала на предприятии EVENT-менеджмент. Технологические аспекты
EVENT-менеджмент. Технологические аспекты Рекламная кампания
Рекламная кампания Кросс-культурный менеджмент
Кросс-культурный менеджмент Opentext efile accelerates digital transformation in central and local government
Opentext efile accelerates digital transformation in central and local government Совершенствование системы управления качеством продукции на предприятии
Совершенствование системы управления качеством продукции на предприятии Навыки будущего для управленца настоящего
Навыки будущего для управленца настоящего CRM система. Описание и возможности CRM системы
CRM система. Описание и возможности CRM системы Электронные замки в гостинице
Электронные замки в гостинице Открытие малого предприятия по перевозке корпусной мебели с составлением бизнес-плана в условиях г. Казани
Открытие малого предприятия по перевозке корпусной мебели с составлением бизнес-плана в условиях г. Казани BMI KIA – бизнес менеджмент дилера
BMI KIA – бизнес менеджмент дилера Деловое общение
Деловое общение Методология и методы исследования в менеджменте
Методология и методы исследования в менеджменте Организация хозяйственных связей
Организация хозяйственных связей Понятие менеджмента. Специфика управленческого труда
Понятие менеджмента. Специфика управленческого труда Субъекты управления
Субъекты управления Оценка результатов деятельности организации. Тема 1.5
Оценка результатов деятельности организации. Тема 1.5 Элементы лидерства
Элементы лидерства 11-я конференция PharmaBusiness-2016
11-я конференция PharmaBusiness-2016 Управление качеством
Управление качеством Классификация организаций. Тема 7
Классификация организаций. Тема 7 Риск-менеджмент
Риск-менеджмент Управление интеграционными трансформациями в промышленности
Управление интеграционными трансформациями в промышленности Роль службы обслуживания и эсплутации номерного фонда в цикле обслуживания гостей
Роль службы обслуживания и эсплутации номерного фонда в цикле обслуживания гостей