Содержание
- 2. Successful operations of the company Effective planning Accurate forecasting
- 3. Forecasting techniques: Mechanical extrapolation Simulation Linear interpolation Exponential smoothing Barometric methods Leading indicators Compound indexes Diffuse
- 4. Mechanical extrapolation Forecasting techniques Originally extrapolation methods are mechanical and not closely linked to economic theory
- 5. However, they are widely used by professional economists who make forecasting Because of they are easy
- 6. Mechanical extrapolation The simplest models: All future values of the studied variable in some way are
- 7. Mechanical extrapolation Forecasting techniques: The simplest models: Unchanging model The predicted value of the variable for
- 8. The vast majority of all economic, political and social decisions are made based on considered the
- 9. TASK: Forcasting based on extrapolation It is known that in 2008 your company's servers were exposed
- 10. 2. The average annual growth rate is an indicator of the intensity changes in the levels
- 11. 3. Chain growth rate is the ratio of each next level of series to previous and
- 12. Time series analysis: Time series consist of values corresponding to certain points or periods Ordered in
- 13. Why fluctuation is typical for the time series? Usually there are four sources of variation in
- 14. 1) Trend (Т) Is a long-term increase or decrease of series Seasonal changes (S) Due to
- 15. 3) Cyclic changes (С) Cover periods of several years, reflect the level of economic boom or
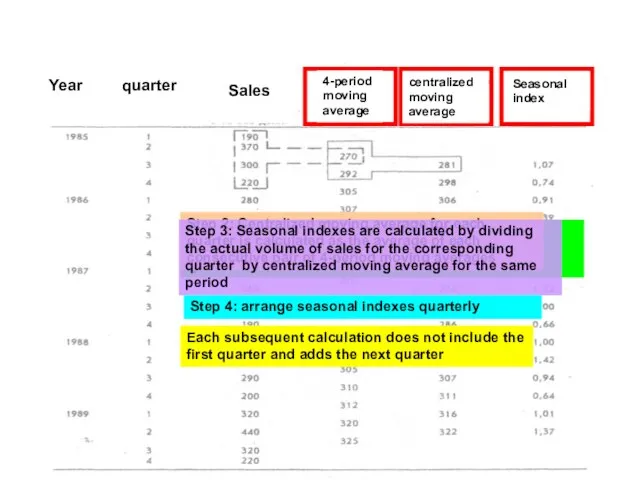
- 16. Seasonal changes and the method of moving average Moving average is calculated by summing the values
- 17. Regroup presented data: Time series analysis: Mechanical extrapolation Forecasting techniques: Using the data presented in the
- 18. Step 1: Moving average over the four periods is calculated using a consistent set of sales
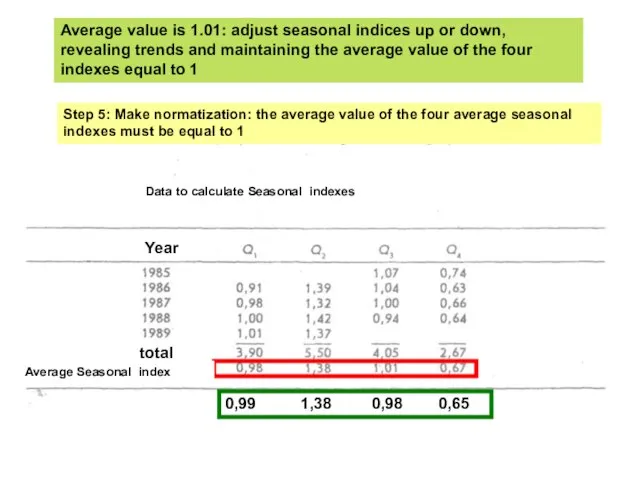
- 19. Step 5: Make normatization: the average value of the four average seasonal indexes must be equal
- 20. Q1: 316 (для 1989) * 0,99 = 312,84 $ Q2: 322 (для 1989) * 1,38 =
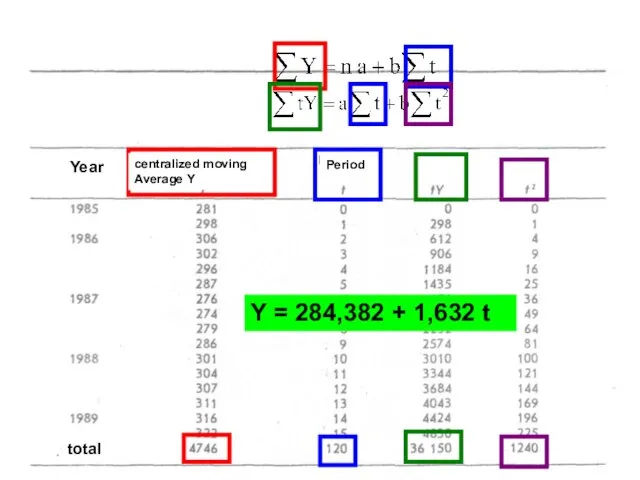
- 21. Designing of trend As a forecasting method assumes that started change in the variable will continue
- 22. ] Y – the observed value of the analyzed variable Y – the predicted value of
- 23. Trend estimates are more reliable if they are based on data released from seasonal effects Seasonal
- 24. Y = 284,382 + 1,632 t Year centralized moving Average Y Period total
- 26. Скачать презентацию














![] Y – the observed value of the analyzed variable Y](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/587663/slide-21.jpg)

