Содержание
- 2. Content: History of the discovery of the disease definition Epidemiology Classification Etiology Pathogenesis Clinical picture case
- 3. History of the discovery of the disease by Dr. Takayasu Takayasu Mikita
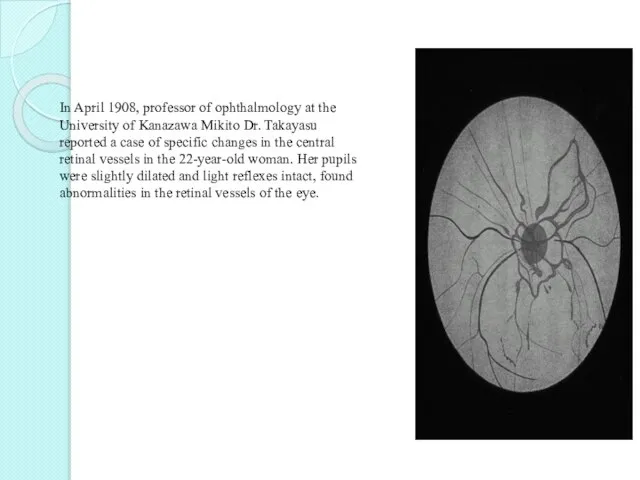
- 4. In April 1908, professor of ophthalmology at the University of Kanazawa Mikito Dr. Takayasu reported a
- 5. Dr. Minoru Nakajima in 1921 described the disease in the following four criteria: (I) affecting the
- 6. Monument Mikita Takayasu in Kanazawa University
- 7. definition Takayasu's disease - rarely diagnosed idiopathic disease, one of the manifestations of chronic granulomatous arteritis
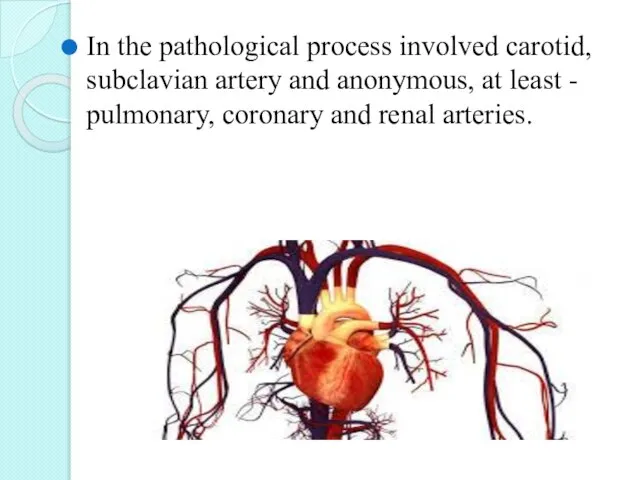
