Содержание
- 2. Seizure
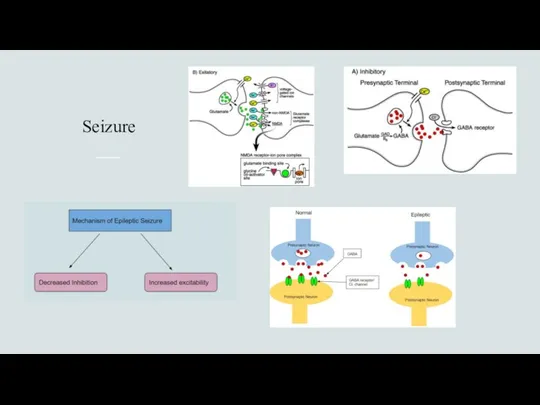
- 3. Seizure and epilepsy Seizure An acute, transient neurological event caused by abnormal electrical discharge within the
- 4. Causes of seizure Vascular Infection Trauma Autoimmune Metabolic Ingestion/withdrawal Neoplasm pSych General vs Partial(focal) Complex vs
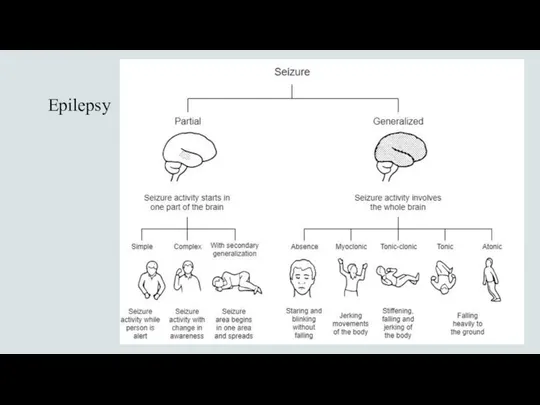
- 5. Epilepsy SIMPLE Small area of the brain Strange sensation Jerking movements Jacksonian march Often remember COMPLEX
- 6. Epilepsy
- 7. Epilepsy Stages Prodromal When symptoms start to appear prior to the big event Aura Does not
- 8. Status epilepticus Seizure lasts more than 5 min Ongoing or without returning to normal Usually tonic-clonic
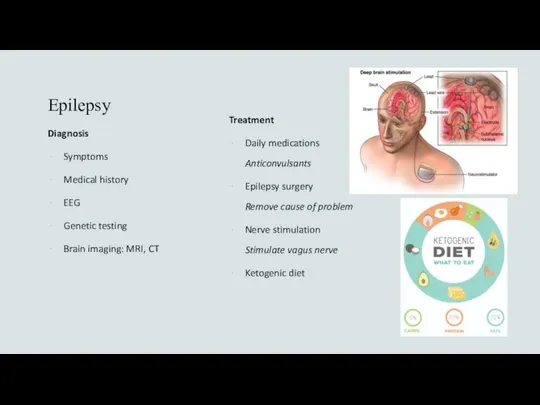
- 9. Epilepsy Diagnosis Symptoms Medical history EEG Genetic testing Brain imaging: MRI, CT Treatment Daily medications Anticonvulsants
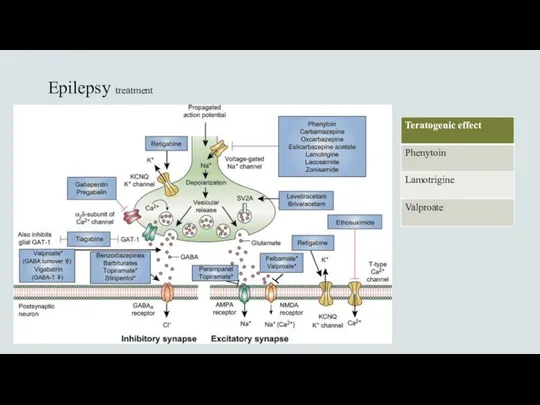
- 10. Epilepsy treatment
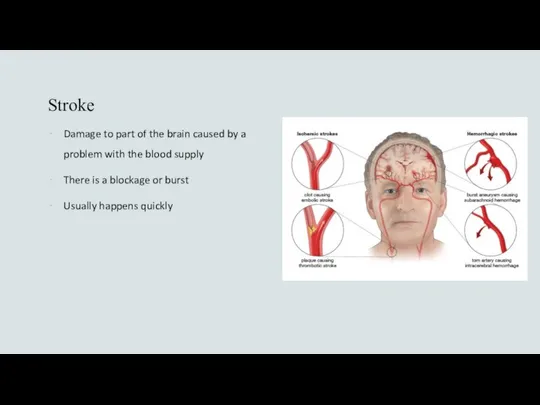
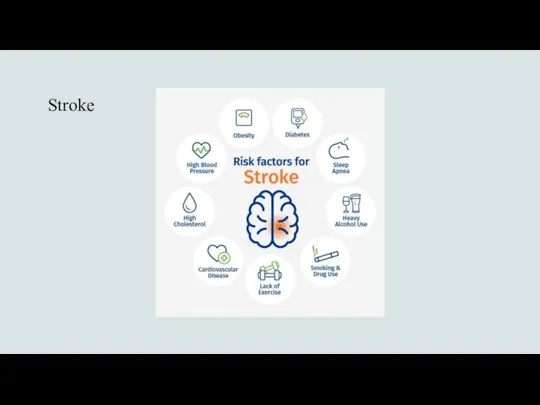
- 11. Stroke Damage to part of the brain caused by a problem with the blood supply There
- 12. Stroke ISCHEMIC Death of tissue due to blockage by Thrombotic – atherosclerotic plaque Embolic – any
- 13. Stroke
- 14. Transient ischemic attack Effects last no longer than 24 hours from onset or the symptoms start
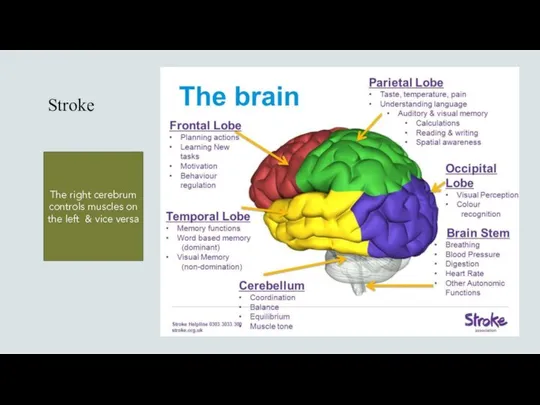
- 15. Stroke The right cerebrum controls muscles on the left & vice versa
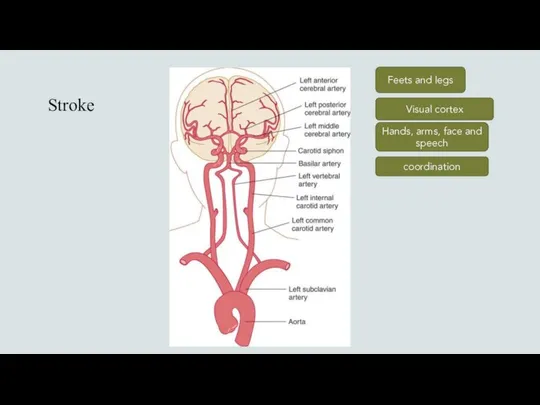
