Содержание
- 2. Complexity in perception of society: Permanent Regular Stable for society can by find ?
- 3. Social philosophy: main problems: Society order Society (general) – Individuality (single) Freedom – Necessity Matter –
- 4. Social atomism only one aspiration of everyone is to be happy – individual happiness Society must
- 5. Social Universalism Society – strong and unique self-dependent reality Exists because of itself
- 6. Antiquity about society & personality: Plato Harmony – basic principle Authority of the leaders (philosophers must
- 7. Antiquity about society & personality: Aristotle Man outside the society is only abstraction Law - basic
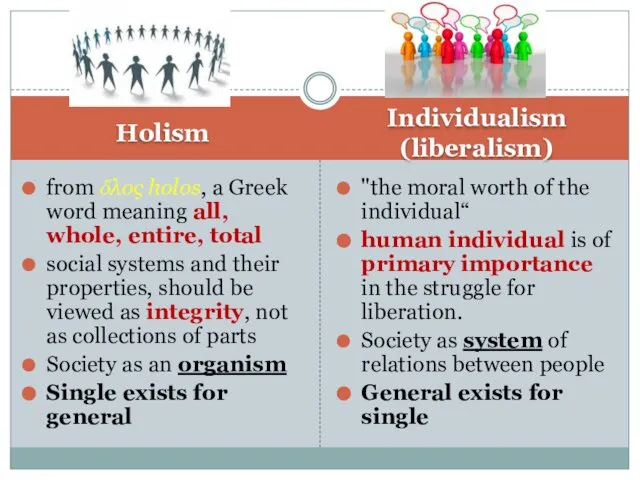
- 8. Holism Individualism (liberalism) from ὅλος holos, a Greek word meaning all, whole, entire, total social systems
- 9. Holism Individualism (liberalism) Sparta – hard administration Athenian democracy – freedom limited by democratically laws
- 10. John Locke (1632 –1704) theory was founded on social contract theory human nature is characterized by
- 11. Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (1770 –1831) All history of mankind is an unfolding of Absolute Reason
- 12. John Stuart Mill (1806 –1873) On Liberty the nature and limits of the power that can
- 13. "social liberty" - protection from "the tyranny of political rulers." He introduced a number of different
- 14. Social justice Can the world be possible without inequality? Where are the measures? What can be
- 15. Freedom Freedom from & freedom for “Escape from Freedom” Erich Fromm “freedom gives person feeling of
- 16. Linear & cyclical history conceptions
- 18. Civilization: Childhood – barbarians Youth – beginning of blossoming Maturity – bloom, prosperity Old age –
- 19. Modern world “Hypertrophy of means (resources, tools) & atrophy of goals” Consumer`s epoch
- 21. Скачать презентацию

















 Научное исследование. Научное познание
Научное исследование. Научное познание Чарльз Сандерс Пирс
Чарльз Сандерс Пирс Немецкий материализм и диалектика
Немецкий материализм и диалектика Осьовий час
Осьовий час Философское учение о познании (гносеология)
Философское учение о познании (гносеология) Основные законы логики
Основные законы логики Риторика Платона
Риторика Платона Типы мировоззрения
Типы мировоззрения Специфика научного исследования
Специфика научного исследования Структура философского знания. Тема 2
Структура философского знания. Тема 2 Познание мира
Познание мира Русский интуитивизм
Русский интуитивизм Основы философии
Основы философии Карл Маркс ( 1818-1883г.г.)
Карл Маркс ( 1818-1883г.г.) Россия в цивилизованном процессе. (Лекция 13)
Россия в цивилизованном процессе. (Лекция 13) Бытие человека. Лекция 11
Бытие человека. Лекция 11 Особенности Древней Индийской философии
Особенности Древней Индийской философии Свідомість. Виникнення свідомості і її суспільна природа
Свідомість. Виникнення свідомості і її суспільна природа Логический квадрат. Взаимоотношения между суждениями
Логический квадрат. Взаимоотношения между суждениями Определи вид данного суждения
Определи вид данного суждения Культура средневекового Китая. Даосизм. Конфуцианство
Культура средневекового Китая. Даосизм. Конфуцианство Введение в философию немецких романтиков
Введение в философию немецких романтиков Философская антропология
Философская антропология Наука как процесс познания
Наука как процесс познания Человек и общество
Человек и общество Философия Нового времени
Философия Нового времени Античная философия и наука
Античная философия и наука Вечное возвращение. Высшая форма утверждения жизни
Вечное возвращение. Высшая форма утверждения жизни