- 8. In the pathological process involved carotid, subclavian artery and anonymous, at least - pulmonary, coronary and
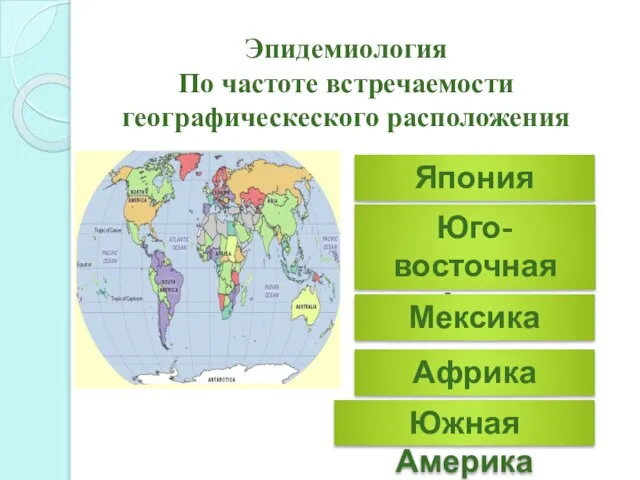
- 9. Эпидемиология По частоте встречаемости географическеского расположения Япония Юго-восточная Азия Мексика Африка Южная Америка
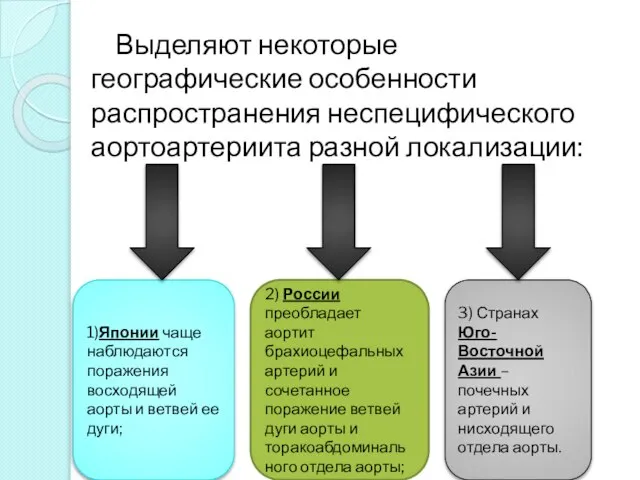
- 10. Выделяют некоторые географические особенности распространения неспецифического аортоартериита разной локализации: 1)Японии чаще наблюдаются поражения восходящей аорты и
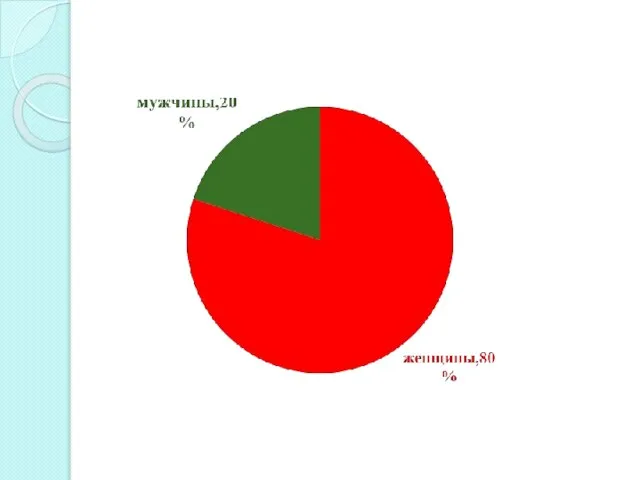
- 11. По частоте , принадлежности полу и возрасту 2,6: 1 000000 населения в год. 15:1 преобладают женщины
