Содержание
- 2. Fractiles Numbers that partition or divide an ordered data set into equal parts. The median of
- 3. Quartiles Approximately divide a data set into 4 equal parts There are 3 quartiles: First, Second,
- 4. 2nd Quartile, Q2 The Median of the entire data set Half the data entries lie on
- 5. 1st Quartile, Q1 The Median of the Lower half of the data set (below Q2) It
- 6. 3rd Quartile, Q3 The Median of the Upper half of the data set (above Q2) It
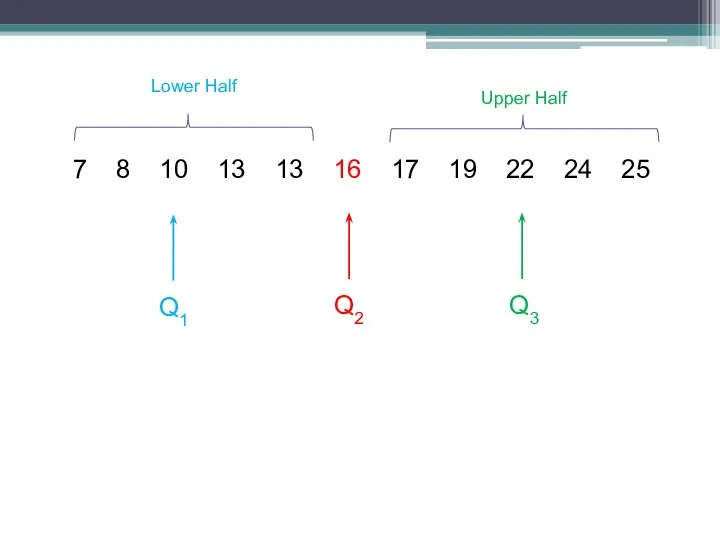
- 7. 7 8 10 13 13 16 17 19 22 24 25 Q2 Q1 Q3 Lower Half
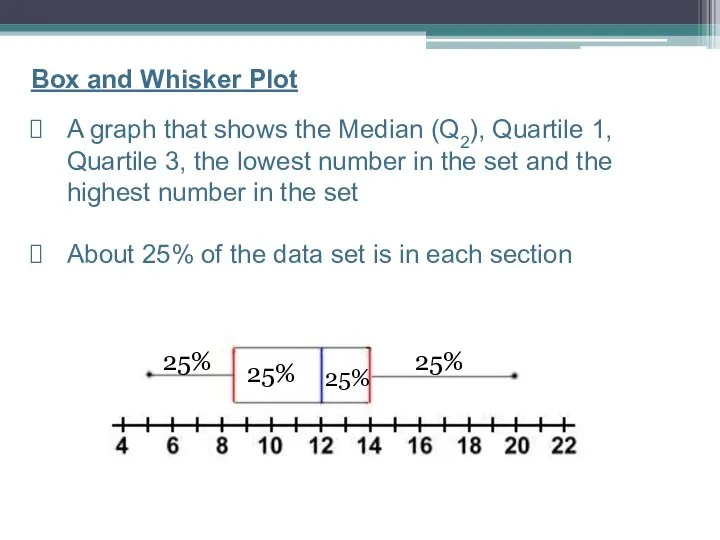
- 8. The Quartiles approximately divide the data into 4 equal parts, therefore 25% of the data is
- 9. Example 1: the test scores of 15 employees enrolled in a CPR training course are listed.
