Содержание
- 2. Lection Gonorrhea Gonorrhoea is an old bacterial disease that is almost exclusively acquired through sexual intercourse.
- 3. Gonorrhea Neisseria gonorrhoea, a gram-negative intracellular diplococcus arranged in pairs with their apposing surfaces slightly flattened
- 4. Course of gonorrhea In virtually all cases transmission is the result of sexual contact. Incubation period
- 5. Pathogenesis Neither congenital, no acquired immunity to gonococcus develops in humans. The formed antibodies do not
- 6. Classification Present classification of gonorrhoea: 1) Fresh: a) acute, b) subacute, c) torpid 2) Chronic 3)
- 7. Clinical features of gonorrhoea Clinical features of gonorrhoea: a) fresh acute gonorrhoeal urethritis (anterior, total) Incubation
- 8. Varieties of gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea in small girls (for pediatricians). As a result of anatomical and physiological
- 9. Complications of gonorrhea Balanoposthitis, Phimosis, Paraphimosis, Thysonitis, Periurethral abscess, Littritis, Cowperitis, Prostatitis, Vesiculitis, Epididymitis, Urethral stricture,
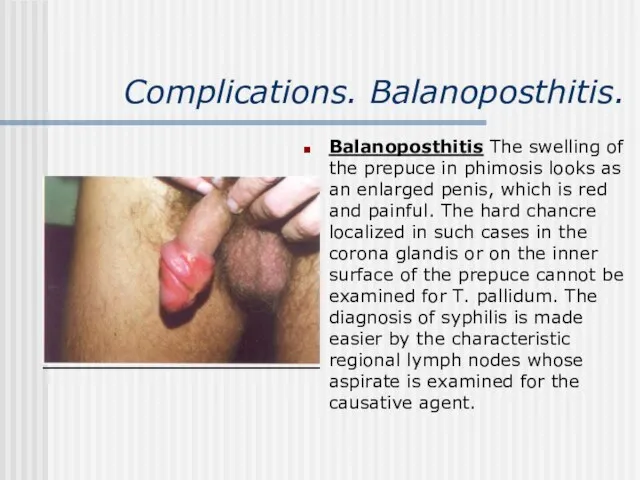
- 10. Complications. Balanoposthitis. Balanoposthitis The swelling of the prepuce in phimosis looks as an enlarged penis, which
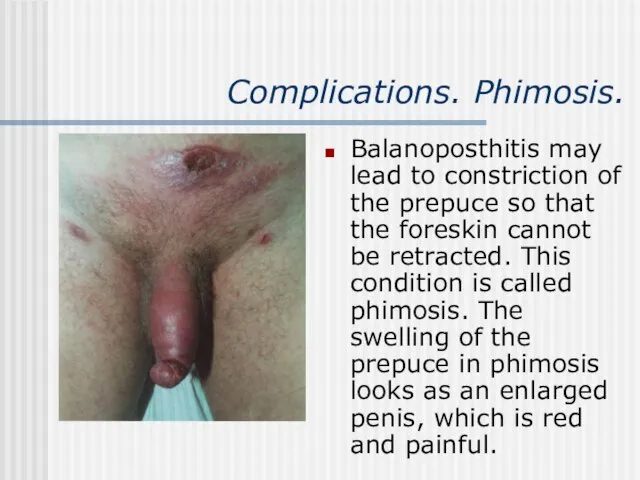
- 11. Complications. Phimosis. Balanoposthitis may lead to constriction of the prepuce so that the foreskin cannot be
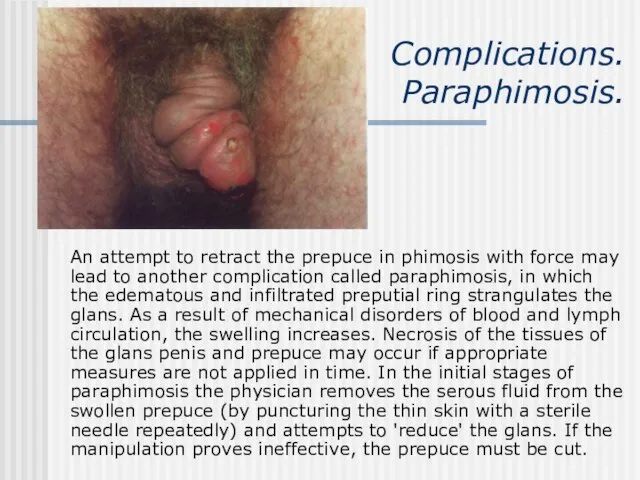
- 12. Complications. Paraphimosis. An attempt to retract the prepuce in phimosis with force may lead to another
- 13. Complications. Cowperitis Cowperitis presents as fever, malaise and severe pain in the perineum with frequency, urgency,
- 14. Thysonitis, periurethral abscess, littritis Thysonitis is an inflammation of thysonic glands. Periuretral abscess - presents as
- 15. Complications. Epididimitis Epididymitis - inflammation of the epididymis, was formerly encountered in gonorrhoea much more frequently
- 16. Urethral stricture Urethral stricture could lead to obstructive symptoms and damages as well as recurrent urinary
- 17. Prostatitis Prostatitis is uncommon as attacks are cut short by the use of antibiotics. Symptoms include
- 18. Prostatitis Catarrhal prostatitis - when the inflammatory process is restricted to the excretory ducts there are
- 19. Treatment of gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is managed by means of antigonococcal agents (antibiotics and sulphanilamides), methods for
- 20. Treatment of chronic gonorrhoea Specific and non-specific immunotherapy (provocation) are used for treatment of chronic, complicated
- 21. Criteria of recovery from gonorrhoea The disappearance of the external signs of the disease after treatment
- 23. Скачать презентацию














 Дисбиозы влагалища. Инфекционно-воспалительные заболевания влагалища и вульвы
