Содержание
- 2. The Skin Hypodermis (subcutaneous fatty tissue) Dermis the true skin Epidermis
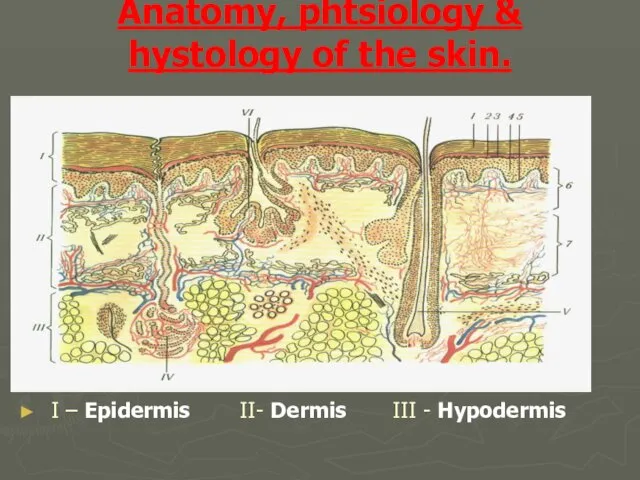
- 3. Anatomy, phtsiology & hystology of the skin. I – Epidermis II- Dermis III - Hypodermis
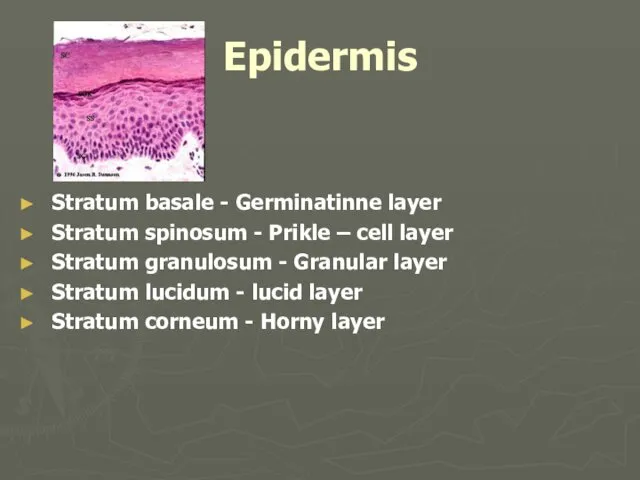
- 4. Epidermis Stratum basale - Germinatinne layer Stratum spinosum - Prikle – cell layer Stratum granulosum -
- 5. Epidermis 1.Stratum basale (germinative layer) Keratinoblastis (1 layer, like a polisade). Melanoblastis (their ratio is 1:11
- 6. Epidermis 2. Stratum spinosum (pricle-cell layer) Dendritic epidermocytis (5-7 layers) Langhan’s cells Hrenstayin’s cells 3. Stratum
- 7. Epidermis 4. Stratum lucidum (lucid layer) These cells contain eleidin. Str. lucidum contains glycogens, lipoids, fatty
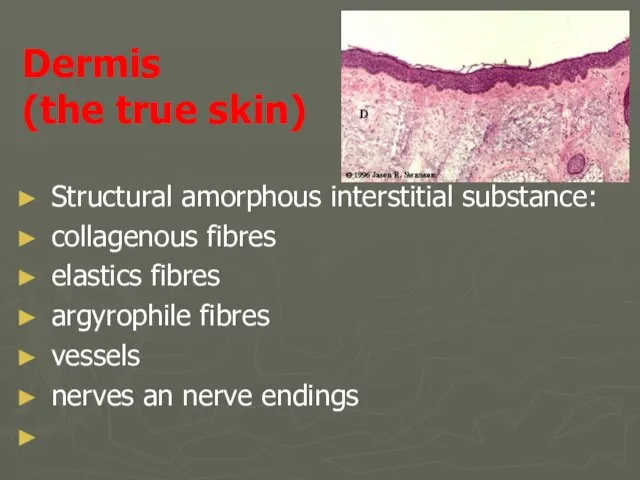
- 8. Dermis (the true skin) Structural amorphous interstitial substance: collagenous fibres elastics fibres argyrophile fibres vessels nerves
- 9. Dermis (the true skin) True homogeneous membrane Lipoids Mucopolysaccharides (mainly, hyaluronic and chondroitin – sulfuric acids)
- 10. Dermis (the true skin) Cells structure Fibroblasts Histiocytes Lymphocytes Mast cells Plasma cells Melanophages Epithelial appendages
- 11. Protective (barrier) functions of the skin Protects the organism from the damaging effect of sun rays
- 12. Protective (barrier) functions of the skin An acid (pH5.0-6,0) water-lipid mantle which attenuatus or neutralizis the
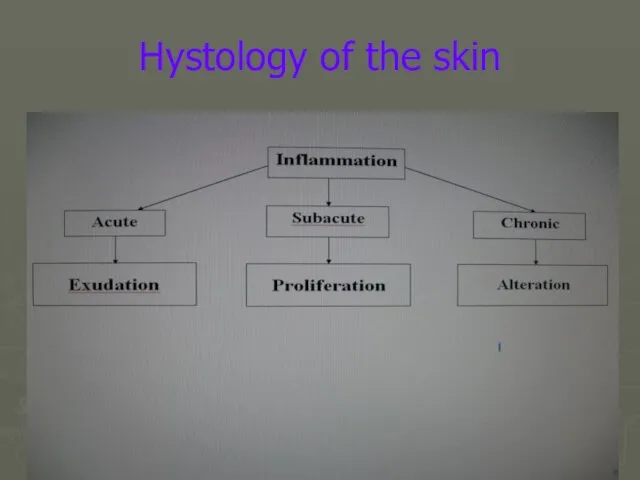
