Содержание
- 2. Day 1 Understanding your role in HMIS, key indicators, understanding your data collection tools, and pivot
- 3. Introductions, Expectations, and ground rules
- 4. Please state: Your name Facility and role One expectation for the workshop The best thing about
- 5. Training Objectives, Design, and Agenda
- 6. Training Objectives To assist participants in understanding their data collection tools better To enable participants to
- 7. Workshop Design You will interact with all your data collection tools and materials from the point
- 8. Agenda Day 1: Understanding your role in HMIS, key indicators, understanding your data collection tools, and
- 9. HMIS Overview and Your Place In It Understanding the system
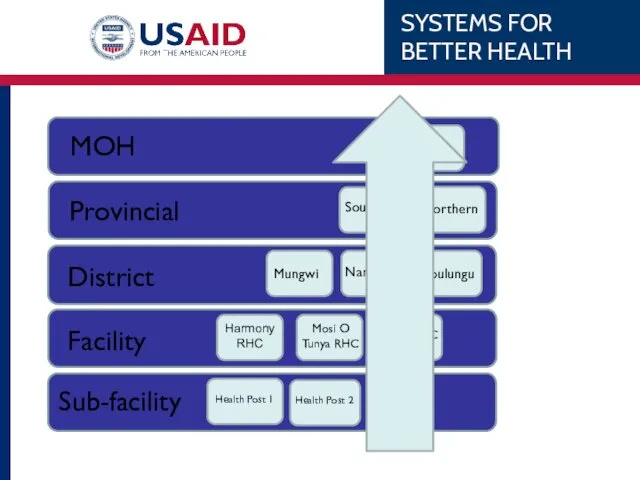
- 10. Understanding the System To understand data collection you have to first understand the health system. A
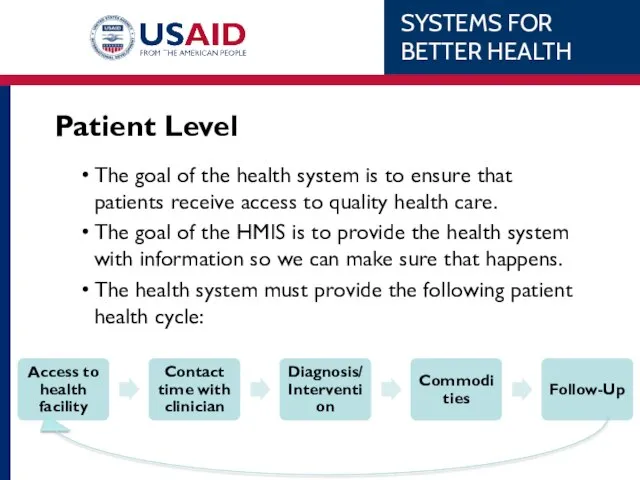
- 11. Patient Level The goal of the health system is to ensure that patients receive access to
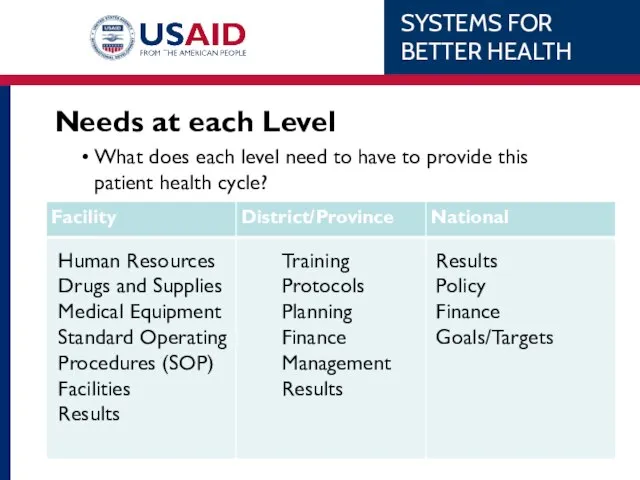
- 12. Needs at each Level What does each level need to have to provide this patient health
- 13. Putting it together National: Results Policy Finance Goals District: Results Finance Training Protocols Management Protocols Facility:
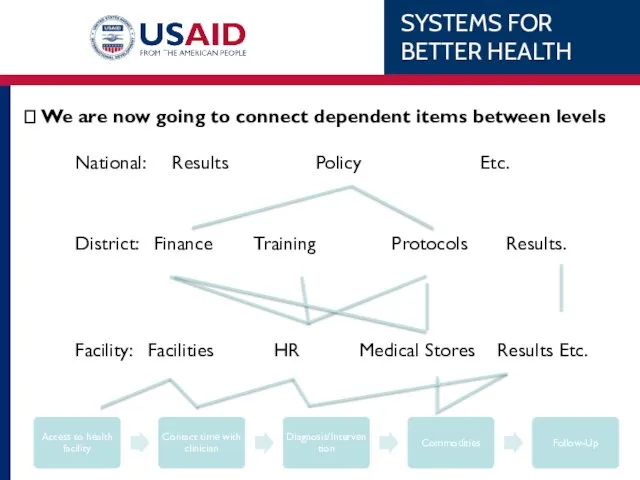
- 14. Understanding the Connectedness Every critical item in the patient cycle does not stand alone. Every item
- 15. ? We are now going to connect dependent items between levels National: Results Policy Etc. District:
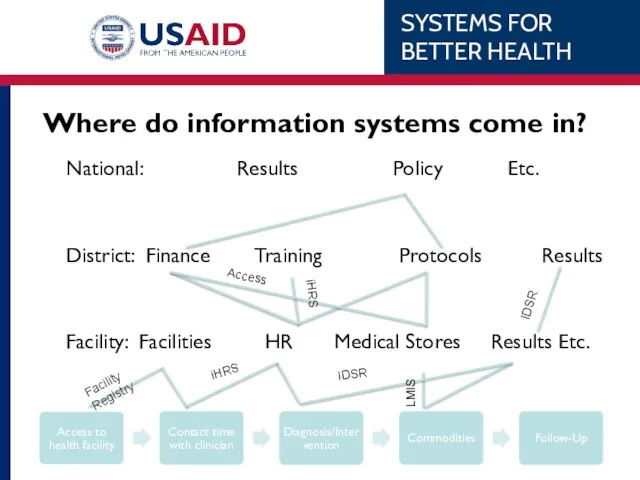
- 16. Where do information systems come in? These information systems allow people who can make decisions to
- 17. Where do information systems come in? National: Results Policy Etc. District: Finance Training Protocols Results Facility:
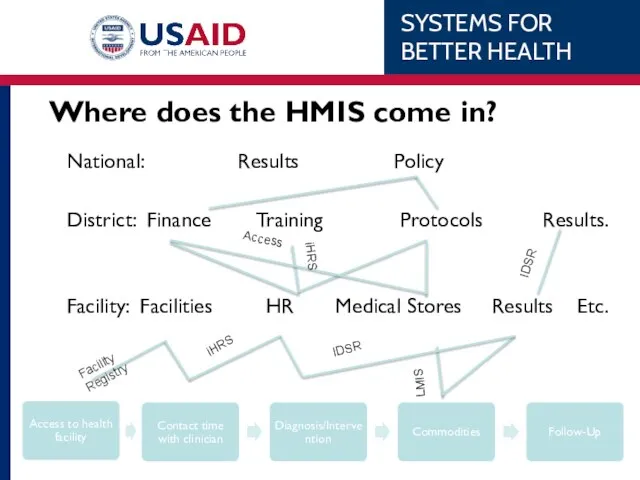
- 18. Where does the HMIS come in? National: Results Policy District: Finance Training Protocols Results. Facility: Facilities
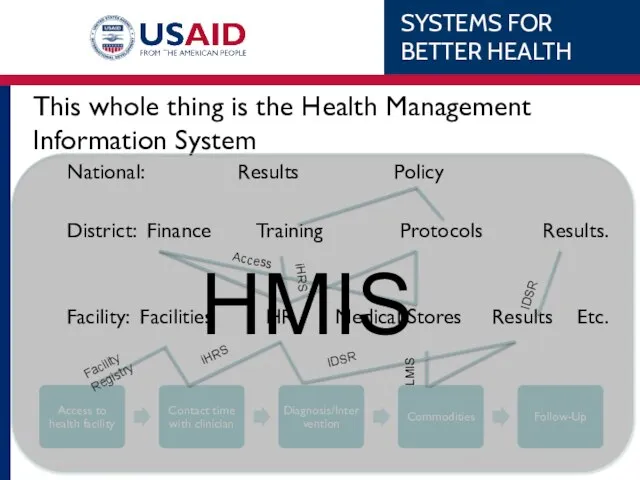
- 19. This whole thing is the Health Management Information System National: Results Policy District: Finance Training Protocols
