Содержание
- 2. Which 3 of these typical problems have affected your organization’s document or records management implementation? Implementation
- 3. The MIKE2 Methodology "MIKE2 (Method for an Integrated Knowledge Environment) is an Open Source methodology for
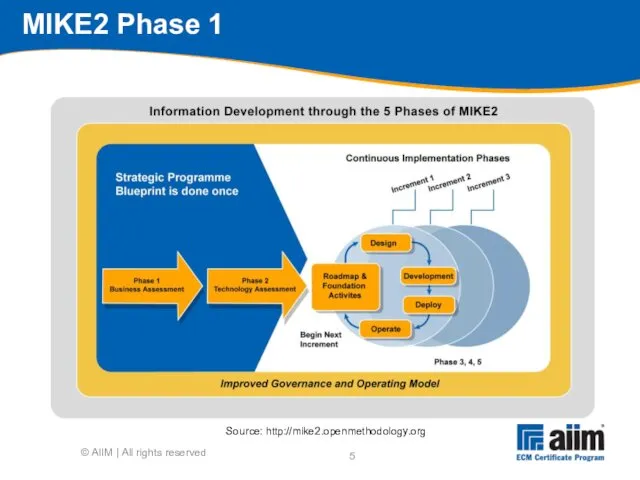
- 4. MIKE2 Phases (description) Phase 1 - Business assessment Phase 2 - Technology assessment Phase 3 -
- 5. © AIIM | All rights reserved MIKE2 Phase 1 Source: http://mike2.openmethodology.org
- 6. Conduct initial direction setting with sponsor Sponsor needs to provide insights Difficult or impossible to do
- 7. Programme charter: Overall approach Should be developed in 3 stages Current-state The environment The principles &
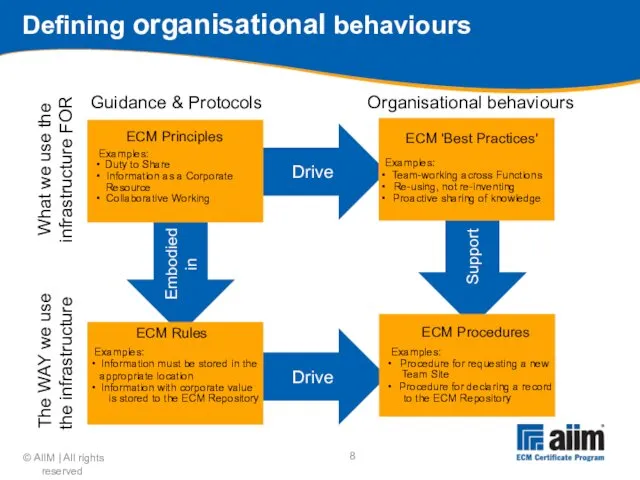
- 8. Drive Drive Support Embodied in Defining organisational behaviours Organisational behaviours Guidance & Protocols What we use
- 9. Organisational QuickScan for information development Analyses current-state of organisation across multiple facets to identify the baseline
- 10. Strategic business requirements Establishes the overall set of strategic business requirements (business case) that translate into
- 11. Strategic business vision Defines what organisation wishes to achieve in the Future-State Done by interviewing executives
- 12. Business blueprint Key deliverable of MIKE2 Final strategic analysis and synthesis of business assessment work Completes
- 13. Eat the elephant one bite at a time Go for specific projects, one at a time
- 14. Prioritise requirements Refines the strategic information requirements Determines the sequence of projects Strategic vs. tactical Within
- 15. Linking tactics to strategy Users / other stakeholders Management / executive board Business area managers Operational
- 16. Business blueprint components Arranged in key sections Executive summary High-level programme plan Business case Strategic case
- 17. © AIIM | All rights reserved MIKE2 Phase 2 Source: http://mike2.openmethodology.org
- 18. Technology assessment Concentrates on the technical aspects of your strategy Technology blueprint Strategically ties the business
- 19. Business drives technology Phase 1 and 2 parallelism Phase 1 deliverables must be completed before phase
