Содержание
- 2. Hygiene of children and teenagers the section of hygiene studying action factors of environment on a
- 3. Primary goals HCT: - studying physical development; -development hygienic requirements to: children's preschool and school establishments,
- 4. The basic methods research in HCT Epidemiological method (studying state of health children's contingents depending on
- 5. Laws of growth and development children - Non-uniformity growth and development organism depending on age –
- 6. SCHEMES AGE PERIODIZATION The biological periodization accepted in HCT: The period new-born (1-10 days); Baby age
- 7. Social age periodization: Day nursery age - till 3 years; Preschool age - 3-7 years; Younger
- 8. Physical development – complex of morphological and functional attributes, determining growth, formation organism of the child,
- 9. THE PURPOSES OF RESEARCH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT: revealing laws of growth and development; estimation individual and population
- 10. METHODS RESEARCH PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT 1. Somatometrical (anthopometrical) - growth, weights of body and circle of chest.
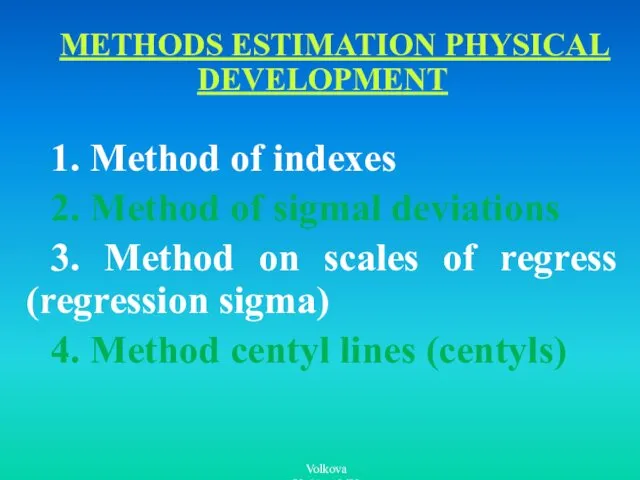
- 11. METHODS ESTIMATION PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT 1. Method of indexes 2. Method of sigmal deviations 3. Method on
- 12. 1. Method of indexes, for example, index Broka: growth in sm - 100 sm = Ideal
- 13. After definition somatometric parameters of the concrete child from it subtract value of average sizes from
- 14. 3. Method on scales of regress (regression sigma), showing on the basis of statistical researches what
- 15. CHILDREN'S PRESCHOOL ESTABLISHMENTS (CPE) Kinds of CPE: - kindergarten (for children 3-7 years), - day nursery
- 16. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO CHOICE SITE OF CPE - Availability to population - radius of service in
- 17. Requirements to functional zones at site of CPE. ZONE BUILDING Systems of building CPE Centralized (is
- 18. ZONE GREEN PLANTINGS Should occupy not less than 50 % of the area of a site.
- 19. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO THE GROUP CELL Group cell is the basic functional part CPE - the
- 20. Group room - the common room or is divided into game room and bedroom. The general
- 21. Hygienic requirements to toys in PCE: 1. Weight: till 3 years - up to 100 g,
- 22. Premises general purpose: gymnastic and music hall (75m2), methodical study, additional: swimming pool, visual hall, study
- 23. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO SCHOOLS Requirements to accommodation schools: availability (radius of service 1,5 km in city
- 24. Zone building - building must be not closer 25m from borders of a site, is surrounded
- 25. Sports zone - stadium with racetracks and holes for jumps, platform for volleyball, sports shells etc.