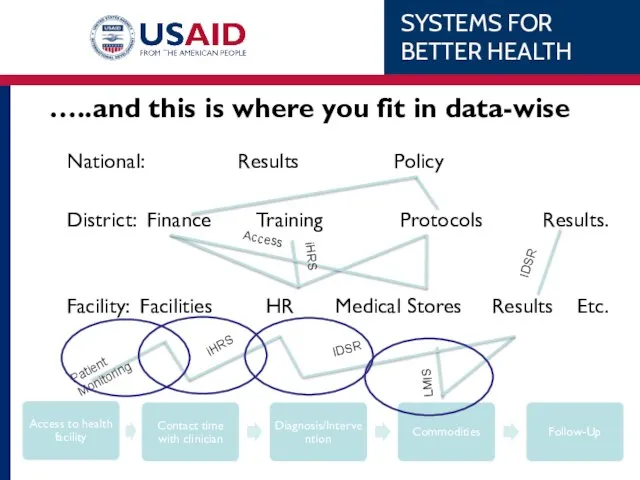
- 20. …..and this is where you fit in data-wise National: Results Policy District: Finance Training Protocols Results.
- 21. Current reporting challenges Discussion
- 22. Facility Level Reporting
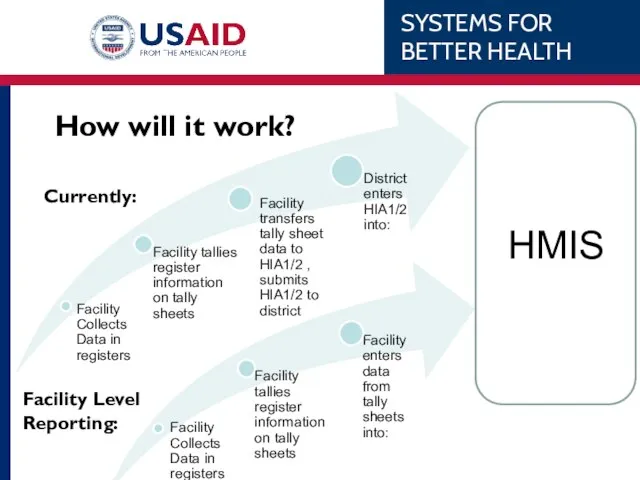
- 23. How will it work? HMIS Currently: Facility Level Reporting:
- 24. Theory of Change By having you (facility staff) directly enter data into the HMIS (DHIS2), we
- 25. Key HMIS indicators Understanding YOUR data
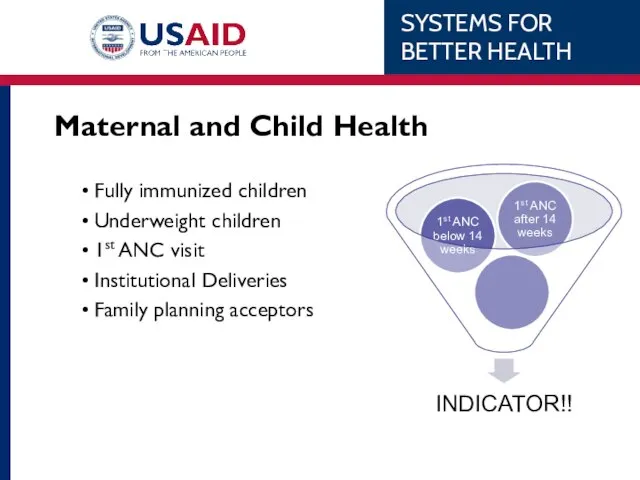
- 26. Maternal and Child Health Fully immunized children Underweight children 1st ANC visit Institutional Deliveries Family planning
- 27. HIV/AIDS PMTCT Virology/Serology General counselling and Testing Current in ART ART retention VMMC
- 28. Tuberculosis Notifications for TB Percentage of Retreatment cases Cure Rate Mortality Rate Commenced on ARVs Commenced
- 29. Sexually Transmitted Infections STI cases STI+ tested for HIV
- 30. Adolescent/Reproductive Health 1st ANC HIV positive adolescents Adolescents on family planning
- 31. Malaria Incidence/1000 Cases under 5 Cases over 5
- 32. Your data collection tools Understanding Facility Registers (DHIO to present)
- 33. Facility Registers These are used to collect raw data Individual data elements are counted against each
- 34. Tally Sheets These “tally” up totals from registers Consolidate register data into a smaller, more digestible
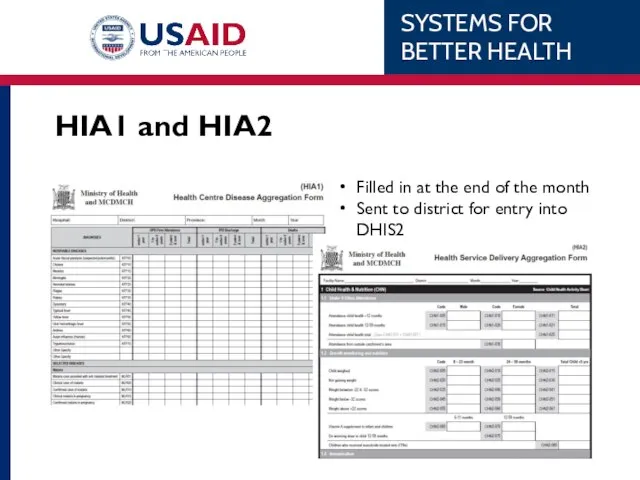
- 35. HIA1 and HIA2 Filled in at the end of the month Sent to district for entry
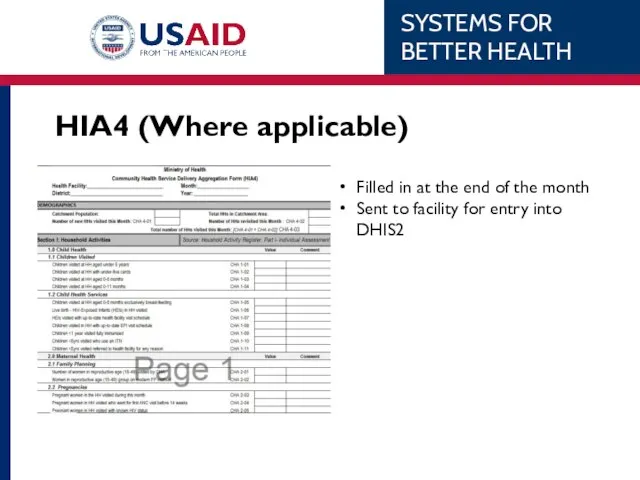
- 36. HIA4 (Where applicable) Filled in at the end of the month Sent to facility for entry
- 37. Exercise Think about registers you have problems with. Depending on what the group comes up with,
- 38. Tips for making the collection and troubleshooting process easier Fill in data as you see patients
- 39. Data Quality
- 40. Generating Quality Data Before submitting reports, data collectors must: Spot-check a small percentage of the data
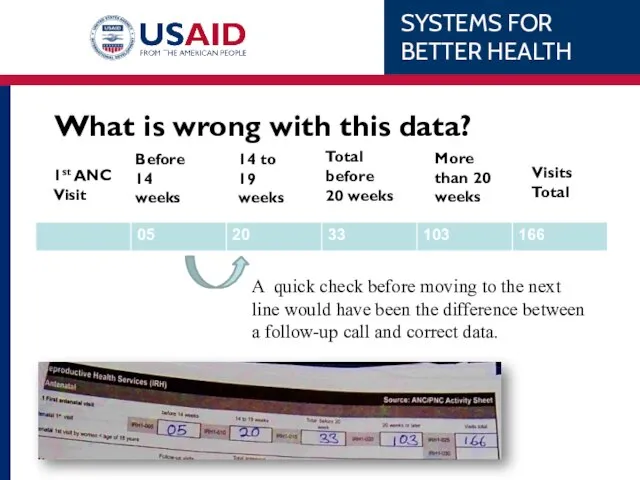
- 41. What is wrong with this data?