- 16. Stroke Feets and legs Hands, arms, face and speech Visual cortex coordination
- 17. Stroke Diagnosis and Treatment CT scan of the head +blood to drop blood pressure a lot;
- 18. Stroke Acute tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) For Ischemic Stroke! Dissolve the clot by activating the protein
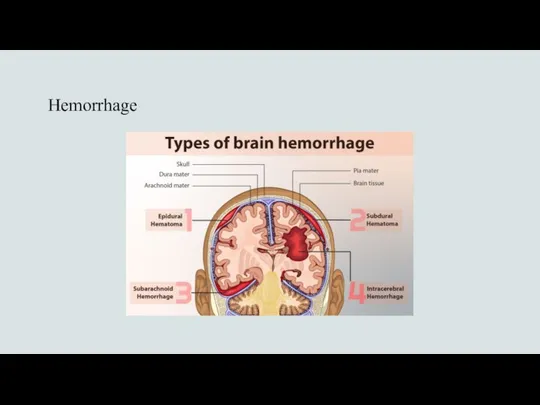
- 19. Hemorrhage
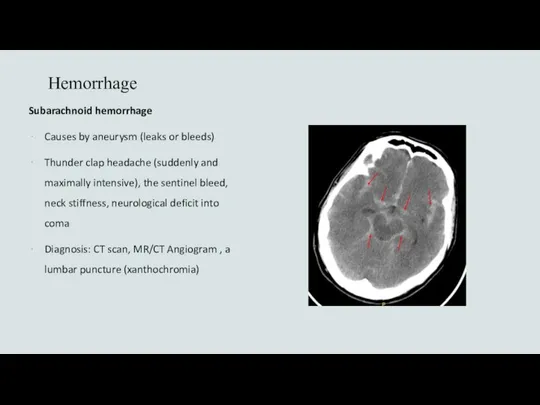
- 20. Hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage Causes by aneurysm (leaks or bleeds) Thunder clap headache (suddenly and maximally intensive),
- 21. Hemorrhage Treatment: BP coil or clip Hydrocephalus: serial lumbar punctures, VP shunt Seizure prophylaxis: levetiracetam Increased
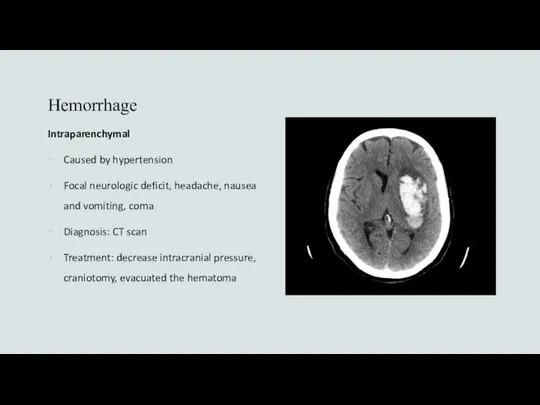
- 22. Hemorrhage Intraparenchymal Caused by hypertension Focal neurologic deficit, headache, nausea and vomiting, coma Diagnosis: CT scan
- 24. Скачать презентацию










 ОГБУЗ Областная больница №2
ОГБУЗ Областная больница №2 Хронические гепатиты
Хронические гепатиты Хронический геморрой
Хронический геморрой Синдром Дауна
Синдром Дауна Введение. Общая фармакология
Введение. Общая фармакология Анемии, лейкозы
Анемии, лейкозы Аускультация сердца
Аускультация сердца ҚР Медициналық сақтандыру
ҚР Медициналық сақтандыру Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь, интенсивная терапия
Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь, интенсивная терапия Эндокринная система. (2 часть)
Эндокринная система. (2 часть) Исправление звукопроизношения у детей. Консультация логопеда