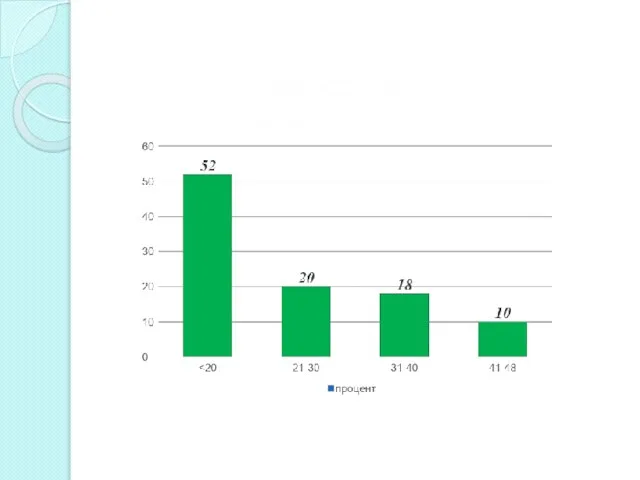
- 13. Возрастная категория
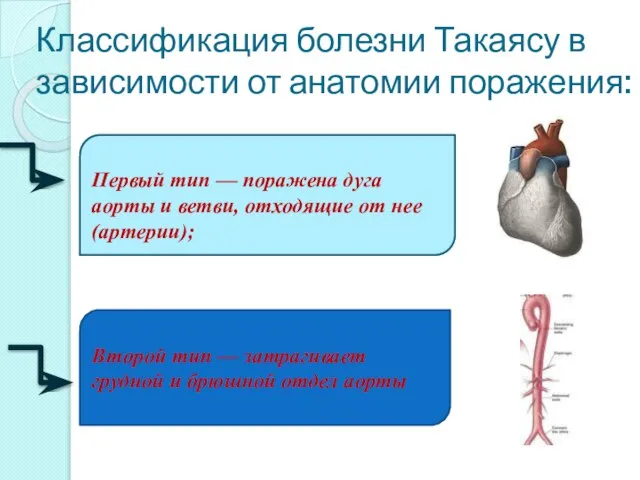
- 14. Классификация болезни Такаясу в зависимости от анатомии поражения: Первый тип — поражена дуга аорты и ветви,
- 15. Третий тип — поражена дуга аорты вместе с грудным и брюшным отделами. Четвертый тип – в
- 16. Современная классификация артериита Такаясу основывается на данных, получаемых в результате ангиографического исследования. В зависимости от сосуда/сосудов,
- 17. Etiology The etiology of systemic vasculitis has not been studied, but traced its connection with infectious-allergic
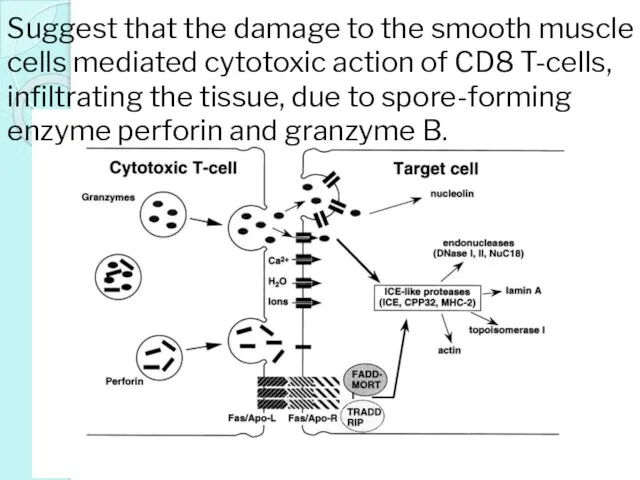
