Содержание
- 2. Rh Disease Occurs during pregnancy when there is an incompatibility between the blood types of the
- 3. Blood Types A, B, O blood groups are specific types of proteins found on the surface
- 4. Rh Factor Proteins (antigens) occurring only on surface of RBC’s Rh + if proteins present Rh
- 5. Nomenclature Correct to say Rh(D) + or – Rh blood system has other antigens: C, c,
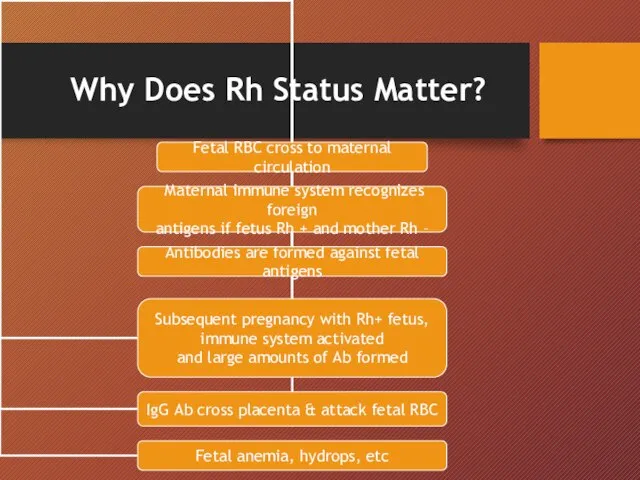
- 6. Why Does Rh Status Matter?
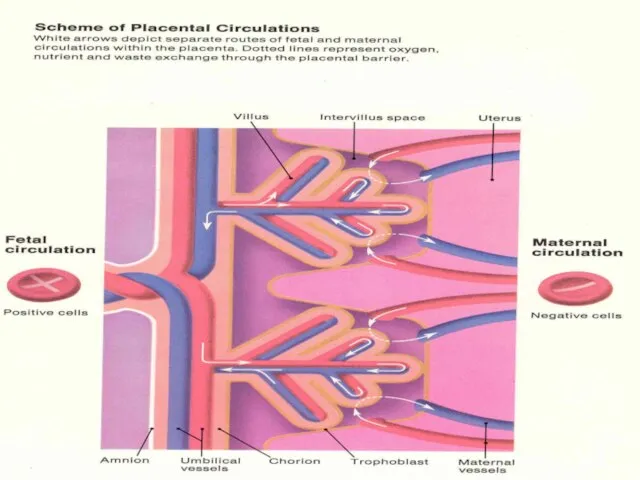
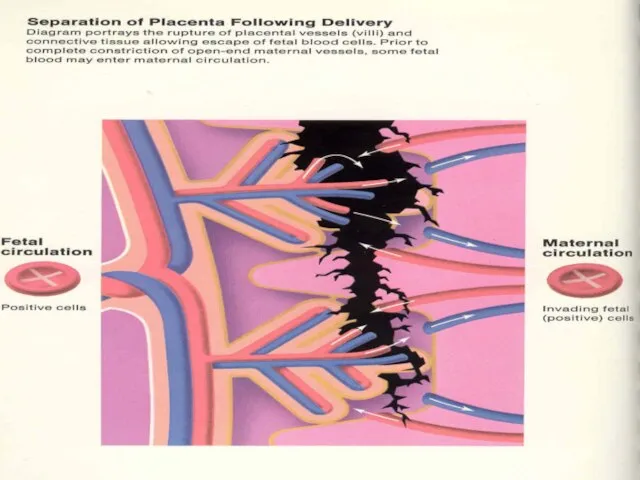
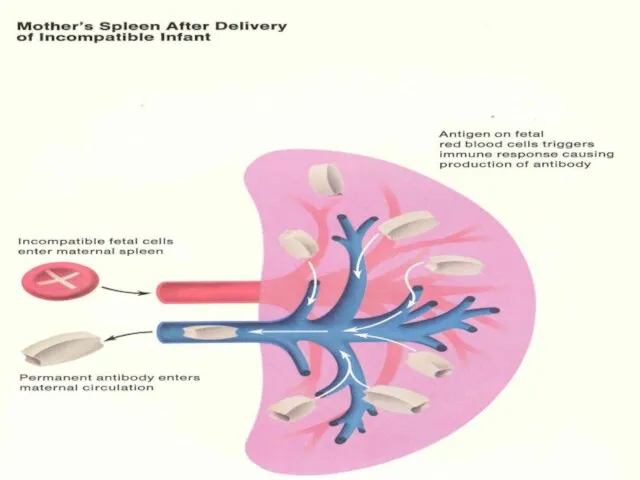
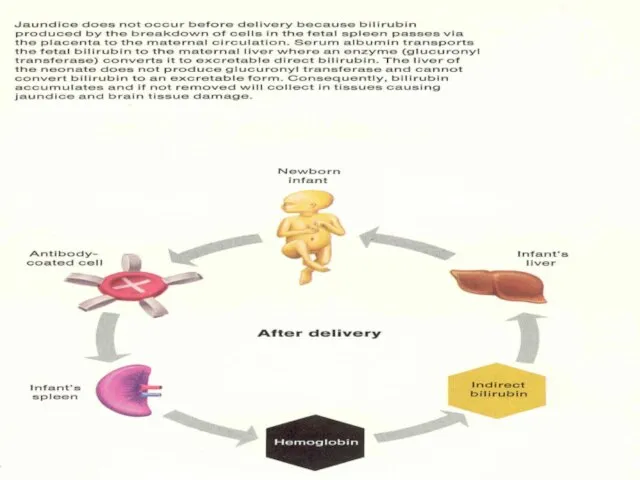
- 13. Pathophysiology Rh(D) antigen expressed by 30 d GA Many cells pass between maternal & fetal circulation
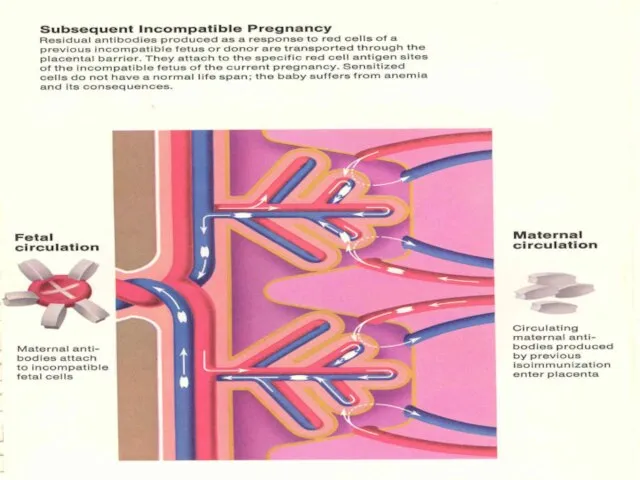
- 14. Pathophysiology cont… Initial IgM followed by IgG in 2 wks- 6 mths Memory B lymphocytes activate
- 17. Causes of RBC Transfer abortion/ectopic partial molar pregnancy blighted ovum antepartum bleeding special procedures (amniocentesis, cordocentesis,
- 18. General Screening ABO & Rh Ab @ 1st prenatal visit @ 28 weeks Postpartum Antepartum bleeding
- 19. Gold Standard Test Indirect Coombs: -mix Rh(D)+ cells with maternal serum -anti-Rh(D) Ab will adhere -RBC’s
