Содержание
- 2. Special Health Care Needs Definition: Persons with a physical, developmental, mental, sensory, behavioral, cognitive, &/or emotional
- 3. Common Special Needs Asthma Down Syndrome Developmental/Behavioral Disabilities Autism Asperger Syndrome ADHD Ectodermal Dysplasia Craniofacial malformations
- 4. Asthma Definition: A chronic disease involving the respiratory system in which the airways occasionally constrict, become
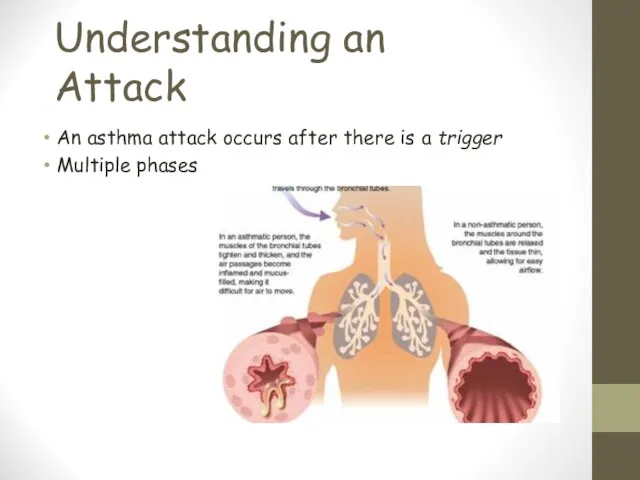
- 5. Understanding an Attack An asthma attack occurs after there is a trigger Multiple phases
- 6. Common Oral Findings Increased dental caries More erosion More calculus More gingivitis Throat irritation (steroids) Candida
- 7. Dental Considerations Good preventive program Rinse/drink water after inhaler use Chronic nebulizer patients ? may require
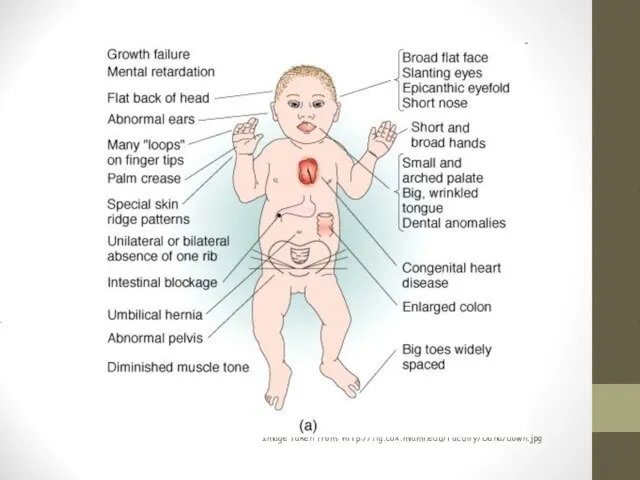
- 8. Down Syndrome Definition: Chromosomal disorder caused by the presence of all or part of an extra
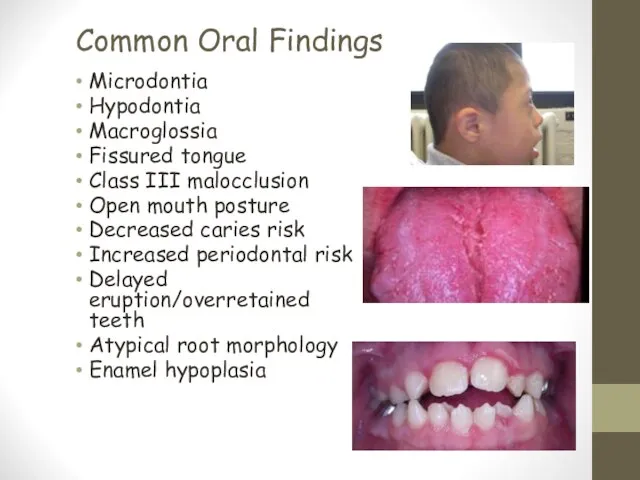
- 9. Common Oral Findings Microdontia Hypodontia Macroglossia Fissured tongue Class III malocclusion Open mouth posture Decreased caries
- 10. Dental Considerations Congential heart disease Compromised immune system Chronic upper respiratory problems Atlanto-axial instability Varying degree
- 11. Image taken from: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/Faculty/Dana/down.jpg
- 12. Developmental/Behavioral Disability Autism spectrum disorder is a general term for a group of complex disorders of
- 13. Signs & Symptoms Doesn’t respond to his/her own name Acts deaf Does not smile socially Does
- 14. Asperger Syndrome Previously, Asperger and Autism were subcategories under the heading of Pervasive Developmental Disorders. The
