Содержание
- 2. (MEDICAL BIOLOGY) PHYLOGENETIC DISORDERS OF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS: CONGENITAL LARYENGEAL WEB BRONCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME
- 3. CONGENITAL LARYENGEAL WEB A rare malformation consisting of a membrane-like structure that extends across the laryngeal
- 5. BRONCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a breathing disorder where an infant's lungs become irritated and
- 6. MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) refers to breathing problems that a newborn baby may
- 8. LOBAR EMPHYSEMA Congenital lobar emphysema is a rare respiratory disorder in which air can enter the
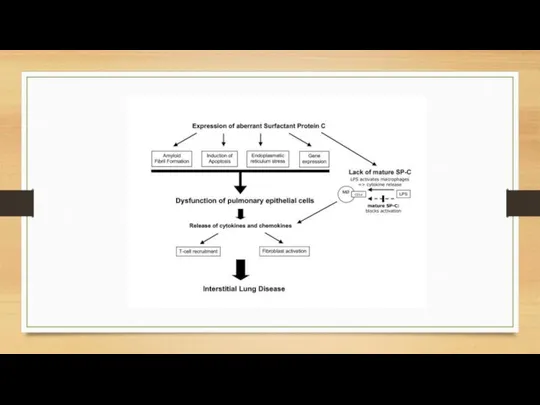
- 9. SURFECTANT METABOLISM DISORDER Surfactant dysfunction is a lung disorder that causes breathing problems. This condition results
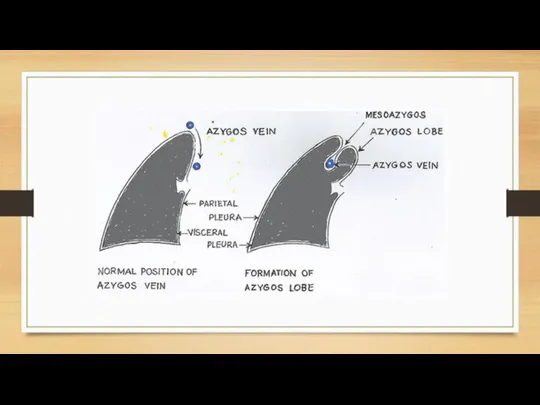
- 11. AZYGOS LOBE An azygos lobe is created when a laterally displaced azygos vein creates a deep
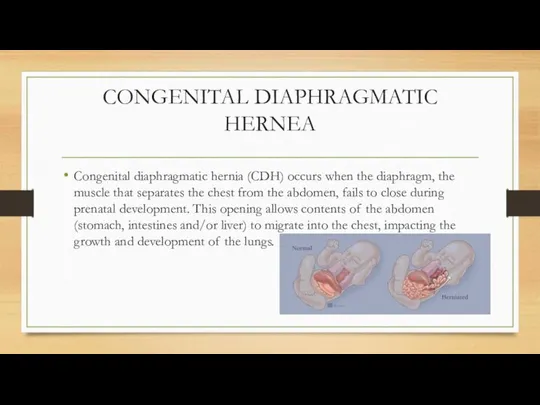
- 13. CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNEA Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) occurs when the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the
- 15. LARYNGEAL-TRACHEO-OESOPHAGAL CLEFT Laryngotracheal cleft (LTC) is a rare congenital defect in which there is a gap
- 17. Скачать презентацию











 Особенности личности одаренного ребенка. Особенности познавательного развития
Особенности личности одаренного ребенка. Особенности познавательного развития Жеке тұлға психологиясының қаралу,зерттелу аспектілері. Тұлға компоненттері
Жеке тұлға психологиясының қаралу,зерттелу аспектілері. Тұлға компоненттері Заболевания дыхательной системы
Заболевания дыхательной системы Биобанки
Биобанки Изменения жизни родителей ребенка с церебральным параличом
Изменения жизни родителей ребенка с церебральным параличом Психология кризисных состояний
Психология кризисных состояний Личность. «В наш век миром правят личности, а не идеи» Оскар Уайльд
Личность. «В наш век миром правят личности, а не идеи» Оскар Уайльд Боль в спине Ксефокам (Лорноксикам®)
Боль в спине Ксефокам (Лорноксикам®) Первая помощь при вывихах
Первая помощь при вывихах Психологическая поддержка ЭКО
Психологическая поддержка ЭКО Клиническая стажировка в кардиологическом отделении Hospital Universitario de Canarias
Клиническая стажировка в кардиологическом отделении Hospital Universitario de Canarias Сердечный цикл, проводящая система сердца, распространение возбуждения по миокарду
Сердечный цикл, проводящая система сердца, распространение возбуждения по миокарду Лаборатории медицинские. Требования к качеству и компетентности
Лаборатории медицинские. Требования к качеству и компетентности Основные симптомы и синдромы при различных пульмонологических заболеваниях
Основные симптомы и синдромы при различных пульмонологических заболеваниях Патология системы дыхания. Лекция № 3
Патология системы дыхания. Лекция № 3 Категории психического. Сознание, личность, деятельность, общение, поведение
Категории психического. Сознание, личность, деятельность, общение, поведение Внутренняя и внешняя среда организации здравоохранения
Внутренняя и внешняя среда организации здравоохранения Контрольная работа по дисциплине Основы рационального питания
Контрольная работа по дисциплине Основы рационального питания Эндокринные болезни
Эндокринные болезни Личностный подход к современной психотерапии зависимостей
Личностный подход к современной психотерапии зависимостей Клещевой энцефалит. Описторхоз
Клещевой энцефалит. Описторхоз Косметикалық кабинеттердің құрылымына және жұмысына қойылатын гигиеналық талаптары
Косметикалық кабинеттердің құрылымына және жұмысына қойылатын гигиеналық талаптары Интересный случай из практики. Нообразование основной пазухи
Интересный случай из практики. Нообразование основной пазухи Перша допомога при пораненнях
Перша допомога при пораненнях Хирургия паразитарных заболеваний
Хирургия паразитарных заболеваний Государственное автономное учреждение здравоохранения Московской области Центральная городская клиническая больница г. Реутов
Государственное автономное учреждение здравоохранения Московской области Центральная городская клиническая больница г. Реутов Комплексное применение продукции MIRRA для здоровья и красоты
Комплексное применение продукции MIRRA для здоровья и красоты Імунний статус організму. Імунодефіцити. Специфічна профілактика інфекційних захворювань
Імунний статус організму. Імунодефіцити. Специфічна профілактика інфекційних захворювань