Содержание
- 2. Topics Covered Sensitivity Analysis Break Even Analysis Monte Carlo Simulation Decision Trees
- 3. How To Handle Uncertainty Sensitivity Analysis - Analysis of the effects of changes in sales, costs,
- 4. Sensitivity Analysis Example Given the expected cash flow forecasts for Otobai Company’s Motor Scooter project, listed
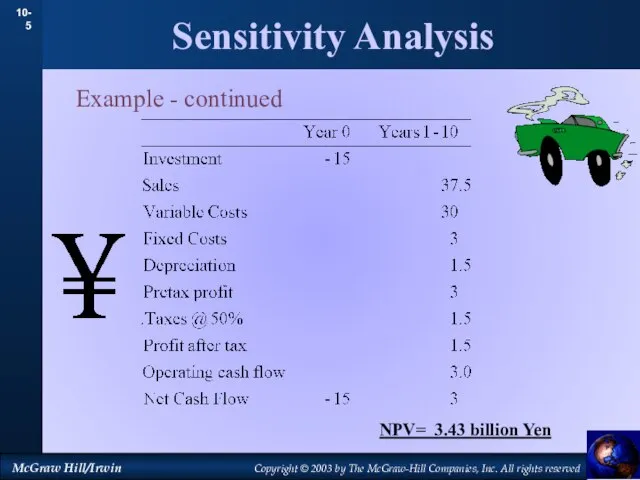
- 5. Sensitivity Analysis Example - continued NPV= 3.43 billion Yen
- 6. Sensitivity Analysis Example - continued Possible Outcomes
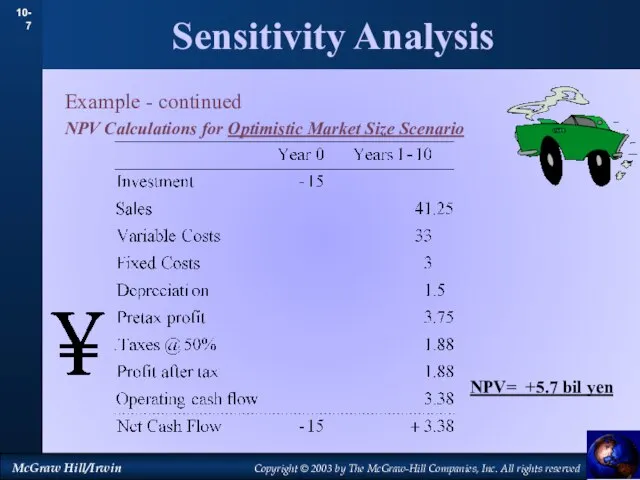
- 7. Sensitivity Analysis Example - continued NPV Calculations for Optimistic Market Size Scenario NPV= +5.7 bil yen
- 8. Sensitivity Analysis Example - continued NPV Possibilities (Billions Yen)