- 18. Suggest that the damage to the smooth muscle cells mediated cytotoxic action of CD8 T-cells, infiltrating
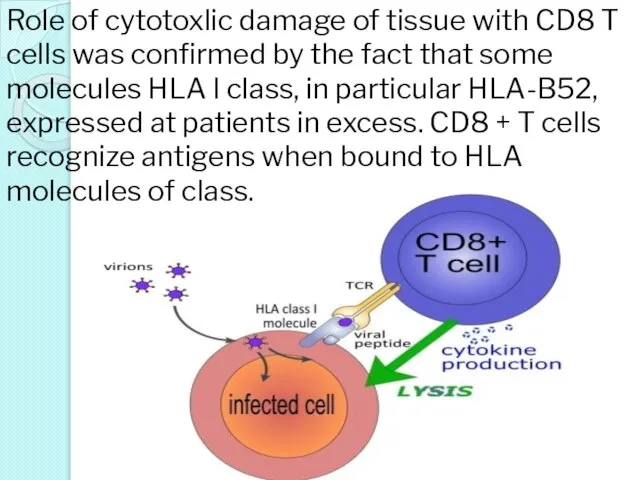
- 19. Role of cytotoxlic damage of tissue with CD8 T cells was confirmed by the fact that
- 20. Currently considered the most probable genetic predisposition to appearance of Takayasu disease. Patients with this syndrome
- 21. Pathogenesis The disease begins with the development of inflammation in the wall of the aorta and
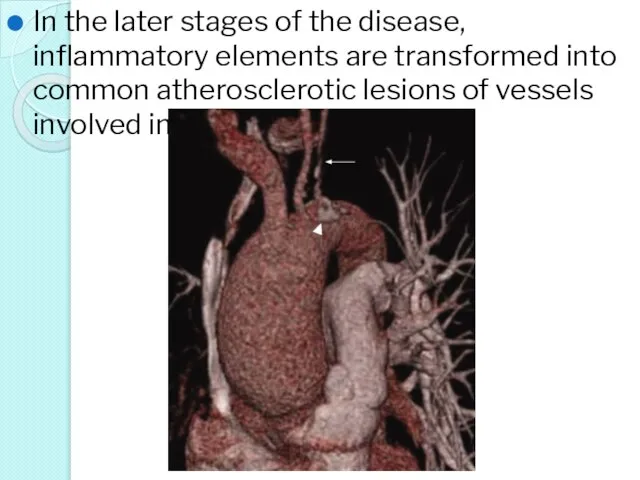
- 22. In the later stages of the disease, inflammatory elements are transformed into common atherosclerotic lesions of
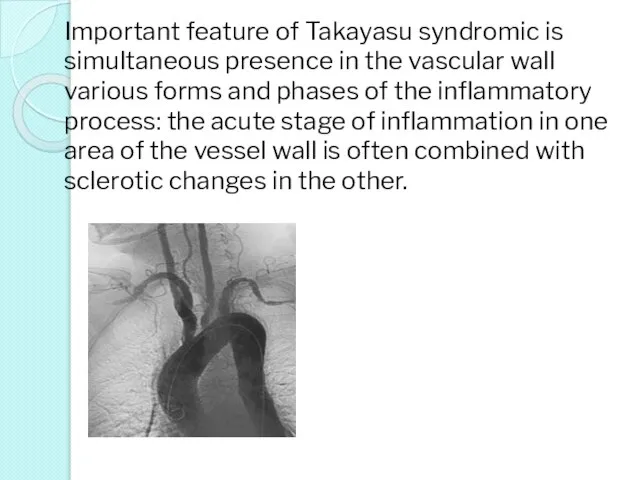
- 23. Important feature of Takayasu syndromic is simultaneous presence in the vascular wall various forms and phases
