Содержание
- 2. “The Monetary System”
- 3. Contents Definition of Money… Kinds Of Money Functions Of Money The Demand For Money Four Money
- 4. What is Money????
- 5. “Money is a good that acts as a medium of exchange in transactions, it is said
- 6. Properties Of Money Liquidity Scarcity Portability Uniformity
- 7. Kinds Of Money Commodity money Convertible paper money Inconvertible money Bank deposits Electronic money
- 8. Commodity money Can be used for other purposes. Have inherent value. Examples Gold, Silk, Cattle, Silver
- 9. Convertible Paper Money The paper money that can be convertible into gold and silver. Examples are
- 10. Inconvertible Paper Money The paper money that can’t be converted into Gold and Silver. Also called
- 11. Bank Deposits In current society most of the money used is Bank deposits… Examples of Bank
- 12. Electronic Money The money stored in certain electronic cash cards. Transactions are made electronically. Examples are
- 13. Functions of Money
- 14. Money as Medium of Exchange No wastage of time. Higher volume of transactions. Remove the problem
- 15. Money as a unit of Account Provide a common measurement for the relative value of goods.
- 16. Money as a store of Value Ability of money to store value over the time. Durability
- 17. Are credit cards money???
- 18. Why people hold money???
- 19. Three motives of holding money!!! Transactions Demand Precautionary Demand Speculative Demand
- 20. Transactions Demand Stock of money to pay everyday expenses. Quick and easy purchases are main push
- 21. Precautionary Motives The stock of money for uncertain expenses. People who don’t want to go for
- 22. Speculative Motives Holding of money due to the expected rise in interest rates. People use to
- 23. INTEREST The major factor to determine the stock of money held by people is the INTEREST!!!
- 24. Money Supply Definitions
- 25. Monetary Base M1 Sum of currency in the hands of non-public and stock of cheque account
- 26. Broad Money M3 plus the public’s deposits at non-bank financial institutions less currency and bank deposits
- 27. Currency Includes coins and paper money. It constitute 20% of the M1 money supply. Its purpose
- 28. Cheque Account Deposits The total of cheque accounts balances in banks convertible to currency on demand
- 29. Determination of Interest Rate
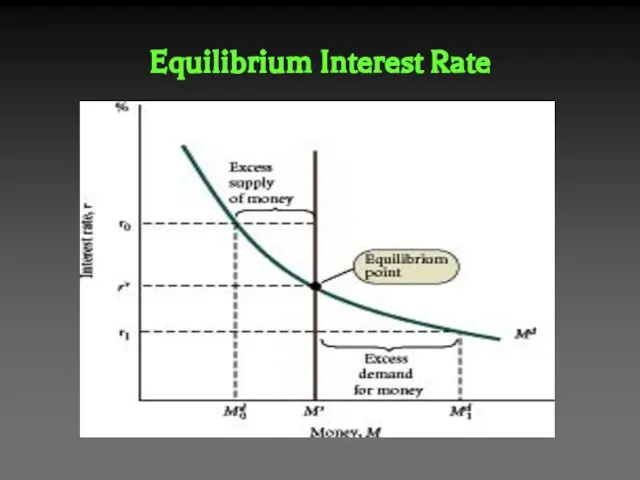
- 30. Equilibrium Interest Rate
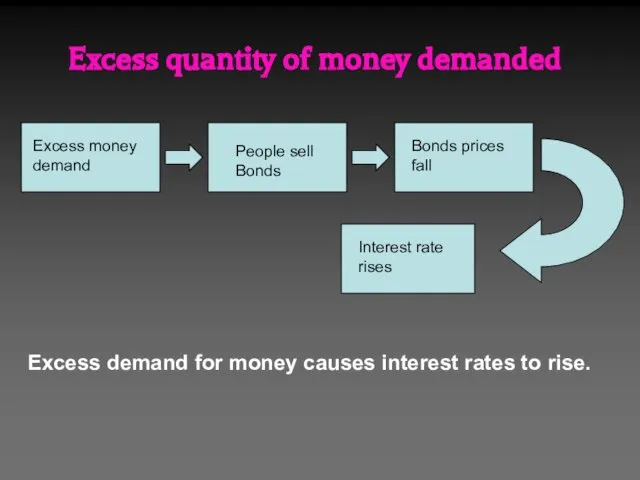
- 31. Excess quantity of money demanded Excess money demand Interest rate rises People sell Bonds Bonds prices
- 32. Excess quantity of money supplied Excess money supplied Interest rate falls People buy Bonds Bonds prices
- 34. Скачать презентацию





























 Вводный семинар из цикла Технологии успешного инвестирования
Вводный семинар из цикла Технологии успешного инвестирования Виды ценных бумаг. Фондовый рынок
Виды ценных бумаг. Фондовый рынок Дополнительные мероприятия на рынке труда Ямало-Ненецкого автономного округа в 2020 году
Дополнительные мероприятия на рынке труда Ямало-Ненецкого автономного округа в 2020 году Финансовый раздел бизнес плана
Финансовый раздел бизнес плана Срочный рынок. Сегментация спот рынков
Срочный рынок. Сегментация спот рынков Основы финансовых вычислений. Практические приложения теории. (Тема 4)
Основы финансовых вычислений. Практические приложения теории. (Тема 4) Состав и содержание сметной документации строительства
Состав и содержание сметной документации строительства Налог на прибыль
Налог на прибыль Міжбанківські розрахунки в Україні
Міжбанківські розрахунки в Україні Қаржы инвестицияларының есебі
Қаржы инвестицияларының есебі Кількісна теорія грошей і сучасний монетаризм
Кількісна теорія грошей і сучасний монетаризм Оценка стоимости земли
Оценка стоимости земли Налог на прибыль. Практическое занятие 5
Налог на прибыль. Практическое занятие 5 Выбытие основных средств
Выбытие основных средств Корпоративные финансы
Корпоративные финансы Финансовая грамотность для населения
Финансовая грамотность для населения За десять лет в десять раз
За десять лет в десять раз Финансовое состояние предприятия
Финансовое состояние предприятия Понятия налоговый вычет и налоговая выгода. Бизнес - справка для доказательства проявления Должной осмотрительности
Понятия налоговый вычет и налоговая выгода. Бизнес - справка для доказательства проявления Должной осмотрительности Регулирование государственных денежных потоков
Регулирование государственных денежных потоков Финансовое злоупотребления в сфере страхования и методы его предотвращения
Финансовое злоупотребления в сфере страхования и методы его предотвращения Размеры стипендиального обеспечения студентов, магистрантов, аспирантов, докторантов АлтГТУ на 1 февраля 2016 года
Размеры стипендиального обеспечения студентов, магистрантов, аспирантов, докторантов АлтГТУ на 1 февраля 2016 года Анализ собственного капитала
Анализ собственного капитала Отчет о проделанной работе администрации Ивановского сельского поселения за 2021 год
Отчет о проделанной работе администрации Ивановского сельского поселения за 2021 год Бюджетная система Россий ской Федерации
Бюджетная система Россий ской Федерации Управление стоимостью капитала корпорации
Управление стоимостью капитала корпорации Элементы денежной системы
Элементы денежной системы Содержание финансового менеджмента и его место в системе управления организацией
Содержание финансового менеджмента и его место в системе управления организацией