- 13. Hystology of the skin
- 14. Hystology of the skin
- 15. Hystology of the skin
- 16. Hystology of the skin
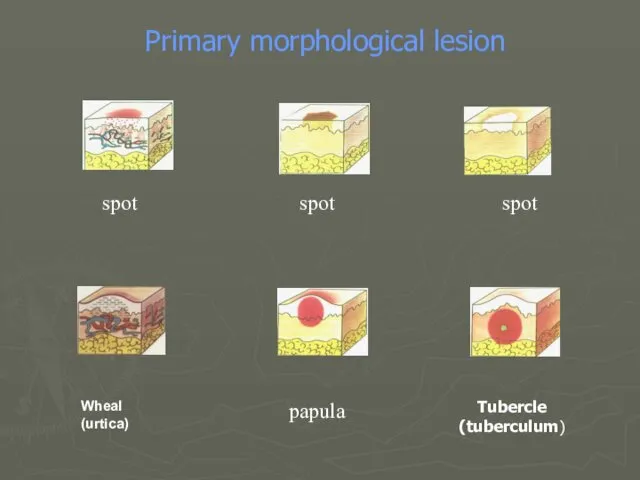
- 19. spot spot spot Tubercle (tuberculum) Wheal (urtica) Primary morphological lesion papula
- 20. Primary morphological lesion Pustule (pustula) Phlyctena Staphyloccal impetigo Nodule (nodus) Vesicle (vesicula) Blister (bulla)
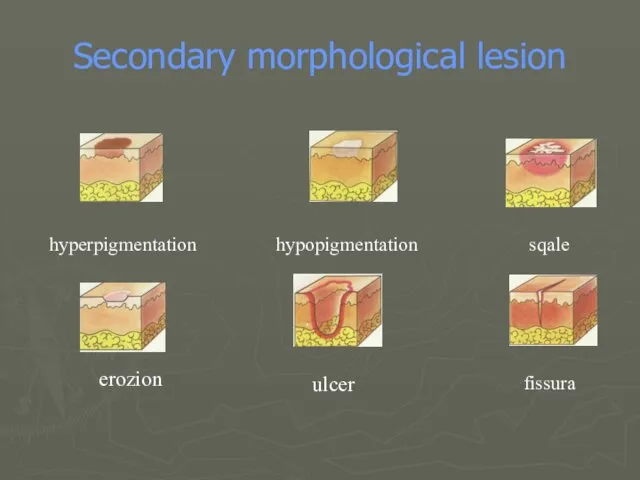
- 21. Secondary morphological lesion hyperpigmentation hypopigmentation sqale erozion ulcer fissura
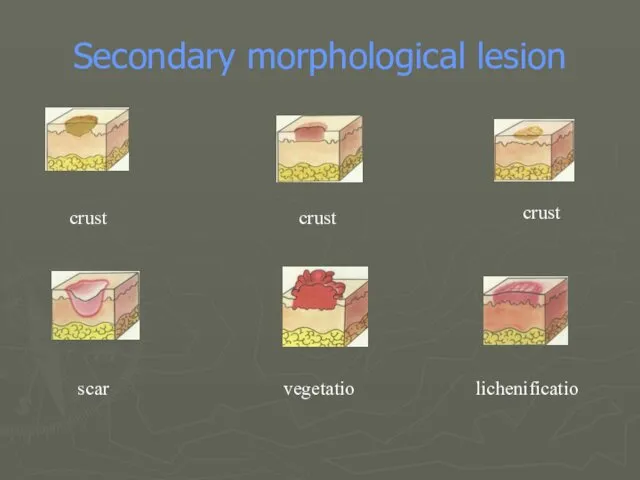
- 22. Secondary morphological lesion crust crust crust scar vegetatio lichenificatio
- 24. Скачать презентацию














 Предмет, объект и задачи психологии как науки
Предмет, объект и задачи психологии как науки Лекарственные средства, влияющие на вегетативную нервную систему
Лекарственные средства, влияющие на вегетативную нервную систему Международный день объятий
Международный день объятий Гонорея
Гонорея Клуб будущих и молодых мам Саратова. Роды
Клуб будущих и молодых мам Саратова. Роды Иммунодефицитный или инфекционно-воспалительный синдром
Иммунодефицитный или инфекционно-воспалительный синдром Гидроторакс
Гидроторакс Административно-принудительные меры медицинского характера
Административно-принудительные меры медицинского характера Учебная версия медицинской информационной системы (МИС)
Учебная версия медицинской информационной системы (МИС) Легочные инфекции. Пневмонии
Легочные инфекции. Пневмонии Фармакотерапия в акушерстве