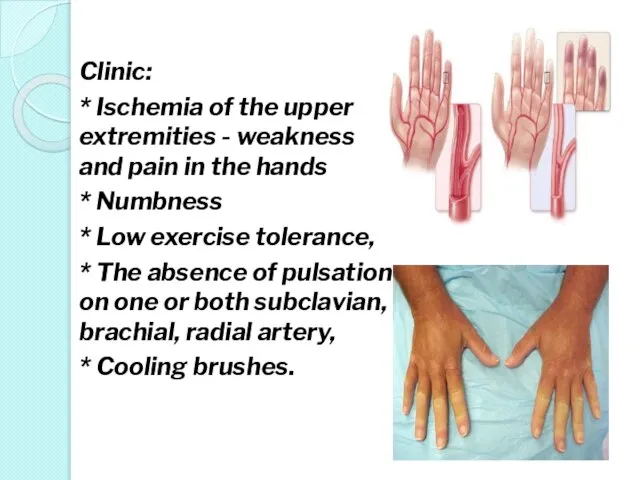
- 24. Clinic: * Ischemia of the upper extremities - weakness and pain in the hands * Numbness
- 25. * A clear difference in blood pressure on the affected and healthy upper limbs, * Higher
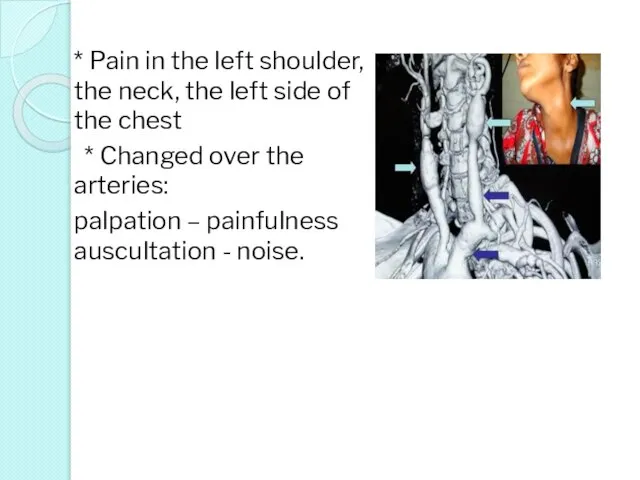
- 26. * Pain in the left shoulder, the neck, the left side of the chest * Changed
- 27. Inflammatory lesion of the vertebral and carotid arteries Takayasu's disease causes neurological symptoms: dizziness, confusion attention
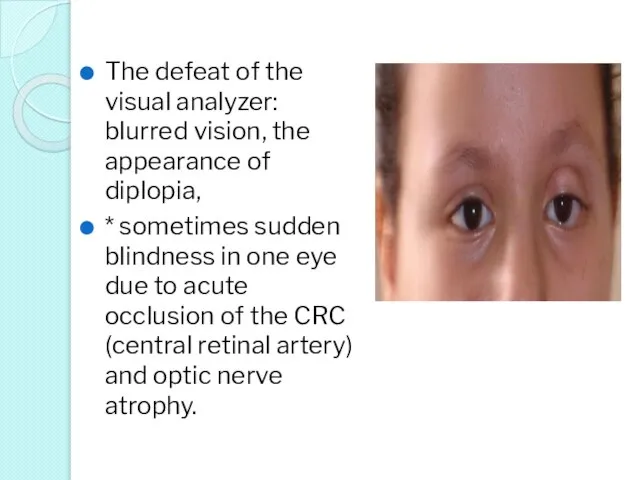
- 28. The defeat of the visual analyzer: blurred vision, the appearance of diplopia, * sometimes sudden blindness