Дисбиозы влагалища. Инфекционно-воспалительные заболевания влагалища и вульвы Эпителий ісіктері
Эпителий ісіктері Как заниматься неврологией, если в клинике нет ничего, кроме рентгена
Как заниматься неврологией, если в клинике нет ничего, кроме рентгена Руминативное мышление в подростковом возрасте
Руминативное мышление в подростковом возрасте Перемещение пациента
Перемещение пациента Вакцины. Вакцинация против пневмококковой инфекции
Вакцины. Вакцинация против пневмококковой инфекции Рабдовирустардың лабараториялық диагностикасы
Рабдовирустардың лабараториялық диагностикасы ХОБЛ в сочетании с бронхиальной астмой
ХОБЛ в сочетании с бронхиальной астмой Движение крови по сосудам
Движение крови по сосудам Предмет психологии. Методы. Психология восприятия и ощущения
Предмет психологии. Методы. Психология восприятия и ощущения Салауатты өмір салтын құру және аурудың алдын алу профилактикасы
Салауатты өмір салтын құру және аурудың алдын алу профилактикасы Асқазан және 12-елі ішек ойық жарасы
Асқазан және 12-елі ішек ойық жарасы Морфологические и функциональные особенности почек и процесса мочеобразования у детей
Морфологические и функциональные особенности почек и процесса мочеобразования у детей Нейронная регуляция
Нейронная регуляция Болезни оперированного желудка
Болезни оперированного желудка Лекция. Физическая реабилитация при повреждениях менисков КС
Лекция. Физическая реабилитация при повреждениях менисков КС 10 секретов Аюрведы для здоровья и долголетия
10 секретов Аюрведы для здоровья и долголетия Основы тифлопедагогики. Основные понятия об анатомическом устройстве глаза и функциях зрения
Основы тифлопедагогики. Основные понятия об анатомическом устройстве глаза и функциях зрения Обструктивный шок
Обструктивный шок Супружеские конфликты
Супружеские конфликты Малярия : актуальность, этиология, эпидемиология, патогенез, классификация, клиника, осложнения, диагностика, лечение
Малярия : актуальность, этиология, эпидемиология, патогенез, классификация, клиника, осложнения, диагностика, лечение Общие правила и установки консультанта
Общие правила и установки консультанта Патофизиология надпочечников
Патофизиология надпочечников Ведение больных после эмболизации маточных сосудов
Ведение больных после эмболизации маточных сосудов Болезни беременности и послеродового периода. Болезни половых органов и молочных желез
Болезни беременности и послеродового периода. Болезни половых органов и молочных желез Жүрек қан-тамыр жүйесі патологияларында қолданылатын дәрілік заттардың жіктелуі, жалпы сипаттамасы және қолданылуы
Жүрек қан-тамыр жүйесі патологияларында қолданылатын дәрілік заттардың жіктелуі, жалпы сипаттамасы және қолданылуы Неотложные состояния в клинике внутренних болезней
Неотложные состояния в клинике внутренних болезней Подготовка пациентов к лабораторным обследованиям. Взятие и доставка биоматериала
Подготовка пациентов к лабораторным обследованиям. Взятие и доставка биоматериала