- 42. Exercise Use the registers and tally sheets you brought with you to identify errors in the
- 43. Day 2 Into DHIS2 -- creating charts and pivot tables, saving favorites, and practicing data entry
- 44. What is DHIS2? District Health Information System Open source software Born out of HISP Zambia’s adopted
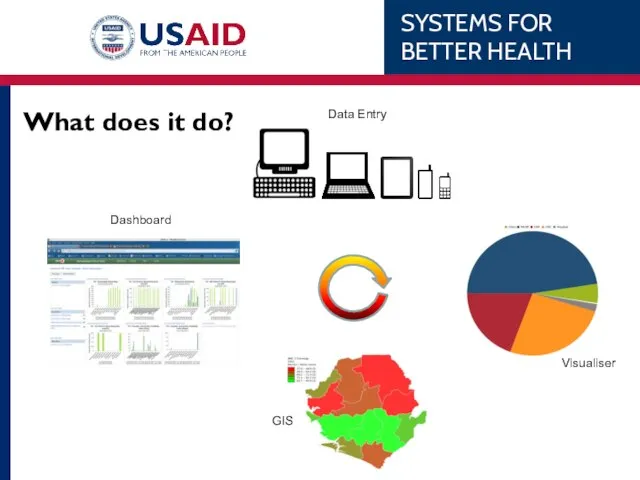
- 45. What does it do?
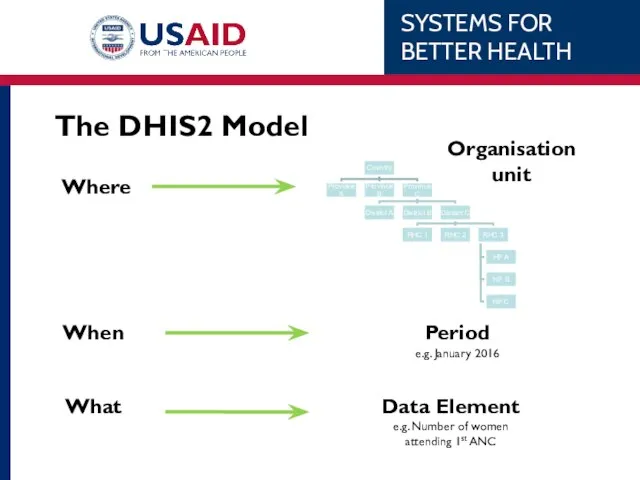
- 46. The DHIS2 Model
- 47. Pivot Tables Module:
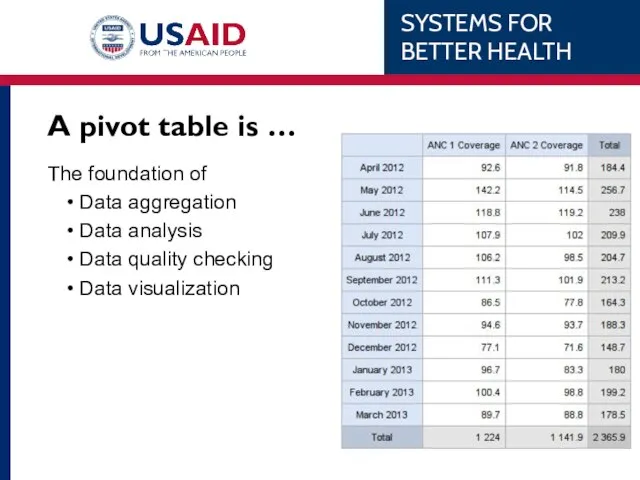
- 48. A pivot table is … A tool that allows you to reorganize or pivot data into
- 49. A pivot table is … The foundation of Data aggregation Data analysis Data quality checking Data
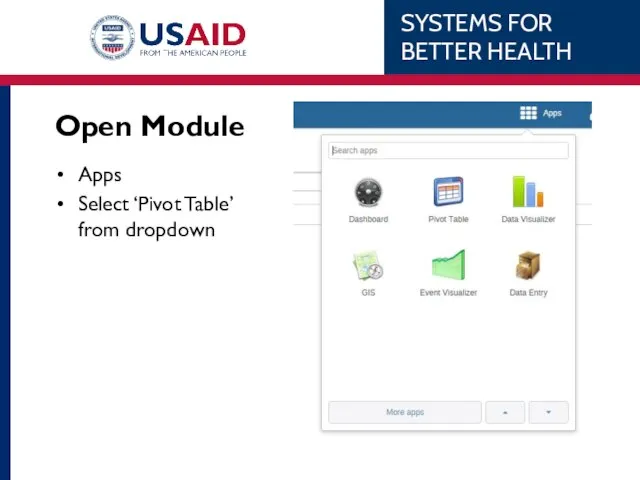
- 50. Open Module Apps Select ‘Pivot Table’ from dropdown
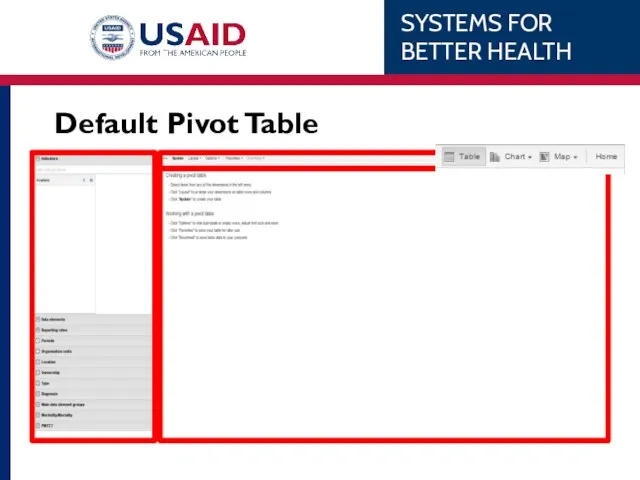
- 51. Default Pivot Table
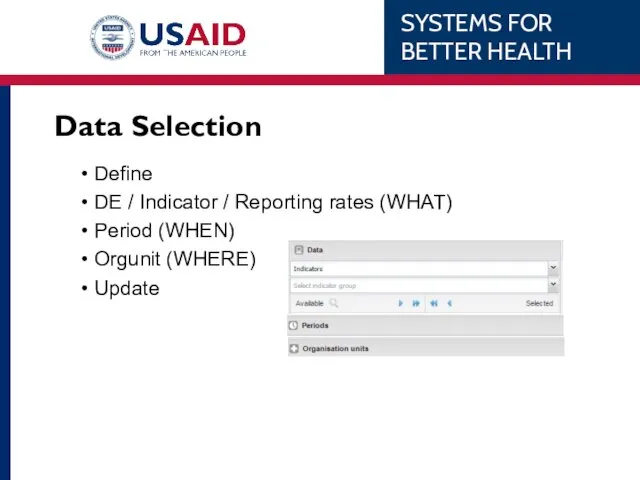