- 20. + Rh(D) Antibody Screen Serial antibody titres q2-4 weeks If titre ≥1:16 - amniocentesis or MCA
- 21. U/S Parameters Non Reliable Parameters: Placental thickness Umbilical vein diameter Hepatic size Splenic size Polyhydramnios Visualization
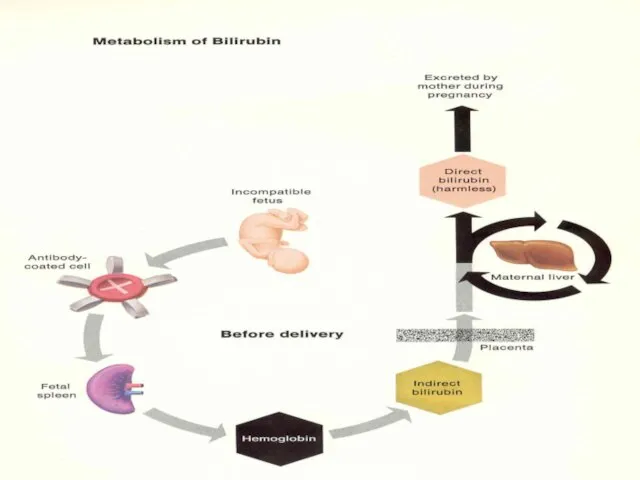
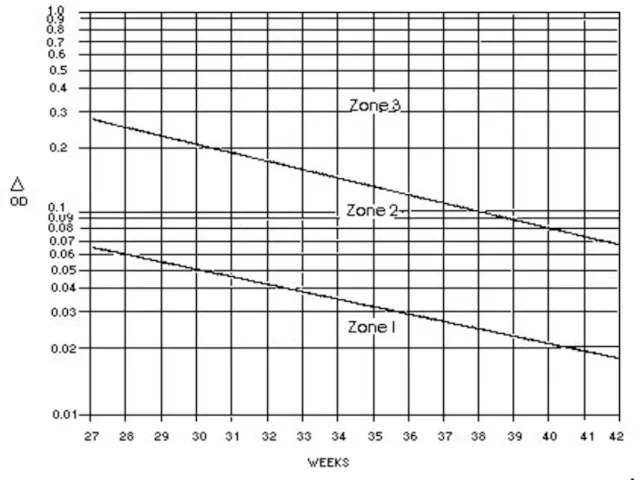
- 23. Amniocentesis Critical titre/previous affected infant Avoid transplacental needle passage Bilirubin correlates with fetal hemolysis ∆ optical
- 25. Liley Curve Zone I – fetus very low risk of severe fetal anemia Zone II –
- 26. Middle Cerebral Artery Dopplers Measures peak velocity of blood flow Anemic fetus preserves O2 delivery to
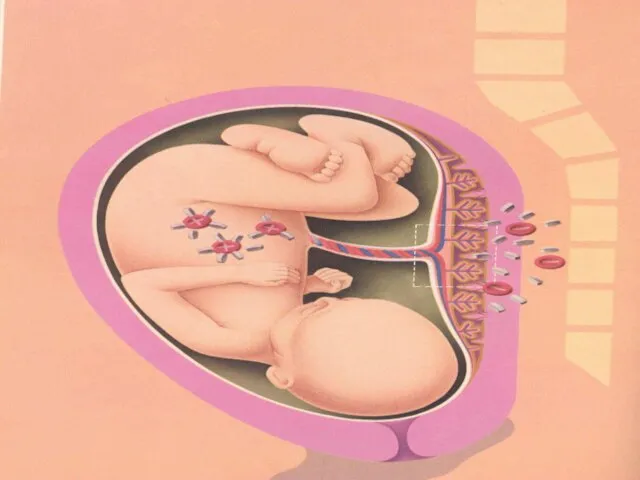
- 27. Fetus at Risk Fetal anemia diagnosed by: amniocentesis cordocentesis ultrasound hydrops middle cerebral artery Doppler Treatment:
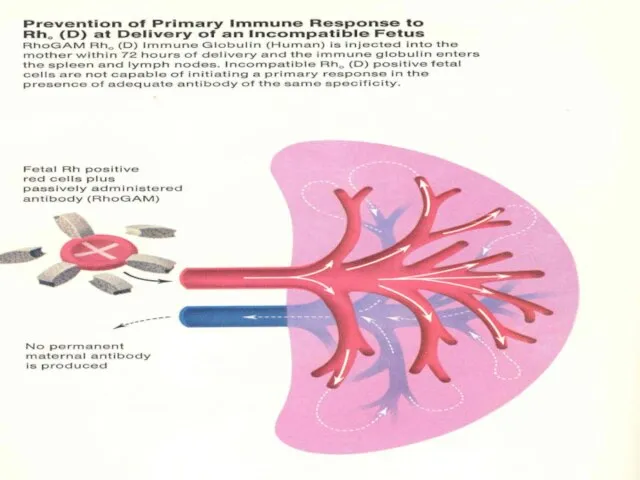
- 28. Infant at Risk Diagnosis: history of HDN antibodies? early jaundice cord DAT (“Coomb’s”) positive (due to
- 31. Скачать презентацию















 Предмет, история и методы психологии физической культуры. Вощинин Александр Владимирович
Предмет, история и методы психологии физической культуры. Вощинин Александр Владимирович Организация вакцинации населения против COVID-19
Организация вакцинации населения против COVID-19 Анаероби. Збудники зоонозних інфекцій
