One or more alternatives lead to a block of possible outcomes with unknown probabilities. Subjective decision-making
Содержание
- 2. One or more alternatives lead to a block of possible outcomes with unknown probabilities Subjective decision-making
- 3. …no reliable data… 3
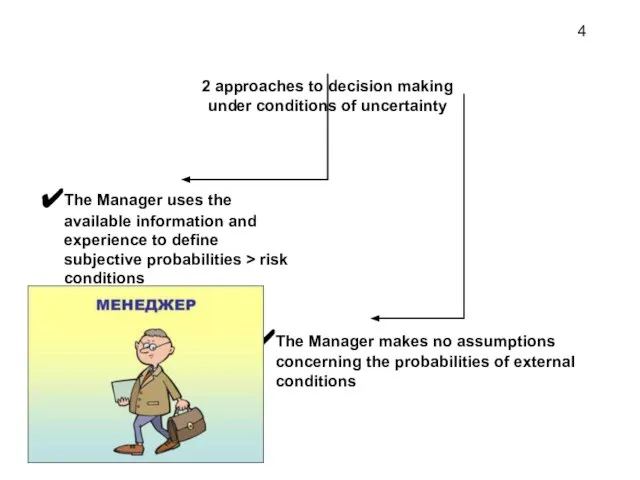
- 4. 2 approaches to decision making under conditions of uncertainty The Manager uses the available information and
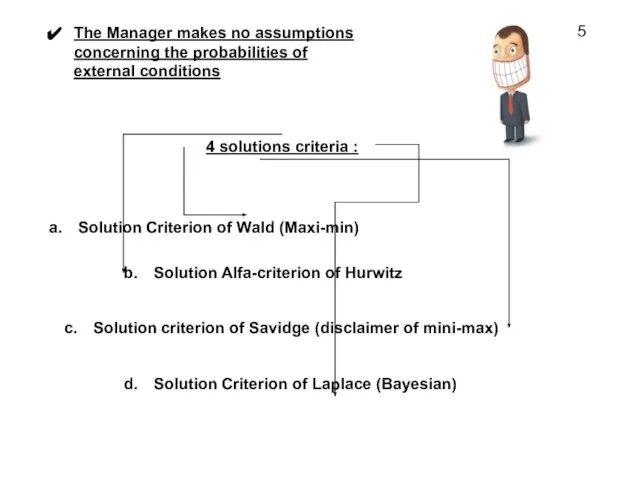
- 5. 4 solutions criteria : Solution Criterion of Wald (Maxi-min) Solution Alfa-criterion of Hurwitz Solution criterion of
- 6. The most suitable criteria? 6
- 7. …take into account philosophy, temperament and viewpoints of the present leadership of the company 7
- 8. Solution Criterion of Wald (Maxi-min) The criterion of conservatism and attempt to maximize reliability External conditions
- 9. Define the worst possible result of each strategy Choose the strategy that provides the best of
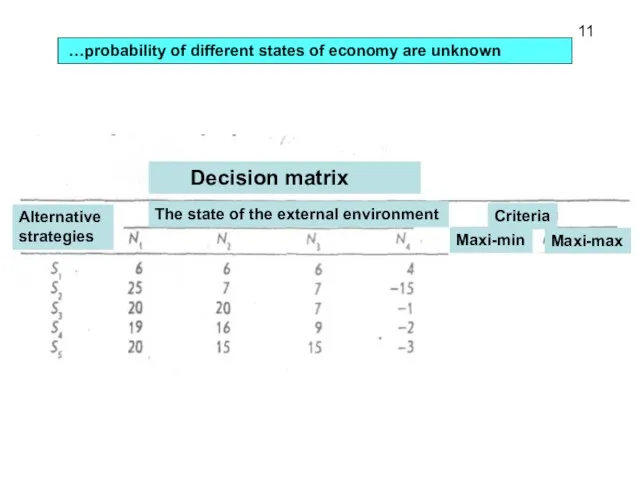
- 10. …probability of different states of economy are unknown 11 Decision matrix The state of the external
- 11. 11 Strategy S1 is just the most conservative - it implies the lowest risks, but at
- 12. The criterion is suitable for small commercial firms whose survival depends on the ability to avoid
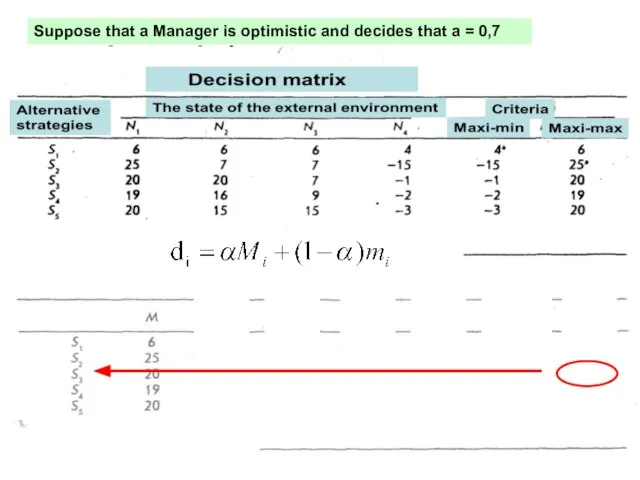
- 13. Solution Alfa-criteria of Hurwitz Determine the index of the solution - d for each strategy, which
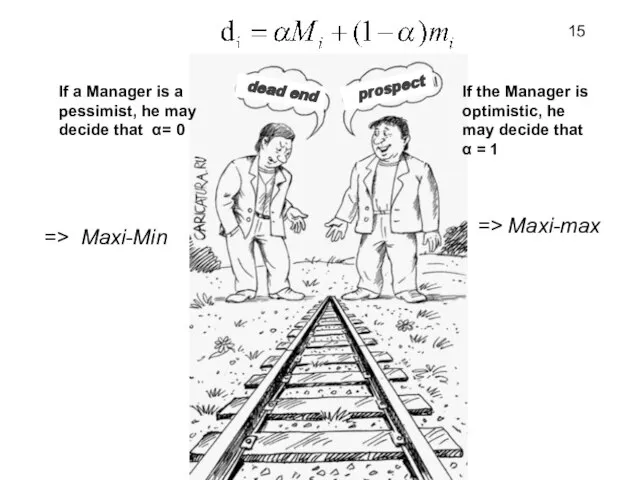
- 14. The coefficient of optimism α is located in the range from 0 to 1 14
- 15. If a Manager is a pessimist, he may decide that α= 0 => Maxi-Min If the
- 16. Suppose that a Manager is optimistic and decides that a = 0,7
- 17. …depends on the amount of …. ….depends on their own relations “Manager for risk”… 17
- 18. Alpha-Hurwitz criterion: draw attention to the worst and the best return of the concrete strategies 18
- 19. Solution criterion of Savage (disclaimer of mini-max) Explores losses incurred as a result of making the
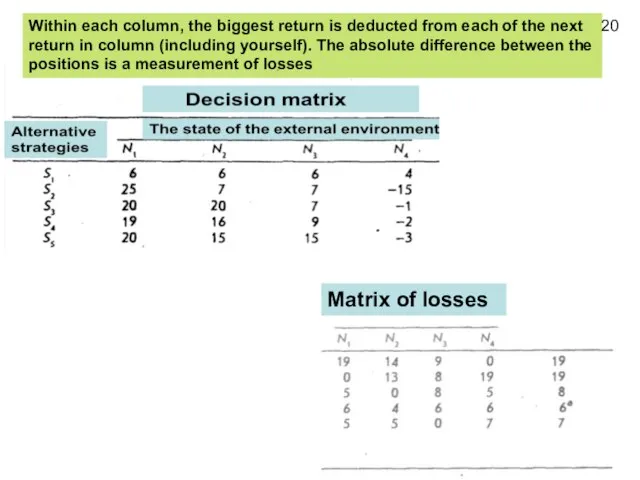
- 20. 20 Within each column, the biggest return is deducted from each of the next return in
- 21. The meaning of measurement of losses: if we have chosen a strategy that provides the most
- 22. But if we choose any other strategy, the loss is the difference between what happens in
- 24. Скачать презентацию















 Организация как система управления
Организация как система управления Холодный поиск