Фармакотерапия в акушерстве ВКР: Профессиональная карта фельдшера при анемии у детей школьного возраста
ВКР: Профессиональная карта фельдшера при анемии у детей школьного возраста Болезнь Помпе
Болезнь Помпе Шұғыл және төтенше жағдайдағы жедел жәрдем беру қызметін ұйымдастыру
Шұғыл және төтенше жағдайдағы жедел жәрдем беру қызметін ұйымдастыру Коронавирус! Обновлённая информация по состоянию на 15 сентября 2020 года
Коронавирус! Обновлённая информация по состоянию на 15 сентября 2020 года Мочевая система
Мочевая система Наследственные болезни человека
Наследственные болезни человека Причины дизонтогенеза. Общие и частные закономерности аномального развития
Причины дизонтогенеза. Общие и частные закономерности аномального развития Опухоли: условие, причина
Опухоли: условие, причина ВКР: Методика физической реабилитации людей пожилого возраста с остеохондрозом шейного отдела позвоночника
ВКР: Методика физической реабилитации людей пожилого возраста с остеохондрозом шейного отдела позвоночника Панкреонекроз
Панкреонекроз Презентация Свойства степени с натуральным показателем
Презентация Свойства степени с натуральным показателем Практически нормальное зрение
Практически нормальное зрение Ингарон. Лекарственная форма
Ингарон. Лекарственная форма Амбулаторлық карта
Амбулаторлық карта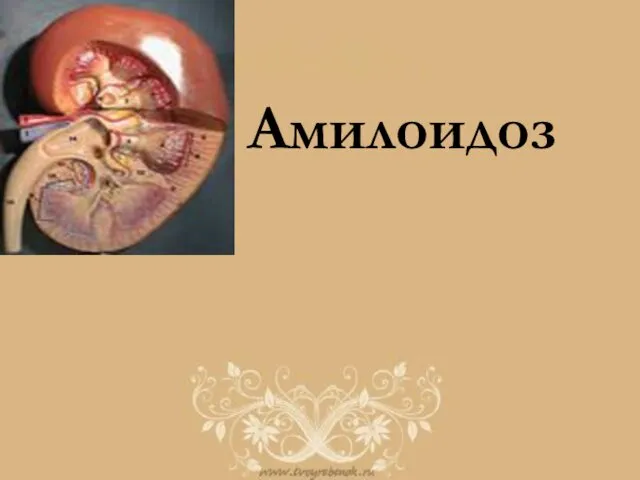 Амилоидоз. Классификация
Амилоидоз. Классификация Внутричерепное давление
Внутричерепное давление Акселерация. Теории акселерации
Акселерация. Теории акселерации