Анаероби. Збудники зоонозних інфекцій Семейство Bacillaceae
Семейство Bacillaceae Соматический гипермутагенез. Клональная селекция лимфоцитов
Соматический гипермутагенез. Клональная селекция лимфоцитов Общая рецептура. Общие принципы выписывания рецепта на жидкие лекарственные формы
Общая рецептура. Общие принципы выписывания рецепта на жидкие лекарственные формы Пухлини органів травлення
Пухлини органів травлення Балалардағы артелиялық гипотензия
Балалардағы артелиялық гипотензия Рентгенологические методы исследования органов брюшной полости
Рентгенологические методы исследования органов брюшной полости Антибиотики
Антибиотики Cимуляциялық орталықта жедел жәрдем көрсету бойынша тәжрибелік дағдыларды игеру
Cимуляциялық орталықта жедел жәрдем көрсету бойынша тәжрибелік дағдыларды игеру каримов
каримов Переговоры как инструмент разведки
Переговоры как инструмент разведки Теория Множественного Интеллекта Говарда Гарднера
Теория Множественного Интеллекта Говарда Гарднера Социально-психологическая поддержка и оказание помощи детям, находящимся в социально опасном положении
Социально-психологическая поддержка и оказание помощи детям, находящимся в социально опасном положении Функциональные заболевания ЖКТ в поликлинической практике. Функциональная диспепсия и синдром раздраженной кишки. Дисбиоз
