- Главная
- Менеджмент
- Risk management process training

Содержание
- 2. CONTENT Overview Why do we need to manage risk Definitions Risk Roles & Responsibilities Risk Management
- 3. OVERVIEW Risk management is one of the key processes in the Care Strategy which supports well
- 4. RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
- 5. RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
- 6. RISK MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTABILITIES
- 7. MATERIAL AND SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
- 8. MATERIAL RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
- 9. SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
- 10. BASELINE RISK ASSESSMENT The baseline risk register documents all risks identified within the organisation When new
- 11. BOWTIE RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY Clearly define the scope Detailed description of the risk event Clear boundaries
- 12. SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND CONTROL OWNERS SLIDE When selecting critical controls, the risk owner would: List
- 13. SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND OWNERS An object, action or system that is independent and that actively
- 14. RISK IDENTIFICATION AND VERIFICATION PROCESS Risk Identification From the baseline risk register, identify material and single
- 15. CONTROL EFFECTIVENESS TESTS Control Effectiveness Test A control effectiveness test is conducted to provide assurance that
- 16. MATERIAL RISK CONTROL ASSESSMENTS The material risk control assessment is completed once the Risk Owner has
- 18. Скачать презентацию
CONTENT
Overview
Why do we need to manage risk
Definitions
Risk Roles & Responsibilities
Risk
CONTENT
Overview
Why do we need to manage risk
Definitions
Risk Roles & Responsibilities
Risk
Baseline risk assessment
Bowtie methodology
Material risk control assessment (MRCA)
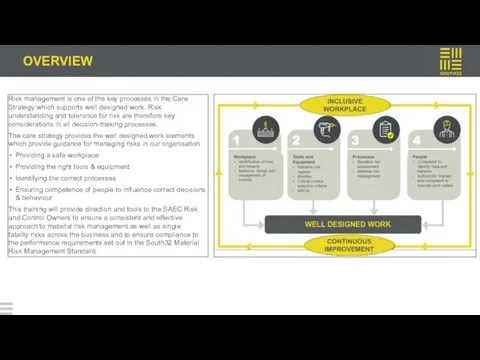
OVERVIEW
Risk management is one of the key processes in the Care
OVERVIEW
Risk management is one of the key processes in the Care
The care strategy provides the well designed work elements which provide guidance for managing risks in our organisation
Providing a safe workplace
Providing the right tools & equipment
Identifying the correct processes
Ensuring competence of people to influence correct decisions & behaviour
This training will provide direction and tools to the SAEC Risk and Control Owners to ensure a consistent and effective approach to material risk management as well as single fatality risks across the business and to ensure compliance to the performance requirements set out in the South32 Material Risk Management Standard.
RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
RISK MANAGEMENT DEFINITIONS
RISK MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTABILITIES
RISK MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTABILITIES
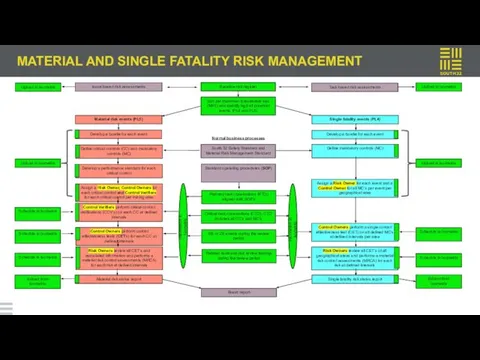
MATERIAL AND SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
MATERIAL AND SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT
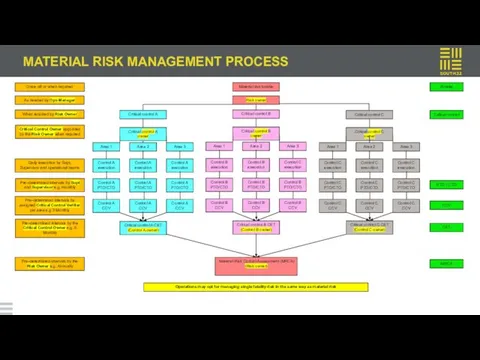
MATERIAL RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
MATERIAL RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
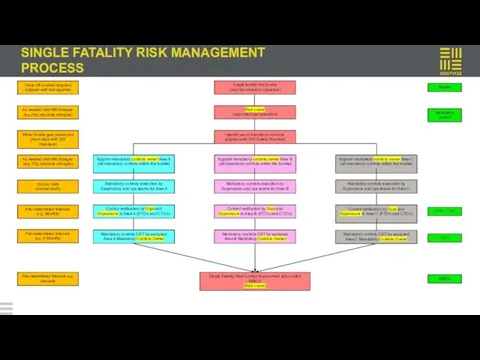
SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
SINGLE FATALITY RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
BASELINE RISK ASSESSMENT
The baseline risk register documents all risks identified within
BASELINE RISK ASSESSMENT
The baseline risk register documents all risks identified within
When new risks are captured on the baseline risk register, the Risk Owner performs an initial assessment to determine the MPI.