- 15. Common Oral Findings Varies depending on the severity Increased caries Poor oral hygiene Overall, few unusual
- 16. Dental Considerations More for autism than Asperger Sensory sensitivity Light, dental tools, water, noise, staff Unpredictable
- 17. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Most common mental disorder among children Hyperactive and unable to control their
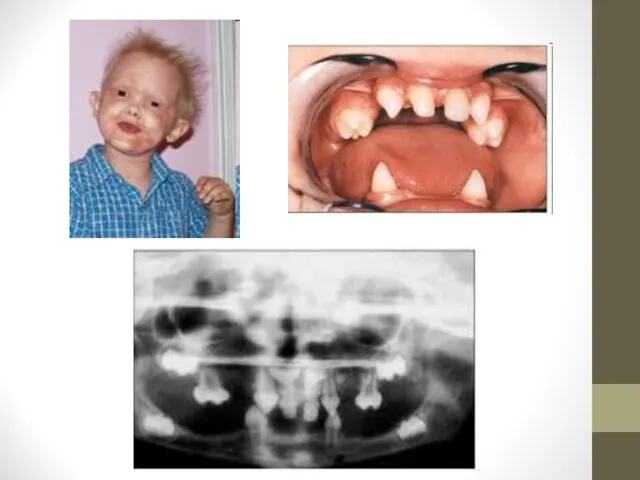
- 18. Ectodermal Dysplasia Definition: Hereditary condition in which there are abnormalities of the cranial-facial structure, digits, and
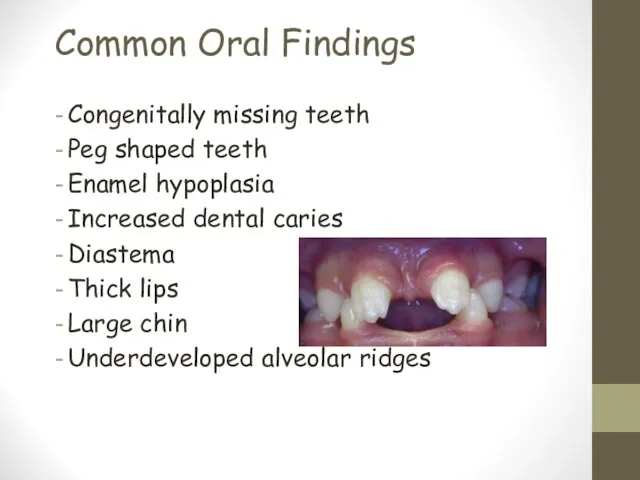
- 19. Common Oral Findings Congenitally missing teeth Peg shaped teeth Enamel hypoplasia Increased dental caries Diastema Thick
- 20. Dental Considerations Caries control Cosmetic dentistry Multiple sets of dentures as the child ages & the
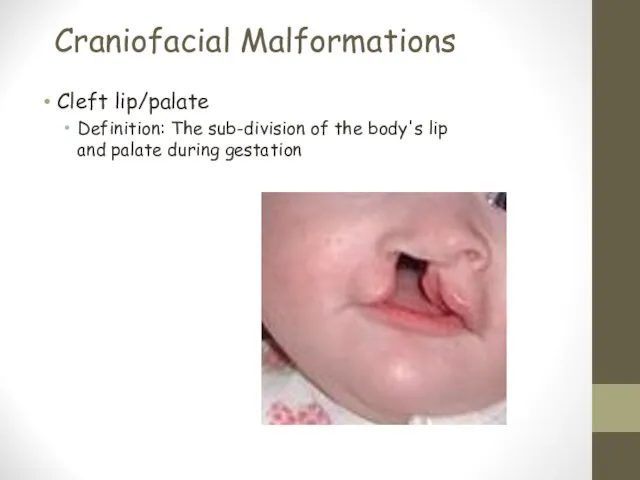
- 22. Craniofacial Malformations Cleft lip/palate Definition: The sub-division of the body's lip and palate during gestation
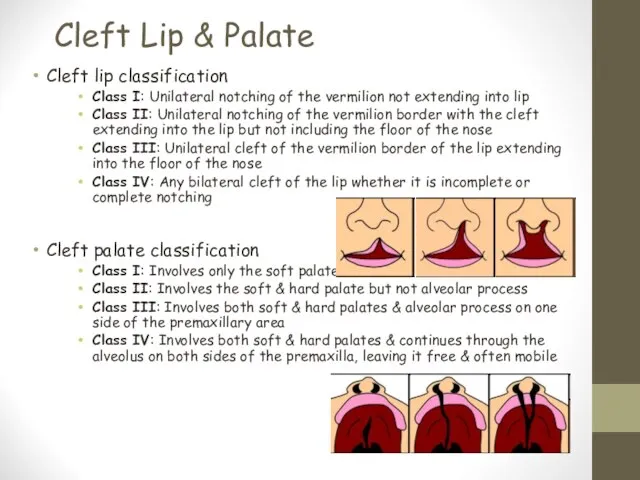
- 23. Cleft Lip & Palate Cleft lip classification Class I: Unilateral notching of the vermilion not extending
- 24. Oral Findings/Dental Considerations Complications Feeding difficulty Speech difficulty Excessive air intake (burps often) Choking Nasal discharge
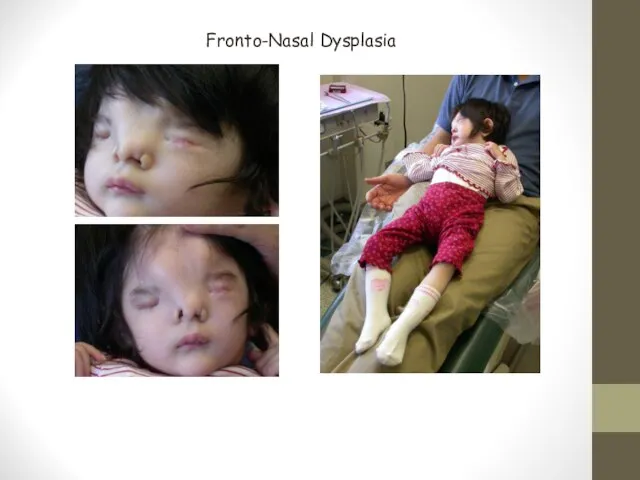
- 25. Fronto-Nasal Dysplasia
- 26. Cerebral Palsy Definition: Cerebral palsy refers to any number of neurological disorders that permanently affects body
- 27. Characteristics Eye problems Delayed reflexes Facial grimacing Swallowing difficulties Poor balance Hearing loss MR in ~50%
