Содержание
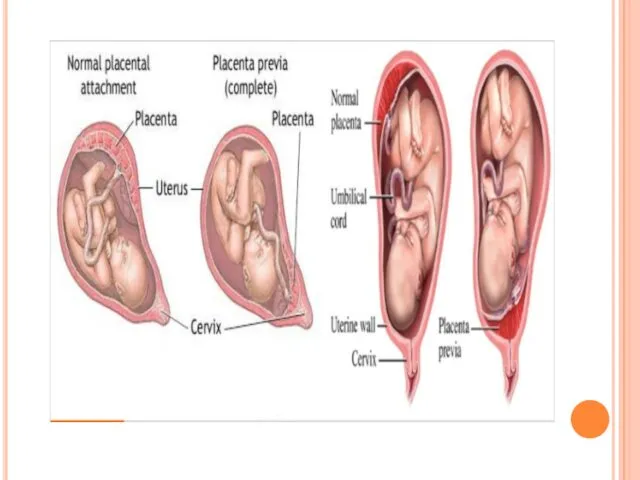
- 2. General considerations Definition In placenta previa, the placenta is implanted in the lower uterine segment and
- 4. Etiology Uncertain High risk factors maternal age: >35 years multiparity: 85% - 90% prior cesarean delivery:
- 5. Etiology Causes Endometrial abnormality Scared or poorly vascularized endometrium in the corpus. Curettage, Delivery, CS and
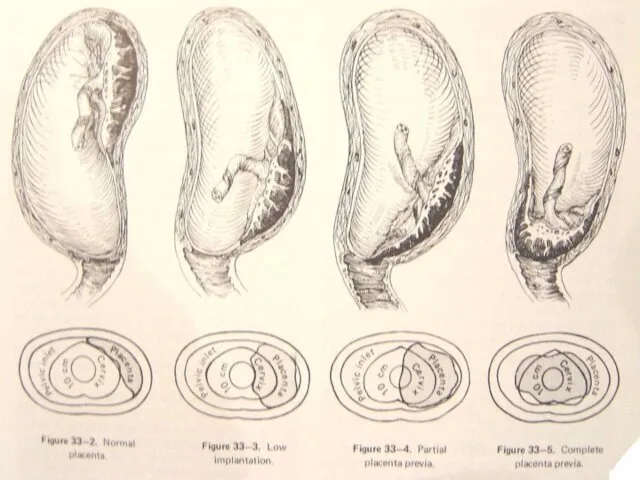
- 6. Classification Total placenta previa The internal cervical os is covered completely by placenta Partial placenta previa
- 7. classification
- 8. Manifestation Painless hemorrhage The most characteristic symptom Time: late pregnancy (after the 28th week) and delivery
- 9. Manifestation Anemia or shock repeated bleeding→ anemia heavy bleeding→ shock Abnormal fetal position a high presenting
- 10. Diagnosis History Painless hemorrhage At late pregnancy or delivery History of curettage or CS
- 11. Diagnosis Signs Abdominal findings Uterus is soft, relaxed and nontender. Contraction may be palpated. A high
- 12. Diagnosis Speculum examination (窥阴检查) Rule out local causes of bleeding, such as cervical erosion or polyp
- 13. Diagnosis Ultrasonography The most useful diagnostic method: 95% Not make the diagnosis at the mid pregnancy.
- 14. Differential Diagnosis Placental abruption vagina bleeding with pain, tenderness of uterus. Vascular previa Abnormality of cervix
- 15. Effects obstetrical hemorrhage Placenta accreta Anemia and infection Premature labor or fetal death or fetal distress
- 16. Treatments Expectant therapy Rest: keep the bed Controlling the contraction: MgSO4 Treatment of anemia Preventing infection
- 17. Treatments Termination of pregnancy CS total placenta previa (36th week), Partial placenta previa (37th week) and
- 18. Treatments Vaginal delivery Marginal placenta previa Vaginal bleeding is limited
- 20. Скачать презентацию















 Ишемическая болезнь сердца
Ишемическая болезнь сердца Тауарлар қорының құрылымы және классификациясы
Тауарлар қорының құрылымы және классификациясы Кибербуллинг: как помочь ребенку в ситуации онлайн-травли
Кибербуллинг: как помочь ребенку в ситуации онлайн-травли Основные синдромы при заболеваниях почек
Основные синдромы при заболеваниях почек Правильное питание для здорового образа жизни
Правильное питание для здорового образа жизни Жоба. Мал дәрігері мамандығы
Жоба. Мал дәрігері мамандығы Органы чувств
Органы чувств Роль медицинской сестры при уходе за наркозависимыми пациентами
Роль медицинской сестры при уходе за наркозависимыми пациентами Хирургическая операция
Хирургическая операция Психологическая помощь онкобольным и их семьям
Психологическая помощь онкобольным и их семьям Черепно-мозговая травма: сотрясение головного мозга
Черепно-мозговая травма: сотрясение головного мозга Организация и методика преодоления «сопротивления воспитанию» в условиях современной школы
Организация и методика преодоления «сопротивления воспитанию» в условиях современной школы Апластикалық және гипопластикалық
Апластикалық және гипопластикалық Ультразвуковая диагностика. Заболеваний щитовидной железы
Ультразвуковая диагностика. Заболеваний щитовидной железы Department of medical statistics of the hospital
Department of medical statistics of the hospital Чувствительность и боль. Виды чувствительности
Чувствительность и боль. Виды чувствительности Профилактика ВИЧ-инфекции в образовательной среде. Информирование о ВИЧ
Профилактика ВИЧ-инфекции в образовательной среде. Информирование о ВИЧ Ерік және сезім психологиясы
Ерік және сезім психологиясы Инструментальные методы исследование органов дыхания у детей
Инструментальные методы исследование органов дыхания у детей Кардиология. Острая сердечно-сосудистая недостаточность у детей
Кардиология. Острая сердечно-сосудистая недостаточность у детей Методы лечения в травматологии и ортопедии. Огнестрельные ранения
Методы лечения в травматологии и ортопедии. Огнестрельные ранения Древние и современные концепции обогащения молочных продуктов
Древние и современные концепции обогащения молочных продуктов Жасөспірімдер мен балалар организіміне ішімдіктің әсерінің зияндылығын анализдеу
Жасөспірімдер мен балалар организіміне ішімдіктің әсерінің зияндылығын анализдеу Отоларингология - диагностика и лечение уха, горла, носа, а также патологий головы и шеи
Отоларингология - диагностика и лечение уха, горла, носа, а также патологий головы и шеи Нейссерии. Род Neisseria
Нейссерии. Род Neisseria Трофобластическая болезнь
Трофобластическая болезнь Профилактика туберкулеза
Профилактика туберкулеза Репродуктивно-респираторный синдром свиней
Репродуктивно-респираторный синдром свиней