A risk assessment must be prepared by a team with experience and understanding of the proposed risk
The risk owner defines the purpose, scope, causes, impact rating of the highest impact type, MPI & RRR of the risk, assigns controls to the risk and improvement actions are registered and workflows to the relevant action owners
If the risk meets MPI materiality criteria it will workflow to the Bowtie risk analysis module. Material for South32 is MPI ≥ level 5; and 9 common fatality risks (ref: Safety Standard v6).
Lower level risks that are managed by operational and functional risk management processes must be excluded from the Bowtie risk assessment process.
BOWTIE RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY
Clearly define the scope
Detailed description of the
BOWTIE RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY
Clearly define the scope
Detailed description of the
Clear boundaries of what has been included and excluded from the risk, where does it start and stop? (E.g. Include: Vehicle collision in the pit and exclude vehicle collision in the processing plant)
Identify causes for this risk event
Causes give rise to the material event as described in the scope
Ineffective controls should not be listed as causes
Identify proactive controls to prevent the cause
Proactive controls must be existing controls
Future controls must be listed as improvement plans
Identify impacts of this risk event
Consider all impact types as per the Impact table in the Material Risk Management Standard
Identify reactive controls to reduce the severity of the event
Reactive controls must be existing controls
Future controls must be listed as improvement plans
SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND CONTROL OWNERS
SLIDE
When selecting critical controls, the
SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND CONTROL OWNERS
SLIDE
When selecting critical controls, the
List all existing proactive & reactive controls
Apply the Critical Control Selection Criteria to each of the controls to determine which would meet the materiality criteria
Once the Risk Owner has selected the possible critical controls, it is his/her responsibility to make
a decision on the final critical controls (typically not more than 3 or 4)
In making this selection, the Risk Owner may consult the Control Owners, Subject Matter Experts or benchmark similar risks and associated controls/critical controls
The Risk Owner appoints a Control Owner based on expertise/area of responsibility
SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND OWNERS
An object, action or system that is
SELECTING CRITICAL CONTROLS AND OWNERS
An object, action or system that is
SLIDE
Once Critical Controls have been selected, Risk owners Identify Control Owners based on the area of expertise or area of responsibility
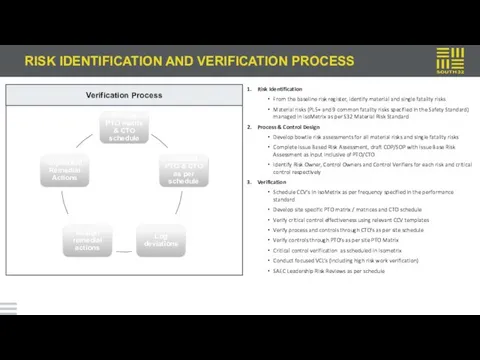
RISK IDENTIFICATION AND VERIFICATION PROCESS
Risk Identification
From the baseline risk
RISK IDENTIFICATION AND VERIFICATION PROCESS
Risk Identification
From the baseline risk
Material risks (PL5+ and 9 common fatality risks specified in the Safety Standard) managed in IsoMetrix as per S32 Material Risk Standard
Process & Control Design
Develop bowtie risk assessments for all material risks and single fatality risks
Complete Issue Based Risk Assessment, draft COP/SOP with Issue Base Risk Assessment as input inclusive of PTO/CTO
Identify Risk Owner, Control Owners and Control Verifiers for each risk and critical control respectively
Verification
Schedule CCV’s in IsoMetrix as per frequency specified in the performance standard
Develop site specific PTO matrix / matrices and CTO schedule
Verify critical control effectiveness using relevant CCV templates
Verify process and controls through CTO’s as per site schedule
Verify controls through PTO’s as per site PTO Matrix
Critical control verification as scheduled in Isometrix
Conduct focused VCL’s (including high risk work verification)
SAEC Leadership Risk Reviews as per schedule
CONTROL EFFECTIVENESS TESTS
Control Effectiveness Test
A control effectiveness test is conducted to
CONTROL EFFECTIVENESS TESTS
Control Effectiveness Test
A control effectiveness test is conducted to
Key focus areas of the effectiveness test include:
Review of controlled documents which support critical controls (SOP/Standards)
Completion of Critical Control Verification and CTO/PTO
Critical control failures and significant events
Internal and external audit findings
Management reviews
The control owner may also want to consider Industry alerts
Assess and record the effectiveness of each identified critical control periodically and at least annually. Consider the reliability of the control and the speed with which it can change or fail when determining the frequency of monitoring. An Adhoc CET should be performed if any of the above factors indicate a critical control failure. In this instance, the CET must be rated as deficient and an action plan put in place.