- 28. Dental Considerations Increased caries risk Enamel erosion Poor gingival health/POH Heavy calculus (if fed with G-tube)
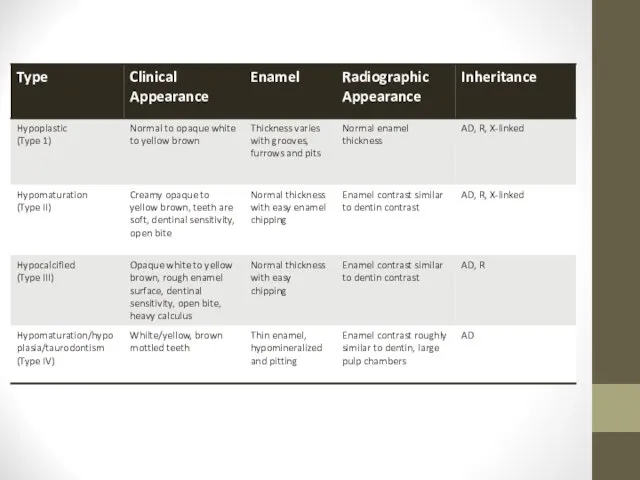
- 29. Amelogenesis Imperfecta Inherited disease 1 in 700-15,000 Subtypes
- 32. Psychological Limitations Anxiety H/o traumatic experience Innate, unprovoked, un-triggered Eating Disorders Anorexia Nervosa Bulimia Nervosa Nervous
- 34. Скачать презентацию





















 Osgood-schlatter disease
Osgood-schlatter disease Лекарственные средства, действующие на систему крови
Лекарственные средства, действующие на систему крови Тері - адам денесінің сыртқы жабыны
Тері - адам денесінің сыртқы жабыны Возможности мультиспиральной компьютерной томографии в диагностике опухолевых и неопухолевых заболеаний поджелудочной железы
Возможности мультиспиральной компьютерной томографии в диагностике опухолевых и неопухолевых заболеаний поджелудочной железы Частная физиология эндокринной системы
Частная физиология эндокринной системы ҚР онкогинекологиялық қызметті ұйымдастыру. Диспансеризация приниптері. Қазақстанда ісік дамуының аймақтық ерекшеліктері
ҚР онкогинекологиялық қызметті ұйымдастыру. Диспансеризация приниптері. Қазақстанда ісік дамуының аймақтық ерекшеліктері Иммунология. В и Т-лимфоциты и кооперация клеток в иммунном ответе. (Лекция 3)
Иммунология. В и Т-лимфоциты и кооперация клеток в иммунном ответе. (Лекция 3) Способы фиксации съемных протезов
Способы фиксации съемных протезов Хирургическое лечение язвенной болезни желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки
Хирургическое лечение язвенной болезни желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки Психотренинг для беременных
Психотренинг для беременных История и теории зоопсихологии