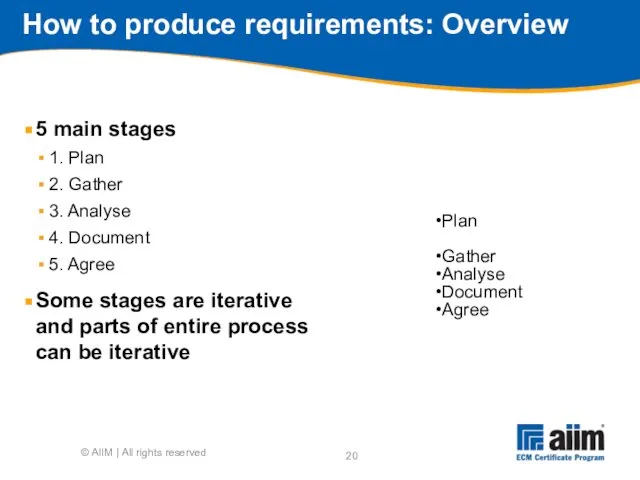
- 20. How to produce requirements: Overview 5 main stages 1. Plan 2. Gather 3. Analyse 4. Document
- 21. Conduct gap analysis of current-state and future-state Identify key gaps between current-state architecture and future-state Where
- 22. © AIIM | All rights reserved MIKE2 Governance model Source: http://mike2.openmethodology.org Improved Governance and Operating Model
- 23. Why information governance? Accountability for organisation’s information assets Good governance Ensures compliance with regulations and legislation
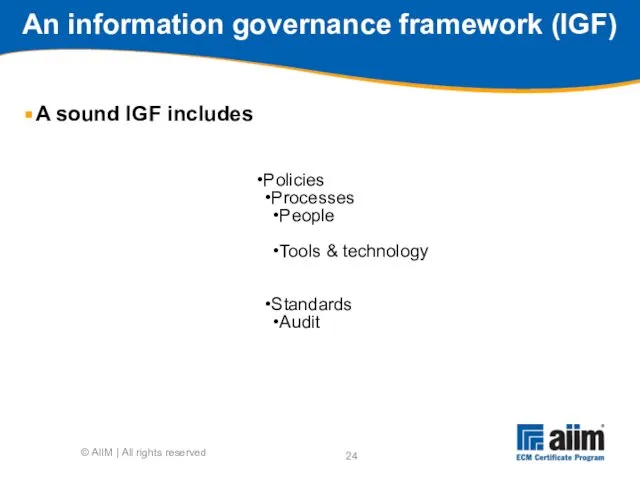
- 24. An information governance framework (IGF) A sound IGF includes © AIIM | All rights reserved Policies
- 25. The role of ECM in information governance ECM environment is Key tool for Information Governance Repository
- 26. Continuous improvement © AIIM | All rights reserved Prevent Risk assessments Training Policies & procedures Executive
- 27. MIKE2 Phase 3 Roadmap Roadmap © AIIM | All rights reserved
- 28. Project roadmap overview Project roadmap is the guide for the entire project In each iteration of
- 29. Identify and prioritise project risks With each iteration, re-examine risks for iteration and project as a
- 30. MIKE2 Phase 3 Foundation activities Software development readiness Enterprise information architecture Taxonomy design Metadata development Solution
- 31. Foundation activities (1) Focused on ensuring that the environment is ready and that basic solution decisions
- 32. Foundation activities (2) Technical and design foundations Iterative Risk assessment and management © AIIM | All
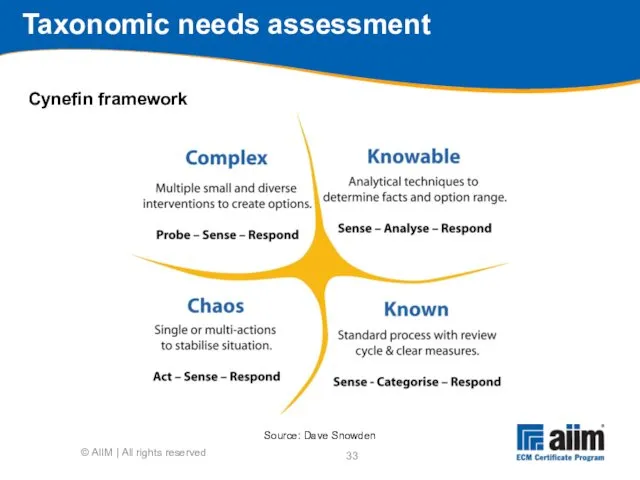
- 33. Taxonomic needs assessment Source: Dave Snowden © AIIM | All rights reserved Cynefin framework
- 34. Developing a taxonomy Identify stakeholders Define purpose Determine approach Collect information Develop scheme Pilot scheme Deploy
- 35. © AIIM | All rights reserved MIKE2 Phase 4 Source: http://mike2.openmethodology.org
- 36. Identify training and administration guide requirements Used to estimate training needs Varies depending on complexity of