- 52. Data Selection Define DE / Indicator / Reporting rates (WHAT) Period (WHEN) Orgunit (WHERE) Update
- 53. WHAT Indicator Data Elements Reporting Rates WHEN Relative e.g. last 12 months Fixed e.g. Feb 2014
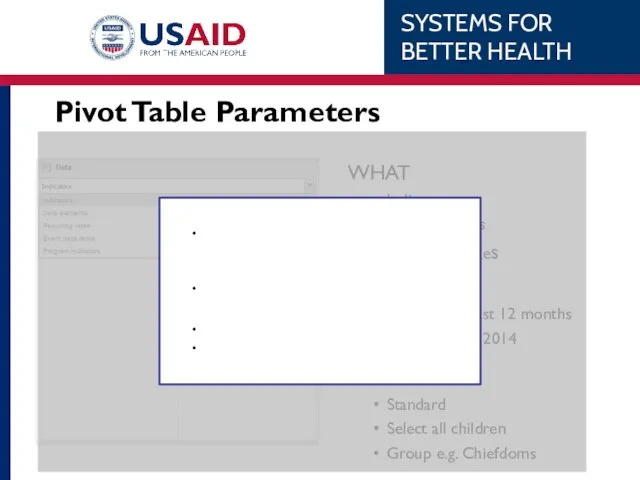
- 54. Pivot Table Parameters: When Relative Months Years Quarters Fixed Days Weeks Months Quarters Years
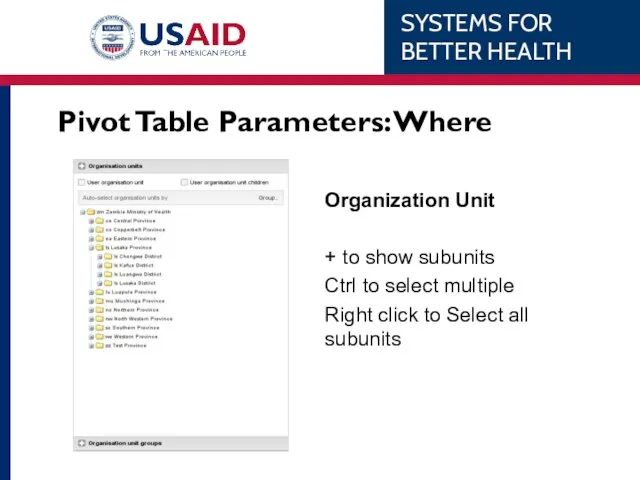
- 55. Pivot Table Parameters: Where Organization Unit + to show subunits Ctrl to select multiple Right click
- 56. Harmony RHC
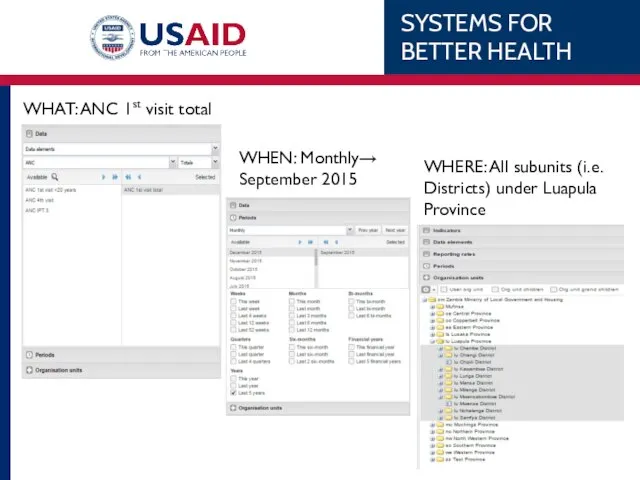
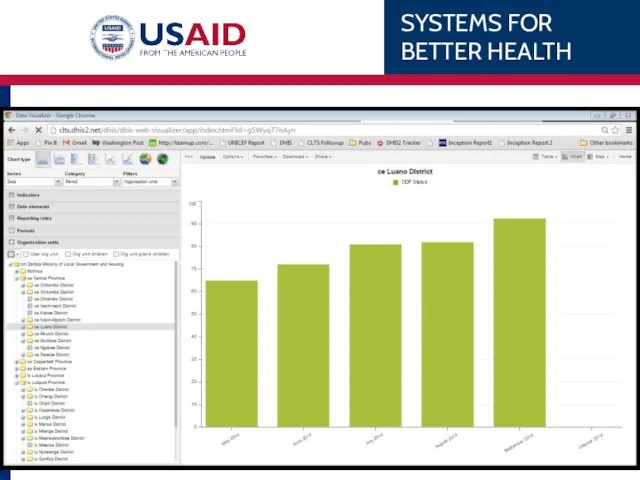
- 57. WHEN: Monthly→ September 2015 WHERE: All subunits (i.e. Districts) under Luapula Province WHAT: ANC 1st visit
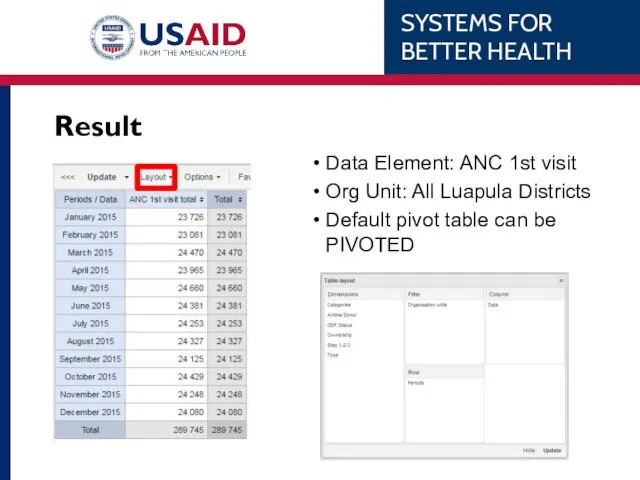
- 58. Result Data Element: ANC 1st visit Org Unit: All Luapula Districts Default pivot table can be