Исправление звукопроизношения у детей. Консультация логопеда тема Петрова
тема Петрова ОРВИ. симптоматика
ОРВИ. симптоматика Ортопедиялық стоматологияда қолданылатын құмалар сипаттамасы
Ортопедиялық стоматологияда қолданылатын құмалар сипаттамасы Гематогенный и спецефические остеомиелиты костей лицевого скелета у детей. Классификация, клиническое течение,
Гематогенный и спецефические остеомиелиты костей лицевого скелета у детей. Классификация, клиническое течение, Концепция психического дизонтогенеза В.В. Лебединского (1985)
Концепция психического дизонтогенеза В.В. Лебединского (1985) Атом энергиясын бейбіт мақсатта пайдалану. Радиоактивті изотоптар мен иондаушы сәулелер көздерін медицинада қолдану
Атом энергиясын бейбіт мақсатта пайдалану. Радиоактивті изотоптар мен иондаушы сәулелер көздерін медицинада қолдану Профилактика населения
Профилактика населения Физиология послеродового периода
Физиология послеродового периода Анализ ТРГ в клинике ортодонтии
Анализ ТРГ в клинике ортодонтии Бронхиальная астма
Бронхиальная астма Колоректальный рак Клиника, диагностика, лечение
Колоректальный рак Клиника, диагностика, лечение Гормональные лекарственные средства
Гормональные лекарственные средства На службе здоровья
На службе здоровья Рельєфна антомія м’язів
Рельєфна антомія м’язів Инфекциялық эндокардит
Инфекциялық эндокардит Установка для терагерцевой и длиноволновой ИК-терапии Инфратератрон
Установка для терагерцевой и длиноволновой ИК-терапии Инфратератрон Контрацепция: защита женского здоровья и не только
Контрацепция: защита женского здоровья и не только