Содержание
- 2. the open Net mobilize technical Internet community provide technical expertise talk to other stakeholders
- 3. Why bother Risk Management is the essence and purpose of all Information Security activities Everything you
- 4. Who cares? 60% of respondents stated company executives are only “somewhat” to “not at all” informed
- 5. What is risk management GRC: Governance, Risk management and Compliance Stage 0: ad hoc Stage 1:
- 6. Nature of risk management gap Cultural (“It is compliance driven stuff, we do not care, we
- 7. Measurement: Quantitative? Risk = Impact ($) * Probability Both variables are mostly unknown, yet estimated. The
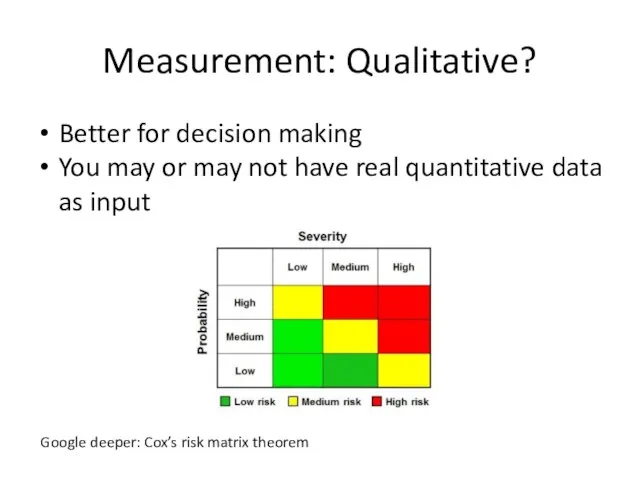
- 8. Measurement: Qualitative? Better for decision making You may or may not have real quantitative data as
- 9. Threat Intelligence “What’s happening out there”? Understanding risk through external context. Not just about 0-days and
- 10. Network operators as natural data source for threat intel Huge coverage Already having tools (IDS, traffic
- 11. Creating effective collaboration How should joint CERT work? Anything is always better than nothing. Coordinate, aggregate,
- 12. Three functions of joint CERT CC: coordinate effort and promote information exchange (here we start!) CSIRT:
- 13. Let’s get practical Why vulnerability management? Most of the breaches involve vulnerability of some kind Manageable
- 14. Vulnerability Management Stage 0: none Stage 0.5: [a]periodic scans, huge vulnerabilities lists, panic and depression (significant
- 15. Why pay premium price Because it is obviously valuable. And there is (or at least seems
- 16. Notable players (VM) Nessus one of best yet cheapest security scanners, but continuous vulnerability management (SecurityCenter)
- 17. Notable players (RM) An Israeli start-up, first (known to me) attempt to break vendor lock-in for
- 18. Industry’s Dirty Little Secret
- 19. As easy as that “Continuous vulnerability management” requires a database backend, vulnerability scanner connectors and a
- 20. How to evaluate vulnerability Like hackers (well, or pentesters ;-) do! The only things you need
- 21. A real life example Winshock (MS14-066) vulnerability Unauthenticated RCE in Windows SChannel code “Exploits are available”,
- 22. Simply put Traditional vulnerability scanning software scares you into thinking you have an immediate and imminent
- 23. Enter Vulners A search engine for exploits and security bulletins, contains 60+K exploits to date Non-profit
- 24. But, wait Vulners exploit search is for humans No formal definition exists for exploit capabilities Time
- 25. Enter ECDML and EACVSS Exploit Capability Definition Markup Language – describe exploit properties via CVE, CPE
- 26. Sorry for non-readable text ;-)
- 27. Back to risk analysis and FAIR methodology
- 28. What’s next Augment risk intelligence with Threat Event Frequency Implement (mostly) automated risk assessments using FAIR
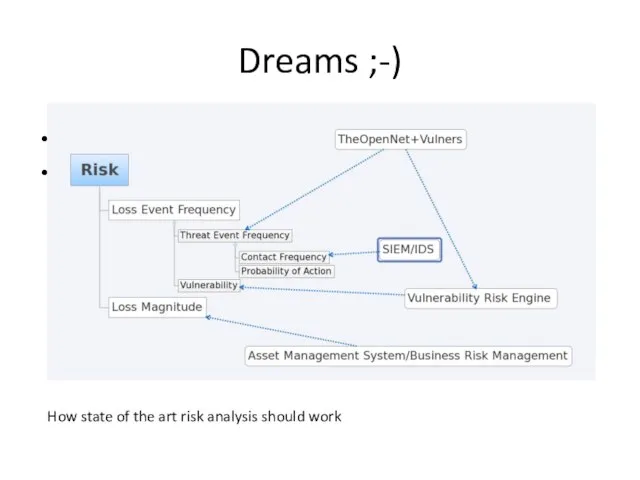
- 29. Dreams ;-) How state of the art risk analysis should work
- 30. Not covered here Advanced vulnerability management issues like detecting and avoiding vulnerability scan gaps, “scannerless” data
- 31. Useful links http://theopennet.ru https://www.vulners.com https://www.seccubus.com