- 59. Pivoting / Changing layout Select ‘Layout’ Drag-n-drop orgunits to rows
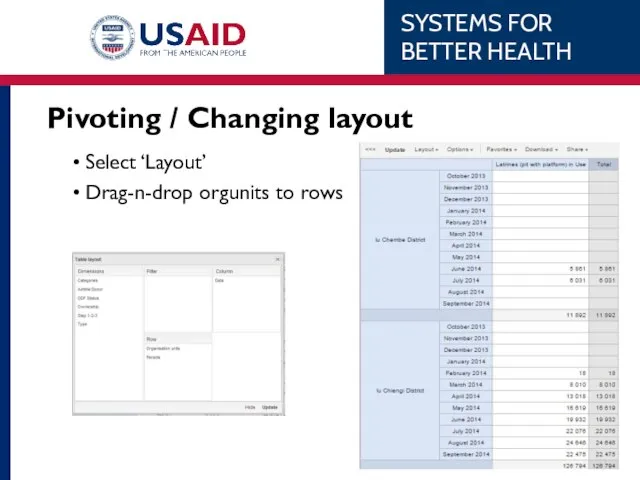
- 60. Pivoting / Changing layout Select ‘Layout’ Drag-n-drop orgunits to column
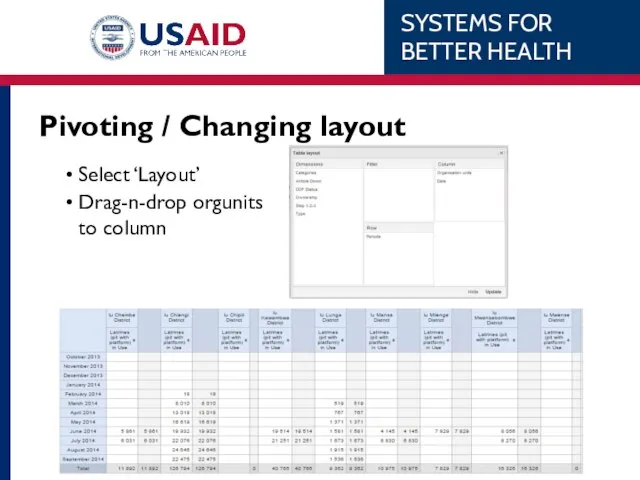
- 61. Options Small modifications in formatting Show totals Show sub-totals
- 62. Worked Example…
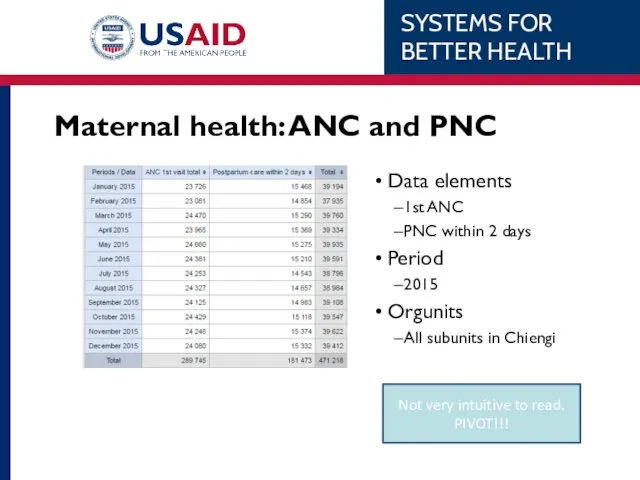
- 63. Not very intuitive to read. PIVOT!!! Maternal health: ANC and PNC Data elements 1st ANC PNC
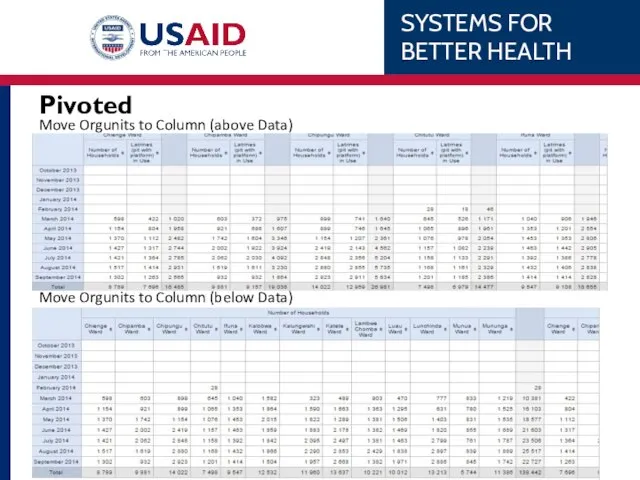
- 64. Move Orgunits to Column (below Data) Move Orgunits to Column (above Data) Pivoted
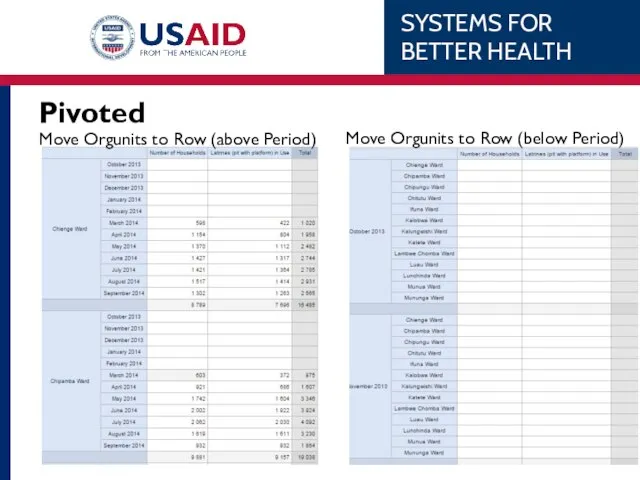
- 65. Pivoted Move Orgunits to Row (above Period) Move Orgunits to Row (below Period)
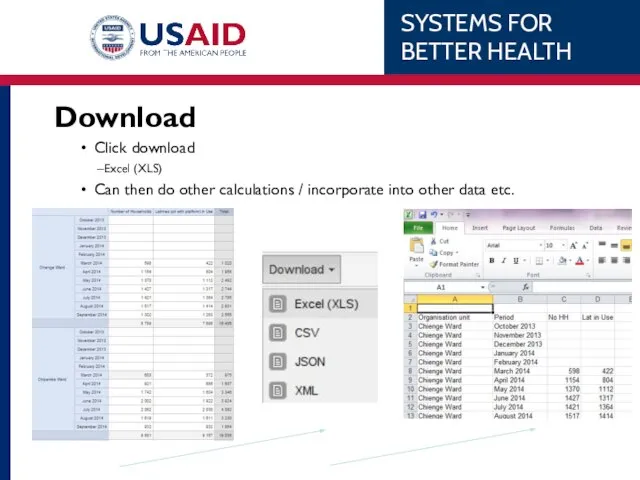
- 66. Download Click download Excel (XLS) Can then do other calculations / incorporate into other data etc.