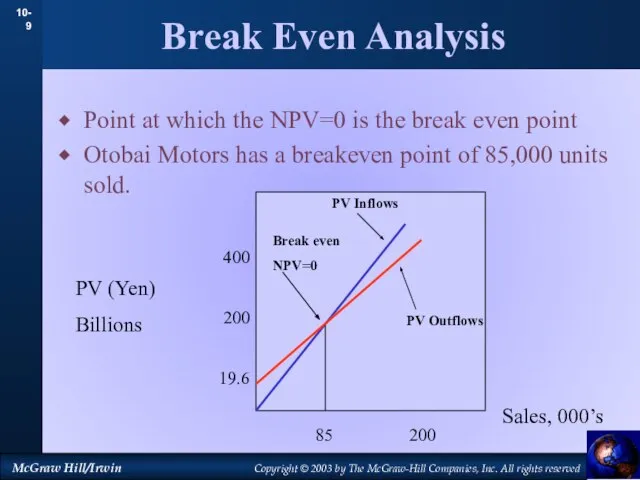
- 9. Break Even Analysis Point at which the NPV=0 is the break even point Otobai Motors has
- 10. Monte Carlo Simulation Step 1: Modeling the Project Step 2: Specifying Probabilities Step 3: Simulate the
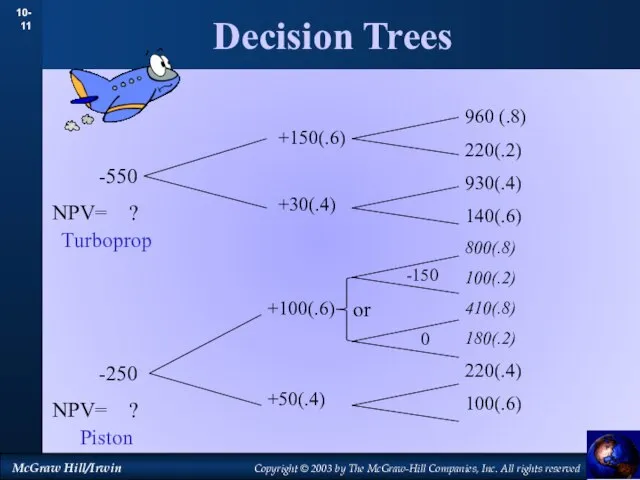
- 11. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) +150(.6) +30(.4) +100(.6)
- 12. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) +150(.6) +30(.4) +100(.6)
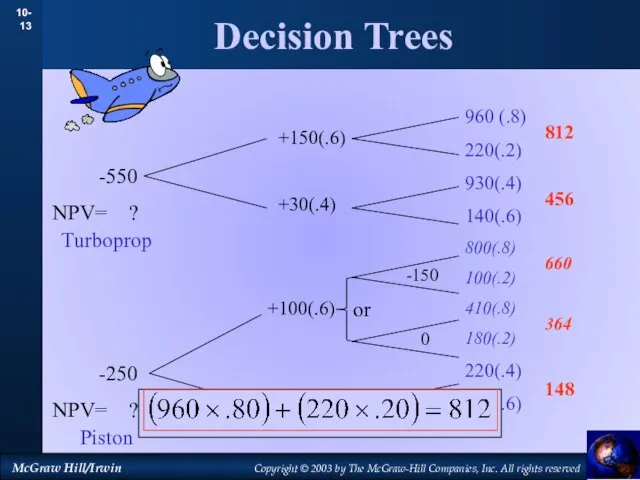
- 13. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) +150(.6) +30(.4) +100(.6)
- 14. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) -550 NPV= ?
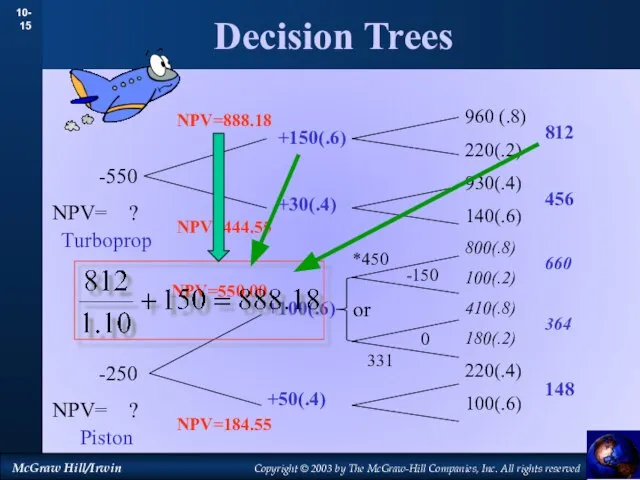
- 15. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) -550 NPV= ?