- 37. Develop outlines for operational manuals There will be multiple operational manuals, targeted at the specific audiences
- 38. Design backup and recovery procedures If your solution is based on a single provider, single repository
- 39. Business value of prototyping © AIIM | All rights reserved Cumulative business value time uncertainty decreases
- 40. All users have raised expectations © AIIM | All rights reserved Source: Apple iTunes Music Store
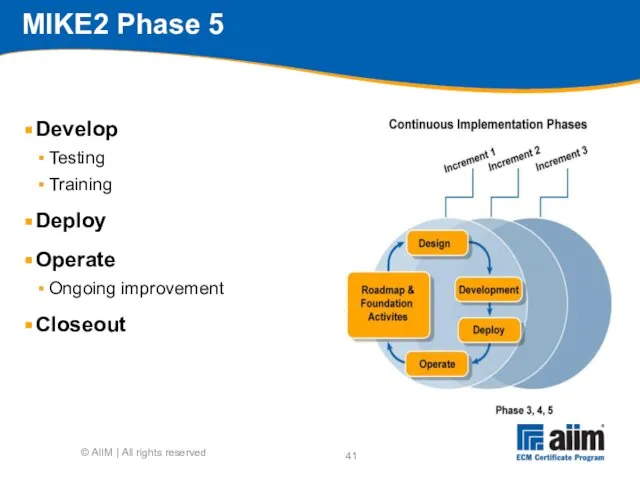
- 41. MIKE2 Phase 5 Develop Testing Training Deploy Operate Ongoing improvement Closeout © AIIM | All rights
- 42. Develop user support documentation Created to provide step-by-step documentation, with appropriate screenshots, to illustrate an entire
- 43. Develop operations support guides Introduction Document distribution list Document change process Application overview Production environment Production
- 44. Technology backplane development Making this available as soon as possible is critical for the development of
- 45. User testing Pilots and model offices are popular approaches Refine design and implementation of new ecm-enabled
- 46. Model offices & pilot: Benefits Technical evaluation Functional testing System integration testing (SIT) End-to-end testing (E2E)
- 47. Production deployment Post-pilot and/or model office work, the environment finally reaches a deployment-ready state Final steps
- 48. Deploy software to production Solution is ready to be released into production, with final evaluation and
- 49. Evaluation and launch Post technical deployment is the final evaluation, scheduled launch and post-launch verification and
- 50. Training feedback loop Collect feedback At the time And later Review, learn and improve Review Learn
- 51. Importance of change readiness assessment Organisational change will always appear threatening People think of job security
- 52. Best practices for implementing change Change needs to be managed, but there are many different methods
- 53. Creating user “wins” Early wins create a “Yes” environment Wins should be promoted widely Leverage existing
- 55. Скачать презентацию










































 Для клиентов BigBon chips
Для клиентов BigBon chips Инструкции для Тайного Покупателя
