No obvious external injury or any evidence of electric shock; or
the patient can have severe external burns.
Some patients can suffer from cardiac arrest after an electric shock/ lightning strike.
The burns which the patient experiences from electric shock are often severe at the site of contact with the electrical source and the ground. Common points of contact are hands, head and heels.
Other than burns, injuries can occur from forceful muscular contraction due to which the patient is thrown clear from electrical source. In such cases, patient may have a spinal injury.
If the patient is having shortness of breath, pain in the chest or abdomen, then it may indicate internal injuries.
Pain with deformity of the hand or foot or other body part can indicate a possible fracture resulting from extreme muscle contraction from the electric shock.
Children who suffer from electrical mouth burn, as a result of biting an electric cord, have a burn on the lip which has a red/ dark, charred appearance.
Patient who has experienced electric shock should be examined for entry and exit marks to help assess the extent of the electric shock.
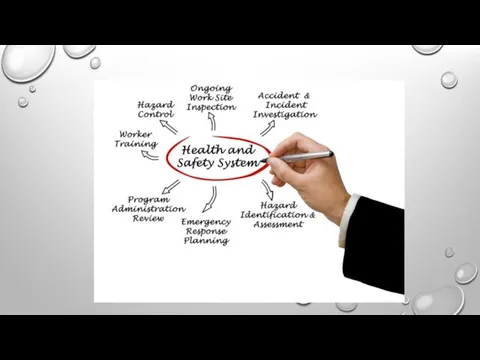
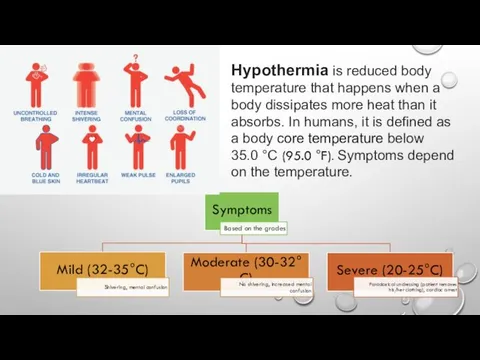
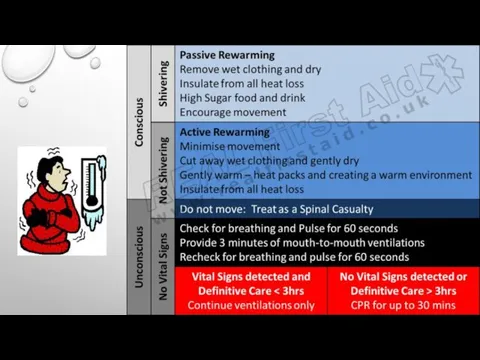
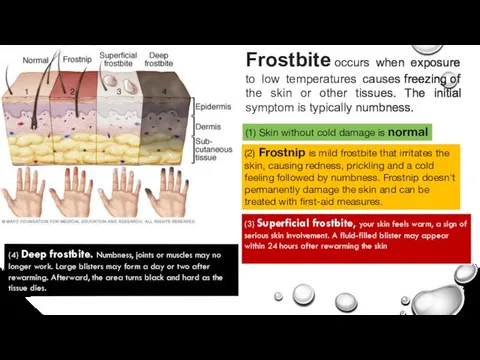
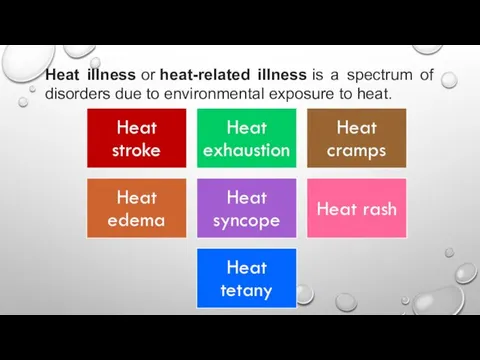
Signs & Symptoms Of Electric Shock















 Lymphoedema and Lymphoedema. Management At MUH
Lymphoedema and Lymphoedema. Management At MUH Аномалии развития и хирургические заболевания ободочной кишки
Аномалии развития и хирургические заболевания ободочной кишки Осложнения язвенной болезни желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки
Осложнения язвенной болезни желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки Руководство ветеринарным делом в Российской Федерации
Руководство ветеринарным делом в Российской Федерации Роль медицинской сестры в профилактике атеросклероза сосудов нижних конечностей
Роль медицинской сестры в профилактике атеросклероза сосудов нижних конечностей Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов
Учение об инфекции патогенность и вирулентность микробов Сосудистая система
Сосудистая система История открытия ВИЧ/СПИДа
История открытия ВИЧ/СПИДа Дифтерия у детей
Дифтерия у детей Предраковые заболевания и доброкачественные новообразования пищевода
Предраковые заболевания и доброкачественные новообразования пищевода Общий анализ крови
Общий анализ крови Работа с группой. Фасилитация и медиация. Лекция 3
Работа с группой. Фасилитация и медиация. Лекция 3 Сахарный диабет и диффузно-токсический зоб. (Тема 35)
Сахарный диабет и диффузно-токсический зоб. (Тема 35) Здоровый образ жизни. Здоровое полноценное питание
Здоровый образ жизни. Здоровое полноценное питание Роль медицинской сестры в профилактике скарлатины и дифтерии у детей
Роль медицинской сестры в профилактике скарлатины и дифтерии у детей Коронавирусы
Коронавирусы Вирус краснухи
Вирус краснухи Искусство в медицине
Искусство в медицине Редкие заболевания с умственной отсталостью
Редкие заболевания с умственной отсталостью Компьютерлік томография
Компьютерлік томография СРС. Круп при острых инфекциях у детей
СРС. Круп при острых инфекциях у детей Правильное питание подростков
Правильное питание подростков Обращение с медицинскими отходами в ГБУЗ Архангельской области Первая ГКБ им. Е.Е. Волосевич
Обращение с медицинскими отходами в ГБУЗ Архангельской области Первая ГКБ им. Е.Е. Волосевич Өкпе абсцесі
Өкпе абсцесі Противовоспалительные средства. Противоподагрические средства
Противовоспалительные средства. Противоподагрические средства Емхана мен аурханның әр түрлі бөлімдерінде емдеу қорғау тәртібінің жүргізу ерекшеліктері. Дене биоиеханикасы
Емхана мен аурханның әр түрлі бөлімдерінде емдеу қорғау тәртібінің жүргізу ерекшеліктері. Дене биоиеханикасы Дифференциальная диагностика кашля
Дифференциальная диагностика кашля Средства действующие на ЦНС
Средства действующие на ЦНС