Some practical considerations when completing a CET include:
Each question is rated as a pass or fail and must be justified with adequate comments to support the rating. This includes uploading supporting documentation or providing relevant document references and providing details of CCV, CTO/PTO and documents reviewed.
An effective and achievable action plan is identified to address critical controls rated as deficient.
MATERIAL RISK CONTROL ASSESSMENTS
The material risk control assessment is completed once
MATERIAL RISK CONTROL ASSESSMENTS
The material risk control assessment is completed once
The MRCA must be completed at least annually. However the following events will also trigger completion:
When a critical control has failed and
Change to the risk
When an action plan has been identified or actioned
Some practical considerations when completing an MRCA
When completing a review of the effectiveness tests, the Risk Owner should consider the following:
Are they adequate and relevant to support ratings?
For any issues raised and critical control failures, have appropriate action plans been raised and actioned?
Is there clear document references or supporting documentation
Each material risk must be assessed and a rating given (Well controlled, Requires some improvement or requires significant improvement). The material risk control assessment must consider the critical control operating assessment results, actual control failure or a control failure that resulted in a similar material risk, internal audit findings, external audit findings and management reviews. Assessments must have sufficient detail to be executed reliably over time. Its purpose is to assess the level of control and tolerability of a material risk. All ratings must be justified.










 Модель согласования Д. Надлера и М. Тушмена : политическая система, организм
Модель согласования Д. Надлера и М. Тушмена : политическая система, организм Основы социального управления
Основы социального управления Разработка стратегии
Разработка стратегии Классификация информации. Управленческая информация
Классификация информации. Управленческая информация Гостиничный продукт. Тема 12
Гостиничный продукт. Тема 12 Система управления персоналом образовательной организации
Система управления персоналом образовательной организации Адаптация персонала
Адаптация персонала Мотивация труда сотрудников и экономических партнеров страховой компании
Мотивация труда сотрудников и экономических партнеров страховой компании Слагаемые профессионального успеха современного руководителя
Слагаемые профессионального успеха современного руководителя Консалтинг. (Лекция 2)
Консалтинг. (Лекция 2) Product Placement: Клипы
Product Placement: Клипы Ресепшионист
Ресепшионист Инновационные процессы в информационных системах
Инновационные процессы в информационных системах Анализ выполнения тактических заданий по программе Кадровый резерв
Анализ выполнения тактических заданий по программе Кадровый резерв Операционный менеджмент и управление проектами
Операционный менеджмент и управление проектами Сутність, функції та завдання логістики. Логістика, як фактор підвищення конкурентоспроможності фірми
Сутність, функції та завдання логістики. Логістика, як фактор підвищення конкурентоспроможності фірми Управление качеством организации предметноразвивающей среды в ДОУ
Управление качеством организации предметноразвивающей среды в ДОУ Организационная структура управления
Организационная структура управления Test execution. Version control systems
Test execution. Version control systems Деловые переговоры
Деловые переговоры Системность, как общее свойство. Основные понятия теории систем
Системность, как общее свойство. Основные понятия теории систем Тайм-менеджмент
Тайм-менеджмент Мотивация Ресечера. Схема оплаты за оформленного кандидата
Мотивация Ресечера. Схема оплаты за оформленного кандидата Функции управления. Целеполагание, програмирование, проектирование
Функции управления. Целеполагание, програмирование, проектирование Руководитель в системе управления персоналом. (Лекция 4.1)
Руководитель в системе управления персоналом. (Лекция 4.1) Управленческое консультирование
Управленческое консультирование Планирование личного времени с использованием технологий стратегического планирования и Time Management
Планирование личного времени с использованием технологий стратегического планирования и Time Management Как отправлять письмо заказчику
Как отправлять письмо заказчику