История и теории зоопсихологии Итоги работы КГБУЗ Манская районная больница 2016-2018 год
Итоги работы КГБУЗ Манская районная больница 2016-2018 год Anemia
Anemia Новые технологии в лечение бесплодного брака
Новые технологии в лечение бесплодного брака Сироты (67)
Сироты (67) Балалар мен жасөспірімдердің денсаулық жағдайына және физикалық дамуына еңбек
Балалар мен жасөспірімдердің денсаулық жағдайына және физикалық дамуына еңбек Фармацевтическая опека. Дисбактериоз, метеоризм, заболевания печени и поджелудочной железы
Фармацевтическая опека. Дисбактериоз, метеоризм, заболевания печени и поджелудочной железы Предмет и методы медицинского и фармацевтического товароведения. Потребительные стоимости товара
Предмет и методы медицинского и фармацевтического товароведения. Потребительные стоимости товара Лекарственные соединения гетероциклического ряда с одним и двумя гетероатомами
Лекарственные соединения гетероциклического ряда с одним и двумя гетероатомами Предмет, цели и задачи психологии. Тема 1.1
Предмет, цели и задачи психологии. Тема 1.1 Заболевания глотки. Абсцессы глотки
Заболевания глотки. Абсцессы глотки Болезнь Брутона
Болезнь Брутона Злокачественные новообразования кожи
Злокачественные новообразования кожи Клинико микробиологическое обоснование профилактики акушерской и перинатальной патологии обусловленной стрептококками группы B
Клинико микробиологическое обоснование профилактики акушерской и перинатальной патологии обусловленной стрептококками группы B Респираторные нарушения у новорожденных
Респираторные нарушения у новорожденных Базовая инфузионная терапия у детей
Базовая инфузионная терапия у детей Формирование и развитие личности
Формирование и развитие личности Лейкоз
Лейкоз