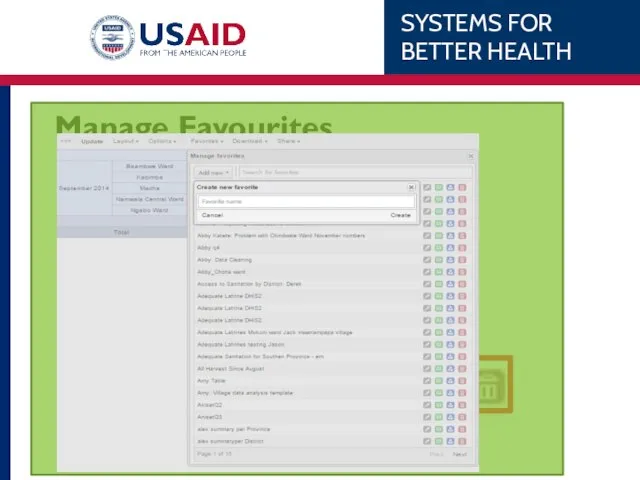
- 67. Manage Favourites Add New Open saved chart Rename Overwrite Share Delete
- 68. Exercise Sheet Work through each example on the worksheet Don’t skip any sections Ask for help
- 69. Charts Module:
- 70. Overview Charts, graphs, and tables provide a great deal of visual appeal. They allow users to
- 71. Overview cont’d In educational settings, charts, graphs, and tables can be used to represent data. Illustrate
- 72. Six things conveyed by charts & graphs Comparisons Relationships Distribution Trends Composition Flow/process, or location
- 73. Reasons for creating charts and graphs Make important trends easily recognizable Allow users to perceive information
- 74. Charting considerations Type of data Purpose of the data Nature of the data or relationship being
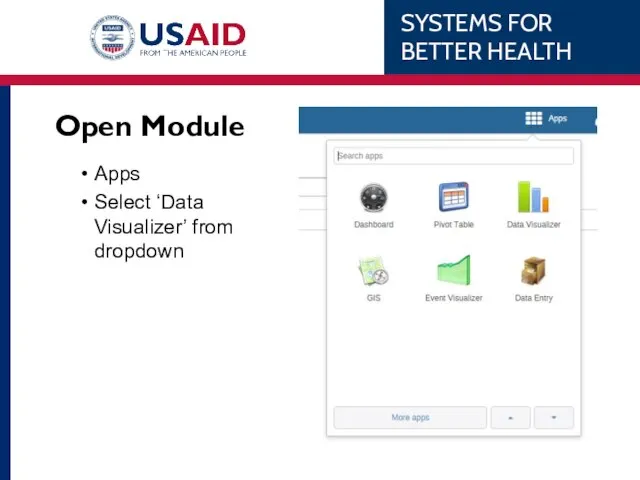
- 75. Open Module Apps Select ‘Data Visualizer’ from dropdown
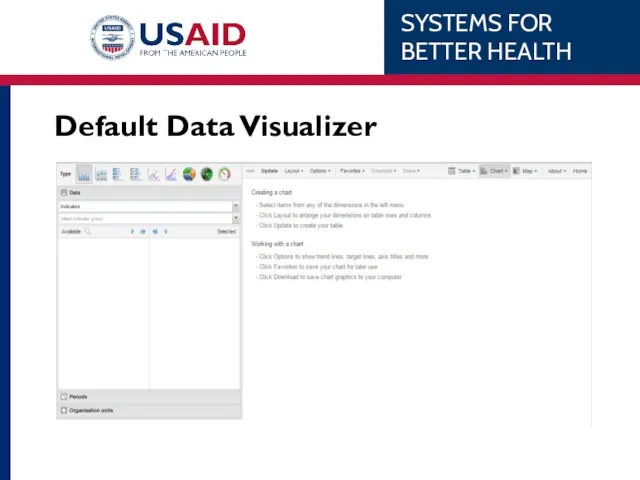
- 76. Default Data Visualizer
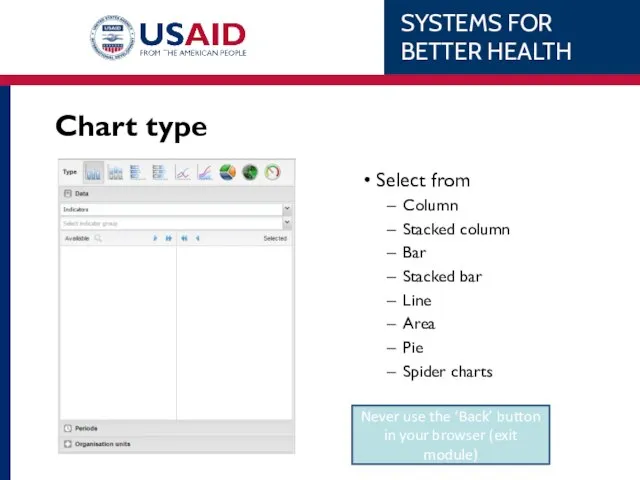
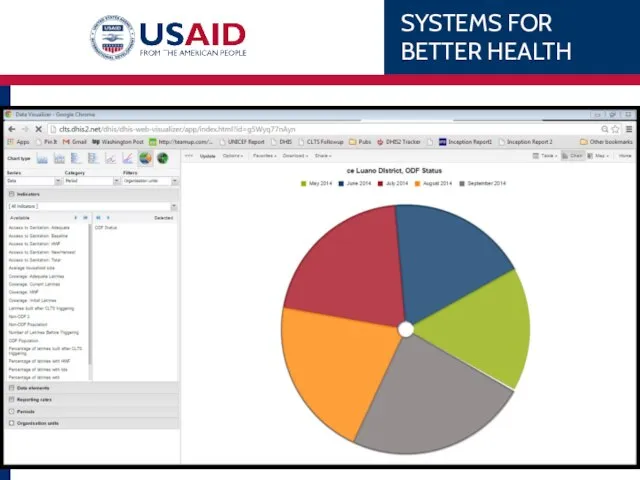
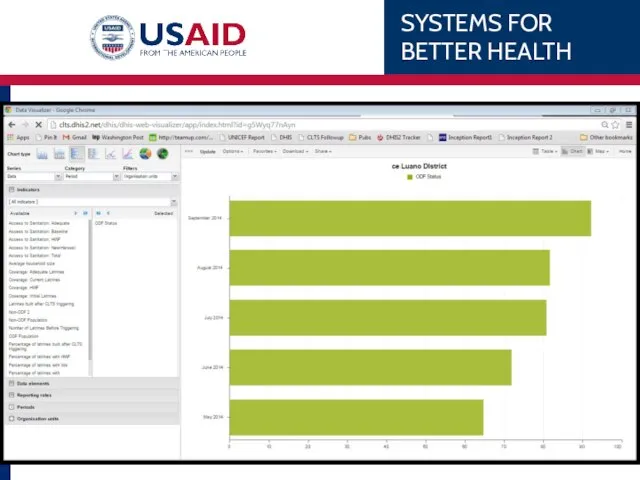
- 77. Chart type Select from Column Stacked column Bar Stacked bar Line Area Pie Spider charts Never
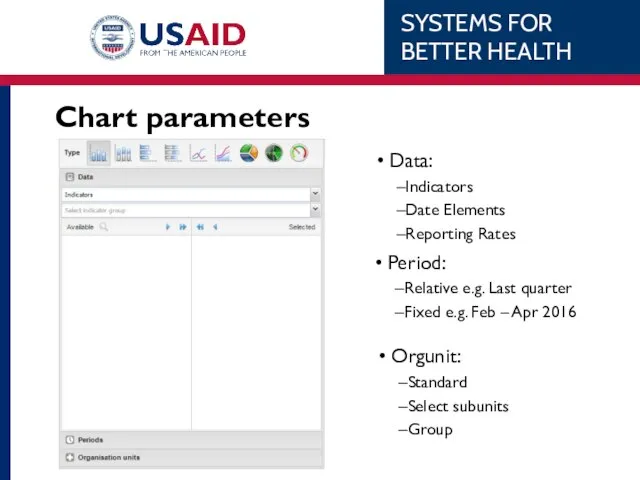
- 78. Chart parameters Data: Indicators Date Elements Reporting Rates Period: Relative e.g. Last quarter Fixed e.g. Feb
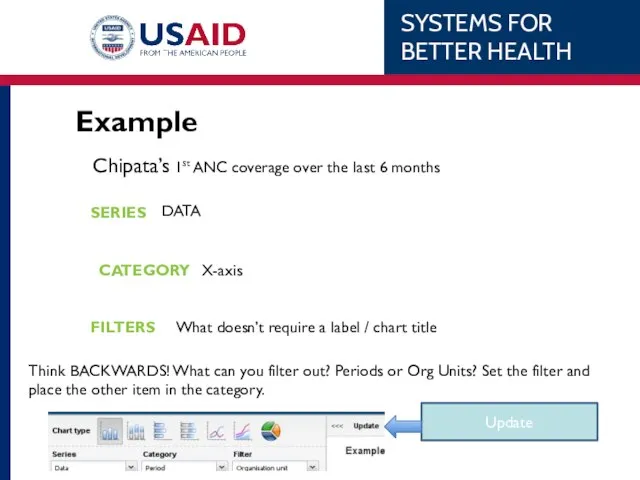
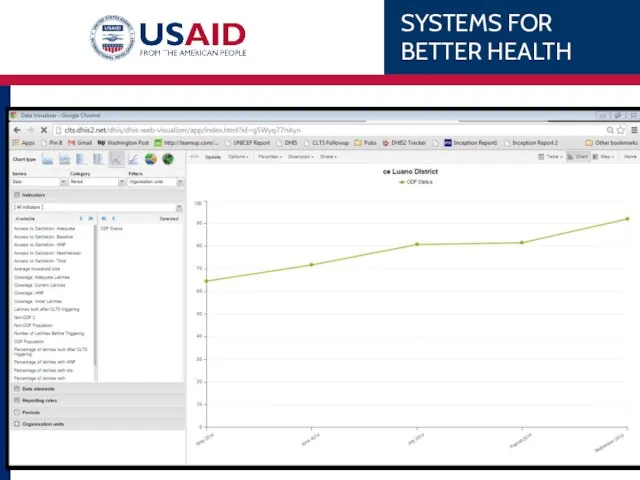
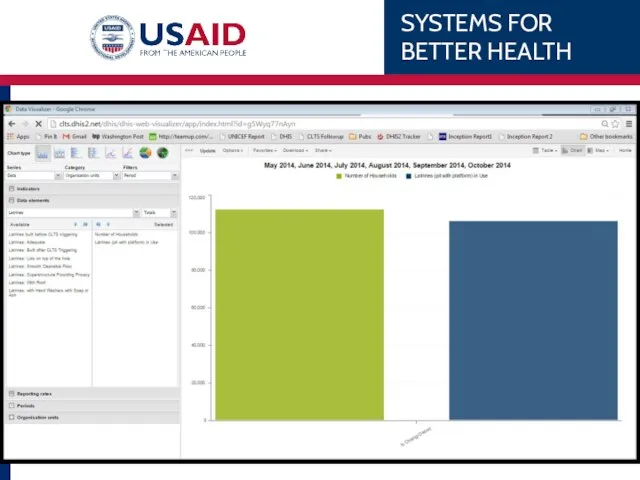
- 79. Example Chipata District’s 1st ANC coverage over the last 6 months. WHAT WHEN WHERE Indicator –
- 81. Example Chipata’s 1st ANC coverage over the last 6 months SERIES CATEGORY FILTERS DATA X-axis What
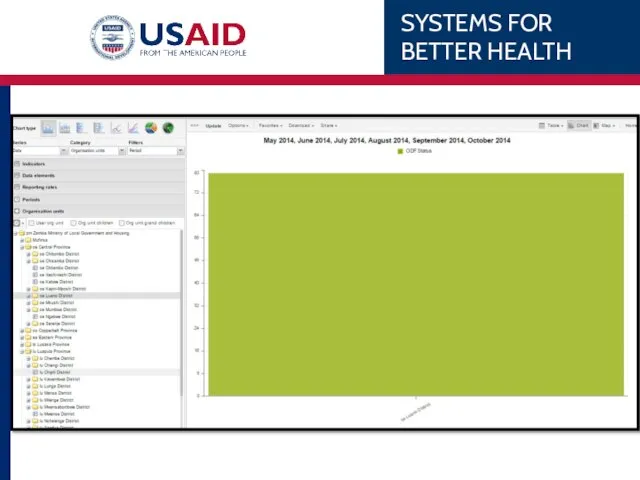
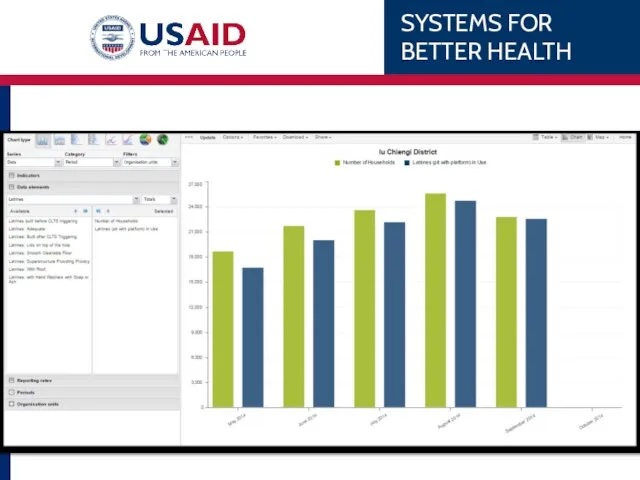
- 86. Chipata’s 1 ANC WHAT WHEN WHERE Data Element – 1st ANC Monthly, last 6 months Eastern
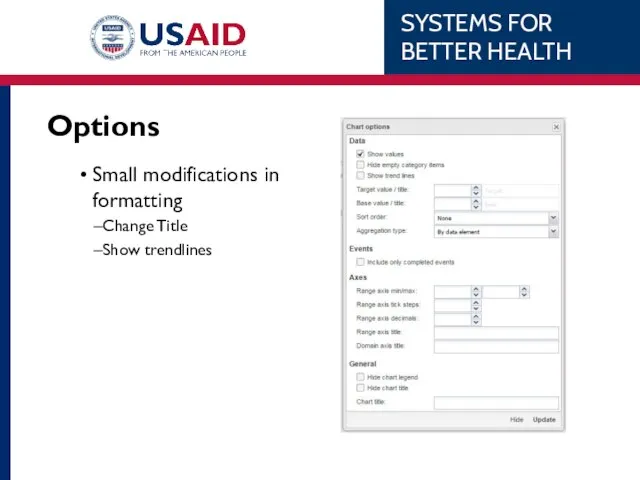
- 90. Options Small modifications in formatting Change Title Show trendlines
- 91. Worked example …
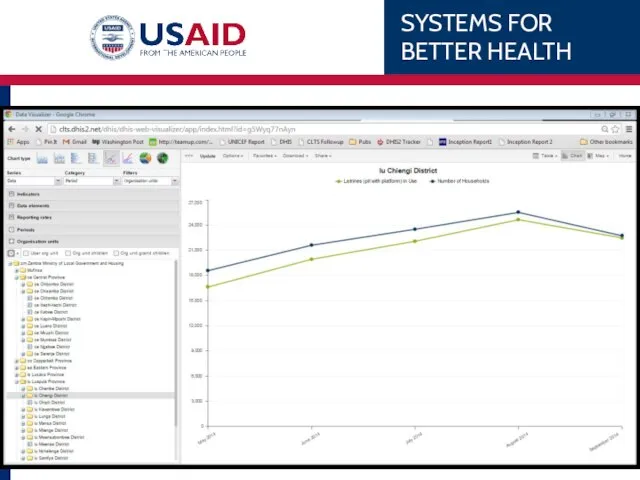
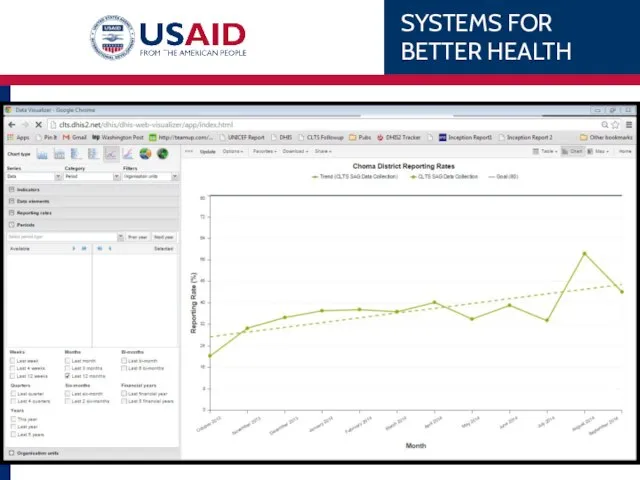