- 29. Vision due to diplopia
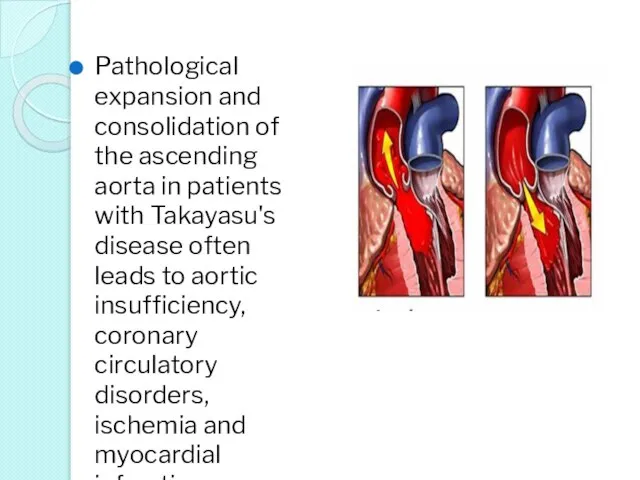
- 30. Pathological expansion and consolidation of the ascending aorta in patients with Takayasu's disease often leads to
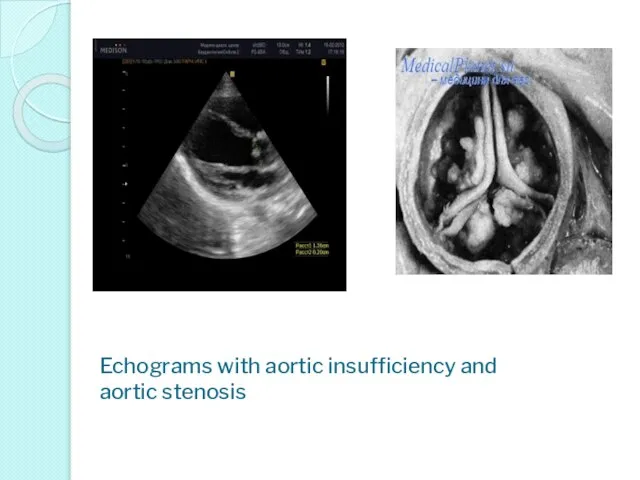
- 31. Echograms with aortic insufficiency and aortic stenosis
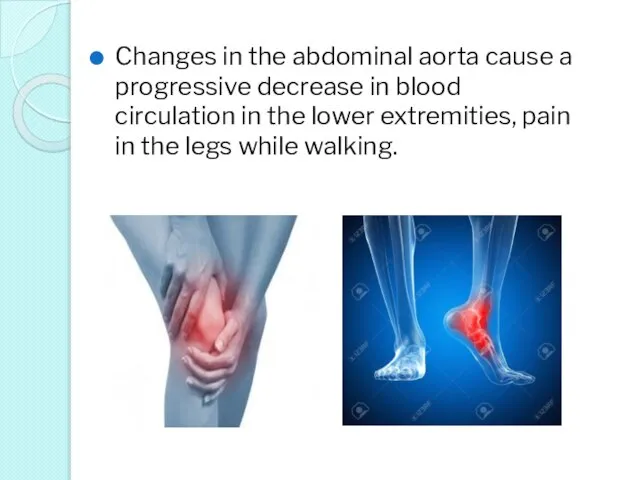
- 32. Changes in the abdominal aorta cause a progressive decrease in blood circulation in the lower extremities,
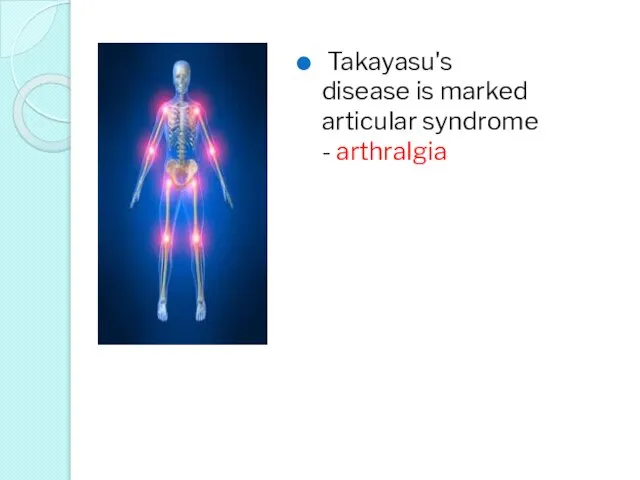
- 33. Takayasu's disease is marked articular syndrome - arthralgia
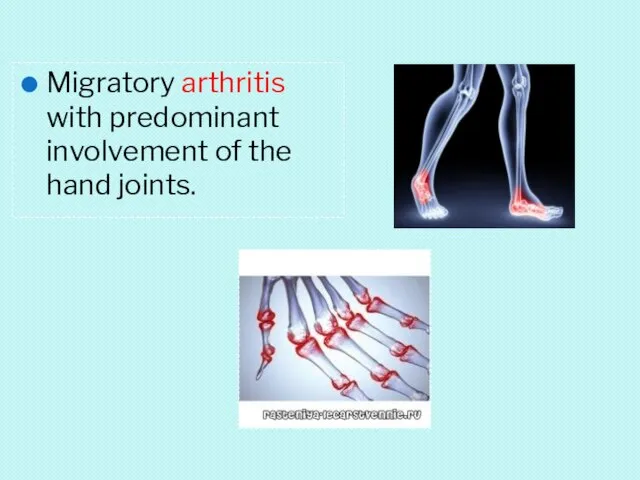
- 34. Migratory arthritis with predominant involvement of the hand joints.