 Разработка методов и моделей доставки тарно-штучных грузов из Юго-Восточной Азии в Россию
Разработка методов и моделей доставки тарно-штучных грузов из Юго-Восточной Азии в Россию Стратегическое управление эффективностью бизнеса ОАО ФосАгро
Стратегическое управление эффективностью бизнеса ОАО ФосАгро Діагностика виникнення і розвитку кризового процесу в туризмі
Діагностика виникнення і розвитку кризового процесу в туризмі Принципы работы в команде
Принципы работы в команде Теоретические основы управления изменениями
Теоретические основы управления изменениями Совершенствование логистической деятельности производственного предприятия
Совершенствование логистической деятельности производственного предприятия Мероприятия по стимулированию продаж
Мероприятия по стимулированию продаж Управление качеством и сертификация услуг общественного питания. Тема 1
Управление качеством и сертификация услуг общественного питания. Тема 1 Стажировка в Болгарии
Стажировка в Болгарии Менеджер по работе с поставщиками
Менеджер по работе с поставщиками Организация как система управления
Организация как система управления Содержание предпринимательской деятельности
Содержание предпринимательской деятельности Концепции управления запасами
Концепции управления запасами Управление человеческими ресурсами
Управление человеческими ресурсами Транспортно-экспедиционная компания ТЭК Росавтотранс Сарапул
Транспортно-экспедиционная компания ТЭК Росавтотранс Сарапул Управление магазином подарков. Урок №11
Управление магазином подарков. Урок №11 Общая характеристика менеджмента
Общая характеристика менеджмента Управление методическим и психологическим сопровождением инноваций в образовательном процессе
Управление методическим и психологическим сопровождением инноваций в образовательном процессе Роль этического менеджмента в современной организации
Роль этического менеджмента в современной организации Менеджменттің пайда болуы
Менеджменттің пайда болуы Менеджмент в образовании
Менеджмент в образовании Деловые коммуникации
Деловые коммуникации Процессная модель
Процессная модель Транспортная система Agam Vergus, приложение TransEgmoVargus
Транспортная система Agam Vergus, приложение TransEgmoVargus Work-life balance подход в управлении рабочим временем молодых сотрудников
Work-life balance подход в управлении рабочим временем молодых сотрудников Участие в организации производственной деятельности в рамках структурного подразделения деревообрабатывающего производства
Участие в организации производственной деятельности в рамках структурного подразделения деревообрабатывающего производства Функции менеджмента: контроль и координация
Функции менеджмента: контроль и координация Что должен знать руководитель о мотивации сотрудников
Что должен знать руководитель о мотивации сотрудников