- 10. Example 2: The tuition costs (in thousands of dollars) for 11 universities are listed. Find the
- 11. Interquartile Range (IQR) The difference between the third and first quartiles IQR = Q3 – Q1
- 12. Find the Interquartile range from Example 1 Q1 = 10 and Q3 = 18 18 –
- 13. Find the Interquartile range from Example 2 Q1 = 17 and Q3 = 31 31 –
- 14. IQR – Interquartile Range (Q3 – Q1) Gives an idea of how much the middle 50%
- 15. Take a look at Example 1 ? The IQR is 8 5 7 9 10 11
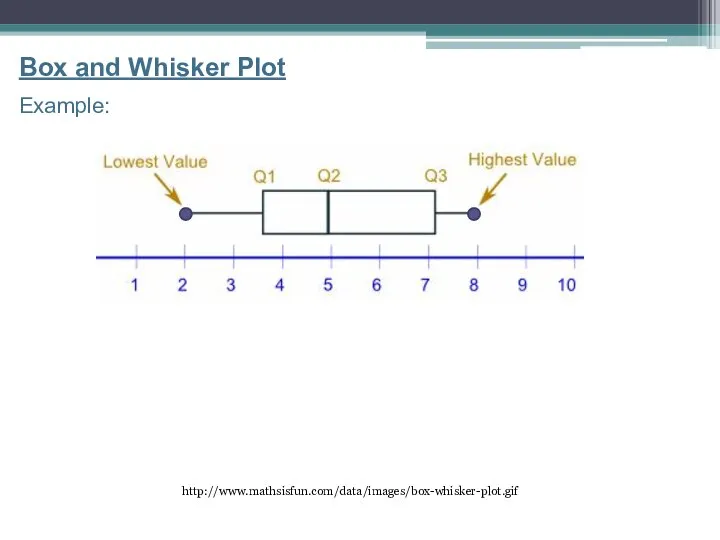
- 16. http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/images/box-whisker-plot.gif Box and Whisker Plot Example:
- 17. Box and Whisker Plot A graph that shows the Median (Q2), Quartile 1, Quartile 3, the
- 18. Steps for creating a box and whisker plot Find the Median (Q2) of all the numbers
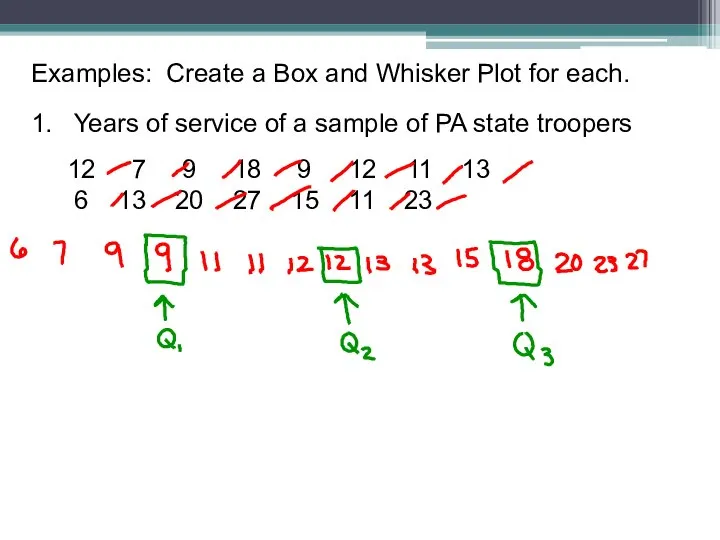
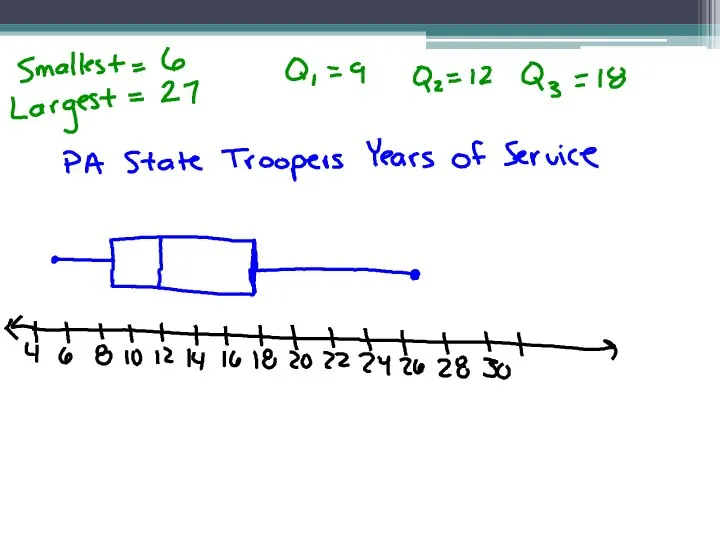
- 19. Examples: Create a Box and Whisker Plot for each. 1. Years of service of a sample
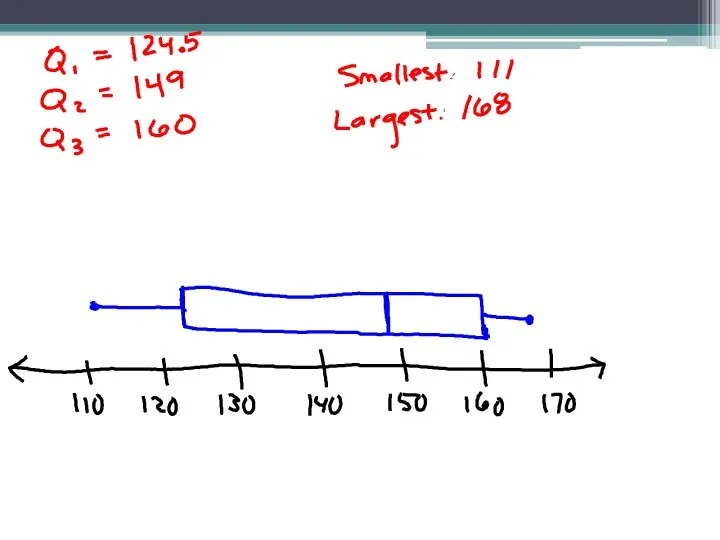
- 21. 2. 111 115 122 127 127 147 151 159 160 160 163 168
- 23. Distribution Shape Based on Box and Whisker Plot If the median is near the center of
- 25. Скачать презентацию
















 Признак перпендикулярности плоскостей
Признак перпендикулярности плоскостей ЕГЭ по математике - 2012. Решаем B13
ЕГЭ по математике - 2012. Решаем B13 Свойства логарифмов
Свойства логарифмов Статистическое изучение взаимосвязи социальноэкономических явлений
Статистическое изучение взаимосвязи социальноэкономических явлений Презентация по математике "Счёт в 1 классе" - скачать бесплатно
Презентация по математике "Счёт в 1 классе" - скачать бесплатно Линейная функция и её график
Линейная функция и её график Презентация на тему Единицы измерения Сантиметр
Презентация на тему Единицы измерения Сантиметр  Абсолютные и относительные величины в статистике