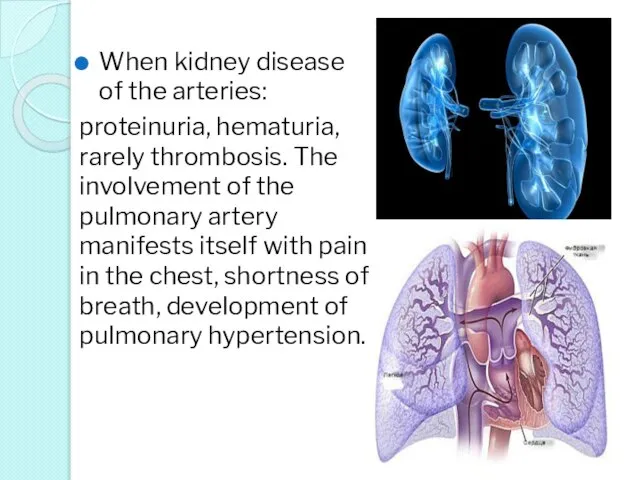
- 35. When kidney disease of the arteries: proteinuria, hematuria, rarely thrombosis. The involvement of the pulmonary artery
- 36. В 24.02.2016 Came to NCP and CS with complains: weight loss arthralgia, general weakness. Ospan Gulbanu
- 37. Anamnesis vitae: Ребенок от 2 беременности, 2 родов с массой 3900 гр, рост 52 см. Беременность
- 38. Status praesens: Состояние средней степени тяжести, сознание ясное. Ребенок повышенного питания, правильного телосложения. Самочувствие не страдает.
- 39. Status praesens: Дыхательная система: дыхание свободное, через нос. В легких дыхание везикулярное, хрипов нет. ЧД 18
- 40. Лабораторные данные: ОАК: эр – 3,2 *1012/л; Нв- 117г/л; тромб- 303т, Л.- 6.5 *109/л; СОЭ –
- 41. Еchocardiography and Doppler -the heart cavity is not expanded -the wall thickness of the myocardium in
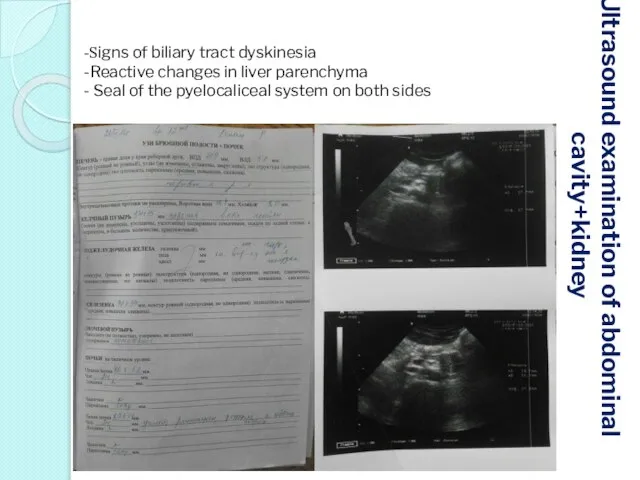
- 42. Ultrasound examination of abdominal cavity+kidney -Signs of biliary tract dyskinesia -Reactive changes in liver parenchyma -
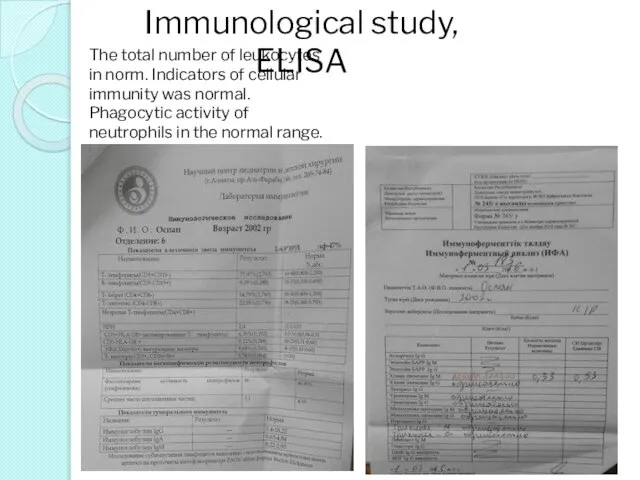
- 43. Immunological study, ELISA The total number of leukocytes in norm. Indicators of cellular immunity was normal.