- 92. Open a saved chart Go to: Favorites Search for “Choma Reporting rates” Select Title
- 93. Choma Reporting Rates Line Chart Series (Data), Category (Period), Filter (Organisation unit) What: Reporting Rates: HIA2
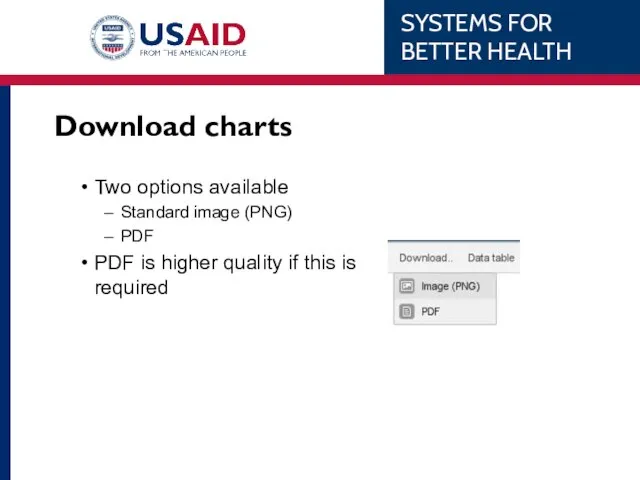
- 95. Download charts Two options available Standard image (PNG) PDF PDF is higher quality if this is
- 96. Manage favorites Rename Overwrite Share Delete
- 97. Exercise Sheet Work through each example on the work sheet Don’t skip any sections Ask for
- 98. Data Entry Module
- 99. When to do data entry Entering HIA 1 and 2 forms Suggested 1 week before reporting
- 100. WARNING! Data entry is live No undo button I error in population data impacts reports on
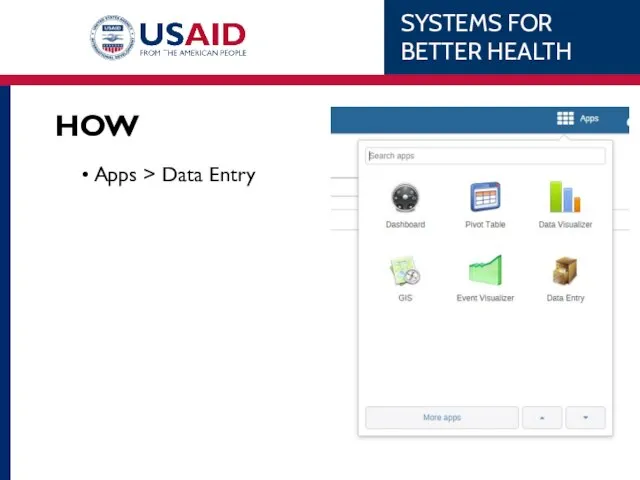
- 101. HOW Apps > Data Entry
- 102. HOW Select facility Select Form Select Period Enter Data
- 103. Worked Examples Use the tally sheets you brought from your facility to enter the data for
- 104. Group Discussion Feedback Closing
- 106. Скачать презентацию



















































 Распространение и методика профилактики зооантропозонозов в Яковлевском городском округе (на примере бешенства)
Распространение и методика профилактики зооантропозонозов в Яковлевском городском округе (на примере бешенства) Патобиохимия печени
Патобиохимия печени Семейная амавротическая идиотия
Семейная амавротическая идиотия Стероидный остеопороз при эндогенном гиперкортицизме
Стероидный остеопороз при эндогенном гиперкортицизме Влияние пива на организм человека
Влияние пива на организм человека Тілдік қатынас негіздері. Ғылыми негіздер
Тілдік қатынас негіздері. Ғылыми негіздер Участие медицинских сестер в организации и проведении вакцинопрофилактики детскому населению
Участие медицинских сестер в организации и проведении вакцинопрофилактики детскому населению Классификация ВОЗ инфекционных болезней, передающихся половым путём. Первичный период сифилиса
Классификация ВОЗ инфекционных болезней, передающихся половым путём. Первичный период сифилиса Внелегочный туберкулез. 2