- 26. Requirements to school building Systems of school construction: 1) Centralized (all premises in one building -
- 27. The basic groups of premises in school: Educational section General purpose premise (lobby, wardrobe, dining room,
- 28. The basic functional unit in school is educational section Educational section - some classes or studies,
- 29. Hygienic requirements to a class room at school The area must be 1,25 m2 on 1
- 30. REQUIREMENTS TO SCHOOL DESKS (TABLES): In each class must be desks not less than 3 sizes,
- 31. Hygienic specifications of school furniture 1. Differention - vertical distance from a table to chair –
- 32. Hygienic requirements to learning children and teenagers In difficult process of learning children it is possible
- 33. Ways of adaptation to learning at school - 1-st stage: Gradual change of dynamic stereotype -
- 34. Age of the beginning learning at school It is determined not by calendar age, but psycho-physiological
- 35. PREVENTION EXHAUSTION AT SCHOOLCHILDREN: 1) Creation optimum hygienic conditions of learning: normal light exposure, ventilation, microclimate,
- 36. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO THE SCHOOL SCHEDULE: а) Restriction amount of lessons per one week: in 1
- 37. Hygienic requirements to structure lesson Phases serviceability of schoolboys : Phase in-work is in the first
- 38. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO MODE OF DAY OF CHILDREN AND TEENAGERS. Main principles of hygienic requirements: -
- 39. THE BASIC COMPONENTS of DAY REGIMEN of CHILDREN And TEENAGERS 1. Dream. In the new-born age
- 40. 2. Stay on fresh air Up to 1,5 years stay on open air is at the
- 41. 3. Educational activity per week At 1,5 - 2 years - some lessons on 8 -
- 42. 4. Game activity or rest: In prescholl age - 4,0 - 5 hours for schoolboys -
- 43. HYGIENIC REQUIREMENTS TO PHYSICAL TRAINING OF CHILDREN: Main principles: Individuality; Adequacy to a state of health
- 44. FEATURES of HYGIENE of NUTRITION of CHILDREN The main feature - high intensity exchange in organism
- 45. FEATURES PROTEIN NUTTRITION IN CHILDREN: More on kg of weight of a body in comparison for
- 46. FEATURES CARBOHYDRATE NUTRITION: - Rather big need on kg of weight of a body (energy); In
- 47. FEATURES MINERAL SUBSTANCES IN CHILDREN’S NUTRITION In view of intensive growth bones - increased receipt Са
- 48. REGIMEN OF DIET Than more small child - the more often receptions of food is necessary:
- 50. Скачать презентацию














































 Период взрослости
Период взрослости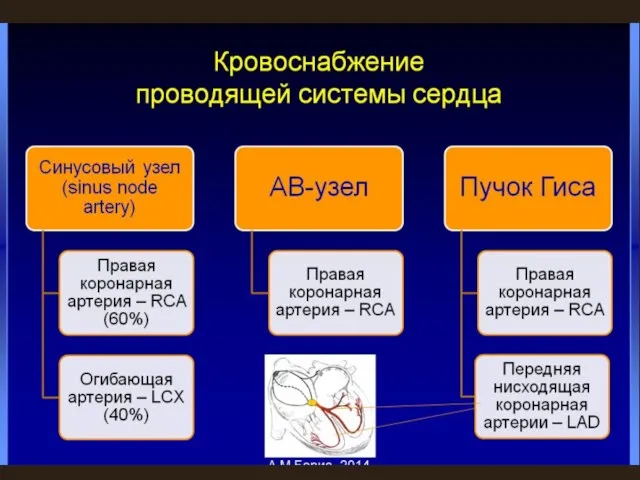 Нарушения кровоснабжения проводящей системы сердца
Нарушения кровоснабжения проводящей системы сердца Халықтың табиғи қозғалысын бағалау
Халықтың табиғи қозғалысын бағалау Правильная осанка - залог здоровья
Правильная осанка - залог здоровья Пищевые токсико-инфекции. Микоплазмоз
Пищевые токсико-инфекции. Микоплазмоз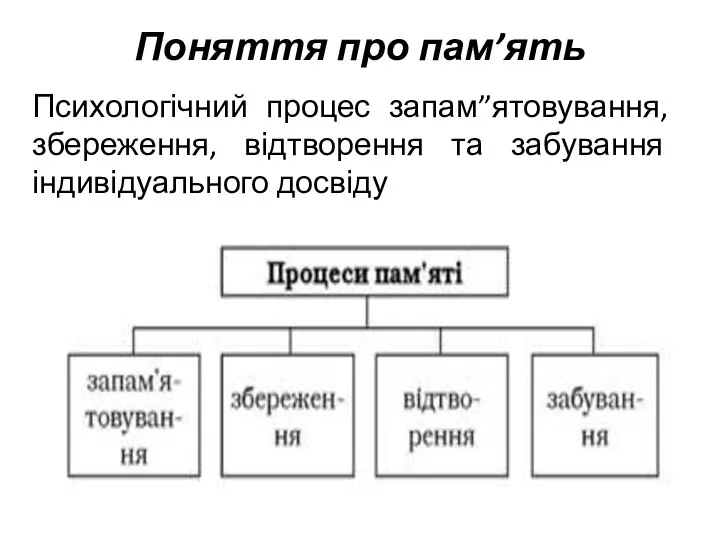 Поняття про пам’ять. Функції пам’ять
Поняття про пам’ять. Функції пам’ять Эпидемиологическая диагностика
Эпидемиологическая диагностика Профилактикалық алгоритмдерді құрудың скринингтік бағдарламалардың нәтижелерін ендіру мен
Профилактикалық алгоритмдерді құрудың скринингтік бағдарламалардың нәтижелерін ендіру мен Предраковые заболевания шейки матки
Предраковые заболевания шейки матки Позитивные отношения
Позитивные отношения Рентгеноскопия
Рентгеноскопия Острый живот в гинекологии
Острый живот в гинекологии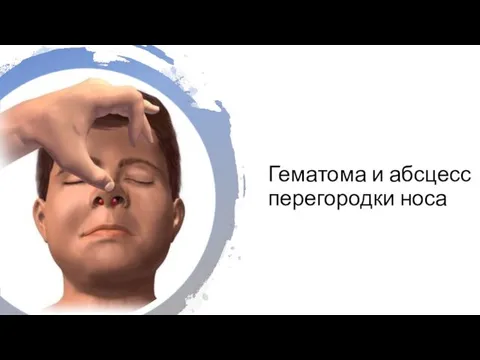 Гематома и абсцесс перегородки носа
Гематома и абсцесс перегородки носа Невідкладна допомога при нирковій кольці та гострій нирковій недостатності
Невідкладна допомога при нирковій кольці та гострій нирковій недостатності Когнитивно – поведенческая психотерапия
Когнитивно – поведенческая психотерапия Генные болезни
Генные болезни Реанимация и интенсивная терапия при острых отравлениях
Реанимация и интенсивная терапия при острых отравлениях Кровотечения в родах и послеродовом периоде
Кровотечения в родах и послеродовом периоде Эндодонтический инструментарий
Эндодонтический инструментарий Туберкулёз. Глобальное распространение туберкулеза
Туберкулёз. Глобальное распространение туберкулеза Выбор метода анестезии
Выбор метода анестезии Етеккір функциясының бұзылыстары. Аменорея. Гипоменструальды синдром
Етеккір функциясының бұзылыстары. Аменорея. Гипоменструальды синдром Синдром Шерешевского-Тёрнера
Синдром Шерешевского-Тёрнера Утверждение порядка проведения профилактического медицинского осмотра и диспансеризации определенных групп взрослого населения
Утверждение порядка проведения профилактического медицинского осмотра и диспансеризации определенных групп взрослого населения Визуальная диагностика
Визуальная диагностика Эндодонтиялық емдеу кезіндегі қателіктер
Эндодонтиялық емдеу кезіндегі қателіктер Синдром Трисомии Х-хромосомы
Синдром Трисомии Х-хромосомы Забота о внутреннем мире
Забота о внутреннем мире