- 44. Невыраженный дисфункциональные изменения, снижение порога возбудимости синхронизирующих срединных структур. ЭЭГ
- 45. Результат микробиологического исследования При исследовании маска из зева- Выделены Str. Dysgalactie IV H. Influencae IV
- 46. Чувствительность микроорганизмов к химиотерапевтическим препаратам Str. Dysgalactie IV Цефалоспорины: Аминогликозиды: -Цефотаксим - Римфампицин -цефаксим Фторхинолоны: -офлаксацин
- 47. Лечение Рост 143 см, Вес 38 кг, Пол: женский Режим щадящий Диета № 15 Метилпреднизалон 16
- 48. Клинический диагноз: Неспецифический аороартерит, активность I степени, рецидивирующее течение. Сопутствующий диагноз: ДЖВП. Реактивный гепатит. Реактивный панкреатит.
- 49. International Journal of Rheumatic diseases 2014; 17: 931-935 p. Комлексное лечение вазоренальной гипертензии при неспецифическим аортоартериите
- 51. Скачать презентацию























 Особенности профессионального общения
Особенности профессионального общения Психология воздействия в следственной практике
Психология воздействия в следственной практике Нәрестелік кезең дағдарысы – әрекет үстінде субъектілікке қол жеткізу (11 ай – 18 ай)
Нәрестелік кезең дағдарысы – әрекет үстінде субъектілікке қол жеткізу (11 ай – 18 ай) Лекция №22. Общие вопросы хирургической инфекции
Лекция №22. Общие вопросы хирургической инфекции Первая помощь при попадании инородного тела в дыхательные пути
Первая помощь при попадании инородного тела в дыхательные пути Информированность населения о мерах профилактики ожирения
Информированность населения о мерах профилактики ожирения Рак почки
Рак почки Мифы о гриппе или зачем нужна прививка?
Мифы о гриппе или зачем нужна прививка? Презентация по медицине Острая анаэробная инфекция. Госпитальная инфекция
Презентация по медицине Острая анаэробная инфекция. Госпитальная инфекция  Класс Mollicutes
Класс Mollicutes Кесарево сечение
Кесарево сечение Оздоровительное воздействие общеразвивающих упражнений на организм ребенка
Оздоровительное воздействие общеразвивающих упражнений на организм ребенка Социально-значимые заболевания как медико-социальная проблема
Социально-значимые заболевания как медико-социальная проблема Биотехнологические производства. Технологические схемы
Биотехнологические производства. Технологические схемы Некомпактный миокард левого желудочка в педиатрической практике
Некомпактный миокард левого желудочка в педиатрической практике Фоновые заболевания шейки матки. Эрозия шейки матки
Фоновые заболевания шейки матки. Эрозия шейки матки Биохимические причины осложнения при сахарном диабете
Биохимические причины осложнения при сахарном диабете Вирусы гепатита А и Е
Вирусы гепатита А и Е Пиелонефрит. Классификация пиелонефрита по типам течении
Пиелонефрит. Классификация пиелонефрита по типам течении Цели и этапы эндодонтического лечения
Цели и этапы эндодонтического лечения ВИЧ/СПИД
ВИЧ/СПИД Динамическое или психодинамическое направление в психотерапии. Разновидности психоанализа
Динамическое или психодинамическое направление в психотерапии. Разновидности психоанализа Артериальная гипертензия
Артериальная гипертензия Термометрия. Уход при лихорадке
Термометрия. Уход при лихорадке Организация первичной медико-санитарной помощи
Организация первичной медико-санитарной помощи Заболевания среднего и внутреннего уха. (Лекция 2)
Заболевания среднего и внутреннего уха. (Лекция 2) Всё имеет смысл, пока мы здоровы
Всё имеет смысл, пока мы здоровы Особо опасные вирусные геморрагические лихорадки: лихорадка Эбола, лихорадка Марбург, лихорадка Ласса
Особо опасные вирусные геморрагические лихорадки: лихорадка Эбола, лихорадка Марбург, лихорадка Ласса