Холодный поиск Организация службы делопроизводства в кадрах
Организация службы делопроизводства в кадрах Практикум: Основы управления персоналом
Практикум: Основы управления персоналом Концепция управления производством Just in Time
Концепция управления производством Just in Time JTB Russia. Информационные технологии в менеджменте
JTB Russia. Информационные технологии в менеджменте Стратегический менеджмент
Стратегический менеджмент Организация производства
Организация производства Анализ деятельности ТОО Dolce - PHARM за 5 месяцев 2022 год
Анализ деятельности ТОО Dolce - PHARM за 5 месяцев 2022 год Управление временем
Управление временем Организация работы с документами
Организация работы с документами Бережливое производство. Организация рабочего места по принципу 5С
Бережливое производство. Организация рабочего места по принципу 5С Энергоменеджмент. Тема1
Энергоменеджмент. Тема1 Система и механизм управления организационными изменениями
Система и механизм управления организационными изменениями Техника работы с клиентом ветеринарной клиники
Техника работы с клиентом ветеринарной клиники Мотивация. Смысл и эволюция понятие мотивация
Мотивация. Смысл и эволюция понятие мотивация Производство расчетов с гостем. Организация и контроль текущей деятельности работников службы приема и размещения
Производство расчетов с гостем. Организация и контроль текущей деятельности работников службы приема и размещения Кадровое делопроизводство. Документация по оформлению трудовых правоотношений при приеме на работу. (Тема 2)
Кадровое делопроизводство. Документация по оформлению трудовых правоотношений при приеме на работу. (Тема 2) Инжиниринг и Реинжиниринг
Инжиниринг и Реинжиниринг Организация производства и управление предприятием ОПиУП
Организация производства и управление предприятием ОПиУП Методы оценки риска
Методы оценки риска Human Capital Management System
Human Capital Management System Проблемы историко-управленческих исследований
Проблемы историко-управленческих исследований Quality request IM051. Delivered Goods remarques
Quality request IM051. Delivered Goods remarques Эффективный сервис и работа с клиентом
Эффективный сервис и работа с клиентом Основы управления персонала. Семинар
Основы управления персонала. Семинар Законы принудительной эффективности управления временем
Законы принудительной эффективности управления временем Роль специалиста по коммуникациям в управленческом бизнес-консалтинге
Роль специалиста по коммуникациям в управленческом бизнес-консалтинге