Абсолютные и относительные величины в статистике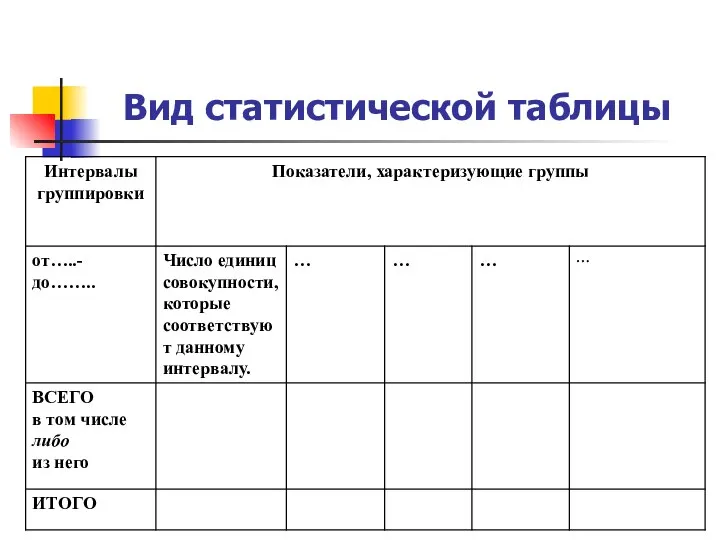 Вид статистической таблицы
Вид статистической таблицы приложение определенного интеграла в геометрии (12 класс)
приложение определенного интеграла в геометрии (12 класс) Model Parameterization in tomography problems. Lecture 4
Model Parameterization in tomography problems. Lecture 4 Логарифмические неравенства
Логарифмические неравенства Вписанная окружность в заданиях ЕГЭ
Вписанная окружность в заданиях ЕГЭ Геометрические фигуры вокруг нас
Геометрические фигуры вокруг нас Четырехугольники и их свойства
Четырехугольники и их свойства Математическое кафе Функция
Математическое кафе Функция Формула корней квадратного уравнения
Формула корней квадратного уравнения Векторы в пространстве
Векторы в пространстве Бой смекалистых
Бой смекалистых Методы многоскоростной обработки сигналов. Полифазные структуры многоскоростных систем
Методы многоскоростной обработки сигналов. Полифазные структуры многоскоростных систем Составление уравнения по условию задачи
Составление уравнения по условию задачи Возведение двучлена в любую натуральную степень
Возведение двучлена в любую натуральную степень Подготовка к ГИА. Изучение поведения функций и построение их графиков. Решение систем уравнений
Подготовка к ГИА. Изучение поведения функций и построение их графиков. Решение систем уравнений Нахождения дроби от числа, числа по его дроби ( 6 класс)
Нахождения дроби от числа, числа по его дроби ( 6 класс) Десятичные дроби и действия над ними
Десятичные дроби и действия над ними Векторная алгебра
Векторная алгебра  Численные методы решения систем нелинейных алгебраических уравнений
Численные методы решения систем нелинейных алгебраических уравнений Статистические методы обработки информации
Статистические методы обработки информации