- 16. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) 812 456 660
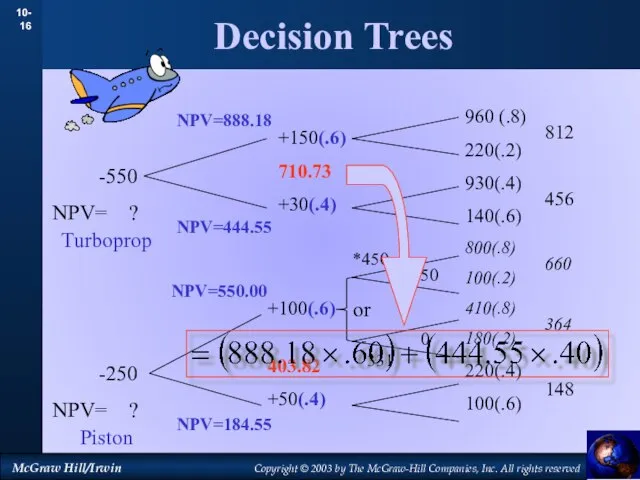
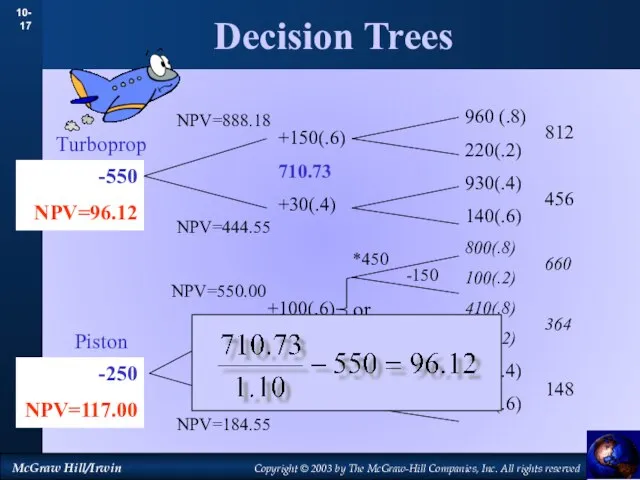
- 17. Decision Trees 960 (.8) 220(.2) 930(.4) 140(.6) 800(.8) 100(.2) 410(.8) 180(.2) 220(.4) 100(.6) 812 456 660
- 19. Скачать презентацию








 Методические рекомендации по вопросам представления сведений и заполнения соответствующейформы справки о доходах
Методические рекомендации по вопросам представления сведений и заполнения соответствующейформы справки о доходах Основы безопасности при использовании банковских карт
Основы безопасности при использовании банковских карт МСФО 19 Вознаграждения работникам
МСФО 19 Вознаграждения работникам Налог на прибыль организаций
Налог на прибыль организаций Слаиды 1 день
Слаиды 1 день Сравнительный подход
Сравнительный подход Особенности инфляционных процессов в РФ на современном этапе
Особенности инфляционных процессов в РФ на современном этапе Формы и системы оплаты труда
Формы и системы оплаты труда Роль и место бизнес-плана
Роль и место бизнес-плана Спонсорский пакет. Первый официальный чемпионат по киберспорту в дисциплине DOTA 2
Спонсорский пакет. Первый официальный чемпионат по киберспорту в дисциплине DOTA 2 Основные показатели деятельности компании ПАО МТС
Основные показатели деятельности компании ПАО МТС Что такое финансы
Что такое финансы Ценные бумаги в финансовом менеджменте
Ценные бумаги в финансовом менеджменте Формирование транспортно-распорядительной логистической инфраструктуры. Терминальнологистические центры (ТРЦ). (Лекция 3)
Формирование транспортно-распорядительной логистической инфраструктуры. Терминальнологистические центры (ТРЦ). (Лекция 3) Меры финансовой поддержки субъектов малого предпринимательства в РФ
Меры финансовой поддержки субъектов малого предпринимательства в РФ Инвестиционное предложение по освоению земельного участка площадью 5,4 Га
Инвестиционное предложение по освоению земельного участка площадью 5,4 Га Двойная запись
Двойная запись Основные параметры исполнения бюджета
Основные параметры исполнения бюджета Оценка рисков инвестиционной деятельности российских нефтегазовых компаний на зарубежных рынках
Оценка рисков инвестиционной деятельности российских нефтегазовых компаний на зарубежных рынках Пособие Дом по Почте
Пособие Дом по Почте Изменение порядка применения КОСГУ в 2019 году
Изменение порядка применения КОСГУ в 2019 году Основні заходи щодо раціонального та економного використання коштів місцевих бюджетів на 2018 рік у галузі освіта
Основні заходи щодо раціонального та економного використання коштів місцевих бюджетів на 2018 рік у галузі освіта Финансовая отчетность хозяйствующего субъекта, как источник информации для оценки его финансовой устойчивости
Финансовая отчетность хозяйствующего субъекта, как источник информации для оценки его финансовой устойчивости Социальное страхование
Социальное страхование Страхование. Закон РФ
Страхование. Закон РФ Повышение эффективности и удобства работы при переходе на 1С: Зарплата и Управление Персоналом 8
Повышение эффективности и удобства работы при переходе на 1С: Зарплата и Управление Персоналом 8 Деньги
Деньги Формы и система оплаты труда
Формы и система оплаты труда