Инструкции для Тайного Покупателя Программа Гостеприимство для команды TETЧER GASTROPUB
Программа Гостеприимство для команды TETЧER GASTROPUB Mad Elephants LLC предложение сотрудничества
Mad Elephants LLC предложение сотрудничества Слагаемые успеха малых медиа
Слагаемые успеха малых медиа Акции лояльности в продвижении торговой марки Jysk
Акции лояльности в продвижении торговой марки Jysk Реализация позиционирования в рекламном дизайне
Реализация позиционирования в рекламном дизайне Планирование и прогнозирование в условиях рынка
Планирование и прогнозирование в условиях рынка Кейс №3. Идеи для новой жизни
Кейс №3. Идеи для новой жизни Выход компании ХХХ на региональные рынки в сфере биллинговых услуг
Выход компании ХХХ на региональные рынки в сфере биллинговых услуг Стеновые самоклеящиеся панели 3D
Стеновые самоклеящиеся панели 3D Интеграционный гид
Интеграционный гид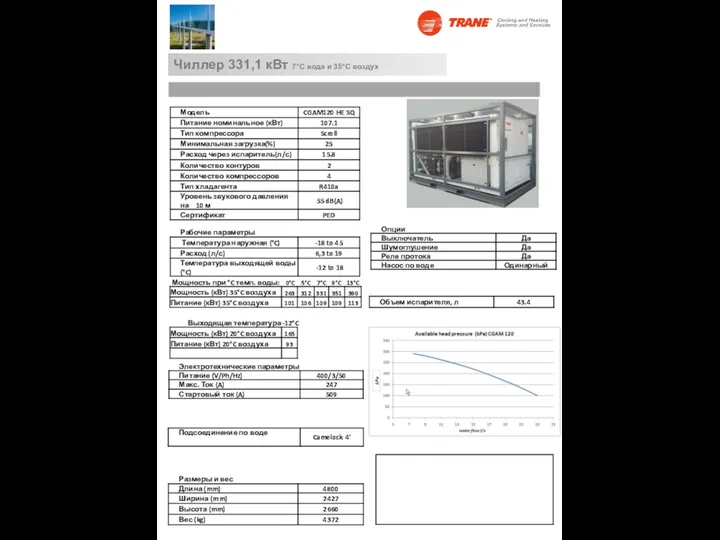 Чиллер 331,1 кВт
Чиллер 331,1 кВт Санаторий Янган-Тау Башкирия, Салаватский р-н с. Янгантау
Санаторий Янган-Тау Башкирия, Салаватский р-н с. Янгантау Мерчандайзинг тәжірибесі
Мерчандайзинг тәжірибесі Аренда коммерческой недвижимости
Аренда коммерческой недвижимости Компания Not Just Milk
Компания Not Just Milk Особенности и перспективы развития маркетинга в туризме. Тема 2
Особенности и перспективы развития маркетинга в туризме. Тема 2 Общая информация – кассы iPOS
Общая информация – кассы iPOS Компания Terno Scorrevolli
Компания Terno Scorrevolli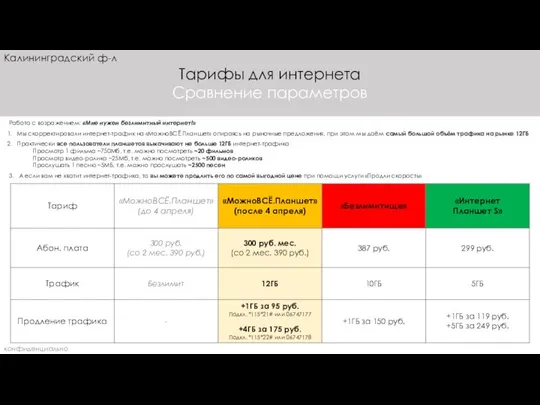 Интернет-тарифы. Калининград
Интернет-тарифы. Калининград Глобальные тренды в маркетинге
Глобальные тренды в маркетинге ООО “СиВер” (часть 5)
ООО “СиВер” (часть 5) Бренд. Человек-бренд. Миссия
Бренд. Человек-бренд. Миссия Вводная часть по этапам сделки. Работа с продавцом и покупателем. Недвижимость
Вводная часть по этапам сделки. Работа с продавцом и покупателем. Недвижимость Прогнозирование и перспективные оценки. Непараметрические методы прогнозирования
Прогнозирование и перспективные оценки. Непараметрические методы прогнозирования Общий прайс 2. Специалист по коммерции Москалюк Н. Я
Общий прайс 2. Специалист по коммерции Москалюк Н. Я Структура Digital продвижения
Структура Digital продвижения