- 33. Скачать презентацию











![Vulnerability Management Stage 0: none Stage 0.5: [a]periodic scans, huge vulnerabilities](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/544159/slide-13.jpg)
















 Корпоративная социальная ответственность и ее реализация в современных российских нефтегазовых компаниях
Корпоративная социальная ответственность и ее реализация в современных российских нефтегазовых компаниях Лидерство и стиль руководства
Лидерство и стиль руководства Основы управления персоналом
Основы управления персоналом Классификация услуг общественного питания. Порядок оказания услуг. Права потребителя услуг предприятия общественного питания
Классификация услуг общественного питания. Порядок оказания услуг. Права потребителя услуг предприятия общественного питания Elementy postępowania strategicznego. Analiza otoczenia i organizacji
Elementy postępowania strategicznego. Analiza otoczenia i organizacji Прохождение опроса в системе АСМА
Прохождение опроса в системе АСМА Tréning na PDR (Prehľad hodnotenia výkonnosti a rozvoja)
Tréning na PDR (Prehľad hodnotenia výkonnosti a rozvoja) Организационное консультирование
Организационное консультирование Характеристика имиджа. Имидж органа власти, как средство воздействия на массовое сознание и управленческий ресурс
Характеристика имиджа. Имидж органа власти, как средство воздействия на массовое сознание и управленческий ресурс Аттестация и оценка персонала
Аттестация и оценка персонала Кадровая политика организации
Кадровая политика организации Сущность и содержание организации как функции менеджмента
Сущность и содержание организации как функции менеджмента Развитие профессиональной культуры современного государственного служащего на основе технологий проектного управления
Развитие профессиональной культуры современного государственного служащего на основе технологий проектного управления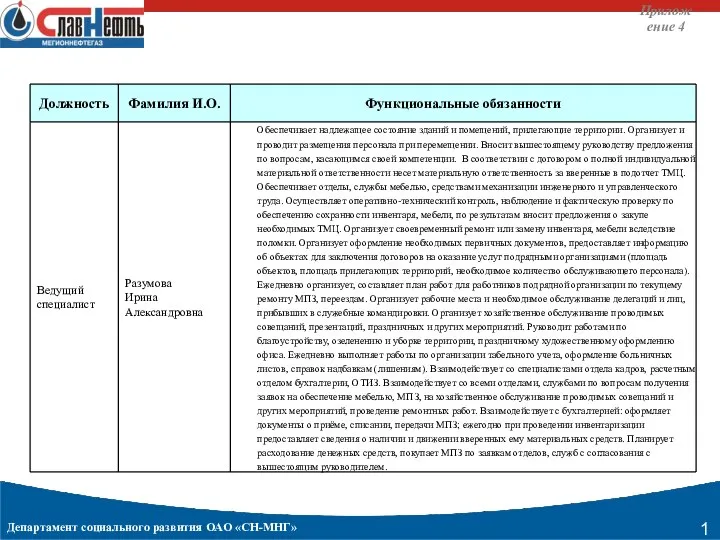 Функциональные обязанности
Функциональные обязанности Методы преодоления сопротивления изменениям
Методы преодоления сопротивления изменениям Nauka o organizacji i przedsiębiorstwie. Potencjał organizacji technologia. (Wyklad 5)
Nauka o organizacji i przedsiębiorstwie. Potencjał organizacji technologia. (Wyklad 5) Тайм-менеджмент для семьи
Тайм-менеджмент для семьи Поняття та класифікація управлінських рішень, вимоги до них
Поняття та класифікація управлінських рішень, вимоги до них Адаптация на новом рабочем месте
Адаптация на новом рабочем месте Понятие и расчёт абсентеизма
Понятие и расчёт абсентеизма Microsoft Dynamics NAV – система автоматизации деятельности предприятия
Microsoft Dynamics NAV – система автоматизации деятельности предприятия Проблемы устойчивого развития предприятия
Проблемы устойчивого развития предприятия Целевая аудитория
Целевая аудитория Выбор оптимального варианта складской системы
Выбор оптимального варианта складской системы Как укротить время. Основные принципы тайм-менеджмента
Как укротить время. Основные принципы тайм-менеджмента Команда Rosa салон красоты
Команда Rosa салон красоты Социологические методы в административно-государственном управлении
Социологические методы в административно-государственном управлении Учебное предприятие Развитие маркетинга
Учебное предприятие Развитие маркетинга