Функциональные заболевания ЖКТ в поликлинической практике. Функциональная диспепсия и синдром раздраженной кишки. Дисбиоз Рентгенодиагностика синуситов
Рентгенодиагностика синуситов Туберкулез. Первичный туберкулезный комплекс в легком
Туберкулез. Первичный туберкулезный комплекс в легком Балалардағы құсу және лоқсу синдромы
Балалардағы құсу және лоқсу синдромы Бета-адреноблокаторы
Бета-адреноблокаторы Болезнь Пейрони. Расстройство эякуляции
Болезнь Пейрони. Расстройство эякуляции Атопический дерматит
Атопический дерматит EQ – эмоциональный интеллект
EQ – эмоциональный интеллект Халықтың белгілі бір категориясымен түзету жұмысының алгоритмін талқылау
Халықтың белгілі бір категориясымен түзету жұмысының алгоритмін талқылау Ресурсы развития лечебно-оздоровительного туризма. Лекция 2
Ресурсы развития лечебно-оздоровительного туризма. Лекция 2 Эргономические особенности организации рабочего места врача-стоматолога. Работа врача с помощником «в четыре руки»
Эргономические особенности организации рабочего места врача-стоматолога. Работа врача с помощником «в четыре руки» Омертвения. Свищи. Язвы
Омертвения. Свищи. Язвы Воспалительные и дистрофические заболевания ВНЧС у детей
Воспалительные и дистрофические заболевания ВНЧС у детей