Внелегочный туберкулез. 2 Острый холецистит
Острый холецистит Об этом должен знать каждый
Об этом должен знать каждый Клинико-лабораторная характеристика энтеровирусных менингитов у детей
Клинико-лабораторная характеристика энтеровирусных менингитов у детей Познай себя в своих друзьях (игровой тренинг)
Познай себя в своих друзьях (игровой тренинг) Деменція
Деменція Канцерогенездің иммунды генетикалық аспектілері. Онкологиялық науқастардың иммунды статусының ерекшеліктері
Канцерогенездің иммунды генетикалық аспектілері. Онкологиялық науқастардың иммунды статусының ерекшеліктері Ткани зуба
Ткани зуба Основополагающие требования, регламентирующие работу санитарно-гигиенической лаборатории
Основополагающие требования, регламентирующие работу санитарно-гигиенической лаборатории Изменения, вносимые в действующие формы федерального изменения в медицине
Изменения, вносимые в действующие формы федерального изменения в медицине Психическое развития детей с нарушениями интеллекта. (Лекция 4)
Психическое развития детей с нарушениями интеллекта. (Лекция 4) Первинна, вторинна і третинна профілактика в стоматології
Первинна, вторинна і третинна профілактика в стоматології Хирургическая анатомия грудной стенки и молочной железы. Оперативная хирургия грудной клетки и молочной железы
Хирургическая анатомия грудной стенки и молочной железы. Оперативная хирургия грудной клетки и молочной железы Политравма. Периоды травматической болезни
Политравма. Периоды травматической болезни Лекарственная аллергия. (Лекция №1)
Лекарственная аллергия. (Лекция №1) Болезнь Фабри-Андерсона: клиническая картина, диагностика, клинические наблюдения
Болезнь Фабри-Андерсона: клиническая картина, диагностика, клинические наблюдения Формирование конструктивных моделей взаимодействия в детско-родительских отношениях
Формирование конструктивных моделей взаимодействия в детско-родительских отношениях Структуры желчевыводящих путей
Структуры желчевыводящих путей Клинический случай меланомы
Клинический случай меланомы Биотрансформация ксенобиотиков, ядов в организме
Биотрансформация ксенобиотиков, ядов в организме